* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 7-2 Answers - Georgetown ISD
Architectural drawing wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
List of regular polytopes and compounds wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Scale invariance wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
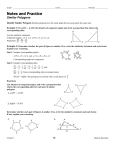
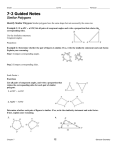
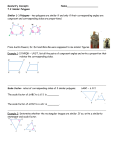
NAME DATE 7-2 PERIOD Study Guide and Intervention Similar Polygons Identify Similar Polygons Similar polygons have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. Example 1 If ABC ∼ XYZ, list all pairs of congruent angles and write a proportion that relates the corresponding sides. : # Use the similarity statement. Congruent angles: ∠A ∠X, ∠B ∠Y, ∠C ∠Z BC CA AB Proportion: − =− =− XY YZ ZX $ " 9 ; Example 2 Determine whether the pair of figures is similar. If so, write the similarity statement and scale factor. Explain your reasoning. Step 1 Compare corresponding angles. ∠W ∠P, ∠X ∠Q, ∠Y ∠R, ∠Z ∠S Corresponding angles are congruent. X 12 8 Q W Step 2 Compare corresponding sides. P 8 PQ 2 QR 12 2 RS 10 2 Z 9 3 ZW − = − =− . Since corresponding sides are proportional, 6 SP 18 9 18 3 YZ 15 3 3 XY WX 12 − =− =− ,−=− =− ,−=− =− , and 15 12 6 S Y R 10 2 3 WXYZ ∼ PQRS. The polygons are similar with a scale factor of − . 2 List all pairs of congruent angles, and write a proportion that relates the corresponding sides for each pair of similar polygons. ( & % 1. DEF ∼ GHJ DE EF FD ∠D ∠G, ∠E ∠H, ∠F ∠J; − =− =− HJ JG GH ' + 8 3 2. PQRS ∼ TUWX ∠P ∠T, ∠Q ∠U, ∠R ∠W, ∠S ∠X; PQ TU QR UW ) RS SP − = − =− =− WX 4 9 6 2 XT 1 5 Determine whether each pair of figures is similar. If so, write the similarity statement and scale factor. If not, explain your reasoning. 3. " 4. ) # 1 + ( & 4 - 22 5 1 PQR ∼ PST; scale factor − no, ∠L ∠E Chapter 7 3 11 , $ % 2 2 12 Glencoe Geometry Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Exercises NAME DATE 7-2 PERIOD Study Guide and Intervention (continued) Similar Polygons Use Similar Figures You can use scale factors and proportions to find missing side lengths in similar polygons. S 32 R x T 38 M 13 y P Use the congruent angles to write the corresponding vertices in order. RST ∼ MNP Write proportions to find x and y. 32 x 38 32 − − =− y =− 16 13 16 16x = 32(13) x = 26 ) The scale factor is N 16 Example 2 If DEF ∼ GHJ, find the scale factor of DEF to GHJ and the perimeter of each triangle. 32y = 38(16) y = 19 & 8 EF 2 − =− =− . 12 HJ 8 10 3 The perimeter of DEF is 10 + 8 + 12 or 30. % 12 + ' 12 Perimeter of DEF 2 − = −− ( Theorem 7.1 3 Perimeter of GHJ 30 2 − =− x 3 Substitution (3)(30) = 2x Cross Products Property 45 = x Solve. Lesson 7-2 Example 1 The two polygons are similar. Find x and y. So, the perimeter of GHJ is 45. Exercises Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Each pair of polygons is similar. Find the value of x. 1. 2. 8 x 4.5 9 10 x x=6 3. 18 12 x = 2.25 4. 18 x+1 36 x + 15 24 18 40 x = 15 30 x=9 20 5. If ABCD ∼ PQRS, find the scale factor of ABCD to PQRS and the perimeter of each polygon. " # 1 2 14 4 scale factor − ; perimeter ABCD = 68; 5 % $ 4 3 25 perimeter PQRS = 85; Chapter 7 5 10 12 2.5 13 Glencoe Geometry