* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 6 PSYCH
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
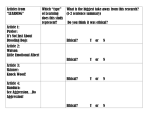
Chapter 6 Learning Learning The Russian Physiologist Ivan Pavlov came up with the concept of Classical Conditioning This is when a person’s or animals response becomes attached to a new stimulus Classical conditioning is an example of learning Learning- the relatively permanent change in behavior that results from experience What experiences have you had that have changed your experience? Feel free to share with the class!! Learning Pavolov stumbled across classical conditioning when studying the digestive system of dogs. Experiment- he would ring a tuning fork and then immediately placed food in front of the dog. He chose the tuning for because it was a neutral stimulus. This means that it had nothing to do with the dog’s response (salivating) when shown the food. A dog does not naturally salivate when it sees a tuning fork it needs to be taught had to do so. Learning After a few trials the dogs began to salivate when they heard the tuning fork even when no food was given. Classical conditioning had occurred. In the experiment the food was the unconditioned stimulus (UCS) This means that the dog was not conditioned to salivate when given the food, as food normally causes a dog to salivate. Learning The salivation of the dog is the unconditioned response (UCR). The dog had not been taught to salivate when seeing the food. Most UCR are reflexes Also in this experiment the tuning fork was the conditioned stimulus (CS) The dog had to be taught or conditioned to salivate when seeing the tuning fork. Learning The salivating of the dog due to the tuning fork was the Conditioned Response (CR) In other words the dogs had been taught to salivate at the hearing the sound of the tuning fork because he/she learned that it was associated with food. Learning Generalization- occurs when similar stimulus is presented like the stimulus that was conditioned Pavlov tried using a bell instead of a tuning fork In that experiment the dog still salivated at the sound of the bell Learning Discrimination occurs when people/animals have the ability to distinguish between two different stimuli. Pavlov tried using a buzzer and the dogs failed to salivate in that experiment! Extinction occurs when there is a gradual disappearance of the conditioned response. Pavlov could have stopped feeding the dogs at the sound of the tuning fork and eventually the dogs would have lost his conditioning Learning John Watson a psychologist did an experiment with a 11 month old boy named Albert. In this experiment he made Albert afraid of rats by placing a white rat in front of him and banging pans behind the boy when he reached out to touch it. After several times of trying to reach for the rat and the banging pans, Albert began to fear the rat. In fact, when he was shown the rat he cried and this experiment showed that classical conditioning could be done to humans as well. Learning Read the story on page 134 and lets think about some of the thinking critically questions as a class. How did the Watson and Rayner condition Little Albert to fear white rats? Why do you think most psychologists today would consider this experiment unethical today?