* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NONCOMMUNICABLE DISEASES
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
Kawasaki disease wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Atherosclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmunity wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Ankylosing spondylitis wikipedia , lookup
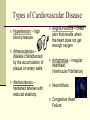
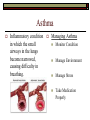
NONCOMMUNICABLE DISEASES CHAPTER 25 Cardiovascular Disease Disease that effects the heart or blood See Figure 25.2 for Diagnosis and Treatment Options See Figure 25.4 to understand Risk Factors Types of Cardiovascular Disease Hypertension – high blood pressure. Atherosclerosis – disease characterized by the accumulation of plaque on artery walls. Ateriosclerosis – hardened arteries with reduced elasticity. Angina Pectoris – chest pain that results when the heart does not get enough oxygen. Arrhythmias – irregular heartbeat. (Ventricular Fibrillation) Heart Attack Congestive Heart Failure Cancer The uncontrollable growth of abnormal cells Tumor – Abnormal mass of tissue that has no natural role in the body. Benign – noncancerous, grows slowly Malignant – cancerous, does not stay in one place. Metastasis – the spread of cancer from the point it originated to other parts of the body. Types of Cancer Lymphomas – cancers of the immune system Carcinomas – cancers of the glands and body linings. (Skin, lungs, digestive tract) Leukemias – cancers of blood-forming organs Sarcomas – cancers of connective tissue. (Bones, ligaments, muscle) RISK FACTORS Tobacco Use Radiation Sexually Transmitted Diseases Dietary Factors Detection and Treatment Self-examinations Checking your body for possible signs of cancer. Many types can be detected this way. Surgery Medical examinations Medical screening/testing by a doctor. Immunotherapy Radiation Therapy Chemotherapy Hormone Therapy Allergies Specific reaction of the immune system to a foreign and frequently harmless substance. The immune system eventually releases histamines – chemicals that can stimulate mucous and fluid production. Diagnosis – breaking out in a rash, blood test or skin test. Asthma Inflammatory condition in which the small airways in the lungs become narrowed, causing difficulty in breathing. Managing Asthma Monitor Condition Manage Environment Manage Stress Take Medication Properly Diabetes Chronic disease that affects the way body cells convert sugar into energy. Type 1 5-10% of all diabetes Appears suddenly and progresses quickly Body fails to produce insulin, glucose builds up in the blood, and cells do not get the energy they need. Autoimmune disease – condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks itself, targeting the cells, tissue, and organs of a person’s own body. Diabetes Type 2 90-95% of all diabetes cases Usually appears after age 40, but growing in number among children and teens Body is unable to make enough insulin or to use insulin properly. Increasing number of older people in the population and growing numbers of obese and inactive young people. Arthritis Group of more than 100 different diseases that cause pain and loss of movement in the joints. Osteoarthritis Disease of the joints in which cartilage breaks down Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease characterized by the debilitating destruction of the joints due to inflammation.