* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Science 10
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
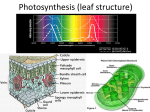
Science 10 Unit C 3.1 staring p.296 Daily worksheet assignment Name: __________________ C 3.1 Cells, Tissues, and Systems Q1) There are advantages and disadvantages to having a large structure that depends on countless single cells. Summarize the ideas presented on p. 297 in the following table: Multicelular Single-celled Advantage Disadvantage Advantage Disadvantage Division of Labour Size: Interdependence of cells Plant Structure Plants are ______________ organisms. As plants __________ and increase in _______, cell begin to have _______________ functions. Groups of ________ performing the same function together are called _________. Tissues contributing to the same _____________ form ________ which are part of a _________. The plant has two organ systems. The _______________ is everything that is ________ ground. It also includes ____________ ,which are swollen ________ that store food, even though they are under ground. The ________________ is everything _________, but also includes ____________ even though they are above ground. Cells divide for ___________ of new tissue and __________ of damaged tissue. ________ is the process of cell division that allows both of these to occur. Cell division does not occur at the same _______ throughout the organism. Areas of intense growth in plants are called ___________. Different ___________ produce root or shoot tissue. Q2) List some ativities that plant tissue needs to be able to carry out: ____________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ____________ tissue or epidermis is the __________ layer of cells that covers all _____________ plants. This tissue is usually _______ cell thick and is responsible for the exchange of __________ and __________ into and out of the plant. In woody plants this tissue is replaced by _________ and __________ during secondary growth. Dermal tissue of the shoot system organs is primarily involve in __________ exchange. It also protects the plant from _________. Cells of the leaves and stem secrete a waxy substance called _________ that resist attack from ____________ and also help reduce _________________. ____________ tissue makes up the majority of the plant and is found as a layer ________ the epidermis. Q3) List the important functions ground tissue carries out: In stems: _________________________________________________________________ In roots: __________________________________________________________________ The cells of ground tissue are _____________ packed together and the ______ spaces allow gases to diffuse rapidly. ____________ tissue is responsible for the ___________ of materials throughout the plant. ____________ tissue moves ___________ and dissolved minerals _____ the roots up the stem to the ___________ where these are used in ____________________. Xylem vessels are thick-walled tubes. the thickening is a result of ______________ and possibly ___________ being deposited. During Xylem development, the cylindrical cells fuse together and the walls at each end become _____________. As a result these cells ____________, leaving the non-living cell walls attached together like a long ___________. _____________ tissue transports _____________ and other dissolved sugars from the __________ to other parts of the plant. The phloem is formed from individual long __________ cells, which have ____________ end walls, through which the ____________ extends. The sieve tube cells remain __________, but lose their _________ (did you know our blood cells do the same thing?!) In many plants, these cells are connected to small, nucleated _________________ that appear to direct their activities. Q4) Where does cellulose come from? _____________________________________________ Q5) How is cellulose used by plants? ______________________________________________ Transported sugars may also be stored as ____ in the ___________, ___________ or ________. Specialization in Plant Cells Cells that are no longer part of the _________________ show the characteristics of only certain parts of their __________________. Cells that become part of the root system are responsible for the _____________ of water and minerals. These cells may produce projections of __________ which ____________ the surface area for absorption. Dermal cells produce __________ to protect the cells from water loss. _______________ on the lower epidermal surface of leaves form tiny pores called ___________ for gas exchange. Cells that become part of the xylem specialize to be able to conduct _________. C3.2 The Leaf and Photosynthesis The leaf is a collection of __________ whose main purpose is to carry out _______________. The Chloroplast: A Unique Plant Organelle Chloroplast organelles contain the green pigment ______________ which helps in carrying out photosynthesis. This is a chemical process in which _____________ from the air and _________ from the soil, in the presence of _______________, produce ____________ and ___________. ______________ + _______________ -------------------------------Æ _______________ + _______________ Q1) Which molecule does the plant use to store the energy from light? __________________. Movement of chloroplasts in the cytoplasm is called _______________________, and is a mechanism that circulates materials and speeds up their ______________ within the cell. Gas Production in Plants We’ve just reviewed one important reaction a plant must undertake; now for the plant to use this energy it’s stored up, a second reaction is needed. This process is called ___________________. This processes begins in the cytoplasm, but ends in the _______________ by way of a series of reactions that release ____________ and produce _____________ and _____________. ______________ + _______________ -------------------------------Æ _______________ + _______________ Cellular respiration is also carried out in animal cells to provide energy. However, plant tissues ___________ at a much _____________ rate than animal tissues, and the CO2 produced is not as obvious during the day since ___________________ will use it up. In the __________ photosynthesis cannot take place, and the CO2 from cellular respiration is ______________. Experiments to investigate gas production in organisms under various conditions may focus on the ________________ of the product or on the _________________ of the reactants. Science 10 Unit C 3.3 staring p.309 Daily worksheet assignment Name: __________________ C3.3 The Leaf Tissues and Gas Exchange Air can enter cells by ________________. However, it would take a long time to get the needed volume of air. To solve this, the leaves have specialized _________ to maximize its exchange. Dermal Tissue ___________ cells form tiny openings or pores called ____________. These regulate the movement of gases. The direction of movement depends on the gasses ____________________. The majority of the _____________ are found in the ___________ epidermis. The guard cells are __________ bean-shaped and, depending on conditions, swell up to _________ the stomata, or shrink away so that the stomata are __________. Light striking the leaf stimulates the guard cells to accumulate ______________ ions by active transport. As a result, the solute concentration increases and water follows by _____________. This causes the guard cells to swell up under increased _________ pressure. Since the outer walls are ________ than the inner walls, the cell will bulge ___________ and be drawn into a crescent shape. Guard cells also help prevent too much water loss. All gasses must ____________ in a film of water on the outside of cells, in order to pass through the cell membrane. As a result, the plants continually lose water. If water is not readily available, the guard cells become _______ and _________ the stomata. The process of water leaving the leaf is called ________________. Q1) How have plants adapted in hot arid areas? How have they adapted in humid areas? _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ Ground Tissue Between the upper and lower epidermis of the leave are specialized ground tissues called _______________. There are two different types of this tissues. The ____________ tissue cells are found just __________ the upper epidermis. These cells are responsible for ______________ so there are many ________________ in this layer of tissue. Between the ____________ tissue and the lower epidermis are loosely packed cells called the ________________ mesophyll tissue. The increase space allows for ___________ by diffusion throughout the leaf. These cells will move _____________ toward the stomata for expulsion and ________________ toward the palisade cells for ____________________. Vascular Tissue The vascular tissue provides the leaf with the ____________ needed for transpiration and for Photosynthesis, and also removes the ___________ formed by this. In the leaf ribs, called __________, there are bundles of xylem and phloem. The __________ transports water, while the ____________ transports sugar. _____________ bundles in the leaves are direct extensions of the vascular bundles of the stem. Gas Exchange in Plants In plants, all gas exchange occurs by ______________. In the leaf, the _______, regulated by guard cells, allow for more efficient intake of gases. Diffusion of ____________ out of the leaf is also maximized by the ________________ in the ground tissue. The leaf is not the only place where exchange occurs. In herbaceous plants there may appear blisters or slashes on the __________________ or on mature ____________. These pores are called _____________ and provide a pathway for __________________.