* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classification
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
History of biology wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
P-type ATPase wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Marine life wikipedia , lookup
Living things in culture wikipedia , lookup
Taxonomy (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Marine microorganism wikipedia , lookup
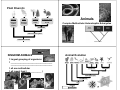
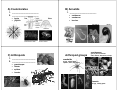
Why do we classify things? Classification provides scientists and Classification students a way to sort and group organisms for easier study. There are millions of organisms on earth! ____________________________________ Organisms are classified by their: ___________________ (how they look) ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ UNITY AND DIVERSITY Organizing the world of organsims The Tree of Life ______________ ______________ ______________ ______________ how they are built how they live organize them into groups of ______________ ______________ In one classification system, there are 2 main groups. In others, there are 3. In the one used by most of the world’s scientists, there are 6 main groups. All living things are placed in one of the six ____________ …which are the most general group (sort of). They are then broken down into smaller groups, then smaller groups, then smaller and so on until there is just one… ____________ is the most specific group… Classification Here is another way of looking at it… Classification of Animal Kingdom _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ Organizing systems Making sense out of the differences That’s my idea baby! Carolus Linnaeus Eastern gray squirrel Sciurus carolinensis K P C O F G Can you make a sentence using the first letter of each classification subgroup? s ________________ devised this in the 1700’s (18th century) using the last two subgroups for the specific species name: ______________ — the branch of science that classifies and names living things GENUS SPECIES ( ___________ ) ( ___________ ) ______________ — a system for naming things In biology there is a two-word system that is used to name organisms. It is called GOLDBERG GOLDBERG GOLDBERG Humans are known as _______ _______ genus ____________________________ The Five Kingdoms __________ __________ __________ __________ __________ JASON BILL WHOOPI species Classification Organisms are grouped among these six kingdoms by: the presence or absence of a nuclear membrane Prokaryotes — _____________________________ Eukaryotes — ______________________________ Eukaryote Prokaryote unicellular ( _______ ) or multicellular (_____) _____________________________ : (heterotrophic or autotrophic) KINGDOMS BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA ___________________________________ Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaebacteria Kingdom Protist Kingdom Fungi Kingdom Plant Kingdom Animal Both Good & Bad… pathogens _________________ beneficial & necessary help in digestion help plants grow make foods ___________________________________ most of these organisms are unicellular (some can exist as multicellular clusters) Bacteria live EVERYWHERE On plants & animals In plants & animals In the soil In the extreme cold In the extreme hot On the living On the dead KINGDOM PROTISTA ___________________________________ ___________________________________ predominantly unicellular Protists Simple Eukaryotes Domain Bacteria Domain Archaebacteria Domain Eukaryotes Common ancestor KINGDOM PROTISTA two main phyla A. Protozoa—animal-like nutrition (heterotrophic) B. Algae—plant like nutrition (autotrophic) Fungi Eukaryotes Domain Bacteria Domain Archaebacteria Common ancestor Domain Eukaryotes KINGDOM FUNGI ___________________________________ ___________________________________ absorbs food from its environment (heterotrophic), does NOT ingest it! organized into branched (usually multicellular) filaments Importance of fungi to humans food production bread beer, wine medicine production antibiotics KINGDOM PLANTS ___________________________________ Plants Multicellular Photosynthetic Eukaryotes ___________________________________ all are multicellular all are ________________ (autotrophic) photo = Domain Bacteria Domain Archaea Common ancestor Domain Eukarya synthesis = Plant Diversity Mosses no water transport system (pipes) Conifers pollen & seeds Ferns water transport, no seeds Flowering plants flowers & fruit Animals Complex Multicellular Heterotrophic Eukaryotes Domain Bacteria seed plants Domain Archaea Domain Eukarya water transport system colonization of land Common ancestor KINGDOM ANIMALS largest grouping of organisms ___________________________________ Animal Evolution sponges jellyfish flatworms roundworms mollusks segmented worms ___________________________________ all are multicellular all ingest food ( ____________ ) insects spiders segmented body separate digestive system left-right symmetry tissues many-celled Ancestral Protist starfish vertebrates internal skeleton A) Coelenterates 1. ________________________ 2. ________________________ hydra jellyfish B) Annelids 1. ________________________ earthworm sandworm leeches fan worm leech crustaceans C) Arthropods 1. _____________________ 2. _____________________ grasshopper lobster spiders insects Arthropod groups gills, 2 pairs antennae crab, lobster, barnacles, shrmp arachnids 8 legs, 2 body parts spiders, ticks, scorpions insects 6 legs, 3 body parts D) Chordates 1. ________________________ 2. ________________________ humans frogs sharks cats becomes brain & spinal cord That’s the buzz… Any Questions? becomes gills or Eustachian tube becomes tail or tailbone becomes vertebrae There are many CLASSES in the chordate PHYLUM! ex. fish, birds, amphibians, reptiles, and mammals