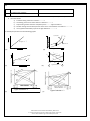
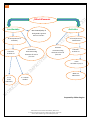
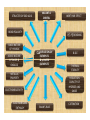
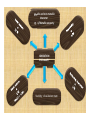
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
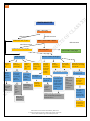
Download Workshop materials for Class XII
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Acid dissociation constant wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Coordination complex wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Stability constants of complexes wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN; NEW DELHI केन्द्रीय ववद्यालया संगठन नई ददल्ली REFERENCE MANUAL CUM REPORT संदर्भ मैनअ ु ल व रिपोर्भ आयोजन स्थल केन्द्रीय ववद्यालया क्रमांक 3, र्ुवनेश्वि, उड़िशा Venue Kendriya Vidyalaya No 3 Bhubaneswar, Odisha Prepared By : ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com OUR PATRONS Shri AvinashDikshit Commissioner KVS New Delhi Shri G.K. Srivastava Additional Commissioner (Admn) KVS New Delhi Dr. Dinesh Kumar Additional Commissioner (Acad) KVS New Delhi Dr. Shachikant Joint Commissioner (Training) KVS New Delhi Dr. Vijayalakshmi Joint Commissioner (Acad) KVS New Delhi Dr. E. Prabhakar Joint Commissioner (Pers) KVS New Delhi Shri M. Arumugam Joint Commissioner (Fin.) KVS New Delhi Shri S. Vijaykumar Joint Commissioner (Admn) KVS New Delhi Special thanks Ms R Kalavathi, Deputy Commissioner, KVS (RO) Bhubaneswar ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com Acknowledgement Course Director USHA ASWATH IYER Deputy Commissioner & Director, ZIET Bhubaneswar Venue Director Shri DamodarPurohit Principal, K.V. 3 Bhubaneswar Resource Persons Mrs Hajra Shaikh Mr Suresh Kumar Sahu Mr Aaditya Kumar Panda PGT (Chemistry) K.V. No3 Bhubaneswar PGT (Chemistry) ZIET Bhubaneswar PGT (Chemistry) K. V. 3 Bhubaneswar Bhubaneswar Region Bhubaneswar Region Supported by ZIET Bhubaneswar Staff Mrs. Hajra Shaikh (PGT-Chem), Mr. K. P. Dash (PGT-Eng), Dr. Abhijit Saha (PGT-Biology), Mr. Nabaghan Nayak (PGT- Math), Mr. Parasuram Shukla (PGT -Econ), Ms T Samrajya Lakshmi(PGT-Phy) Dr. Santosh Gupta (Librarian),Mrs. SantiLataPadhy(UDC) ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com From the Director’s Desk Academics is an important part of any school and Kendriya Vidyalayas have proved their academic brilliance with their consistent performance of over 94% pass in the Class XII Board Exams. There is a growing need to improve the qualitative results too. The idea of developing worksheets graded for different levels of learners was designed keeping in mind that an improvement in qualitative results will automatically result in quantitative improvement. The materials have been developed by the teachers of the six participating regions: Bhubaneswar, Ranchi, Guwahati, Kolkata, Silchar and Tinsukia under the inspiring leadership of Ms Jayalakshmi Raju, Principal, K V Srikakulam (Bhubaneswar Region) and the dedicated guidance of the three Resource Persons, Mr A K Panda and Mr S K Sahu, both PGT Chemistry of K V 3 Bhubaneswar and Ms Hajra Shaikh (ZIET Bhubaneswar). I request the participating teachers to use this material and to share it with other colleagues and students. Kindly send your suggestions so that we can improve these materials. Wishing all of you the very best in the 2014 Board Exams and in your future too. USHA ASWATH IYER DIRECTOR ZIET BHUBANESWAR ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com केन्द्रीय ववद्यालय श्रीकाकुलम KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA, SRIKAKULAM PEDDAPADU, SRIKAKULAM DIST. – 532 401 (A.P.) Ref. No. 1-45 /KV-SKL/2013-14/ Dated 13.08.2013 Everything starts with a dream or concept in your mind…. The dream is given form by putting it on paper……… The construction process begins……………… The workshop has been a powerful tool and technique modeler to streamline our dream towards achieving invincible results in chemistry. The questions banks and concept mapping will go a long way in revolutionizing the information disseminated and equipping the students with easy to follow preparation techniques. It provides a logical, systematic introduction to all aspects besides answering several questions both from the point of the students and the teachers. To my colleagues and friends across the country whose valuable inputs have made publication of this material possible and on behalf of myself, my colleagues, and my past, present, and future students: Thank you! K.Jayalakshmi Raju Principal. K.V.Srikakulam & Associate Director For Chemistry PGTs Work Shop, ZIET,Bhubaneswar ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 8 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 9 I Time Table: Participants Details Allotment of Work SWOT Analysis Relating class Xi to Class XII Learning Methods and Aids to Memory Effective revision strategies Worksheets o Chapter 1& 2 o Chapter 3&4 o Chapter 5 &6 o Chapter 7, 8, 9 o Chapter 10,11,12 : o Chapter 13,14 : o Chapter 15,16 : 10 11 14 15 20 26 49 56 60 65 70 75 78 Question banks (minimum level of learning) o Chapter 1,2,3,4,5 88 o Chapter 6,7,8,9,10 124 o Chapter 11,12,13,14,15,16 164 Question banks ( frequently asked questions including HOTS) o Chapter 1,2,3,4,5 193 o Chapter 6,7,8,9,10 202 o Chapter 11,12,13,14,15,16 261 Concept Mapping 270 Daywise Report 303 Memories 304 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 10 3 DAY WORKSHOP ON IMPROVING RESULTS IN CLASS XII CHEMISTRY TIME TABLE 8/2/2013 8/3/201 3 Registration + Inauguration Friday Prayer and review of previous day Linking class XI to class XII/Linking Practicles to theory; Mr Sahu Saturday Prayer and review of previous day Learning Styles/ Aids to memory; Mr Panda 11.00- 13.00 Making into groups (10 min) / Explaining preparation of worksheets (30 min)presentation by Mr Panda / Identifying concepts (30 min)/ Preparation of worksheet Preparation of Question bank Concept Mapping/ Explanation and Preparation ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 14.00 - 15.30 Preparation of worksheets Preparation Question bank Consolidatin g 15.3015.45 TEA BREAK Thursday Aims and objectives of the workshop/ SWOT analysis/motivation; Mrs Hajra Shaikh 10.4511.00 LUNCH BREAK 8/1/2013 9.15- 10.45 TEA BREAK 9.00-9.15 13.0 014.0 0 15.45- 17.30 Preparation of worksheets Preparation of Question Bank Plenary and Valedictory 11 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN ZIET:: BHUBANESWAR Workshop on improvement of results of class XII - Period of Workshop 01.08.13 to 03.08.13 at K V No.3 Bhubaneswar DETAILS OF PARTICIPANT Sl. N o 1 Name of Participant (in BLOCK Letters) Name of KV in ENGLISH हिन्दीमे MS. SUSHMA MANDA श्रीमतीसुषमामण्डा PGT Chem श्रीबीश्रीधर PGT Chem NO.2, NSB VIZAG श्रीजयंतकुमारसािू PGT Chem DHENKANAL 2 MR. B. SREEDHAR 3 MR. JAYANTA KUMAR SAHOO 4 Design ation MRS. PRAVASHINI. ROY श्रीमततप्रभाससनीरॉ Region Cate. SC / ST Mobile No. E-mail id Emplo yee Code Date of Joining in KVS in ENGLISH हिन्दीमे in ENGLISH NAD VIZAG नएडीवैजाग BHUBANESWAR Gen 9989818812 [email protected] om 29605 16/08/95 जाग BHUBANESWAR OBC 7893426497 bevarasreedhar@yahoo. com 13965 30/09/97 धेनकनाल BHUBANESWAR Gen 9861442317 [email protected] 11386 12/10/2002 क्र. 2एनएसबीवै क्र. 1 भव ु नेश्वर (II PGT Chem NO.1, BBSR(2S) पड़ाव) BHUBANESWAR Gen 9437164302 [email protected] 10233 20/01/89 नता PGT Chem SAMBALPUR सम्बलपुर BHUBANESWAR OBC 9437855954 [email protected] om 15274 5/9/2003 PURI पूरी BHUBANESWAR OBC 8018159290 [email protected] 10233 24/10/08 NO.1, CUTTACK क्र. 1 कटक BHUBANESWAR Gen 9438011119 [email protected] m 11861 20/11/93 TURA तुरा GUWAHATI SC 9805736409 [email protected] 47503 29/10/09 JAGIROAD जागीरोड GUWAHATI Gen 7896102816 [email protected] 8270 25/10/08 य श्रीमतीस्ममतामिा 5 MRS. SMITA MOHANTA 6 MS. RASHMITA SAHOO श्रीमतीरस्श्मतासािू PGT Chem 7 DR. C R TRIPATHY डॉचितरं जनत्रिपाठी 8 MR. TEK CHAND श्रीटे किंद PGT Chem PGT Chem 9 MR. MUKESH KR. AGARWAL श्रीमुकेशकुमारअग्र वाल PGT Chem ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 12 10 11 12 MR. Mohd SALEEM SIDDIQUI MR. ARUP KUMAR ROY MISS MERCY LALROHLUOHMAR श्रीमोिम्मदसलीम श्रीअरूपकुमाररॉय PGT Chem PGT Chem िमार PGT Chem डॉमधुकुमारीगुप्ता PGT Chem PGT Chem ससद्दीक़ी सुश्रीमसीललरोिुलू 14 Dr MADHU KUMARI GUPTA Mr OM PRAKASH MEENA 15 Dr A K LAHA श्रीएकेलािा 16 A K MANI श्रीएकेमणण PGT Chem PGT Chem A HAQUE श्रीअनवरुलिक़ PGT Chem 13 17 18 19 20 21 22 DEWENDRA JHA PIYUSH KUMAR MISRA SANDHYA SANNIGRAHI SH. JAI JAI RAM SINGH, DR. HEMANT KUMAR, श्रीओपीमीणा NEHU SHILLONG नेिुसशल्लोंग GUWAHATI OBC 9612651759 ALIPURDUAR अलीपरु द्वार GUWAHATI Gen 8967304633 salim.siddiqui74@yahoo. com aruproychemistry2011@ gmai.com HASIMARA िसीमारा GUWAHATI ST 9093931494 [email protected] BENGDUBI बेंगडूबी GUWAHATI Gen 7602759187 madhukumarigupta@re diffmail.com 47125 2/12/2010 PORT BLAIR-1 पोटट ब्लेयर -1 KOLKATA ST 9679508515 [email protected] 44253 8/4/2009 DUM DUM OF डमडमओएफ KOLKATA Gen 8100218136 36798 11/2/1994 No2 Port Blair बमङ्गिी KOLKATA SC 9433970544 [email protected] om ardhendukona72@gmail .com 37249 15/10/97 KOLKATA Gen 9163990213 anwarulhaque604@yaho o.com 40622 9/2/1994 कंिरपरा KOLKATA Gen 9434188594 [email protected] ASANSOL असान्सोल KOLKATA Gen 9434071362 [email protected] sandhya63sannigrahi@g mail.com जोकाआइआइ एम JOKA IIM KANCHRAPARA -1 ADRA आद्रा KOLKATA Gen 9732129499 NO. 1, DHANBAD क्र. 1 धनबाद RANCHI Gen 9472792322 डॉिे मंतकुमार PGT Chem PGT Chem PGT Chem CRPF, RANCHI श्रीपीकेसमश्रा श्रीएससस्न्नग्राफ श्रीजयजयरामससंि 35389 5/10/1988 25/01/12 13/9/86 46075 25/10/08 35335 21/10/94 1103 22/7/95 36074 15/3/94 RANCHI Gen 8757757794 [email protected] om रााँिी RANCHI Gen 9835170231 krmanojsharma111@gm ail.com 6268 21/8/95 गोमोि GOMOH 23/10/09 क्र. 1 PGT Chem PGT Chem PGT Chem श्रीडीएनझा 8271 सीआरपीएफ 23 SH MANOJ KUMAR, श्रीमनोजकुमार 24 SH. BRAJESH KUMAR श्रीब्रजेशकुमार PGT Chem No 1 HEC, RANCHI एिईसीरााँिी RANCHI OBC 8987555635 [email protected] 37449 2/9/2003 श्रीभीष्मकान्त PGT Chem PGT Chem NAMKUM, RANCHI नमकमरााँिी RANCHI OBC 9431366869 [email protected] om 51682 20/10/08 TATANAGAR टाटानगर RANCHI Gen 9835505361 [email protected] 25 26 SH. BHISMA KANT, MRS. SANTWANA KABI , श्रीमतीसांत्वनाकबी ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 2/3/1994 13 27 MRS Mahadevi PRADHAN, 28 MR. ANIL KUMAR SHARMA 29 Mr BHARAT KUMAR PANDYA श्रीमतीमिादे वीप्रधा न श्रीअतनलकुमारश माट श्रीभरतकुमारप ण््या श्रीसतीशकुमारटीटी 30 MR.SATHEESH KUMAR T T V 31 SH.SAJEESH KUMAR TV 32 SH. PRATHEESH .N श्रीप्रतीषएन 33 DR ABHYAS YADAV डॉअभ्यासयादव 34 SH PRAVEEN BUTE श्रीप्रवीणबट ू े 35 SH NARESH KUMAR श्रीनरे शकुमार 36 SH.BABLU KUMAR श्रीबबलूकुमार वी श्रीसजीषकुमारहट वव PGT Chem SUNDARGARH सुंदरगढ़ RANCHI OBC 8260171112 [email protected] om 48159 30/01/12 PGT Chem HAFLONG िाफलोंग SILCHAR Gen 9859473785 [email protected] m 45135 19/01/12 PGT Chem BAGAFA बागफा SILCHAR Gen 8974364120 bharatpandya2112@gm ail.com 45654 1/8/2009 PGT Chem LUMDING लमडडंग SILCHAR OBC 7896699987 sateeshkumarttv@gmail. com 8906 21/10/08 KUNJABAN कंु जबान SILCHAR Gen 9862827352 [email protected] om SILCHAR ससल्िर SILCHAR OBC 9085359082 [email protected] 50045 23/10/08 DIMAPUR दीमापुर TINSUKIA OBC 9774128085 32930 26/08/03 NO.1,TEZPUR क्र. 1 तेज़परु TINSUKIA OBC 8876093581 [email protected] [email protected] m 55919 9/2/2009 KIMIN कीसमन TINSUKIA SC 9612328008 45677 24/10/08 PASIGHAT पासीघाट TINSUKIA OBC 9863485426 [email protected] [email protected] om 49074 21/01/12 PGT Chem PGT Chem PGT Chem PGT Chem PGT Chem PGT Chem ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 14/2/11 14 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, BHUBANESWAR 3 DAY WORKSHOP ON IMPROVING RESULTS IN CLASS XII CHEMISTRY SL NO 1 2 3 REGION Bhubaneswar Guwahati Kolkatta Worksheet in Chapters^ 1,2,5 4,3,6 10,11,12 4 Ranchi 5 6 Concept Mapping in chapters # 13,14 15,16 1,2,3 7,8,9 Question bank in chapters* 1-5 for FAQ with minimum learning level 6- 10 for FAQ with minimum learning level 11- 16 for FAQ with minimum learning level 1-5 for above average Silchar 15,16 6 -10 for above average 7,8,9 Tinsukia 13,14 11-16 for above average 10,11,12 4,5,6, Note ^ Worksheets are to be prepared on a concept in the chapter. At least three concepts in each chapter should be taken up. Questions should be of one mark. Worksheet should include HOTS. Submit with Answers. * Q bank should be prepared such that the weak student feels encouraged. Q bank for board pattern student should be such that there is some challenge for the brighter student Submit with Answers # Concept mapping is done on one concept and not on an entire chapter. Hence there can be many concept maps in a chapter Submit as soft copy only All these should be typed in Calibri font, font size 12, space 1 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 15 SWOT Analysis Making The Most Of Your Talents And Opportunities Chance favours the prepared mind --Louis Pasteur Your Talent, Your Success • • You are most likely to succeed in life if you use your talent to your fullest extent Similarly you will suffer fewer problems if you know what your weaknesses are, and if you manage these weaknesses so that they don’t matter in the work you do. The Power of SWOTWhat makes SWOT specially Powerful is that with a little thought it can help you uncover opportunities that you would not have other wise spotted. And by understanding your weaknesses you can otherwise manage the threats that might otherwise hurt your abilities. View yourself through SWOT If you look at yourself through SWOT Framework, you can start seperating yourself from your peers, and further develop the specialised talent and abilities you need to advance in your career. Strengths What advantages do you have that others don’t? What do you do better than others? What personal resources can you access? What do other people ( boss, peers) see as your strength? Which of your achievements are you most proud of? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 16 What values do you believe in that others fail to exhibit? Are you part of a network that nobody is involved in? if so what connections do you have with influential people? Your perspective Consider this from your perspective, and from the point of view of the people around you. Don’t be modest or shy , be as objective as you can. If you have any difficulty with this write down a list of your personal charecteristics. Some of these will hopefully be strengths. Consider your strengths: Think about your strengths in relation to the people around you.For example, if you are very good in mathematics, and the people around you are also good in maths, then this is not likely to be a strength in your current role, it is only a necessity . Opportunities: A teacher goes on an extended leave; Can I take his role partially—say Exam department or CCA What new technology can help you? Learn more about computers—use them not only for power points but also for video recording. Do you get good contacts because of your nature that helps you benefit the school What trend do you see in your school how you can take advantage of these— eg: A circular to go to Foreign schools; study their requirements and work accordingly. Are any of the teachers failing to do anything important? Can you take advantage of their mistakes? Bring out something important and new that comes into the notice of the head. Do the teachers complain about something? Could you create an opportunity by providing a solution Potential Opportunities: • • • Networking events or educational classes A new role or project that forces you to learn new skills, like public speaking, international relations. Learning a foreign language for a potential opportunity of going abroad. • • Look Look at your strengths and ask yourself if these open up any opportunities Look at your weaknesses and ask yourself whether you can open up opportunities by eliminating these weaknesses. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 17 Threats What obstacles do you currently face at work? Are any of your colleagues competing with you for projects or roles? Is your Job (or the demand for the things you do) changing? Does changing technology threaten your position? Could any of your weaknesses lead to threats? Analyse Performing this analysis will lead to key information –it will point out what needs to be done and put problems into perspective. Key POINTS: A SWOT matrix is a framework for analyzing your strengths and weaknesses as well as oppertunities and threats that you face Helps you focuss on strengths Helps minimize your weaknesses. Assists in taking the greatest possible advantage of opportunities available to you. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 18 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 19 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 POLYMERS BIOMOLECULES CHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFE SURFACE CHEMISTRY 9 AMINES KINETICS 8 ALDEHYDES, KETONES, CARBOXYLIC ACID ELECTRO CHEMISTRY 7 ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS SOLUTIONS 6 HALO ALKANES AND HALO ARENES 5 CO ORDINATION COMPOUNDS 4 D BLOCK ELEMENTS 3 P BLOCK ELEMENTS 2 PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICES 1 SOLID STATE MARKSHEET in % 13-Apr 13-May 13-Jun 13-Jul 13-Aug 13-Sep 13-Oct 13-Nov 13-Dec 14-Jan 14-Feb This table can be used by the student to analyse his/ her weaknesses and strengths in XII chemistry. It can be further modified by identifying concepts in each chapter. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 20 CONCEPTS IN CLASS XI WHICH ARE USED IN CLASS XII (Which need to be mastered for better performance in class XII) Organic Chemistry –Some Basic Principles IUPAC Naming and structure—Including all functional groups (Some common names) Isomerism—geometrical, structural Classification of organic compounds Fundamental concepts of organic Reaction Mechanisms Homolytic and Hetrolytic Cleavage, Neucleophiles and Electrophiles, Electron movement in organic reactions Electron displacement effects in Covalent Bonds— I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Inductive Effect( +I And –I effect) Resonance effect ( writing resonance structures, predicting stabilities of resonance structures) a. Resonance effect ( +R and -R ) Hyperconjugation Reaction intermediates Stability of carbocations, carboanions and free radicals Types of organic reactions and their mechanisms [Substitution SN1, SN2; Addition Reactions; Elimination Reactions—alpha and beta, rearrangement reactions, polymerisation & condensation reactions ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 21 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 22 Hydrocarbons WurtzReaction,MarkovnikovRule,Kharash Effect(Peroxide effect)Ozonolysis ,Polymerizationand cyclicPolymerization, Aromatization , Isomerization,bayer’s reagent ,lindlar’scatalyst, dehydrohalogenation, Reaction—β-eliminationofhaloalkanes ( SaytzeffRule)Aromaticity, Resonance and stabilityofBenzene, ElectrophilicsubstitutionReactions--FriedelCraftReaction– alkylationandAcylation, NitrationAndhalogenations,Sulphonation, ElectrophilicadditionReactions--MarkovnikovRule, Free RadicaladditionReactions-KharashEffect(Peroxide effect)Directiveinfluenceofa functionalgroupinmonosubstitutedbenzene, ringactivatingandDeactivatinggroup towardselectrophile, MechanismofMarkovnikovRuleandKharash EffectPreparationand PropertiesofAlkane, alkene ,Alkyne, Benzene, AcidicCharacter ofAlkynes,alkenes and alkanes Effectofbranching on theboilingpointofisomericisomericcompounds (alkanes ,alcohols,haloalkanes)EffectofH-bondingon BPofalcohols,Carboxylicacids,Aminesetc.Understandingacidicand basiccharacterusingresonanceandInductiveeffect ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 23 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 24 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 25 REDOX REACTIONS Understandingtheconceptof RedoxReactions( bothoxidationandReductionhalfcell reaction),Calculationof Oxidationnumber.Identificationof oxidizingand reducingagentin a given reactionTypes of redox reactions–Combination,Decomposition,Displacement,DisproportionationReactions, Competitive electrontransferreactions--Metalactivityorelectrochemicalseries Balancingof redox reactions--halfreactionmethod( Ion–electronmethod) inacidic and basicmediumRedoxreactionsas thebasisfor Titrations. Redoxreactionsand electrodeprocesses--FeasibilityofRedoxcouple,Standard Hydrogenelectrode, Standard electrodepotential, Cell Representation , carriers of current,Sign ofelectrode,Halfcellreaction. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 26 EFFECTIVE REVISION STRATEGY By A.K PANDA , PGT ( CHEM) ,K V NO-3 ,BBSR PROBLEMS – Under performance of students despite having talents is a real disturbing phenomenon in the present days student mass . Poor attention span , fickleness , lack of determination , lack of self -belief Students complain they often forget whatever they learnt yesterday Learning through passive notes is the major stumbling block for better performance Solution : Revision is an art, and the people who master this art minimize time spent revising BUT maximize result. Effectiveness of revision is the “Maximization of Productivity” of technique adopted while learning . Qualitative revision guarantees better result . The purpose of revision :Revision means going over work in order to: (a) Check your understanding through organized notes (b) Make links between different topics to see how the whole subject/topics fits together. (c) Remind yourself of material you have forgotten. Record information you need to remember and then you can play it back to yourself. (d) Reinforce your learning. Through preparation of “Active Learning” material . (e) Identify and fill gaps in your knowledge. (f) To prepare a concept map or Mater Card which will give a panoramic view of whole chapter /topic / subjects ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 27 for quick view just before examination . (G) Reduction of anxiety just before the exam day Revision techniques :There are countless ways of revising. The least effective ways :- Just reading through notes over and over. The most effective ways :- Where you interact with the material, making it meaningful to yourself, for example: THROUGHREVISION GROUPS – groups of friends who help one another to revise by supporting, explaining, discussion and testing. Get someone else (your class mate) to test you, preferably a friend doing the same exam or by the teacher very often to lessen the anxiety and improvise the perfection Discussing the key word revision cards with other students ensure better performance . Through Master card preparation ( Preparation of Cards for effective drilling and time bound revision) Learning through organized materials helps longterm retention . Using your text book and class notes to organize the concepts in the fashion of outline notes and practice it (the key word revision cards) to bring out the maximum information with out assistance from your study material . to answer a question or address a problem you have not previously tackled. Hints and clue may be utilized to reconstruct a memory that has been organized . Identify the key points- words, phrases and diagrams ,examples and evidence for each topic keeping in mind that questions from past papers and text book questions are covered up . Preparation of outline active notes – An organized and intelligent question bank compel the students to search the answer from books and other allied materials –In a nut shell they are trained to read books and improvise self- study . This could be a true reflection of a chapter in a couple of work sheets . Revise in short bursts- Small chuncks are easier to remember. Frequent short-spells of learning are more effective than long ones . Several shorter practices spread out over a period of time will do much more good than a marathon session where your progress is impaired by fatigue. When studying, don’t be afraid to take a short break and then return to your work. Lengthy materials are divided into convenient units . Recalling through structured active sheets enhances output . ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 28 Go over the same material quite quickly several times rather than spending a long time on one occasion. (Cards are prepared for target setting in small chunks) We can move the “recall” from the SHORT-TERM to the LONGTERM memory through the series of revise and recapitulation cycle. Learning through Question Framing – Preparation of question framing indicators . Summarizing material under headings onto index cards. Prioritizing and leveling the questions: Make a priority list of questions and concepts in consultations with teachers and Stick to your list for the target specific exam . vis-à-vis syllabus and previous year question bank Set realistic goals with respect to time available . Reworking the material into a chart or diagram. ( MIND MAPS- cycle , linear ,interconnecting ,classification , spider map etc.) Make links, comparisons and contrasts between different areas of your program. Association and linking the concepts and terms helps to remember . Mnemonics can be a helpful way to memorize facts. Prepare for questions that combine two different topics. For slow learners (or Bloomers) : Repetition is extremely helpful in turning short-term memories into long term memories. Without repetition, short-term memory vanishes. * Fragmentation of big targets into various small achievable realistic targets (Confidence Building Measures) [Some of the above methods are tried by us in our day to day learning activities to ensure better performance and retaining in long term memory . ] What to revise? Syllabus for the exam is clear or not ? Difficult topic first? or Easy topic first ---------- Thre is no correct order . Choose the order that meets your needs ? Setting a positive challenge ? From where to revise ? when to revise ? What type Of exam I am to face ? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 29 Is it Monthly Test / Unit Test , Pre-Board , Board . Spoting Exam Questions ( PYQ- 5 Years ) Devise questions around a topic . List past exam questions. Grouping them into types of questions as per emphasis . Add questions which make other angle to the topic . Check to see which questions occur most frequently in past papers -- A rough guide to the likelyhood of particular question occurring . We must scan the question setter’s mind as per the trend . We must be in a position to predict the Questions for upcoming years . Question framing is not random . There is a specific structure in terms of level of questions and also with respect to concepts . List useful definitions . / key words / ideas / concept (as a part of revision) It helps to plan your revision Build-up good notes from which to revise Subject Syllabus Topics Subtopics -- Revise around these questions / Topics / Subtopics KEY –WORD REVISION CARDS # KEY –WORD REVISION CARDS are popular and effective way of developing your revision notes . # Revision Cards ( Key facts cards) – smaller than post card is better OBJECTIVES :- The intention is to record the minimum number of words to retain a full understanding of the information the next time you look at and use the cards . (Active processing and condensing them ) Keeping whole chapter’s note in small area has a great psychological effect . Enabling one to feel in control . Revising from a series of small non-bulky cards seems so much more manageable than overwhelming piles of A4 notes . (It manages voluminous revision ) Key words are designed to stimulate your recall of the topic without the necessary to write complex sentences Brief out line notes on a card can quickly capture the moment . ( try to condense a considerable amount of information on to it ] ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 30 Caution:- Borrowed Revision Cards are not that much of effective than your own cards . Always consult main notes if a point on your card is not clear . Cards are dynamic in nature and easy to use at any point :-There must be scope for amendment in your notes . What is the ideal time to make ? After completion of topic , immediately the outlines notes should be made as the topic is fresh in your mind .You must keep your material organized for the purpose of doing well in exam . Cards must contain ------ Recording / Recalling / diagrammatic data / Cross-sectional drawing / graphs / Tables / formula . Its practicability – Anytime –Anywhere Cross verifications helps in any areas which are not fully understood enables problem areas to be addressed at the early stage rather than just before exams . ,. Original Learning - Number of spaced revision final reproduction . Forgetting is made less and less rapid by repeated learning of the same material . . Memory Tree will be sharper with each repetitions . As if weapons are to be hi-tech to counter the volley of questions you are to face in exam ( as battle field) . Flash Cards - How to Use Flash Cards to Study Chemistry Flash cards are a quick, easy, visual way of setting priorities—both for the subjects themselves and for the minutia within said content area. By using flash cards to plan your study sessions, you can quickly identify essential versus negligible information. In algebra, for instance, you can create a stack pertaining to fractions, one to quadratic equations, and another to decimals, and simply arrange stacks based on the focus of the information. Great study habits are not simply confined to the human brain. There are other outside tools that can help maximize learning potential and get those synapses firing. One such tool is the flash card—something so simple, yet so effective Making education fun ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 31 One of the biggest reasons group studiers prefer flash cards is because they really can break the monotony and make education fun. Flashcards remain one of the best tools for memorizing information. The most common way to create flashcards is to use index cards. Students can simply write the question on one side and the answer on the opposite side and test themselves repeatedly. However, there are several ways to modify this process to enhance the learning experience. Memorize Facts & Reinforce Concepts with Flash Cards Flash cards can be a great study aid. You can use them to help memorize facts, lists, and structures as well as to reinforce important concepts. Here's how to prepare and use flash cards to study. Flashcards for Individuals and Flashcards for Study Groups Tackling advanced subjects Flash cards can make difficult subjects easier. Working with subjects that are so far off what one is used to naturally creates confusion when information starts piling up. The razor-precision focus that flash cards force your brain into keep you from getting overwhelmed when you encounter new and unfamiliar areas. Customizing the learning experience Flash cards are editable—either by hand or computer—and they provide unending support for the learner as he seeks to take charge of his studies and customize the experience in such a way that is interesting, effective and fun. It’s not enough to know the information; one must also be able to recall as much of it as he can within a set time framework with as much accuracy as possible This technique will enable the brain to recognize the most essential details of a concept or fact when it turns up on an exam or other crucial situations. Learning Facts with Flash Cards Start with a stack of blank index cards. On one side of a card, write a question or name of a structure you need to memorize. On the back of the card, write the answer. Limit yourself to one fact per card. Prepare as many cards as you need. To use the cards effectively, view the question and quiz yourself. Do you know the answer? Check the back of the card. If you answered correctly, set the card aside. If you were wrong, place the card on the back of your stack so that you will see it again. Proceed through your stack of cards. Set aside cards you get right and continue through cards you get wrong until you have gotten all questions/answers correct. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 32 Now shuffle the cards and repeat the process. Practice makes perfect, so if you get frustrated, set the cards aside and come back to them. Go through your cards every day (or more often, if you are cramming). Question framing Session Students must be intimated in advance about the lesson and the concept to be revised on a selected day for the upcoming examinations . Questions to be framed by the student (a) on a selected concept (b) Related to the concept outside the chapter after the questions based on chapter and concepts are over Teacher must give chance to the passive students to ask questions . (CBM for students) ( as each group has few members of active students and passive students- Duty of leader of group is to activate and train these passive students) passive students: who usually do not participate in group participation . 9 may be bright learners or just bloomers ) Gradation of questions ( easy , HOT , etc. ) – Verification of correctness of QS . through students and subsequent compilation. ( as the teacher has no time to all this - taking the help of students ) Use of flash cards , stimulate the mind of some students , try to frame the questions based on the answer they know. Teachers must classify these QS as MLL question and related to TBQ and PYQ of CBSE . # Advantages : * If someone can frame questions , he or she knows about the answer and understand the topic well , or questions * Familiarity with questions will reduce fear from facing questions Confidence will increase Concepts will be revised and its fundamentals will become clear ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 33 Questions of graded difficulty will be available as question bank related to the topic Alertness in the class will be visible as everybody would like to participate in the question Anser Session . Incentive must be given to the group member for best question framing . competitiveness will be developed . By showing the flash cards . EFFECTIVE REVISION STRATEGY PROBLEMS – Under performance of students despite having talents is a real disturbing phenomenon in the present days student mass . Poor attention span , fickleness , lack of determination , lack of self -belief Students complain they often forget whatever they learnt yesterday Learning through passive notes is the major stumbling block for better performance Solution : Revision is an art, and the people who master this art minimize time spent revising BUT maximize result. Effectiveness of revision is the “Maximization of Productivity” of technique adopted while learning . Qualitative revision guarantees better result . The purpose of revision :Revision means going over work in order to: (a) Check your understanding through organized notes (b) Make links between different topics to see how the whole subject/topics fits together. (c) Remind yourself of material you have forgotten. Record information you need to remember and then you can play it back to yourself. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 34 (d) Reinforce your learning. Through preparation of “Active Learning” material . (e) Identify and fill gaps in your knowledge. (f) To prepare a concept map or Mater Card which will give a panoramic view of whole chapter /topic / subjects for quick view just before examination . (G) Reduction of anxiety just before the exam day Revision techniques :There are countless ways of revising. The least effective ways :- Just reading through notes over and over. The most effective ways :- Where you interact with the material, making it meaningful to yourself, for example: THROUGHREVISION GROUPS – groups of friends who help one another to revise by supporting, explaining, discussion and testing. Get someone else (your class mate) to test you, preferably a friend doing the same exam or by the teacher very often to lessen the anxiety and improvise the perfection Discussing the key word revision cards with other students ensure better performance . Through Master card preparation ( Preparation of Cards for effective drilling and time bound revision) Learning through organized materials helps longterm retention . Using your text book and class notes to organize the concepts in the fashion of outline notes and practice it (the key word revision cards) to bring out the maximum information with out assistance from your study material . to answer a question or address a problem you have not previously tackled. Hints and clue may be utilized to reconstruct a memory that has been organized . Identify the key points- words, phrases and diagrams ,examples and evidence for each topic keeping in mind that questions from past papers and text book questions are covered up . Preparation of outline active notes – An organized and intelligent question bank compel the students to search the answer from books and other allied materials –In a nut shell they are trained to read books and improvise self- study . This could be a true reflection of a chapter in a couple of work sheets . ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 35 Revise in short bursts- Small chuncks are easier to remember . Frequent short-spells of learning are more effective than long ones . Several shorter practices spread out over a period of time will do much more good than a marathon session where your progress is impaired by fatigue. When studying, don’t be afraid to take a short break and then return to your work. Lengthy materials are divided into convenient units . Recalling through structured active sheets enhances output . Go over the same material quite quickly several times rather than spending a long time on one occasion. (Cards are prepared for target setting in small chunks) We can move the “recall” from the SHORT-TERM to the LONGTERM memory through the series of revise and recapitulation cycle. Learning through Question Framing – Preparation of question framing indicators. Summarizing material under headings onto index cards. Prioritizing and leveling the questions: Make a priority list of questions and concepts in consultations with teachers and Stick to your list for the target specific exam . vis-à-vis syllabus and previous year question bank Set realistic goals with respect to time available. Reworking the material into a chart or diagram. (MIND MAPS- cycle, linear ,interconnecting ,classification , spider map etc.) Make links, comparisons and contrasts between different areas of your program. Association and linking the concepts and terms helps to remember . Mnemonics can be a helpful way to memorise facts. Prepare for questions that combine two different topics. For slow learners (or Bloomers) : Repetition is extremely helpful in turning short-term memories into long term memories . Without repetition , short-term memory vanish. * Fragmentation of big targets into various small achievable realistic target (Confidence Building Measures) [ Some of the above methods are tried by us in our day to day learning activities to ensure better performance and retaining in long term memory . ] ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 36 What to revise ? Syllabus for the exam is clear or not ? Difficult topic first ? or Easy topic first ---------- There is no correct order . Choose the order that meets your needs ? Setting a positive challenge ? From where to revise ? when to revise ? What type Of exam I am to face ? Is it Monthly Test / Unit Test , Pre-Board , Board . Spoting Exam Questions ( PYQ- 5 Years ) Devise questions around a topic . List past exam questions. Grouping them into types of questions as per emphasis . . Add questions which make other angle to the topic . Check to see which questions occur most frequently in past papers -- A rough guide to the likelyhood of particular questions. Occurring We must scan the question setter’s mind as per the trend . We must be in a position to predict the Qs . for upcoming years . Question framing is not random . There is a specific structure in terms of level of questions and also with respect to concepts . List useful definitions . / key words / ideas / concept (as a partr of revision) It helps to plan your revision Build-up good notes from which to revise Subject Syllabus Topics Subtopics -- Revise around these questions / Topics / Subtopics KEY –WORD REVISION CARDS # KEY –WORD REVISION CARDS are popular and effective way of developing your revision notes . # Revision Cards ( Key facts cards) – smaller than post card is better OBJECTIVES :- The intention is to record the minimum number of words to retain a full understanding of the information the next time you look at and use the cards . (Active processing and condensing them ) Keeping whole chapter’s note in small area has a great psychological effect . Enabling one to feel in control . Revising from a series of small non-bulky cards seems so much more manageable than overwhelming piles of A4 notes . (It manages voluminous revision ) ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 37 Key words are designed to stimulate your recall of the topic without the necessary to write complex sentences Brief out line notes on a card can quickly capture the moment . ( try to condense a considerable amount of information on to it ] Caution:- Borrowed Revision Cards are not that much of effective than your own cards . Always consult main notes if a point on your card is not clear . Cards are dynamic in nature and easy to use at any point :-There must be scope for amendment in your notes . what is the ideal time to make ? After completion of topic , immediately the outlines notes should be made as the topic is fresh in your mind .You must keep your material organized for the purpose of doing well in exam . Cards must contain ------ Recording / Recalling / diagrammatic data / Cross-sectional drawing / graphs / Tables / formula . Its practicability – Anytime –Anywhere Cross verifications helps in any areas which are not fully understood enables problem areas to be addressed at the early stage rather than just before exams . ,. original Learning - No. of spaced revision final reproduction . Forgetting is made less and less rapid by repeated learning of the same material . . Memory Tree will be sharper with each repetitions . As if weapons are to be hi-tech to counter the volley of questions you are to face in exam ( as battle field) . Flash Cards - How to Use Flash Cards to Study Chemistry Flash cards are a quick, easy, visual way of setting priorities—both for the subjects themselves and for the minutia within said content area. By using flash cards to plan your study sessions, you can quickly identify essential versus negligible information. In algebra, for instance, you can create a stack pertaining to fractions, one to quadratic equations, and another to decimals, and simply arrange stacks based on the focus of the information. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 38 Great study habits are not simply confined to the human brain. There are other outside tools that can help maximize learning potential and get those synapses firing. One such tool is the flash card—something so simple, yet so effective Making education fun One of the biggest reasons group studiers prefer flash cards is because they really can break the monotony and make education fun. Flashcards remain one of the best tools for memorizing information. The most common way to create flashcards is to use index cards. Students can simply write the question on one side and the answer on the opposite side and test themselves repeatedly. However, there are several ways to modify this process to enhance the learning experience. Memorize Facts & Reinforce Concepts with Flash Cards Flash cards can be a great study aid. You can use them to help memorize facts, lists, and structures as well as to reinforce important concepts. Here's how to prepare and use flash cards to study. Flashcards for Individuals and Flashcards for Study Groups Tackling advanced subjects Flash cards can make difficult subjects easier. Working with subjects that are so far off what one is used to naturally creates confusion when information starts piling up. The razor-precision focus that flash cards force your brain into keep you from getting overwhelmed when you encounter new and unfamiliar areas. Customizing the learning experience Flash cards are editable—either by hand or computer—and they provide unending support for the learner as he seeks to take charge of his studies and customize the experience in such a way that is interesting, effective and fun. It’s not enough to know the information; one must also be able to recall as much of it as he can within a set time framework with as much accuracy as possible This technique will enable the brain to recognize the most essential details of a concept or fact when it turns up on an exam or other crucial situations. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 39 Learning Facts with Flash Cards Start with a stack of blank index cards. On one side of a card, write a question or name of a structure you need to memorize. On the back of the card, write the answer. Limit yourself to one fact per card. Prepare as many cards as you need. To use the cards effectively, view the question and quiz yourself. Do you know the answer? Check the back of the card. If you answered correctly, set the card aside. If you were wrong, place the card on the back of your stack so that you will see it again. Proceed through your stack of cards. Set aside cards you get right and continue through cards you get wrong until you have gotten all questions/answers correct. Now shuffle the cards and repeat the process. Practice makes perfect, so if you get frustrated, set the cards aside and come back to them. Go through your cards every day (or more often, if you are cramming). Question framing Session Students must be intimated in advance about the lesson and the concept to be revised on a selected day for the upcoming examinations . Questions to be framed by the student chapter and concepts are over (a) on a selected concept (b) Related to the concept outside the chapter after the questions based on Teacher must give chance to the passive students to ask questions . (CBM for students) ( as each group has few members of active students and passive students- Duty of leader of group is to activate and train these passive students) passive students: who usually do not participate in group participation . 9 may be bright learners or just bloomers ) Gradation of questions ( easy , HOT , etc. ) – Verification of correctness of QS . through students ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 40 and subsequent compilation. ( as the teacher has no time to all this - taking the help of students ) Use of flash cards , stimulate the mind of some students , try to frame the questions based on the answer they know. Teachers must classify these QS as MLL question and related to TBQ and PYQ of CBSE . # Advantages : * If someone can frame questions , he or she knows about the answer and understand the topic well , or questions * Familiarity with questions will reduce fear from facing questions Confidence will increase Concepts will be revised and its fundamentals will become clear Questions of graded difficulty will be available as question bank related to the topic Alertness in the class will be visible as everybody would like to participate in the question Anser Session . Incentive must be given to the group member for best question framing . competitiveness will be developed . By showing the flash cards . KEY –WORD REVISION CARDS # KEY –WORD REVISION CARDS are popular and effective way of developing your revision notes . # Revision Cards ( Key facts cards) – smaller than post card is better Key words are designed to stimulate your recall of the topic without the necessary to write complex sentences Brief out line notes on a card can quickly capture the moment . ( try to condense a considerable amount of information on to it ] Caution Borrowed Revision Cards are not as much of effective as your own cards . Always consult main notes if a point on your card is not clear . Cards are dynamic in nature and easy to use at any point :-There must be scope for amendment in your notes . ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 41 What is the ideal time to make ? After completion of topic , immediately the outlines notes should be made as the topic is fresh in your mind .You must keep your material organized for the purpose of doing well in exam . Cards must contain ----- Recording / Recalling / diagrammatic data / Cross-sectional drawing / graphs / Tables / formula . ITS PRACTICABILITY Anytime –Anywhere Reliability of cards Cross verifications helps in any areas which are not fully understood enables problem areas to be addressed at the early stage rather than just before exams . , Advantage Original Learning - No. of spaced revision final reproduction. Forgetting is made less and less rapid by repeated learning of the same material. Memory Tree will be sharper with each repetitions. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 42 \ ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 43 1. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. CO /CO2 H3BO3 /H2SO4 BCl3/TlCl3 BCl3 /CCl4 33[BF6] /[AlF6] PbCl4 /SnCl4 Al2O3 /B2O3 BCl3 /BH3 BCl3 /SiCl4 2. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. CRACK THE CODE IN THE FOLLOWING PAIRS CLASS-XI–P-BLOCK ELEMENTS BCl3 /AlCl3 3. H3BO3/H3PO3 GaCl /TlCl 21. PBI4/PbCl4 PbO2 /SnCl2 22. Diamond /Graphite BF3 /BCl3 23. BH3 /[BH4]ֿ PbCl2 /PbCl4 24. Ga /Al TlCl/TlCl3 25. Water Gas /Producer AlF3 /AlCl3 Gas Carbon /Silicon 26. BCl3/PCl3 B2H6 /H3BO3 27. N(CH3)3 / N(SiH3)3 33. BF3 /[BF4]ֿ ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 4. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. CO2 /SiO2 Nitrate /Phosphate HNO3 /H3PO4 BF3/NF3 22[SiF6] /[SiF6] SiCl4/CCl4 on ? rac pr ot cha fo r ng ffi n ty uci te ra r ed ea gr s ha ch ar ter lity? ac wh i ch i stab mal g xin mo re her pl e om er T rc h as tte h i gh be ich as h as hh ? ha Wh hi c ich Which ( N-H / P-H ) BDE is more ? ch whi W Wh ter? 44 e' s m l o sR ott en fi s hs me ll W h hi c NH 3 / PH 3 e? atil oc pr so di s rm th A gC ne l? 's ho er in H mo re mo re hi c bb as Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com ne fo Ha hh h as bo ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India ch o in hi c ich W W hi es s? W Which one d h ic Wh ? Which is more Basic? Wh ore is m al s ? Which is more Acidic? vol is d use n sig nd b oi an l i ng gl e p oi nt? &w hy ? 45 SESSION Students must be intimated in advance about the lesson and the concept to be revised on a selected day for the upcoming examinations . Questions to be framed by the student (a) on a selected concept (b) Related to the concept outside the chapter after the questions based on chapter and concepts are over Teacher must give chance to the passive students to ask questions . (CBM for students) (as each group has few members of active students and passive students- Duty of leader of group is to activate and train these passive students) Who are passive students: who usually do not participate in group participation. (may be bright learners or just bloomers ) Gradation of questions ( easy , HOT , etc. ) – Verification of correctness of QS . through students and subsequent compilation. ( as the teacher has no time to all this - taking the help of students ) Use of flash cards , stimulate the mind of some students , try to frame the questions based on the answer they know. Teachers must classify these QS as MLL question and related to TBQ and PYQ of CBSE . Advantages : If someone can frame questions , he or she knows about the answer and understand the topic well , or questions Familiarity with questions will reduce fear from facing questions Confidence will increase Concepts will be revised and its fundamentals will become clear Questions of graded difficulty will be available as question bank related to the topic Alertness in the class will be visible as everybody would like to participate in the question Answer Session . Incentive must be given to the group member for best question framing . competitiveness will be developed . By showing the flash cards . NaCl Common salt ki Dandi march ---- From the angle of chemistry THE SOLID STATE : 1# NaCl is a -------------------(amorphous , crystalline) substance . 2# NaCl belongs to ----------- crystal system ? ( cubic , hexagonal , triclinic , orthorhombic ) 3# NaCl shows a property of ---------------- ( isotropic , anisotropic) ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 46 4# Which one conducts both in molten and aqueous state but not conduct in solid state ( Na , NaCl) 5# NaCl is is which type of crystal ? ( covalent , metallic , ionic , molecular) 6# NaCl belongs to --------------- type crystal ? ( primitive , bcc , fcc) 7# What is the Co-ordination number of NaCl ? 8# NaCl belongs to --------------------- type of packing ? ( ABABAB… , ABCABCABC…..) 9# In NaCl crystal , which one present in octahedral voids ? (Na+ , Cl-) 10# NaCl crystal act as ------( insulator , semiconductor , conductor) at room temperature . 11# How many number of chloride ions present in a cubic unit cell of Na Cl ? 12# When NaCl is heated conductivity ---------------------- ( increases , decreases) 13# F-Centre is ---------------------- type of defect ( stoichiometric , non-stoichiometric) 14# NaCl shows ---------------------- defect ( Frenkel , Shottky ) 15# NaCl is ----------------- ( diamagnetic , paramagnetic) substance . 16# What happens when NaCl crystals are heated in a atmosphere of sodium vapours ? 17# When NaCl added in SrCl2 , what type of defect is observed ? ( Shottky defect , frenkel defect , impurity) 18# F-centre shown by NaCl crystal is ----------------- in colour ? ( pink , yellow , violet) 19# If NaCl is doped with 10-3 mol% of SrCl2 ,The concentrations of cation vacancies are ---20# Refractive index of which solid is /are observed to have the same value along all directions ? ,Quartz , Glass , PVC) 22# What percent of octahedral voids are occupied in NaCl crystal ? ( 25% , 50% , 100%) 23# When NaCl crystal is heated what happens to its Co-ordination number ? (increases , decreases) ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com ( NaCl 47 CHAP-2 : SOLUTIONS 24# What inter-particle interaction is present when NaCl is dissolved in water ? 25# Vapour pressure is ---------------(increased , decreased) when NaCl is added in water . 26# Which has more Freezing point and why ? ( Distilled water or Sea water ) 27# What is the van’t Hoff factor of NaCl in very dilute solution in Water? 28# Whose boiling point is more and why ? ( 1mol of NaCl in 100 mL water , 1 mol of Glucose in 100mL water) 29# Which has more osmotic pressure and why ? (1M NaCl solution , 1M Glucose solution) 30# Name the process used to get fresh water from salt water . 31# Why NaCl act as de-icing agent ? 32# How NaCl helps to preserve meat ? 33# 1% NaCl solution is called ------- (hypertonic , hypotonic , isotonic) solution to the plasma concentration of human blood cell ? 34# When you measure molar mass through colligative properties ,why NaCl shows abnormal molecular mass but nor glucose ? 35# When a person takes lot of salt or salty food , he/she experience water retention in tissue cells and intercellular spaces because of ---------------- . The resulting puffiness or swelling is called ------------------------- . 36# When 5.85g of NaCl is added in 100 mL water , then the Formality(or Molarity)of the aq. Solution is -------- M 37# When heated solubility of NaCl in water -------------------------- ( decreases , increases) 38# Aqueous NaCl solution is ------------------- solution ( ideal , non-ideal) 39# Aqueous NaCl solution is shows ----------------(positive , negative , no ) deviations from Raoult’s Law . 40#” Kya apke tooth paste me NAMAK HAI” ? Why NaCl is added in tooth paste ? 41# Whose “i” (van’t Hoff factor ) is more and why ? ( 0.1m , 0.01m) 42# Why doctors asked the patient to take low sodium salt for high B.P patient ? 43# Why do you gargle luke warm salt water ? CHAP-3 : ELECTROCHEMISTRY 44# NaCl is --------------------(strong , weak) electrolyte 45# Which one is used in salt bridge more frequently ? ( NaCl , KCl) 46# Corrosion becomes --------------- (faster . slower) in saline condition. 47# When dilution occurs in Aq. NaCl solution , conductivity ------(decreases , increases) 48# Write the Kohlrausch limiting molar conductivity equation for NaCl ? 49# Molar conductivity of aq. NaCl -----(increases , decreases) with dilution linearly with √C 50# What happens when aqueous NaCl is electrolysed at platinum electrode ? 51# What happens when molten NaCl is electrolysed at platinum electrode ? 52# Say True of False . Limiting molar conductivity cannot be obtained for aq. NaCl graphically . ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 48 53# Which one show more limiting conductivity in water at 298 K ? ( Na+ , K+ ) 54# How much Chlorine gas in terms of gram would produced when 96500 C is passed in aq NaCl solution . CHAP-5 : SURFACE CHEMISTRY : 55# NaCl in water is a ------------------------- ( crystalloid , colloid) 56# Say TRUE or FALSE . -- Aq . solution of NaCl will show Tyndal Effect . 57# What happens when NaCl is added in positively charged sol ferric hydroxide ? 58# Which has better coagulation capacity for potitively charged ferric hydrohyde sol ? ( NaCl , Potassium Ferrocyanide) 59# Name the enzyme that shows high catalytic activity in presence of NaCl which provides Na+ . 60# What is the charge of sol developed when NaCl is added in excess of AgNO3 solution ? Chap-7 : p-BLOCK ELEMENTS 61# Name the gas obtained when NaCl is treated with Conc . H2SO4 . 62# Name the gas produced when NaCl is reacted with MnO2 and Conc . H2SO4 . ? 63# What do you observe when Aq.NaCl is treated with acidified KMnO4 solution ? 64# Which is more covalent in nature ? ( LiCl , NaCl ) Miscellaneous ---------65# Why NaCl is added in soap preparation ? 66# Why a small amount of NaCl is added during the preparation of egg albumin sol . So on ------- and so on --------------------It’s not an End -------------------please continue …… ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 49 WORKSHEETS Chapter 1: Solid State CONCEPT: Close packing of SOLIDS I)Match the following COLUMN-A a) b) c) d) COLUMN-B Sqaure close packing in two dimension Hexagonal close packing in two dimensions Hexagonal close packing in threedimensionsl cubic close packing in three dimensions 1 2 3 4. Triangular voids Pattern of spheres is repeated in every fourth layer. Pattern of spheres is repeated in alternate layers layer. Co-ordination number-4 II) Multiple choice questions. 1. Percentage of empty space in a body centre cubic arrangement is a) 74 b) 32 c) 26 2.The total no of tetrahedral voids in fcc is a) 6 b) 8 c) 10 3. Which of the following statement is/ are not true in the hexagonal close packing. a) Packing efficiency 74% b) C.N=12 c) Tetrahedral voids of the second layer are covered by the spheres of the third layers. d) Spheres of the fourth layer are exactly aligned with those of the first layer 4. In which pair most efficient packing is present. a. hcp & bcc c. hcp& ccp b. bcc& ccp d. bcc& simple cubic 5. In which of the arrangement octahedral voids are formed a. Hcp c. fcc b. bcc d. simple cubic III) FILL IN THE BLANKS 1. The C.N of each sphere in hcp is ----------- while that of bcc is __________. 2. An octrahedral void is ----------------times larger than a tetrahedral void. 3. ABAB… type of packing is called---------- where as ABCABC…type of packing is called fcc. 1/2 4. For bcc, r=3 a /4, then for fcc, r=---------. Ans: I) a-4, b-1, c-3, d-2 II) 1-d, 2-8, 3-d, 4-c III) 1. 12 & 8; 3. HCP 2. two 4. √2 a/4 CONCEPT: CLASSIFICATION OF SOLIDS ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com d) 68 d) 12 50 A) Match the following COLUMN-A COLUMN-B a) Ionic crystal 1 Graphite b) Metallic crystal 2 Ice c) Covalent crystal 3 MgO d) Non polar crystal 4 Gold e) Hydrogen bonded crystal 5 Dry ice 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. B) Multiple choice questions. Which of the following is a network solid? a. I2 b. SO2 (solid) c. d. Diamond Argon Which of the following is not an electrical conductor? a. Ar b. Mg c. TiO d. H2O i. only b) iii. a &d ii. only c) iv. b, c&d Which of the following is not a characteristic of a crystalline solid? a. True solid c. isotropic in nature b. long range order d. definite heat of fusion A solid is very hard, electrical insulator in solid state as well as in molten state& melts at extremely high temperature . It may be a. covalent solid c. molecular solid b. metallic solid d. ionic solid Iodine molecules are held in crystals by a. London forces b. coulombic forces c. d. dipole- dipole interactions covalent bonds C:FILL IN THE BLANKS ( BY choosing appropriate words given in the bracket)(isotropy, valence electrons, amorphous) 1. 2. 3. Graphite is a good conductor due to presence of -----------. Glass is a ---------- solid as it shows fluidity. If the electrical conductivity is same in all direction through a solid the substance is an amorphous solid& this property is called ------------. ANS A: a-3 b-4, c-1, d-5, e-2 B:1-c, 2-iii, 3-c, 4-a, 5-a C: 1. Free electrons 2. Psuedo solid 3. Isotropy CONCEPT: DEFECTS IN CRYSTALS A) Match the following ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 51 COLUMN-A COLUMN-B a) Schottky defect 1 Crystals become coloured b) Doping silicon with aluminium 2 n-type of semiconductors are formed c) Doping silicon with arsenic 3 NaCl with Sr & some cationic sites vacant. d) Heating NaCl crystal in presence of sodium vapour. 4 Density of the crystals decreases 5 p- type of semiconductore is formed e) +2 Impurity defects Ans: a-4, 1. 2. 3. b-5, c-2, d-1, e-3 B) Multiple choice question Which kind of defects are introduced by doping? a. dislocation defect b. Schottky defect Which of the following is also known as dislocation defect? a. Schottky defect b. Frenkel defect Which of the following defects are shown by AgBr a. Schottky defect b. Frenkel defect c. d. Frenkel defect Electronic defects c. d. nonstoichiometric defect simple interstitial defect c. d. metal excess defect metal deficiency defect i. a &b iii. a &c ii. c &d iv. b&d 4. To get an n-type of semiconductor from silicon it should be doped with a substance with valence --------electrons a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 5 5. Schottky defect is observed in the crystal when a. some cations move from their lattice sites to interstitial sites b. equal number of cations and anions are missing from the lattice c. some lattice sites are ocuupied by the electrons d. some impurity is present in the lattice Ans: 1 a 2d 3a 4d 5b FILL IN THE BLANKS 1. NaCl crystals have some yellow colour is due to the presence of -----------. 2. The process of adding impurities to a crystalline substance so as to change its properties Like conductivities etc is called ---------------3. Frenkel defect is shown by crystals having low coordination number & ---------- difference in the size of the cations & anions. 4. Schottky defect in ionic crystals always results in --------- of density. 5. ----------- crystal defect is produced when NaCl is doped with MgCl2. Ans: ( F-centre ,doping, large, decrease, impurity defect) Prepared by: Bhubaneswar Region ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 52 UNIT-1: TOPIC: SOLID STATE : worksheet for class-xii FILL IN THE BLANKS/ CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER CONCEPT- Defects chap-solid state CONCEPT- Defects chap-solid state CH-SOLID STATE CARD -7 [1×5=5M] CH-SOLID STATE CARD -8 [1×5=5M] 28# The excess of lithium in LiCl makes it pink is 33# When an electron is trapped in an anion due to ----------------------------vacant centre , it is called ------------------------. 29 # The compound that shows both Schottky 34# Si , Ge can be doped with a group -------------and Frenkel defect is ----------------------elements to produce p-type semiconductor. 30# Doping ---------(minimizes , maximizes) the ( Gp- 12,13,14,15) forbidden energy gap . 35# Solar cell is an efficient -------------------------31# The forbidden energy is maximum in -------( photo-diode , photo-triode) ( Ge , Mg , NaCl ,Ge doped with In ) 36# Diode acts as a ------- ( rectifier , amplifier) 32# Which one show metal excess defects 37# ---------------- oxide is like metallic cu in its ( FeO , ZnO) conductivity and appearance . 28- f centres, 29- AgBr; 30-min; 31-NaCl, 32-ZnO 33-F centre; 34-13gp, 35- photo-diode, 36-a rectifier, 37CONCEPT- Defects chap-solid state CH-SOLID STATE CARD -9 [1×3=3M] 38# The process of adding an appropriate amount of suitable impurity to increase the conductivity of a intrinsic semi-conductor like S , Ge is called 39# When in a substance the magnetic moments of the domains are alligned in parallel and antiparallel directions in unequal numbers , the phenomenon observed is called ----------- . (ferromagnetism, anti-ferromagnetism, ferrimagnetism) 40# In which type of semi-conductor , electron holes are moving towards negatively charged plate under the influence of electric field ? ( ptype , n-type) Ans: 38-doping, 39-ferrimag, 40- p-type CONCEPT- Defects chap-solid state CH-SOLID STATE CARD -10 [1×3=3M] 41# If an atom is missing from its lattice site and it occupies the interstitial site , the electrical neutrality as well as the stoichiometry of the compound are maintained . This type of defect is called -------------------- defect . 42# The set of molecular orbitals generated due to overalp of atomic orbitals having very close in energy is called --------43# Frenkel defect is shown by the crystals having --------------- (high , low) co-ordination number and ---- ( large , small) difference in the size of the cations and the anions . CONCEPT- Amorphous and crystalline solids CH-SOLID STATE CARD -11 [1×6=6M] 44# ---------------- is a covalent crystal ( Iodine , NaCl , ice , Carborundum) 45# Which one will show anisotropy ? ( quartz , paraffin wax , rubber , quartz glass ) 46# ---- solids conducts electricity in molten state but not in solid state. ( molecular , ionic , metallic , covalent) 47# ---------------- solids have very high melting point ( molecular , ionic , metallic , covalent) 48# Solar cell is an efficient ------------------( photo-diode , photo-triode) 49# Photovoltaic material is -------------------( Amorphous silicon , Pure silicon crystal) 50# Some of the glass from ancient civilizations which are with us are milky in appearance due CH-SOLID STATE---MISCELLANEOUS CARD -12 [1×5=5M] WRITE TRUE OR FALSE . Ans: 41-frenkel, 42-energy band, 43-low 51# In end –centred unit cell of an atomic substance there are four atoms per unit cell. [ ] 52# In rock-salt structure, the number of formula units per unit cell is four. [ ] 53# Schottky defects disturb the ratio of cations and anions in the compound . 54# NaCl is a paramagnetic substance. [ ] 55# A compound having radius ratio (r+/r-) in the ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 53 to ---44-carborundum, 45-quartz, 46-ionic, 47-ionic, 48-photo diode 49- amorphous silicon, 50flowing of glass followed by crystallisation, 51-f, 52-t, 53- f, 54- f, 55-t range 0.732—1 generally CH-SOLID STATE---MISCELLANEOUS CARD -13 [1×5=5M] WRITE TRUE OR FALSE . CH-SOLID STATE---MISCELLANEOUS CARD -14 [1×5=5M] WRITE TRUE OR FALSE . 56# Fe3O4 is ferrimagnetic .Among the three type of arrangement , hcp,ccp,and bcc, the most efficient packing is bcc. [ ] 61# 14 kinds of space lattices are possible in the crystal. [ ] has CsCl structure. [ ] 62# Pure alkali halides show Frenkel Defects . [ 57# If the radius ratio is in the range 0.225—0.414 the cation prefers to be present in an octahedral void. [ ] 58# Diamond is an example of atomic solid. [ ] 59# Orthorhombic unit cell has least symmetry [] 60# F-centre is a type of stoichiometric defect.[ ] 63# When temperature increases conductivity of semi-conductor decreases. [ ] 64#Frenkel defect is shown by ionic substance in which there is a large difference in the size of ions[ ] 65# The existence of different chemical compounds in the same crystallineform is called allotropy. [ ] 61-t, 62-t, 63-f, 64-t, 65-f 56-f, 57-f, 58-t, 59-f, 60-t ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com ] 54 answersQ.26# Q.27# Q.28# Q.29# Q.30# diamagnetic ZnO F-Centre ,Electron trapped in anion vacant centre AgBr minimizes Q.31# Q.32# Q.33# Q.34# Q.35# NaCl ZnO F-centre 13 Photo-diode Q.36# Q.37# Q.38# Q.39# Q.40# Rectifier ReO3 Doping Ferrimagnetism p-type Q.41# Q.42# Q.43# Q.44# Q.45# Frenkel defect Bands Low Carborundum quartz Q.46#. Q.47# Q.48# Q.49# Q.50# ionic covalent photo-diode Amorphous silicon Due to some crystallization Prepared by : Mr A K PANDA , PGT(CHEMISTRY) ,KV NO-3 , BBSR SOLUTIONS Colligative properties 1. Why the boiling point of solution is higher than pure liquid ? 2. Fill the space of column -B by matching with Column -A by taking following values: ∆H mix< 0 and ∆V mix< 0 ; ∆H mix = 0 and ∆V mix = 0 ;∆H mix> 0 and ∆V mix> 0 Column –A Column -B A Ethyl alcohol and water B CCI4 and Benzene or toluene C Water- nitric acid D Aniline –acetone ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 55 E Chloro benzene-Bromobenzene F n-hexane and n-heptane 3. 4. Ammonia dissolve in water and Fluorine dissolve in water will not obey Henry's law why? Fill in the blanks. a) Constant boiling mixtures are called -----------? b) The boiling point of one molal solution is known as --------? c) Liquid having similar structure and polarity form ----------type of solution? d) Solution having same osmotic pressure have same concentration are known as -----------? e) The symptom observed by a person at high altitudes is ------------? 5. Identify the portions from the following graphs: P0 P Vapour pressure Solvent Slope = ? P X (A) ? Solution Temperature (B) 0 P1 P= P1 + P2 P20 0 P2 P1 P o Slope = P2 V.P o P1 P2 (C) X1 = 0 X1 = 1 ? X2 = 0 X2 (D) A M.F Type of solution =? X2 = 1 B B Type of solution =? (E) (F) Type of solution = ? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 56 Liquid (G) Vapour pressure Vapour pressure 1 atm Solvent Solution ? O Temperature Tb Solid ? Tf Tb (H) Solvent Solution 0 Tf Temperature Answers 1.Ans. Due to lowering in v.p 2. Ans A & B =>∆H mix> 0 and ∆V mix> 0 C & D =>∆H mix< 0 and ∆V mix< 0 E & F =>∆H mix = 0 and ∆V mix = 0 3. Ans. Because ammonia highly soluble and fluorine highly reactive with water. 4.Ans.a- Azeotrope; b- molal elevation constant/ Ebulliscopic constant ; c- Ideal solution; d- Isotonic solution ; e- Anaxia 0 5. Ans A- KH ; B = ∆P ; C = p1 ; D = ideal solution ; E= +ve deviation ;F= -ve deviation G. ∆Tb H. ∆Tf Concentrations 1. Under what condition molarity and molality will be same? 2. 15ppm by mass = -------- (w/w) % 3. Out of 1M and 1m aqueous solution which is more concentrated 4. What is the molarity of water? (taking density of water =1g/cc) 5.What will be the mole fraction of water in equimolar solution of ethanol? 6.Determine the correct order of the property mentioned against them : (a) 10% Glucose (p1), 10% Urea (p2) , 10% Sucrose(p3) { Increasing osmotic pressure} (b) 0.1 M NaCl ; 0.1M Urea ; 0.1M CaCl2 { Increasing order of boilig point} (c) 0.1 g NaCl; 0.1g KCl; 0.1 g LiCl Increasing order of V.P} Answers 1.Ans : Density of the solution is unit. -3 2. Ans 1.5 X 10 3. Ans. 1M as density of water is 1gm/ml 4.Ans 55.55 moles 5.Ans 0.5 6.(a) Sucrose< Glucose < Urea (b)Urea< NaCl < CaCl2 (c) LiCl < NaCl < KCl Concept: Van't Hoff's Factor 1. What is the Vant Hoff factor in K4[Fe(CN)6] ? 2.What will be the van’t Hoff factor for O.1 M ideal solution? 3. Out of 1M CaCl2 and 1 M AlCl3 which having higher vapour pressure? 4.How the vant't Hoff factor changes with decrease of molality of the solution? 5. Match the following Column –A Column -B ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 57 A 100% Dissociation of NaCl 0.5 B 100% Dissociation of AlCl3 1.5 C 100% Dissociation of Na2SO4 2 D 100% Dissociation of Al2(SO4)3 5 E 50% Dissociation of AgCl 3 F 75% Dissociation of AgBr 1.75 G 100% dimerisation of benzoic acid 4 Answers 1. Ans. Five 2. Ans. Van't Hoff factor = 1, because ideal solution does not undergo dissociation or association 3. Ans. 1 M CaCl2 , if we assume 100% dissociation, i for CaCl2 is 3 and for AlCl3 is 4 and relative lowering of V. P. is directly proportional to i. 4. Ans. Increases Chapter No:3 Electrochemistry Worksheet 1 Concept 1: Commercial cells. Match the following: S.No. Cell Electrolytes used 1 Dry Cell A Aq.KOH 2 Fuel Cell B ZnO and Aq.KOH 3 Lead Storage Battery C A paste of NH4Cl and ZnCl2 4 Zn/Hg Cell D Dil.H2SO4 State True or False 1. Dry cell does not provide a constant voltage throughout life. 2. A Zn/Hg Cell is superior to dry cell. 3. A Fuel Cell has about 70% chemical efficiency. 4. The lead storage battery is an example of primary cell. VSQ related with dry cell For the lechlanche cell write (a)The chemical reactions the: involved at cathode. Ans: ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 58 (b). Change in oxidation state of Mn Ans: (c). The complex entity formed between Zn2+(aq) and NH3(g) Ans: Concept 2: Units of conductivity,molar conductivity etc. Match the following: S.No. Property Unit 1 Conductivity S-1cm 2 Conductance S cm2mol-1 3 Molar Conductivity cm-1 4 Cell Constant Scm-1 5 Resistivity S Concept 3: Products of electrolysis Predict the products of electrolysis for : Concept Commercial cells. 1.An aqueous solution of AgNO3 Ans : using Ag electrodes 2.An aqueous solution of CuSO4 Ans : using Cu electrodes 3.An aqueous solution of AgNO3 Ans: using Pt electrodes 4.An aqueous solution of NaCl Ans: using Pt electrodes Answer Key (Electrochemistry) Type of questions Answer Match the following State True or False Dry Cell :: A paste of NH4Cl and ZnCl2 Fuel Cell :: Aq.KOH Lead Storage Battery :: Dil.H2SO4 Zn/Hg Cell :: ZnO and Aq.KOH 1. Dry cell does not provide a constant voltage throughout life.[T] 2. A Zn/Hg Cell is superior to dry cell.[T] 3. A Fuel Cell has about 70% chemical efficiency.[T] 4. The lead storage battery is an example ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 59 VSQ related with dry cell Units of conductivity,molar conductivity etc. Match the following: Products of electrolysis Predict the products of electrolysis for : of primary cell.[F] (a)The chemical reactions involved at cathode. Ans : MnO2 + NH4+ + e- Mn(OH)O + NH3 (b). Change in oxidation state of Mn Ans : +4 to +3 (c). The complex entity formed between Zn2+(aq) and NH3(g) Ans : [Zn (NH3)4]2+ Conductivity :: Scm-1 Conductance :: S Molar Conductivity :: S cm2mol-1 Cell Constant :: cm-1 Resistivity :: S-1cm Worksheet Chapter:4 (Chemical Kinetics) State whether given statement is true or false. 1. The unit of K for first order reaction is molL-1s-1. 2. The radioactive decay follows zero order kinetics. 3. For r =k[A]2[B],the order of reaction is 3 ( ) 4. For second order reaction unit of k is mol-2L2s-1. 5. For a reaction order and molecularity are always same. 6. Order of reaction is always a whole number whereas molecularity can be fractional. () ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) MCQ 1.The order of reaction for,r=k[A]2[B] is (a). 1 b) 0 (c)2 (d) 3 2.A reaction 50% complete in 2 hours and 75% in 4 hours, the order of reaction will be (a).0 b) 1 (c)2 (d) 3 3.For a reaction A+B C,the rate law is given by r=k[A]1/2[B]2 the order of reaction is: (a).0 b) 5/2 (c)2 (d) 3/2 4. What is the unit of K if rate ==K{A}2{B} (a) s-1 (b) mol L-1 (c) mol-2L2s-1 (d) mol-1Ls-1 5.What is the molecularity of reaction for the following elementary reaction: 2A+B------------------------C (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 0 6.What is the order for following photochemical reaction: H2+Cl2------------2HCl ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 60 (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 0 Concept: Order of reaction Predict the order of reaction for following graphs: rate b) rate (conc)2 Conc a) log[R] R time P d)rate conc Concept: Half Life period and relation with rate constant Fill in the blanks: (a).The relationship between t/2 and k for first order reaction is____________. (b).The half period is independent to concentration of reactants for ___________order reaction. (c).The radioactive decay follows___________________order kinetics. (d).The rate constant and rate of reaction have same units’ for______________order reaction. (e).The half-life period is inversely proportional to concentration of reactants for______________order reaction. (f).If the value of t/2 for first order reaction is 693 s, the value of K will be__________ (g).The half period is directly proportional to initial concentration of reactants for __________order reaction. Answer Key State whether given statement is true or false. -1 -1 1. The unit of K for first order reaction is molL s . 2. The radioactive decay follows zero order kinetics. 2 3. For r =k[A] [B],the order of reaction is 3. -2 2 -1 4. For second order reaction unit of k is mol L s . 5. For a reaction order and molecularity are always same. 6. Order of reaction is always a whole number whereas molecularity can be fractional. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com (T) (F) ( T) (F) (F) (F) 61 MCQ 2 1.The order of reaction for,r=k[A] [B] is Ans. 3 2.A reaction 50% complete in 2 hours and 75% in 4 hours, the order of reaction will be Ans.1 1/2 2 3.For a reaction A+B C,the rate law is given by r=k[A] [B] the order of reaction is : Ans. 5/2 2 4. What is the unit of K if rate ==K[A] [B] -2 2 -1 Ans. mol L s 5.What is the molecularity of reaction for the following elementary reaction: 2A+B------------------------C Ans.3 6.What is the order for following photochemical reaction: H2+Cl2------------2HCl Ans. 0 Concept: Order of reaction Predict the order of reaction for following graphs: a) rate b) rate (conc)2 Conc Ans. Ist order b) log[R] R Ans:2nd order P d)rate time conc Ans.Istorder Ans.Zero order SURFACE CHEMISTRY CONCEPTS OF ADSORPTION (Choose the correct option) ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 62 1. Which among the following is mainly a surface phenomenon? (Adsorption, Absorption 2. Which gas will be adsorbed more ? (CO2 , H2) 3. High pressure is more favourable in case of ? (Physisorption, Chemisorption, Both ) 4. In which case extent of adsorption is more? (Charcoal Block, Powdered charcoal ) 5. Which type of adsorption decreases with increase of temperature ? (Physisorption, Chemisorption) 6. Adsorption is always (Endothermic, exothermic ) Ans:- 1)adsorption 2) CO2 3). Both4 )Powdered charcoal5)Physisorption 6) Exothermic Adsorption Fill in the Blanks 1. log x/m=log k+1/n ---(Ans:- log p ) 2. Froth floatation makes use of-------- process (Ans:- Adsorption) 3. Enthalpy of adsorption is more in case of ----------------- ( Ans:- Chemisorption) 4. The dispersion medium in the case of smoke is ------------ (Ans:- Air ) 5. ------------ Process is the reverse of Adsorption (Ans:- Desorption ) Ans:- 1)log p 2)adsorption 3) Chemisorption 4) air 5) desorption III Match the following:Column A 1). The process of settling of colloidal particles 2). Scattering of light by colloidal particles 3). Movement of colloidal particles under an applied electrical field 4). Potential difference between the fixed layer and the diffused layer of opposite charges around a colloidal particle 5) Zig-zag motion of colloidal particles observed under ultramicroscope 6. Process of converting a precipitate into colloidal sol by shaking it with a small amount of electrolyte 7. Liquid-liquid colloidal systems 8. Process of removing a dissolved substance from a colloidal solution by means of diffusion through a suitable membrane Answers:- 1-c, 2- a, 3-e, 4-h , 5-b , 6-g ,7-f, 8- d Column B (a)Tyndall effect (b)Brownian movement (c) Coagulation (d) Dialysis (e)Electrophoresis (f)Emulsions (g)Peptization (h)Zeta potential IV) Name it. 1. Give an example of shape selective catalyst. 2. Substance which increases the activity of the enzymes is called 3. The concentration above which the micelle formation takes place 4. The temperature above which the micelle formation takes place 5. Name an example of macromolecular colloid. Answers:-1) ZSM-5 2)Co enzyme 3) CMC 4) Kraft temperature 5) polystyrene V .Give reasons:1.Why does the sky appear blue ? 2.Why FeCl3 is better for coagulation of blood than KCl? 3.Why does the smoke get precipitated by Cottrell precipitator? 4.Why is an animal hide soaked in tannin before use in leather industry ? 5 How are deltas formed? Answers:-1.Due to scattering of blue light by dust particles along with water ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 63 I. suspended in air 3+ + 2.According to Hardy schulze rule ,Fe has more flocculating power than K 3.The charge of colloidal smoke particles gets neutralized by oppositely charged plates in chimney. 4.Due to mutual coagulation of positively charged animal hide particles and negatively charged colloidal particles of tannin. 5.Colloidal clay particles carried by river water are coagulated by electrolytes In sea water. Worksheet CHAPTER 6 PURIFICATION OF METALS CONCEPTS COVERED : i) Process of refining ii) Reactions utilized in various processes iii) Identification of reagents used in various processes Match the column Column A II. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Column B 1. Zone refining (A) Zirconium , Titanium 2. Van Arkel method (B) Aluminium 3. Electrolytic process (C) gallium 4. liquation (D) Zinc 5. Distillation (E) Tin Multiple choice questions: Which of the following reaction involves during Mond’s process? (a) Ni + 4CO Ni(CO)4 (c) Both a & b (b) Ni(CO)4 Ni + 4CO (d) Zr + 2I2 Which of the expression is related with electrochemical principle? 0 0 0 0 (a) ∆G = -RTln K (c) ∆G =∆H - T∆S 0 0 (b) ∆G = - nFE (d) None of these During refining by electrolysis, impure copper is taken as (a) Cathode (c) Both a and b (b) Anode (d) None of these Chromatography purification is based on the principle of (a) Chemical kinetics (c) Adsorption (b) Electrochemistry (d) Absorption Pure metals get deposited at which electrode (a) Cathode (b) Anode (c) Both a and b (d) None of these III. One word answer questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Give one example of a metal purified by zone refining. Give one example of a metal purified by vapour phase refining. Give one example of a metal purified by electrolysis. Give one example of a metal purified by liquation. Give one example of a metal purified by distillation. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com ZrI4 64 IV. Choose the correct word from the list and fill the blanks: Words- cresol, CaF2, NaCN, FeSiO3, pine oil. 1. During froth floatation process, the froth is stabilized using ________________. 2. For an ore containing PbS and ZnS, ________________is used as a depressant. 3. The sulphide ore is made more hydrophobic using collectors like _________. 4. During the extraction of copper having iron as impurity, the slag formed is _________. 5. Apart from cryolite, _________can be used in the metallurgy of aluminium IV. Identify the process: 1. 2Al2O3+ 3C 4Al + 3CO2 2. ZrI4 Zr + 2I2 3. CaO + SiO2 CaSiO3 4. ZnCO3 ZnO + CO2 5. ZnS + 3 O2 2 ZnO + 2SO2 V. Match the ore with the processes involved during the extraction of the metal: Ore: bauxite, zinc blende, haematite, copper pyrite, zinc carbonate. Process: reduction with coke, leaching, reduction in a blast furnace, roasting of sulphide ore, electrochemical reduction, reduction in a reverberatory furnace. VI. Analogy 1. Al2O3: NaOH:: Ag2S: ____ 2. FeO:SiO2::SiO2:_____. 3. Aluminium : bauxite :: silver:______ 4. Ni: Ni(CO)4:: Zr:________5. Na[Al(OH)4]:CO2::[Au(CN)2] :_________. KEY ANSWER I.Match the column Column A II. Column B Zone refining Gallium Van Arkel method Zirconium , Titanium Electrolytic process Alunimium Liquation Tin Distillation Zinc Multiple choice questions: 1.Which of the following reaction involves during Mond’s process? (a) Ni + 4CO Ni(CO)4 (b) Ni(CO)4 Ni + 4CO Ans : Both a and b 2.Which of the expression is related with electrochemical principle? 0 0 ∆G = - nFE 3. During refining by electrolysis, impure copper is taken as Anode ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 65 4. Chromatography purification is based on the principle of Adsorption 5. Pure metals get deposited at which electrode Cathode III 1.Give one example of a metal purified by vapour phase refining.[ Titanium} 2.Give one example of a metal purified by electrolysis.{ Silver} 3.Give one example of a metal purified by liquation.{Tin} 4.Give one example of a metal purified by distillation.{Zn} 5.Give one example of a metal purified by zone refining.[Ga] (IV)Choose the correct word from the list and fill the blanks: 1.During froth floatation process, the froth is stabilized using _cresol, _______________. 2.For an ore containing PbS and ZnS, ____ NaCN, ____________is used as a depressant. 3.The sulphide ore is made more hydrophobic using collectors like pine oil._________. 4.During the extraction of copper having iron as impurity, the slag formed is __ FeSiO3, _______. 5.Apart from cryolite, ___ CaF2, ______can be used in the metallurgy of aluminium. (V) Identify the process: (a) 2Al2O3+ 3C 4Al + 3CO2. Hall- heroult process (b) ZrI4 Zr + 2I2Van Arkel method (c)CaO + SiO2 CaSiO3. Extraction of iron (d) ZnCO3 ZnO + CO2. Calcination (e) ZnS + 3 O2 2 ZnO + 2SO2I. Roasting (VI) Match the ore with the processes involved during the extraction of the metal: Ore: bauxite, zinc blende, haematite, copper pyrite, zinc carbonate. Process: reduction with coke, leaching, reduction in a blast furnace, roasting of sulphide ore, electrochemical reduction, reduction in a reverberatory furnace. Answer - 1Leaching and electrochemical reduction, 2. roasting of sulphide ore and reduction with coke, 3. reduction in blast furnace, 4. roasting of sulphide ore and reduction in a reverberatory furnace,5. reduction with coke VII. Analogy 1 Al2O3: NaOH :: Ag2S: ____ ( NaCN) 2. FeO:SiO2::SiO2:_____.(CaO) 3. Aluminium : bauxite :: silver:______(silver glance) 4. Ni: Ni(CO)4:: Zr:________-(ZrI4) 5. Na[Al(OH)4]:CO2::[Au(CN)2] :_________.(Zn) ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 66 CONCEPT : HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS CHAP: P-BLOCK ELEMENTS CLASS-XII CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS – CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS – P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-1[1×5=5] P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-2[1×5=5] 1# Whose boiling point is more ? (H2O, H2S) 2# Which is more basic ? ( NH3 , BiH3) 3# Which is thermally more stable ? ( H2Se , H2S ) 4# Which is more reducing in nature ? (H2O, H2S) 5# Which is more acidic ? (H—I , H—F , H—Cl ) 1-H2O, 2-NH3, 3-H2S, 4- H2S, 5-H—I ,6-NH3, 7-NH3, 8-3, 9phosphonic acid, 10-HOClO3 CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS –P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-3[1×5=5] 11# Which one disproportionate on heating (H3PO3 , H3PO4) 12# Which has more B.P ? ( water , HF) 13# Which is a better complexing agent ? ( Ammonia , Phosphine ) 14# Which can act both oxidizing as well as reducing agent ? ( H2S , SO2) 15# What is Oleum? ( Pyrosulphuric acid, Pyrophosphoric acid ) 6# Which has more bond angle ? (NH3 , BiH3 , PH3) 7# Which dissolves more in water ? (PH3 , NH3 ) 8# What is the basicity of H3PO4? ( 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ) 9# Which is more reducing ? (Phosphinic acid , Phosphonic acid) 10# Which is more acidic ? (HOCl ,HOClO3) CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS – P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-4[1×5=5] 16# H2SO4 is prepared by ( Ostwald’s Process , Contact Process ) 17# What is the covalence of nitrogen in N2O5 ? ( 3, 4 , 5) 18# Which one exists ? ( R3P=O , R3N=O ) 19# Which decolourise acidified KMnO4 solution ? ( moist SO3 , moist SO2) 20# When copper metal is treated with dilute nitric acid ,what is produced along with Cu(NO3)2 and H2O ( NO2 , NO) 16-contact process, 17-5, 18-R3P=O, 19- moist SO2, 20- NO 11-H3PO3, 12-H-F, 13-ammonia, 14SO2, 15-pyrosulphuric acid CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS –P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-5[1×5=5] 21# The spontaneous combustion of which gas is technically used in Holme’s Signals ?( H2S or PH3) 22# Name the common acid used in pickling of stainless steel , oxidizer in rocket fuels and in explosives ( H2SO4 or HNO3 ) 23# Which gas is poisonous and has rotten fish smell ( hydrogen sulphide , phosphine) 24# Which one of the oxides will not have two different N— O bond length ? (N2O5 , N2O3 , N2O4) 25# Which acid is more acidic ?(CrO ,CrO3 , Cr2O3) 21-PH3, 22-HNO3, 23-phosphine, 24- N2O4, 25- CrO3 CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS –P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-7[1×5=5] CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS – P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-6[1×5=5] 26# The catalyst used in Contact Process are-------( Pt/ Rh-gauge at 500K and 9 bar , V2O5) 27# Which is the anhydride of HNO3 ( N2O3 , N2O5 , NO2) 28# Which one is colourless gas , neutral , reactive, paramagnetic and dimerise (NO2 , NO , N2O4) 29# Which one does not have P—O—P linkage ( pyrophosphoric acid , polymetaphosphoric acid , Hypophosphoric acid ) 30# Which acid is stronger ?(Perchloric acid , H2SO4) 26-V2O5, 27-N2O5, 28-NO, 29- hypo phosphoric acid, 30perchloric acid CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS – P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-8[1×5=5] 31# Spontaneous combustion of which one is technically used in Holme’s Signals 36# The gases produced in the thermal decomposition reaction of Pb(NO3)2 and NH4NO3 are respectively (a)N2O , NO (b) N2O ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 67 ( Ca3P2 , CaC2 , PH3) ,NO2 (c) NO, NO2 (d)NO2 , N2O 32# The acid contain -----------------bond have strong reducing properties (P—OH , P—H) . 37# The ONO bond angle is maximum in - + (a) NO3 (b) NO 2ˉ 33# Which one is not responsible for ozone layer depletion? ( NO2 ,NO ,CFC) 34# Which statement is incorrect about White Phosphorous: P4 has (a) six P—P single bonds (b) Four P—P single bonds(c) 0 four lone pairs of electrons (d) PPP angle of 60 35# The number of P—O—P bonds in cycltri metaphosphoric acid is (a) zero (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4 31-PH3, 32-P—H, 33-NO2, 34-b, 35- 3, 36- d, 37-a, 38-d, 39-c, 40-d (c) NO2 (d) NO2 38# Which of the following has least bond angle (a) H2O (b) H2S (c) H2Se (d) H2Te 39# Which statement is wrong for NO (a) It is anhydride of nitrous acid (b) It’s dipole moment is 0.22 D (c) It forms dimer (d) It is paramagnetic 40# Which of the following hydrogen halide is most volatile (a) HF (b) HCl (c) HBr (d) HI CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS – CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS – P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-9[1×5=5] P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-10[1×5=5] 41# Arrange in increasing order of basic strength -- NH3 , BiH3 , PH3 , AsH3 , SbH3 ----------------------- 46#The conditions to maximize the yield of sulphuric acid by Contact Process are --------- 42# Arrange In increasing order of acidic strength -- HBr ,HCl ,HF , HI . ------------------------------ 47# The two areas in which H2SO4 plays an important role are 1.---------- 2.--------------48# Out of HOF and HOCl , relatively stable oxo-acid is ----------------------------49# HClO4 is more acidic than HOCl because -----50# Give one chemical equation to show the dehydrating action of conc. H2SO4 .------------------- 43# The optimum conditions for the production of ammonia are -----------------------------------------45# The chemical compound responsible for Brown –Ring in nitrate test is ------------------------------41-BiH3<SbH3 < AsH3< PH3 < NH3; 42-HF< HCl< HBr< HI ; 43- high pressure and low temperature of 773K; 45- [Fe(H2O)5NO]SO4 46- high pressure and low temp, as activation energy is high preheated gases are used. 47-industries, and laboratories, 48-HOCl, 49-ClO4- ion is stabilized by resonance, 50-C12H22O11 + H2SO4 12CO2 + 11H2O CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS – CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS – P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-11 P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-12 MATCH THE FOLLOWING : I [1×5=5] MATCH THE FOLLOWING : II : [1×5=5] COLUMN-I COLUMN-II COLUMN-I COLUMN-II 1.NO2 A. Oxidizing agent 1.Oleum A. Disproportionate when heated ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 68 2.Conc. H2SO4 B . Acid having reducing properties 2.Phosphine B. Pyrosulphuric acid 3.H3PO2 C. Odd electron molecule 3. Hydrohen sulphide C.Rotten fish smell 4. HNO3 D. Decolourise acidified KMnO4 solution 4. Phosphonic acid D. Ozone depleting compound 5. SO2 E. Having dehydrating action 5. Nitric Oxide E. Rotten egg smell 1-C, 2-E, 3-B, 4-A, 5-D 1-B, 2-C, 3-E, 4-A, 5-D CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS – CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS – P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-13 [1×5=5] P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-14 Answer the following by Choosing from the perenthesis :( Fluorine ,Chlorine , Ammonia , Sulphuric acid , nitrous acid ) 1. 2. 3. 4. Oxo acids obtained through Contact Process Oxoacids which disproportionate ++ Hydrides of Gr-15 which give deep blue colour with Cu Halogen that is prepared through Oxidation of HX by Deacon’s Process 5. Halogen form only one oxoacids . 1- Sulphuric acid, 2- nitrous acid, 3-Ammonia, 4-Chlorine, 5-Flourine CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS – P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-15 [1×5=5] Just Name it [1×5=5] 1. 2. Hydrides of Gr-15 used in Holme’s Signal A powerful oxidizing compound which is produced when Conc. H2SO4 is electrolyzed ? 3. Oxoacids obtained through Ostwald’s Process ? 4. Name the oxoacids , which is a constituent of Aquaregia 5. Strongest reducing hydrides of Gr-15 . 1- PH3, 2-H2S2O8, 3-HNO3, 4-HNO3 + HCl, 5-BiH3 CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS – P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-16 [1×5=5] Give reason / Account for the following : 1# In aqueous solution , HI is stronger acid than HCl . 2# Hydrogen fluoride has a much higher boiling point than hydrogen Chloride . 3# NH3 is a stronger base than PH3 . 4# In the structure of HNO3 molecule , The N—O bond (121pm) is shorter than N—OH bond(140pm) 5# H3PO2 and H3PO3 act as good reducing agents while H3PO4 does not ? Give reason / Account for the following : 6# Iron dissolves in HCl to form FeCl2 and not FeCl3 . 7# H2O is a liquid while , inspite of higher molecular mass , H2S is gas . 8# HBr and HI can’t be prepared by treating metal bromides or iodides with conc. H2SO4 . 9#Draw the structure of SO2 molecule Comment on the nature of two S–O bonds formed in SO2 molecule. Are the two S–O bonds in this molecule equal ? 10# Why BiH3 the strongest reducing agent among all the hydrides of group -15 elements ? CONCEPT : HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS CHAP: P-BLOCK ELEMENTS CLASS-XII CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS –P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-17[1×5=5] CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS – P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-18[1×5=5] ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 69 Give reason / Account for the following : 11# In solution of H2SO4 in water , the second dissociation constant Ka2 , is less than the first dissociation constant Ka1 12# H2O is a liquid while , inspite of higher molecular mass , H2S is gas . 13# In which one of the following structures, NO 2 + and NO2 ˉ , the bond angle has higher value ? 14# NH3 is a stronger base than PH3 . OR , 15# Why the bond angle of PH3 molecule is lesser than that in NH3 molecule ? Give reason / Account for the following : 16# Dscribe the favourable conditions for the manufacture of (i) ammonia by Habber’s Process (ii) Sulphuric acid by Contact Process (2) 17# Which is stronger acid in aqueous solution ( HCl , HI) 18# Arrange HClO3 , HClO2 , HClO ,HClO4 in order of increasing acid strength . Give reason for your answer (2m) 19# Although the H-bonding in hydrogen fluoride is much stronger than that in water , yet water has a much higher boiling point than hydrogen fluoride . Why ? 20# Why do chlorine water on standing loses its yellow colour? CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS –P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-19 [1×5=5] CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS – P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-20[1×5=5] Arrange the Following in increasing order against the properties mentioned :1# Bond Dissociation Enthalpy:(a) Br—Br , I—I , Cl—Cl , F—F (b) H—I , H—F, H—Br,H—Cl (c) O—H, H—Te, H—Se, H—S. (d) N—N, P—P, As—As 2# Base Strength:BiH3 , NH3 , AsH3 , SbH3 , PH3 Ans1)a-I2< Br2<F2< Cl2; b-HI< HBr< HCl< HF; c: H—Te <H—Se <H—S< O—H ; 2BiH3< SbH3< AsH3 < PH3< NH3 CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS –P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-21 [1×5=5] Arrange the Following in increasing order against the properties mentioned :1# Acid strength:(a) H—I , H—F , H—Br , H—Cl (b) HF, CH4 , H2O , NH3 (c) H2O, H2Te , H2Se , H2S 2# Thermal Stability:(a) H2O , H2Te , H2Se , H2S (b) PH3 , BiH3 , AsH3 , SbH3 , NH3 Ans: 1)a)H—F < H—Cl< HBr< HI, b) NH3< CH4< H2O < HF, c) H2O< H2S< H2Se< H2Te 2) a- H2Te< H2Se< H2S< H2O; b- BiH3< SbH3< AsH3< PH3< NH3 CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS – P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-22 [1×5=5] Arrange the Following in increasing order against the properties mentioned :- Arrange the Following in increasing order against the properties mentioned :- 1# Bond Angle:- (a) H2Se , H2O, H2S ,H2Te 1# Covalent Character :- (a) Cr2O3 , CrO, CrO3 (b) PH3 , BiH3 , AsH3 , SbH3 , NH3 2# Boiling Point :- (a) H2S , H2O , H2Te , H2Se (b) PH3 , BiH3 , AsH3 , SbH3 , NH3 3# Volatility:- H2O , H2Te , H2Se, H2S (b) P2O5,Sb2O5, As2O5 (c) BeCl2, MgCl2 ,CaCl2, BaCl2 2# Acid Strength:(a) HOClO2 , HOClO , HOCl ,HOClO3 (b) HOCl , HOI ,HOBr ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 70 CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS –P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-23 [1×5=5] CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS – P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-24 [1×5=5] Arrange the Following in increasing order against the properties mentioned :- Arrange the Following in increasing order against the properties mentioned :- 1# Reducing properties: 1# Acidic Character -- (a) H2O, H2Te , H2Se , H2S (a) H2SO3 &H2SO4 (b) H3PO4 , H3PO2 , H3PO3 (b)GeO2 ,ClO2 ,As2O3 ,Ga2O3 2# Acidic Character -- (c) P2O5 ,SO3 , N2O5 , CO2 , SiO2 (a) N2O, N2O5, N2O3 ,NO , N2O4 (d) Al2O3 ,CaO, Cl2O7 ,SO3 (b) ClO2 , Cl2O7 ,Cl2O , Cl2O6 (e) BF3 ,BBr3 , BCl3 (c) HNO2 & HNO3 CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS –P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-25 [5M] CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS – P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-26 [5M] IDENTIFY THE FOLLOWING COMPOUNDS IDENTIFY THE FOLLOWING COMPOUNDS 1# (A) reacts with H2SO4 to form purple coloured solution (B) which reacts with KI to form colourless compound (C). The colour of (B) disappears with acidic solution of FeSO4. With concentrated H2SO4 (B) forms (D) which can decompose to give a black compound (E) and O2. Identify (A) to (E) and write equations for the reactions involved. 2# When conc. sulphuric acid was added to an unknown salt present in a test tube, a brown gas (A) was evolved. This gas intensified when copper turnings were also added into this tube. On cooling, the gas ‘A’ changed into a colourless gas ‘B’. (a) Identify the gases A and B. (b) Write the equations for the reactions involved. (3M) CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS –P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-27 [5M] IDENTIFY THE FOLLOWING COMPOUNDS 3# A colourless inorganic salt (A) decomposes completely at 0 about 25 C to give only two products, (B) and (C), leaving no residue. The oxide (C) is a liquid at room temperature and neutral to moist litmus paper while the gas (B) is a neutral ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 71 oxide. White phosphorus burns in excess of (B) to produce a strong white dehydrating agent. Write balanced equations for the reactions involved in the above process. Gradual addition of KI to Bi(NO3)3 solution initially produces a dark brown precipitate which dissolves in excess of KI to give a clear yellow solution. Write chemical equations for the above. CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS – CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS – P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-11 P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-12 MATCH THE FOLLOWING : I [1×5=5] Answer MATCH THE FOLLOWING : II : [1×5=5] COLUMN-I COLUMN-II COLUMN-I COLUMN-II 1.NO2 C. Odd electron molecule 1.Oleum B. Pyrosulphuric acid 2.Conc. H2SO4 E. Having dehydrating action 2.Phosphine C.Rotten fish smell 3.H3PO2 B . Acid having reducing properties 3. Hydrohen sulphide E. Rotten egg smell 4. HNO3 A. Oxidizing agent 4. Phosphonic acid 5. SO2 D. Decolourise acidified KMnO4 solution A. Disproportionate when heated 5. Nitric Oxide D. Ozone depleting compound CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS – CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS – P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-13 [1×5=5] P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-14 Answer Just Name it [1×5=5] 6. Oxo acids obtained through Contact Process Sulphuric acid 7. Oxoacids which disproportionate --nitrous acid 8. Hydrides of Gr-15 which give deep blue colour with Cu++ -- Ammonia 9. Halogen that is prepared through Oxidation of HX by Deacon’s Process ---Chlorine 10. Halogen form only one oxoacids .--- Fluorine , 6. Hydrides of Gr-15 used in Holme’s Signal -- PH3 7. A powerful oxidizing compound which is produced when Conc. H2SO4 is electrolyzed ?— Peroxodisulphate ion 8. Oxoacids obtained through Ostwald’s Process ? -sulphuric acid 9. Name the oxoacids , which is a constituent of Aquaregia . HNO3 . 10. Strongest reducing hydrides of Gr-15 . – BiH3 Answers: CONCEPT: HYDRIDES , OXIDES AND OXOACIDS – ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 72 P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-19 –Answer (a) I—I < F—F < Br—Br < Cl—Cl (Bond Dissociation Enthalpy)—Interelectronic repulsion (b) H—I < H—Br < H—Cl < H—F © H—Te < H—Se <H—S <H—O (d ) As –As < N—N < P—P > 2# BiH3 < SbH3 < AsH3 < PH3 < NH3 ( Base Strength) – small size of N – High electron density in Ammonia P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-20–Answer 1# 1# (a) H—F < H—Cl < H—Br < H—I (Acid strength)—Lower BDE of HI,large size of I (B) CH4 < NH3 < H2O < HF © H2O < H2S < H2Se < H2Te 2# (a) H2Te < H2Se < H2S < H2O ( Thermal Stability) ---BDE (b) BiH3 < SbH3 < AsH3 < PH3< NH3 P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-21–Answer 1#(a) H2Te < H2Se < H2S < H2O ( Bond Angle )----- Size of central atom , electronegativity, repulsion of bond pairs. (b) BiH3 < SbH3 < AsH3 < PH3< NH3 2# (a) H2S < H2Se < H2Te < H2O (b) PH3 < AsH3 < NH3 < SbH3 < BiH3 3#(a) H2O < H2Te < H2Se ( Boiling Point) -- H-Bond and Vander waal’s force (Boiling Point) -- H-Bond and Vander waal’s force < H2S (Volatility)--- H-Bond and Vander waal’s force P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-22–Answer 1# (a) CrO <Cr2O3 <CrO3 (b) As2O5 < Sb2O5<P2O5 (c) BaCl2 < CaCl2 < MgCl2 < BeCl2 2# (a) HOCl < HOClO < HOClO2 < HOClO3 ( Acid Strength) – Stability of its conjugate base , charge dispersal , Oxidation states. (b) HOI < HOBr < HOCl ( Acid Strength) ---Stronger the O—X bond – Weaker the O— H bond – More the acidic character. P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-23–Answer 1# (a) H2O < H2S < H2Se < H2Te ( Acid Strength and Reducing Character) --- BDE (b) H3PO4 < H3PO3< H3PO2 2#(a) N2O < NO < N2O3 < N2O4 < N2O5 (Acidic Character) – Higher oxidation states, covalent character (b) Cl2O < ClO2 < Cl2O6 < Cl2O7 ( Acid Strength)-- Higher oxidation states, covalent character (c) HNO2 < HNO3 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 73 P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-24–Answer (a) H2SO3 < H2SO4 (Acidic character) (b) Ga2O3 < GeO2 < As2O3 < ClO2 (Acidic Character) © SiO2 <CO2 < P2O5< N2O5 < SO3 (d) CaO < Al2O3 < SO3 < Cl2O7 (e) BF3 < BCl3 < BBr3 (Acidic Character)—Effective 2p—2p overlap in BF3 reduces the electron deficiency of B , make it less acidic. CONCEPT : ANOMALOUS PROPERTIES CHAP: P-BLOCK ELEMENTS CLASS-XII ANOMALOUS PROPERTIES ANOMALOUS PROPERTIES P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-1 [1×5=5] P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-2 [1×5=5] II # CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER FROM GIVEN OPTIONS . II # CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER FROM GIVEN OPTIONS . 6# Which one exists ? ( R3P=O , R3N=O ) 1# Whose boiling point is more ? (H2O, H2S) 7# Which is more reactive ? ( Red— P , White – P ) 2# Which dissolves more in water ? (PH3 , NH3 ) 3# Which is more basic ? ( NH3 , BiH3) 8# Which has more catenation properties ? ( N or P ) 9# Which is possible ( ClF3 or FCl3) 4# Which has more oxidizing ability ( Cl2 , F2) 10# Which is more reactive ( Nitrogen gas , Phosphorus) 5# Which has more bond dissociation enthalpy ? ( F—F , Cl—Cl) ANOMALOUS PROPERTIES ANOMALOUS PROPERTIES P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-3 [1×5=5] P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-4 [1×5=5] II # CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER FROM GIVEN OPTIONS . Give Reason for each of the following :1 # NCl5 does not exist but NCl3 exits 11# Whose sigma bond strength is more?(O—O , S—S) BUT both PCl3 & PCl5 exists . 12# Whose Ionisation energy is more ? ( N ,O ) 13# Which one does not release white fumes of HCl 2# Why does R3P = O exist but R3N = O does not (R = alkyl group)? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 74 upon hydrolysis ( PCl5 , PCl3 , SiCl4 ,NCl5) 3#Nitrogen exists as diatomic molecule and phosphorus 14# Which is more stable ? (NF3 , NCl3) as P4. Why? 15# Which has more negative gain enthalpy ? ( F , Cl ) 4# Oxygen & nitrogen are gases BUT sulphur and phosphorus are found in solid state at room temp. 5# BiCl3 is more stable than BiCl5.Explain ANOMALOUS PROPERTIES ANOMALOUS PROPERTIES P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-5 [1×5=5] P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-6 [1×5=5] Give Reason for each of the following :- Give Reason for each of the following :- 6 # Although electron gain enthalpy of fluorine is less negative as compared to chlorine, fluorine is a stronger oxidising agent than chlorine. 11# Are all the five bonds in PCl5 molecule equivalent? Justify your answer 7# Explain why fluorine forms only one oxoacid, HOF. 12# The O—O bond energy is less than the S—S bond energy. ( sigma bond) OR Sulphur exhibits a stronger tendency for catenation as compared to oxygen. 8# ClF3 exists but FCl3 does not Explain 9# Why does nitrogen show catenation properties less than phosphorus? 10 # The electron gain enthalpy of Sulphur is more than Oxygen . 13 # NH3 is a good complexing agent but NF3 is not . 14# On being slowly passed through water PH3 forms bubbles but NH3 dissolves . 15# Why does NH3 form hydrogen bond but PH3 does not? ANOMALOUS PROPERTIES ANOMALOUS PROPERTIES P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-7 [1×5=5] P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-8 [1×5=5] Give Reason for each of the following :- Give Reason for each of the following :- 16# Why does NH3 act as a Lewis base ? OR NH3 acts as ligand or good complexing agent 21# I3ˉ is known but F3ˉ is not. + OR , NH3 has higher H affinity than PH3. 22# HF is least volatile , whereas HCl is the most volatile.OR,HF has higher B.P than HCl OR, HF is liquid and HCl is gas 23#Oxygen and fluorine both stabilize higher oxidation states of metals but oxygen exceeds fluorine in doing so . 17# Why is H2O a liquid and H2S a gas ? 18# SCl6 is not known but SF6 is known . 24 # Bismuth is a strong oxidizing agent in pentavalent state. 19# SF6 exists but SH6 does not 20# SF6 is known but OF6 is not formed .Explain. 25# PH3 has lower boiling point than NH3. Why? CONCEPT : ANOMALOUS PROPERTIES CHAP: P-BLOCK ELEMENTS CLASS-XII ANOMALOUS PROPERTIES ANOMALOUS PROPERTIES ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 75 P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-9 [1×5=5] P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-10 [1×5=5] Give Reason for each of the following :- Give Reason for each of the following :- 26 # Explain why NH3 is basic while BiH3 is only feebly basic. 31#Why is N2 less reactive at room temperature? 27 # Why does the reactivity of nitrogen differ from phosphorus? 32# Fluorine exhibits only –1 oxidation state whereas other halogens exhibit + 1, + 3, + 5 and + 7 oxidation states also. Explain. 28# Why does white ppt. of AgCl dissolves in ammonia solution. 29# Though nitrogen exhibits +5 oxidation state, it does not form pentahalide. Give reason. 30# There is a large difference between the melting and boiling points of Oxygen and Sulphur . 33# Considering the parameters such as bond dissociation enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy and hydration enthalpy, compare the oxidising power of F2 and Cl2. 34# Fluorine never acts as a central atom in its compounds with other halogens . 35 # In trimethylamine, the nitrogen has a pyramidal geometry whereas in trisilylamine,it has a planar ANOMALOUS PROPERTIES ANOMALOUS PROPERTIES P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-11 [1×5=5] P-BLOCK ;CL-XII ----CARD-12 [1×5=5] # Arrange the Following in increasing order against the properties mentioned :- # Arrange the Following in increasing order against the properties mentioned :- 1# Catenation property:- 1# Electron Gain Enthalpy :- (a) As , N, P , Sb (a) I , Br , Cl , F (b) Se ,S , Te ,O (c) F, Cl , O , S 2# Electronegativity:- (a) Cl ,F, Br, I 2# Ionisation Enthalpy:- (b) O , N , F , C 3# Stability:- Q.1 # H2O (a) O , N , F , C Fˉ(aq) , I ˉ(aq) , Clˉ(aq) , Brˉ(aq) Q.2# NH3 (b) N , O, P ,S Q.3# H2S (b) Ar , Ne , He , Xe , Kr Q.4# H2S ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com Q.5# H—I 76 Q.6# NH3 Q.7# NH3 Q.8# 3 Q.9# Phosphinic acid Q.10# HOClO3 Q.11# H3PO3 Q.12# water Q.13# Ammonia Q.14# SO2 Q.15# Pyrosulphuric acid Q.16# Contact Q.17# 4 Q.18# R3P=O Q.19# moist SO2 Q.20# NO Q.21# PH3 Q.22# HNO3 Q.23# phosphine Q.24# N2O4 Q.25# CrO3 Q.26# V2O5 Q.27# N2O5 Q.28# NO Q.29# Hypophosphoric Q.30# Perchloric acid Process acid Q.31# PH3 Q.32# P—H Q.33# NO2 Q.34# Four P—P single bonds Q.35# Q.36# NO2 , N2O Q.37# NO2+ Q.38# H2Te Q.39#(a) It is anhydride of nitrous acid Q.40# HCl Q.41# , BiH3 , Q.42# HF , Q.44# Q.45# [Fe(H2O)5(NO)]2+ SbH3, AsH3 ,PH3, NH3 HCl , HBr, HI . Q.43# 200 atm , 700K ,Fe2O3 with small amount of K2O , Al2O3 Q.46# 2 bar , 720 K , V2O5 catalyst for converting SO2 to SO3 and absorbing SO3 in Conc. H2SO4 . Q.47# Fertiliser making , Lead storage battery Q.48#HOCl Q.49#CLO4 - is resonance stabilized due to 4 oxygen atoms Q.50# 3 C12O11H22 +conc.H2SO4 12C + 11H2O ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 77 CHEMICAL TEST TO DISTINGUISH BETWEEN PAIR OF COMPOUNDS LEVEL A TEST REAGENT INFERENCE 1- Iodoform test(Alcohols) 0 0 0 2-Lucas test (1 ,2 ,& 0 3 Alcohols) 3-Neutral ferric chloride test (Phenol) ZnCl2/HCl Turbdity immediately in 3 Alcohols Neutral FeCl3 Voilet colour 4-Bromine water test(Phenol) Br2/H2O White ppt 5-Iodoform test(Aldehydes&Ketones -COCH3,Alcohol(-C(OH)CH3 NaOH/I2 Yellow Ppt of CHI3 6-Tollens test(Aliphatic & Aromatic Aldehydes) Amm.AgNO3 Silver mirror at walls of test tube 7-Fehling test(Aliphatic Aldehydes) Fehling A & Fehling B Reddish Brown ppt of Cu2O 8-Azo dye test(Aniline) NaNO2 + HCl than reacts with NaOH/I2 Yellow Ppt of CHI3 Aniline forms BDC with - napthol 9-Isocyanide test(10 Aniline) 0, 0, CHCl3 + KOH Unpleasent odur or smell of Isocyanide C6H5SO2Cl Product of 1 Amines soluble in alkali. 0 azo dye Yellow Productcolour of 2 Amines are insoluble in alkali. 0 0 10-Heinsberg test(1 2 3 Amines) 11-Sodium bicarbonate test (Acids) NaHCO3 Effervesence due to CO2 12. aq.NaOH and AgNO3 test Ppt formed if-Cl/-X directly attached 3 Test tosp for Halides Carbon Distinguish By a Single Chemical Test(WITH CHEMICAL EQUATION) LEVEL B 1. All aldehydes ( R-CHO) give Tollens’ Test and produce silver mirror. RCHO + 2 [Ag(NH3)2]+ + 3 OH- RCOO- + 2 Ag + 2H2O + 4 NH3 Tollens’ Reagent silver ppt Note: HCOOH(methanoic acid ) also gives this test, ketones(RCOR) do not give this test 2. All aldehydes (R-CHO) and ketones(RCOR) give 2,4-DNP test RCOR + 2,4-DNP Orange ppt R-CHO + 2,4-DNP Orange ppt Aldehydes and ketones having CH3CO- (keto methyl) group give Iodoform Test. Alcohols having CH3CH- group also give Iodoform Test. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 78 CH3CHO + 3I2 + 4 NaOH CHI3 + HCOONa + 3 NaI + 3H2O Yellow ppt The following compounds give Iodoform Test: ethanol (C2H5OH), propan-2-ol (CH3CH(OH)CH3), ethanal(CH3CHO), propanone(CH3COCH3), butanone ( CH3COCH2CH3) , pentan-2-one (CH3COCH2 CH2CH3) , acetophenone ( PhCOCH3 ) 4. All carboxylic acids ( R-COOH) give Bicarbonate Test RCOOH + NaHCO3 RCOONa + CO2 + H2O effervescence 5. Phenol gives FeCl3 Test C6H5OH + FeCl3 (C6H5O)3Fe + 3 HCl (neutral) (violet color) 6. All primary amines (R/Ar -NH2) give Carbyl Amine Test R-NH2 + CHCl3 + KOH(alc) R-NC + KCl + H2O offensive smell 7. Aniline gives Azo Dye Test ( Only for aromatic amines) C6H5NH2 + NaNO2 + HCl C6H5N2+Cl- ; then add β-naphthol orange dye 8. All alcohols (ROH) give Na-metal test R-OH + Na R-ONa + H2 bubbles 9. For esters (RCOOR) : Hydrolyses first. Then see the products ( acid & alcohol) and give a test to identify them 10. All alkenes (C=C) and alkynes (C≡C) decolorizes Br2 – water from red to colorless 11. Lucas Test to distinguish primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols Lucas reagent: ZnCl2/HCl 30-alcohol + Lucas reagent immediate turbidity 20-alcohol + Lucas reagent turbidity after sometime 10-alcohol + Lucas reagent no turbidity CBSE QUESTIONS Give one chemical test to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds: 1. Methylamine and dimethylamine 12. Ethanal and Propanal 2. Secondary and tertiary amines 13. Acetone and Acetaldehyde 3. Ethylamine and aniline 14. Acetaldehyde and Benzaldehyde 4. Aniline and benzylamine 15. Ethanoic acid and Ethnoyl chloride 5. Aniline and N-methylaniline 16. Methanol and Ethanol 6. Propanal and Propanone 17. Propanol and Propan-2-ol 7. Acetophenone and Benzophenone 18. 2-Methyl Propan-2-ol and Propanol 8. Phenol and Benzoic acid 19. Phenol and Cyclohexanol 9. Benzoic acid and Ethyl benzoate 20. 10,20,&30 Alchols 10. Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one 21. 10,20,& 30 Amines 11. Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone 22. Formic acid and Acetic acid ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 79 WORK SHEET Match the following :Sl no 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Column A Sl Column B No Neutral Ferric Chloride solution a Test for carboxylic acid Iodoform test b Test for p- , s- t- alcohol Azodye test ( NaNO2 +HCl) and beta-napthol c Test for p- , s- t- amines aq.NaOH and AgNO3 test d Test for any aldehyde Hinsberg’s reagent ( benzene sulphonyl chloride e Test for phenol and KOH) Tollen’s Reagent (ammoniacal AgNO 3 solution) f Test for chloride 0 Lucas Test ( anh. ZnCl2 + conc.HCl ) g Test for alphatic and aromatic 1 -amine 0 NaHCO3 solution h Test for aromatic 1 -amine i Isocyanide Test Or Carbylamine Test Test for ethanol. Ethanal , Fehling’s solution (alkaline sol. Of CuSO4 + j Acetophenone Sod.Pot.Tartarate Which one will give + ve test for the reagent 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11) 12) 13) 14) 15) NaOH + I2 ( Propanal and Ethanal) . Neutral FeCl3 solution( Phenol , Acetic Acid ) Ammoniacal AgNO 3 solution ( Propanone and Propanal) NaHCO3 solution ( Benzoic acid and Phenol ) CHCl3 and alcoholic KOH ( Ethanamine and N-ethyl Ethanamine) 0 0 Benzene sulphonyl chloride .( 2 amine and 3 amine) ( NaNO2 +HCl) and beta-Napthol ( CH3NH2 and Aniline ) anh. ZnCl2 + conc.HCl (Isopropyl alcohol , Propanone) aq.NaOH and AgNO3 test ( Chlorobenzene ,Cyclohexylchloride) alkaline sol. Of CuSO4 + sod.pot.tartarate ( Acetone and Acetaldehyde) Hinsberg’s reagent (Methylamine and dimethylamine) Tollen’s Test ( Formic acid and Acetic acid ) aq.NaOH and AgNO3 test (Benzyl chloride and Chlorobenzene) Acidic hydrolysis of ester + Iodoform test. ( Methyl Acetate and Ethyl Acetate) Na-metal test ( Ethanol and Ethoxyethane ) MCQ 1. Which of the following compound will give positive idoform test. a. 3-methylpropan-2-ol c. 1-methylcyclopentanal b. 1-phenylpropan-1-ol d. 3-phenylpropan-2-ol i. a &c iii. b & c ii. a & d iv. b and d 2. Propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol can be distinguished by_____________ a. Lucas test c. Tollen’s reagent test b. Ferric chloride test d. Na metal test 3. Lucas test is associated with___________ . a. Alcohol b. phenol c. Aldehyde d. Carboxylic acid ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 80 4. ___________ alcohol react immediately with anhydrous ZnCl2 + HCl and give insoluble Chloride. a. Methanol c. Isopropylalcohol b. Butanol d. 2- methylpropan-2-ol 5. C2H5OH and C6H5OH can be distinguished by a. Br2+ H2O c. FeCl3 b. I2+NaOH d. both B and C 6. C2H5CHO and (CH3)2CO be distinguished by testing with a. Phenyl Hydrazide c. Fehlings solution b. Hydroxylamine d. Sodium Bisulphide 7. Silver mirror test can be used to distinguished between a. Ketone and Acid c. Aldehyde And Acid b. Phenol and Acid d. Alcohol and phenol 8. The pair of compounds in which both the compounds give positive with tollen’s reagent a. Glucose and Sucrose c. Acetophenone and Hexanal b. Fructose and Sucrose d. Glucose and Fructose 9. Acetone and Acetaldeyhde are differentiated by a. NaOH+I2 c. HNO3 b. [Ag(NH3)2]+ d. I2 10. Which of the following pairs can be distinguished by sodium hypoiodite a. CH3CHO and CH3COCH3 b. CH3CH2CHO and CH3COCH3 c. CH3CH2OH and CH3CH2CHOHCH3 d. CH3OH and CH3CH2 CHO 11. CH3CHO and C2H5CH2CHO can be distinguished by a. Bendict test c. Tollen’s test b. Iodoform test d. Fehlings solution test 12. Dye test can be used to distinguished between a. Ethylamine and Acetamide c. Urea and Acetamide b. Ethylamine and Aniline d. Methylamine and Ethylamine 13. Hinsbergs reagent is : a. Benzenesulphonyl chloride c. Phenyl iocyanide b. Benzenesulphonic acid d. Benzenesulphamide 14. Iodoform can be prepared from, all except. a. Ethyl methyl ketone b. Isopropyl alcohol c. 3-methylbutan-2-one d. Isobutyl alcohol STATE TRUE OR FALSE 1 Formic acid reduces Tollens’ reagent 2Carboxylic acids do not give characteristic reactions of carbonyl Group 3Acetic acid does not give sodium bisulphite addition product 4Benzaldehyde does not give Fehling’s test. 5 Can iodoform be prepared from ethanol ? Prepared By : Mr Suresh Kumar Sahu, PGT Chem, K V No 3 Bhubaneswar& Resource Person ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 81 WORK SHEET-CHAPTER-13 CONCEPT 1: IUPAC NOMENCLATURE 1.Match the following: a.CH3NH2 (i) Ethanamine b.C2H5NH2 (ii) Benzamine c.(C2H5)2NH (iii)N-Ethyl Ethanamine d.C6H5NH2 (iv)N,N-Dimethyl methanamine e.(CH3)3N (v) Methanamine Ans1.Match the following: a.CH3NH2 (v) Methanamine b.C2H5NH2 (i) Ethanamine c.(C2H5)2NH (iii)N-Ethyl Ethanamine d.C6H5NH2 (ii)Benzamine e.(CH3)3N (iv) N,N-Dimethyl methanamine 2.Write the IUPAC name of following: a. C6H5-NH-CH3 b. CH3-NH-C2H5 c.(C6H5)-N-CH3 Ans2.Write the IUPAC name of following: S.N. Compounds IUPAC Name a C6H5-NH-CH3 N-Methylaniline b CH3-NH-C2H5 N-Methylethanamine c (C6H5)2-N-CH3 N-Methyl N-phenylaniline 3. The IUPAC name of (CH3)2-N-C2H5: a) N,N-Diethylethanamine b) N,N-Dimethylethanamine c) N,N-Ethylmethylmethanamine d) Dimethylmethanamine 4. Choose the appropriate answer of the following: a) IUPAC name of CH3-NH-CH3 (i) Ethylmethylamine (ii) Methylethylamine (iii) N-Methylethanamine (iv) N-Ethylmethanamine b) Common name of CH3CH2NH2 ? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 82 (i) Ethylamine (ii) Ehanamine (iii)Dimethylamine (iv)None C) IUPAC name of (C6H5)2NH ? (i) Diphenylamine (ii) N-Phenylbenzenamine (iii) 1,2-Diphenylamine (iv) All d) Common name of (CH3)2CH-NH2 (i) Isopropylamine (ii) Ethaemethanamine (iii) Methaneehaneamine (iv) 2-Methylethanamine 5) Arrange the following alkyl groups in decreasing order Methyl,Ethyl,Isopropyl,n-Butyl CONCEPT 2: BASIC CHARACTER Of AMINES Q.1 Wtite the relation between Basicity of Amine & Pkb Q.2 Arrange the following in decreasing order of Pkb values C2H5NH2 , C6H5-NH-CH3 , (C2H5)2NH, C6H5NH2 Q.3.Arrange the following Amines in increasing order of Basic character. a. CH3NH2 , (CH3)2NH, .(CH3)3N in Aq.Solution & in Gaseous Phase b. C2H5NH2 , (C2H5)2NH , (C2H5)3N in Aq.Solution Q.4 Which one is more Basic & Why? C6H5NH2 or C2H5NH2 Q.6 Name the factors affecting the Basicity of Amines in Aq.Solution & in Gaseous Phase . Q.7 Match the following . Column (I ) Amines Column(II) Pkb Values Methanamine 3.27 N-Methylmethanamine 3.29 N,N-Dimethylmethanamine 3.38 Ethanamine 4.22 Benzamine 3.25 CONCEPT-3: BOILING POINT Of AMINES (i) Write the Factors Affecting the Boiling Point of Amines (ii) Why is Primary Amine have higher Boiling Point than that Sec & Tert-Amines ? (iii) Arrange the following Amines in decreasing order of B.P. 1O , 2O , 3O 4. Match the following Compounds (I) (II) Boiling point(K) ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 83 (I)C4H9NH2 390.3 (II)(C2H5)2NH 300.8 (III)C2H5N(CH3)2 310.5 (IV)C2H5CH(CH3)2 329.3 (V) C4H9OH 350.8 5.Why are alcohols have higher B.P than that of amines of comparable molecular mass ? CONCEPT-2: TO DISTINGUISH BETWEEN Pri ,Sec & Tert -Amines 1.Distinguish between the (a) CH3NH2 and (CH3)2NH (b) Aniline & N-Methyl Aniline (c) Sec- Amine & TertAmine CONCEPT-3 : NAME REACTIONS (i) Carbyl amine reaction (ii) Sandmayer reaction (iii) Gatterman reaction WORK SHEET-CHAPTER-14 (BIOMOLECULES) CONCEPT -1: CLASSIFICATION OF CARBOHYDRATES Q1.Which Polysaccharides is stored in the liver of Animals. Q2.Name two Carbohydrates which acts as Biofuel. Q3.What are the Constituents of Starch ?. Q4. What are the Constituents of Maltose ?. Q5.What is invert Sugar ? CONCEPT- 2 : MCQ Q 1. Glycogen is ? (a) monosacchride (b) disaccharide (c) polysaccharide (d) none Q2.Which of the following carbohydrate is not digested in human body ? (a) glucose (b)fructose (c) cellulose (d) lactose Q3. Which disaccharide is present in milk ? (a) maltose (b) lactose (c) sucrose (d) none Q4.Functional group present in glucose (a) aldehyde (b) ketone (c) alcohol (d) amine Q5.Hydrolysis products of lactose (a) two units of glucose (b) glucose & fructose (c) glucose & galactose (d) none CONCEPT -3 : CLASSIFICATION Of VITAMINS Q1.Match the followings. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 84 COLUMN -I COLUMN-II Vitamins A Rickets Vitamins B1 scurvy Vitamins B2 Pernicious anaemia Vitamins B6 convulsions Vitamins B12 cheilosis Vitamins C Beri-beri Vitamins D Night blindness Q2. What are the fat soluble and water soluble vitamins. Q3. Why can’t vitamins c is not stored in our body?. CONCEPT- 4: MCQ -PROTEIN & NUCLEIC ACID Q1.Which of the following is an Example of Non- Essential Amino Acid ? (a) Glycine (b) Valine (c) Histidine (d)Lysine Q2. Which of the following Contain Fibrous Protein ? (a)Keratin (b) Albumin (c) Insulin (d) None Q3. Which of the following base is not Present in DNA ? (a) Adenine (b) Guanine (c)Thymine (d) Uracil Q4. Which of the following is not a type of RNA ? (a) m-RNA (b)r-RNA (c) t-RNA (d) -RNA KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN CHAPTER 15 POLYMERS WORK SHEETS CONCEPTS: 1. Classification of Polymers 2. Uses of Polymers 3. Preparation of Polymers 1. Classification Of Polymers CARD :01 NO QUESTIONS I Odd One Out 1 Buna-s,Buna-N,Neoprene,Polyesters(Mol.Forces) 2 Protein,Starch,Cellulose,Nylon-6(Sourse of formation) 3 Polythene,Teflone,Poly styrene,Nylon-6(Mode of polymerization) 4 Polythene,Polystyrene,Polyvinyls, bakelite(Thermoplastic polymers) CARD :02 NO QUESTIONS II Match the following A 1 Co-polymers 2 Homo-Polymers B Bakelite Teflon 3 Thermolplastics Buna-S 4 Thermosettings PVC ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 85 CARD:03 Fill in the Blanks Linear polymers:PVC ; Cross linked polymers:---Fibres:Polyesters ; Thermosetting:------------------------ III 1 2 3 1 CARD:04 Match the following A HDPE 2 PHBV 3 4 Natural rubber Poly amides IV 4 Addition polymers:----------------; Condensation Polymers:Terylene Poly amides:Nylon-66 ; Polyesters: ----------------- V 1 2 CARD:05 True or False Buna-N is an addition polymers. Polythene is a fibre. VI 1 2 3 4 Orlon is a homopolymer Melamine-formaldehyde is not a condensation polymer. 3 4 2. Bio degradable Ziegler- Natta Catalyst CARD:06 True or False PHBV is a bio-degradable polymer Benzoyl peroxide is used as an initiator in polymerisation Chlorine is used for vulcanization of rubber. Fibres are having high tensile strength Uses of Polymers CARD:01 I B Condensation polymers Isoprene CARD :02 Match the following A II Match the following B A B 1 Teflon Unbreakable Crockery 1 BUNA-S Specialty Packaging 2 Bakelite Oil Seals,tank lining 2 Polyethene Rain coats,hand bags 3 BUNA-N Electrical switches 3 PVC Insulators 4 Melamineformaldehyde Non-stick utensils 4 PHBV Automobile tyres. CARD:03 I CARD:04 Fill in the blanks II Fill in the blanks 1 ------------ is used in glass reinforcing material in safety helmets. 1 Heating a mixture of raw rubber with sulphur and appropriate additive is called------------ 2 ------------- is used for making auto tyres,floortiles,cable insulation,etc. 2 5 % Sulphur is used as a cross linking agent in the manufacture of-------------- 3 ------------- is used for making combs,phonograph 3 --------------- is used for the making of Paints and lacquers. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 86 records,electrical switches,etc. 4 ----------- is used for making conveyor belts,gaskets,etc. 4 CARD:05 ----------------- is used for making ropes,toys,pipes ,etc. CARD:06 V True of False VI True or False 1 Bakelite is used in the manufacture of unbreakable cups. 1 Polystyrene is a copolymer as well as addition polymers. 2 HDPE is used for manufacturing buckets,dustbins & pipes. 2 HDPE is an addition as well as thermoplastic. 3 PAN is used as a substitute for wool in making commercial fiber as Orlon/acrylon. 3 Condensation polymerization is otherwise called Chain growth polymer. 4 Nylon -6 is not used for making tyre cords& fabrics. 4 Novolac is used in Paints. III Preparation of polymers CARD :01 Column A Column B Column C Name of the polymer Monomer of the polymer Uses of the polymer Polythene Tetrfluoroethene Oil seals, Tank lining CF2=CF2 Teflon Ethene (Polytetrfluoroethene) CH2=CH2 Automobile tyres and Foot wears Buta-1,3-diene Buna S + Acrylonitrile CH2=CH-CH=CH2 + CH2=CH-CN Buna N Buta-1,3-diene + Styrene Lubricant, Insulator and making non-stick cooking ware. Insulator, ,Packing material, CH2=CH-CH=CH2 + C6H5CH=CH2 CARD:02 Name of the Polymer Name of the Monomers Nylon 66 Melamine + Methanal Nylon 6 3-Hydroxybutanoic acid + 3-Hydroxypentanoic acid Bakelite Glycine H2N-CH2-COOH Melamine + Amino caproic acid H2N (CH2)5-COOH Hexamethylene diamine + Adipic acid NH2(CH2)6NH2 HOOC(CH2)4COOH ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 87 PHBV (biodegradable) Caprolactum Nylon 2 – Nylon 6 Phenol + Methanal (biodegradable) Terylene(Dacron) Ethane-1,2-diol + Benzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid CARD:03 III.Fill in the blanks 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Ethene is monomer unit for the preparation of ………………. (PVC/polythene) Hexamethylene diamine + …….. are used to prepare Nylon 66. (Adipic acid/ Lactic acid) Ziegler Natta catalyst is used for the synthesis of ………………… (HDP/LDP). PHBV is an example of ……………… polymer. (Biodegradable/ Non-Biodegradable) Dacron/terylene are the best example of ___________ (Polyamides/Polyesters) PhthalIic acid and ethylene acid are the monomers of ___________. (Glyptal/Dacron) CARD:04 Write the name of the polymer whose structure is shown below: Hint: Bakelite/Nylon-66/Buna-S/Terylene/Neoprene 1. 2. CARD :05 Write the name of the monomers from the polymer whose structure is given below: Chapter -16 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 88 Chemistry in everyday life List of concepts1. Therapeutic action of drugs 2. Chemicals in food 3. Cleansing agents (A)Therapeutic action of drug: CARD-01 Which of the following will you take during 1. allergy? (Paracetamol, bromphenaramine) 2. Pick up the bactericidal antibiotic-(penicillin, Tetracyclin) Which drugs relieves the pain? (Analgesics, 3. Antipyretics) Which is not a tranquilizer? (Veronal, seconal, 4. furacine) CARD-02 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 0.2 % phenol solution is used as________. ____________ is a well-known antihistamine. _____________ is also known as morning after pill. (mifepristone) A mixture of synthetic estrogen and progesterone derivatives is largely used as ___. Disinfectants are used on inanimate objects while __________ are used on living tissues. CARD-03 CARD-04 1. Match the following: Column-1 Antipyretic Analgesic- narcotic Antibiotic Antiseptic Disinfectant 1. Column-2 Codeine Tincture of Iodine Aspirin 1 % phenol Chloramphenicol CARD-05 Q State whether true or false. 1. Analgesics lower down body temperature. 2. Bromphenaramine can act as both antiallergic and antacid. 3. Amoxicillin is a broad spectrum antibiotic. 4. The barbituric acid act as Tranquilizers. 5. Aspirin is used in prevention of heart attacks. (B)Chemicals in food: CARD-01 Match the following: Column-A Dettol Iodine in alcoholwater mixture Column-B Antiseptic for eyes Mixture of chloroxylenol and terpineol Tincture of Iodine Aq. Boric acid solution CARD-06 Q What is the action of following drugs on the human body1. Luminal, seconal, Veronal 2. Bromphenaramine, Terfenadine 3. Ranitidine, cimetidine 4. Ofloxacin, Amoxicillin, Penicillin 5. Mifeprestone, Norethindrone, Novestrol CARD-02 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 89 1. The food additives used to prevent the oxidation of food are called_______ 2. The food additives used to prevent the spoilage of food due to microbes are called_______ 3. The food additives that sweeten the food but do not add calorie are ________ CARD-03 Match the following: Column-1 Column-2 Antioxidant Aspartame Preservative Sugar Artificial sweetener Sodium benzoate Natural sweetener BHA Artificial sweetener that breaks at cooking temperature Sucrolose Q 1. 2. 3 4. Q 1. 2. 3. 4. State whether true or false. Sucrolose is trichloro derivative of sucrose. Alitame is not largely used because the control of sweetness of food is difficult. Sucrolose provides calories. Salts of sorbic acid and propanoic acid used as preservatives. CARD-04 Give reason for the following: The people suffering from diabetes are advised to use artificial sweeteners. Aspartame is used in cold food items only. Alitame is not much in use as artificial sweetener. Antioxidants are generally reducing agents. (C)Cleansing agents: CARD-01 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. CARD-02 Chemically soaps are sodium or potassium salts of ___________. Chemically detergents are sodium or potassium salts of ___________. _____________ is an example of detergent. _____________ is an example of soap. Among detergent and soap,________ Is better cleansing agent. 1. Match the following: Column-1 Column-2 Cationic detergent Sodium stearate Anionic detergent Ester of stearic acid and Cetyltrimethyl polyethyleneglycol ammonium bromide Sodium lauryl sulphate Non-ionic detergent Soap CARD-03 CARD-04 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 90 Q. Give reason for the following: 1. Nowadays long chain hydrocarbon is preferred over branched one to prepare 2. detergents. 3. Detergents are preferred in hard water. 4. Soaps form scum in hard water. NaCl is used for precipitation of soap. Q 1. 2. 3. 4. State whether true or false. Soap can be used in hard water. Soaps are better cleansing agents than detergents. Soap solution will turn blue litmus to red. Soap is a biodegradable polymer. Answers: 1. Classification Of Polymers CARD :01 CARD :02 NO QUESTIONS NO QUESTIONS I Odd One Out II Match the following 1 Polyesters(Mol.Forces) 2 Nylon-66(Sourse of formation) 3 4 A B 1 Co-polymers PVC Nylon-6(Mode of polymerization) 2 Homo-Polymers Buna-S bakelite(Thermoplastic polymers) 3 Thermolplastics Teflon 4 Thermosettings Bakelite CARD:03 III Fill in the Blanks 1 :Bakelite 2 :Urea-Formaldehyde 3 4 CARD:04 IV Match the following A B 1 HDPE :LDPE; 2 PHBV Ziegler- Natta Catalyst Bio degradable : glyptal 3 Natural rubber Isoprene 4 Poly amides Condensation polymers CARD:05 CARD:06 V True or False VI True or False 1 True 1 True 2 False 2 True 3 True 3 False 4 False 4 True 2. Uses of Polymers CARD:01 I CARD :02 Match the following A II B Match the following A ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com B 91 1 Teflon Non-stick utensils 1 BUNA-S 2 3 Bakelite BUNA-N Electrical switches Oil Seals,tank lining 2 3 Polyethene PVC 4 Melamine-formaldehyde Unbreakable Crockery 4 PHBV CARD:03 CARD:04 III Fill in the blanks IV Fill in the blanks 1 Dacron 1 Vulcanisation 2 Polystyrene 2 Tyre rubber 3 Bakelite 3 Glyptal 4 Neoprene 4 Polypropene CARD:05 3. Automobile tyres. Insulators Rain coats,hand bags Specialty Packaging CARD:06 V True of False VI True or False 1 False 1 True 2. True 2 True 3. True 3 False 4 False 4 True Uses of Polymers CARD :01 Column A Column B Column C Polythene Name of the polymer Teflon(Poly tetrfluoroethene) Buna S Ethene CH2=CH2 Monomer of the polymer Tetrfluoroethene CF2=CF2 Insulator, ,Packing Uses of the polymer material, Insulator Lubricant, Buta-1,3-diene + StyreneCH 2=CHCH=CH2 + C6H5CH=CH 2 Buta-1,3-diene + Acrylonitrile and making tyres nonAutomobile stick cooking ware. andseals, Foot Tank wearslining Oil Buna N CARD:02 Name of the Polymer Nylon 66 Nylon 6 Bakelite Melamine PHBV (biodegradable) Nylon 2 – Nylon 6 (biodegradable) Terylene(Dacron) CARD:03 III CH2=CH-CH=CH2 + CH2=CH-CN Name of the Monomers Hexamethylene diamine + Adipic acid Caprolactum Phenol + Methanal NH2(CH2)6NH2 HOOC(CH ) COOH Melamine + Methanal 2 4 3-Hydroxybutanoic acid + 3Hydroxypentanoic acid Glycine + Amino caproic acid H H2N (CH2)5-COOH 2N-CH2-COOH + Benzene-1,4Ethane-1,2-diol dicarboxylic acid Fill in the blanks: ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 92 1.polythene. 2.Adipic acid. 3.HDP. 4.Biodegradable polymer. 5. Polyesters. 6. Glyptal. CARD:04 1. Buna-S 2. Terylene 3. Nylon-66 4. Bakelite CARD:05 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 93 Answer:5 1. Vinyl chloride 2. 1,3 butdiene + Acrylonitrile 3. Hexamethylenediamine + Adipic acid 4. Ethelene glycol + Terephthalic acid Chapter -16 Chemistry in everyday life List of concepts1. Therapeutic action of drugs 2. Chemicals in food 3. Cleansing agents (A)Therapeutic action of drug: 1. 2. 3. 4. CARD-01 Which of the following will you take during allergy? (Paracetamol, bromphenaramine) Pick up the bactericidal antibiotic-(penicillin, Tetracyclin) Which drugs relieves the pain? (Analgesics, Antipyretics) Which is not a tranquilizer? (Veronal, seconal, furacine) 1. CARD-02 0.2 % phenol solution is used as________. 2. ____________ is a well-known antihistamine. 3. _____________ is also known as morning after pill. (mifepristone) 4. 5. CARD-03 A mixture of synthetic estrogen and progesterone derivatives is largely used as ___. Disinfectants are used on inanimate objects while __________ are used on CARD-04 living tissues. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 94 1. Match the following: Column-1 Antipyretic Analgesic- narcotic Antibiotic Antiseptic Disinfectant 1. Column-2 Codeine Tincture of Iodine Aspirin 1 % phenol Chloramphenicol Match the following: Column-A Column-B Dettol Antiseptic for eyes Iodine in alcoholwater mixture Aq. Boric acid solution Mixture of chloroxylenol and terpineol Tincture of Iodine CARD-05 CARD-06 Q 1. State whether true or false. 2. Analgesics lower down body temperature. 1. Luminal, seconal, Veronal 3. Bromphenaramine can act as both antiallergic and antacid. 2. Bromphenaramine, Terfenadine 3. Ranitidine, cimetidine 4. Ofloxacin, Amoxicillin, Penicillin 5. Mifeprestone, Norethindrone, Novestrol 4. 5. What is the action of following drugs on the human body- Amoxicillin is a broad spectrum antibiotic. The barbituric acid act as Tranquilizers. Aspirin is used in prevention of heart attacks. (B)Chemicals in food: CARD-01 1. 2 3. The food additives used to prevent the oxidation of food are called_______ The food additives used to prevent the spoilage of food due to microbes are called_______ The food additives that sweeten the food but do not add calorie are ________ Q 1. 2. 3. 4. CARD-03 1. Match the following: Q Column-1 Column-2 Antioxidant Aspartame Preservative Sugar Artificial sweetener Sodium benzoate Natural sweetener BHA Artificial sweetener Sucrolose that breaks at cooking C)Cleansing agents: temperature CARD-01 1. 2. 3. 4. CARD-02 State whether true or false. Sucrolose is trichloro derivative of sucrose. Alitame is not largely used because the control of sweetness of food is difficult. Sucrolose provides calories. Salts of sorbic acid and propanoic acid used as preservatives. CARD-04 Give reason for the following: The people suffering from diabetes are advised to use artificial sweeteners. Aspartame is used in cold food items only. Alitame is not much in use as artificial sweetener. Antioxidants are generally reducing agents. CARD-02 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 95 1. 2. 3. 4. Q. 1. 2. 3. 4. Chemically soaps are sodium or potassium salts of ___________. Chemically detergents are sodium or potassium salts of ___________. _____________ is an example of detergent. _____________ is an example of soap. Among detergent and soap,________ Is better cleansing agent. CARD-03 Give reason for the following: Nowadays long chain hydrocarbon is preferred over branched one to prepare detergents. Detergents are preferred in hard water. Soaps form scum in hard water. NaCl is used for precipitation of soap. 1. Match the following: Column-1 Cationic detergent Anionic detergent Non-ionic detergent Soap Q 1. 2. 3. 4. Column-2 Sodium stearate Ester of stearic acid and polyethyleneglycol Cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide Sodium lauryl sulphate CARD-04 State whether true or false. Soap can be used in hard water. Soaps are better cleansing agents than detergents. Soap solution will turn blue litmus to red. Soap is a biodegradable polymer. Chemistry in everyday life Solutions (A)Therapeutic action of drug: CARD-01 1. Bromphenaramine 2. penicillin 3. Analgesics 4. furacine CARD-02 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Antiseptic Cemetidine Mifepristone Antifertility drugs Antiseptic. CARD-03 1. CARD-04 Match the following: 1. Column-1 Match the following: Column-2 Antipyretic Aspirin Analgesic- narcotic Codeine Antibiotic Chloramphenicol Antiseptic Tincture of Iodine Disinfectant 1 % phenol Column-A Column-B Mixture of chloroxylenol and terpineolof Iodine Tincture Dettol Iodine in alcoholwater mixture Aq. Boric acid solution CARD-05 Antiseptic for eyes CARD-06 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 96 Q 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. State whether true or false. F F T T T Q 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is the action of following drugs on the human bodyTranquilizers Anti-histamine Anti-histamine and Antacid Anti-biotic Antifertility drug Q 1. 2. 3. 4. CARD-02 State whether true or false. T T F T Q CARD-04 Give reason for the following: (B)Chemicals in food: CARD-01 1. 2. 3. Anti-oxidants Preservatives Artificial Sweeteners CARD-03 1. Match the following: Column-1 Antioxidant Preservative Artificial sweetener Natural sweetener Artificial sweetener that breaks at cooking temperature Column-2 BHA Sodium benzoate Sucrolose Sugar Aspartame The people suffering from diabetes are advised to use artificial sweeteners because they do not add calories Aspartame is used in cold food items only because it breaks at cooking temperature. Alitame is not much in use as artificial sweetener because with this it is hard to control sweetness. Antioxidants are generally reducing agents because they will be easily oxidized by air in comparison to food. 1. 2. 3. 4. (C)Cleansing agents: 1. 2. 3. 4. CARD-01 Chemically soaps are sodium or potassium salts of fatty acids Chemically detergents are sodium or potassium salts of sulphonic acids Lauryl sulphate is an example of detergent. Sodium palmitate is an example of soap. Among detergent and soap, detergent is better cleansing agent. CARD-02 1. Match the following: Column-1 Cationic detergent Anionic detergent Non-ionic detergent Soap CARD-03 Column-2 Cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide Sodium lauryl sulphate Ester of stearic acid and polyethyleneglycol Sodium stearate CARD-04 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 97 Q. 1. 2. 3. 4 Give reason for the following: Nowadays long chain hydrocarbon is preferred over branched one to prepare detergents because they are bio degradable Detergents are preferred in hard water because they do not form scum with hard water. Soaps form scum in hard water because it forms insoluble calcium and magnesium salts with soap NaCl is used for precipitation of soap for salting out. Prepared by Q State whether true or false. 1. F 2. F 3. F 4. T i) Bharat Kumar Pandya ii) Sajeesh Kumar TV iii) Satheesh Kumar TTV iv) Anil Kumar Sharma v) Pratheesh N Prepared by Silchar Region ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 98 QUESTION BANK (MLL) CHAPTER 1:SOLID STATE 1 MARK QUESTIONS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. What type of solids are electrical conductors, malleable and ductile? Give the significance of lattice point. Name the parameters that characterize the unit cell What is the two dimensional coordination number of a molecule in square close packed structure. Which of the following lattice has the highest packing efficiency , (I)simple cubic (II ) BCC (III) HCP What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by ( i) ZnS (ii) AgBr What type of substances make better permanent magnets? Justify your answer. Why glass is considered as super cooled liquid? Why KCl appear s pink when heated in K vapors ? Give the relationship between density and edge length in an unit cell. what is F-centre? Give the coordination number of fcc structure. Give an example of a solid that shows both schottky and frenkel defect What defect is observed when CdCl2 is doped with AgCl? Give an example of a network solid. Give an example each of 13-15 & 12-16 compounds. How is quartz different from quartz glass? What is a semiconductor? FeO is mostly found with a composition of Fe0.95 O 1.00 . Why? What is a n-type semiconductor? 2 MARKS QUESTIONS 1. The edge length of a unit cell having molecular weight 75g/mol is 5 A0 which crystallizes in bcc lattice . If the density is 2g/cc then find the radius of the metal atom. 2. Potssium crystallizes in bcc lattice. Calculate the approximate number of unit cell in 1gm of potassium. (atomic mass of K = 39) 3. A compound is formed by two elements M &N .The element N forms ccp & atoms of M occupy 1/3rd of tetrahedral voids. What is the formula of the compound? 4. A unit cell consists of a cube in which there are atoms A at the corners and atoms B at the face centres.Two A atoms are missing from the two corners of a unit cell.Whati is the formula of the compound. 5. Analysis shows that nickel oxide has formula Ni 0.98 O 1.00 .What fraction of nickel exist as Ni 2+ and Ni 3+. 6. If NaCl is doped with 10-3 mol % of SrCl 2 . What is the concentration of cation vacancy? 7. Under what conditions will sodium chloride conduct electricity 8. Name the binding force in each of the following. (a) Molecular (b) Ionic (c) Covalent (d) Metallic. 9. Differentiate between anisotropy & isotropy by giving examples. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 99 10. Derive the relationship between edge length and radius of atom in fcc unit cell. 3MARKSQUESTION 1. Calcium metal crystalises in a fcc lattice with edge length of 0.556nm calculate the density of the metal if it contains , (i) 0.5% frenkel defect (ii) 0.2% schottky defect. 2. How is ferromagnetism different from paramagnetism & antiferromagnetism & explain what type substances show antiferromagnetism 3. What is electrical conductivity due to in (i) metals (ii) ionic solids (iii) semiconductors 4. What is the difference between schottky defect & frenkel defect . 5. Derive an expression for the calculation of density of the cubic crystal of an element whose edge is “a “pm & atomic mass is M 6. How would account for the following a. Frenkel defcts are not found in alkali metal halides. b. schottky defects lower the density of related solids. c. impurity dopped silicon is a semiconductor . 7. . Define the following terms in relation to crystaline solids a. Unit cell b. co ordination number c. P- type semiconductor ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 100 8. What type of defect can arise when solid is heated ? which physical property is affected by it & in what way? 9. An element has bcc structure with cell edge of 288pm .The density of the element is 7.2 gm /cm 3. How many atoms are present in 208 gm of the element.? 10. (I ) Solid A is very hard , electrical insulator in solid as well as molten state & melt at extremily high temprature what type of solid is it ?(II) A compound forms hcp structure. what is the total no of voids in 0.5 mol of it ? how many of these are tetrahedral voids ? , ANSWERS1 MARK QUESTIONS 1. metallic 2. It signifies position of constituent particles of the unit cell 3.edge lengths a,b,c and angles (alpha,beta,&gamma) 4.4 5.hcp 6.(i)frenkel (ii). Both schottky and frenkel 7.ferromagnetic, domains aligned in the same direction 8.pseudo solid or shows fluidity 10.density=Z .M/a3.NA 9. F- centres 12.12 13.AgBr 11. vacant anionic sites occupied by electrons 14.impurity defect 15.SiC 16.AlP,ZnS 17.long range order of constituents in quartz, short range order of constituents in quartz glass 18.energy gap between valence band and conduction band is small or conductivity range is between 10-6ohm-1 m-1 to 104 ohm-1 m-1 19. Metal deficiency defect 20. When a group -14 element is doped with gr-15 element an electron 0f gr-15 element remains as free electron. That increases conductivity 2 MARKS QUESTIONS 1.r = 216.5pm 2. 7.72*1021 3.M2N3 4.AB4 5.Ni 2+ =96% Ni 3+ = 4% 6. 10 -3 /100 mol= 10-5x 6.022x1023=6.022x 1018 7.molten state or in aq. Solution forces(b)electrostatic(c) covalent bond(d) metallic bond 9.Substances show different properties in diffrent direction & the reverse 3 1 2 3 a. b. c. 4 8. (a) vanderwaals 10. a= 2.2 1/2 r MARKS QUESTIONS (i) d =1.5458g cm-3 (ii)1.5427g cm-3 Attracted strongly by magnetic field ,paramagnetic substances are weakly attracted substances not attracted ,antiferromagnetic due to flow of electrons flow of ions in solution or melt and defects in solid due to presence of impurities and defects Schottjy defect- vacancy defect,density lowers frenkel defect- interstitial defect density is not affected. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 101 5 6 (i) similar size of cations and anions(ii) equal no of cations and anions are missing results into decrease in mass (iii)due to presence of free electrons or creation of positive hole. 7 (i)it is the smallest portion of the crystal lattice which when repeated in all directions gives the entire lattice.(ii) Number of nearest neighbour iii) gr-14 doped with gr-13 creates positive hole. 8 Vacancy defect, density decreases because some atoms ,ions leave the crystal completely. 9 M = 51.8gmol-1 no of atoms = 24.16 x 1023 10 i) covalant network solid , sillicon carbide ii) no of o.v =0.5 mol no of t.v =1.0 mol total voids =1.5 mol Prepared by : Bhubaneswar Region CHAPTER 2-SOLUTIONS 1 MARK QUESTIONS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 What is molarity? What do you understand by saying that molality of a solution is 0.2? Why is the vapour pressure of a liquid remains constant at constant temperature? Define Azeotropes? Which substance is usually added into water in the car radiator to act as antifreeze? Which liquids form ideal solution? Which property of solution depend only upon the number of moles of solute dissolved and not on the nature of the solute? Write one example each of solid in gas and liquid in gas solution? What is molal elevation constant or ebullioscopic constant? Define van’t Hoff factor. Two liquids A and B boil at 120 C and 160 C respectively. Which of them has higher vapour pressure at 70 C? What happens when blood cells are placed in pure water? What is the effect of temperature on the molality of a solution? Write Henry’s law. What is an antifreeze? Why cutting onions taken from the fridge is more comfortable than cutting onions lying at room temperature? What will be the van’t Hoff factor for O.1 M ideal solution? What is the optimum concentration of fluoride ions for cleaning of tooth? What role does the molecular interaction play in the solution of alcohol and water? Henry law constant for two gases are 21.5 and 49.5 atm, which gas is more soluble . ANSWER KEY FOR 1 MARK 1 2 3 The number of moles of solute dissolved in one litre or 1dm3 of solution is known as molarity. This means that 0.2 mol of the solute is dissolved in 1Kg of the solvent At equilibrium, the rate of evaporation = rate of condensation. Hence the vapour pressure of a liquid is constant at constant temperature. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 102 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Constant boiling mixtures are called Azeotropes Ethylene glycol is usually added into water in the car radiator to act as antifreeze. Liquids having similar structure and polarities Colligative properties. Solid in gas e.g. Camphor in nitrogen gas. Liquid in gas – e.g. Chloroform mixed with N2 gas The elevation in boiling point which takes place when molality of the solution is unity, is known as ebullioscopic or molal elevation constant. The ratio of the observed colligative property to the theoretical value is called van’t Hoff factor. Lower the boiling point, more volatile it is .So liquid A will have higher vapour pressure at 70 oC. Water molecules move into blood cells through the cell walls. So, blood cells swell and may even burst. No effect. The solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of the gas at a given temperature. An antifreeze is a substance which is added to water to lower its freezing point. e.g. Ethylene glycol The vapour pressure is low at lower temperature. So, less vapours of tear – producing chemicals are produced Van't Hoff factor = 1, because ideal solution does not undergo dissociation or association. The optimum concentration of fluoride ions for the cleaning of tooth is 1.5 ppm. [If it is more than 1.5 ppm it can be poisonous and if less than 1.5 ppm it ineffective.] Positive deviation from ideal behavior. KH is inversely proportional to solubility SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS OF 2 MARK 1 2 3 State Raoult’s law. Prove that it is a special case of Henry’ law? List two conditions that ideal solutions must satisfy. Explain ideal and non-ideal solutions with respect to intermolecular interactions in a binary solution of A and B. 4 a. b. What are minimum boiling and maximum boiling azeotropes? Can azeotropes be separated by fractional distillation? 5 When a non-volatile solute is added to solvent,there is increase in boiling point of solution.Explain. b. Define ebullioscopic constant and give its units. 6 How did Van’t Hoff explain the abnormal molecular masses of electrolytes like KCl in water and non-electrolytes like benzoic acid in benzene. 7 When a pressure higher than the osmotic pressure is applied on the surface of the solution separated from a solvent by semi permeable membrane, what will happen? 8 The freezing depression of 0.1M sodium chloride solution is nearly twice that of 0.1 M glucose solution. Explain? 9 The depression in freezing point is a colligative property. Explain. 10 Equimolar solution of glucose and Common salt are not isotonic. Why? a. Answer key ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 103 1 Raoult’s law states that partial pressure of a volatile component of a solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction. It is a special case of Henry’ law because it becomes the same when “Kh” (Henry constant) is equal to pressure of pure solvent. 2 3 4 5 6 7 a. Hmixing and Vmixing of ideal solutions should be zero. b. They should obey Raoult’s law over the entire range of concentration. For the given binary solution of A and B, it would be ideal if A-B interactions are equal to AA and B-B interactions and it would be non-ideal if they are different to each other.The deviation from ideal behavior will be positive if A-B interactions are weaker as compared to A-A and B-B. The deviation will be negative if A-B interactions are stronger as compared to A-A and B-B. (i) Minimum boiling azeotropes are the non-ideal solutions showing positive deviation while maximum boiling azeotropes are those which show negative deviation. Because of positive deviation their vapour pressures are comparatively higher and so they boil at lower temperatures while in case of negative deviation, thevapour pressures are lesser and so higher temperature are required for boiling them.(ii) No, azeotropes can’t be separated by fractional distillation (i) When a non-volatile solute is added to a volatile solvent the vapour pressure of pure solvent decreases because a part of the surfaceis occupied by non-volatile solute which can’t volatilise. As a result, thevapour pressure of solution decreases andhence, the solution requires a comparatively higher temperature to boil causing an elevation of boiling point. (ii) Ebullioscopic constant is defined as the elevation in boiling point of a solution of a nonvolatile solute when its molality is unity. Its units are K Kg mol -1 The molecular mass of KCl in aqueous medium has been observed to be almost half than expected and it has been explained as dissociation of KCl into K + ions and Cl- ions when actual no. of particles become double and so become the colligative properties but since molecular mass is always inversely proportional to colligative property it becomes almost half.In case of benzoic acid in benzene, association of molecules take place when they dimerise and their no. becomes almost half and so molecular mass doubles as a result. Reverse osmosis will take place. We will observe the movement of solvent molecules from the solution to solvent phase and the level of solution will decrease. + 8 - Sodium chloride being ionic compound ionizes as (NaCl Na + Cl ) in aqueous solution. The concentration of solute particles in this case becomes approximately 0.2 M which is twice the concentration of glucose solution. Consequently, freezing point depression of NaCl solution is also approximately twice that of glucose solution. 9 The freezing point depression depends upon the molal concentration of the solute and does not depend upon the nature of the solute .It is therefore, a colligative property 10 Glucose is a non electrolyte, when added to water it do not break up into ions whereas Common salt is an electrolyte when added to water it breaks up to give Sodium and chloride ions , The number of particles in solution of Common salt are nearly double the number of particles in the solution of glucose so the osmotic pressure of common salt solution is nearly twice that if Glucose solution. SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS OF 2 MARK 1. 2. 3. State Raoult’s law. Prove that it is a special case of Henry’ law? List two conditions that ideal solutions must satisfy. Explain ideal and non-ideal solutions with respect to intermolecular interactions in a binary solution of A and B. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 104 4. a. b. (i) What are minimum boiling and maximum boiling azeotropes? (ii) Can azeotropes be separated by fractional distillation? 5. When a non-volatile solute is added to solvent,there is increase in boiling point of solution.Explain. d. Define ebullioscopic constant and give its units. 6. How did Van’t Hoff explain the abnormal molecular masses of electrolytes like KCl in water and non-electrolytes like benzoic acid in benzene. 7. When a pressure higher than the osmotic pressure is applied on the surface of the solution separated from a solvent by semi permeable membrane, what will happen? 8. The freezing depression of 0.1M sodium chloride solution is nearly twice that of 0.1 M glucose solution. Explain? 9. The depression in freezing point is a colligative property. Explain. 10. Equimolar solution of glucose and Common salt are not isotonic. Why? c. Answer key Ans.1 Raoult’s law states that partial pressure of a volatile component of a solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction. It is a special case of Henry’ law because it becomes the same when “Kh” (Henry constant) is equal to pressure of pure solvent. Ans.2 1. Hmixing and Vmixing of ideal solutions should be zero. 2.They should obey Raoult’s law over the entire range of concentrations. Ans.3 For the given binary solution of A and B, it would be ideal if A-B interactions are equal to A-A and B-B interactions and it would be non-ideal if they are different to each other.The deviation from ideal behavior will be positive if A-B interactions are weaker as compared to A-A and B-B. The deviation will be negative if A-B interactions are stronger as compared to A-A and B-B. Ans4(i) Minimum boiling azeotropes are the non-ideal solutions showing positive deviation while maximum boiling azeotropes are those which show negative deviation. Because of positive deviation their vapour pressures are comparatively higher and so they boil at lower temperatures while in case of negative deviation, thevapour pressures are lesser and so higher temperature are required for boiling them.(ii) No, azeotropes can’t be separated by fractional distillation. Ans5(i) When a non-volatile solute is added to a volatile solvent the vapour pressure of pure solvent decreases because a part of the surfaceis occupied by non-volatile solute which can’t volatilise. As a result, thevapour pressure of solution decreases andhence, the solution requires a comparatively higher temperature to boil causing an elevation of boiling point. (ii) Ebullioscopic constant is defined as the elevation in boiling point of a solution of a non-volatile solute when its molality is unity. Its units are K Kg mol-1 Ans.6 The molecular mass of KCl in aqueous medium has been observed to be almost half than expected and it has been explained as dissociation of KCl into K + ions and Cl- ions when actual no. of particles become double and so become the colligative properties but since molecular mass is always inversely proportional to colligative property it becomes almost half. In case of benzoic acid in benzene, association of molecules take place when they dimerise and their no. becomes almost half and so molecular mass doubles as a result. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 105 Ans.7 Reverse osmosis will take place. We will observe the movement of solvent molecules from the solution to solvent phase and the level of solution will decrease. + - Ans 8 Sodium chloride being ionic compound ionizes as (NaCl Na + Cl ) in aqueous solution. The concentration of solute particles in this case becomes approximately 0.2 M which is twice the concentration of glucose solution. Consequently, freezing point depression of NaCl solution is also approximately twice that of glucose solution. Ans.9 The freezing point depression depends upon the molal concentration of the solute and does not depend upon the nature of the solute .It is therefore, a colligative property Ans 10 Glucose is a non electrolyte, when added to water it do not break up into ions whereas Common salt is an electrolyte when added to water it breaks up to give Sodium and chloride ions , The number of particles in solution of Common salt are nearly double the number of particles in the solution of glucose so the osmotic pressure of common salt solution is nearly twice that if Glucose solution. QUESTIONS FOR 3 MARK 1. A 5% solution of sucrose C12H22O11 is isotonic with 3% solution of an unknown organic substance. Calculate the molecular mass of unknown substance. 2. A solution of Barium Chloride is prepared by dissolving 3.100 g of it in 250 g of water. The solution boils at 100.083oC. Calculate the Van’t Hoff factor and Molality of this solution.(Kb for water = 0.52 Km-1, Molar mass of BaCl2 = 208.3 g mol-1) 3. Why semi permeable membrane is so important in the phenomenon of osmosis? What are isotonic, hypo tonic and hyper tonic solutions? Does osmosis take place in all three types of solutions? 4. Which will have more osmotic pressure and why? Solution prepared by dissolving 6g/L of CH3COOH orSolution prepared by dissolving 7.45g/L of KCl 5. What is Bends ? If a diver had the "bends", describe how this can be treated. 6. At 300 K. 18g of glucose present per litre its solution has an osmotic pressure of 4.98 bars .If the osmotic pressure of solution is 1.52 bars on the same temperature, what would be its concentration? 7. The freezing depression of 0.1M sodium chloride solution is nearly twice that of 0.1 M glucose solution. 8. Calculate the amount of NaCl must be added to 1000 ml of water so as to reduce its freezing point by two Kelvin. For water Kf = 1.86 K Kg mol-1 , give that the density of water is 1.0 g ml-1 and NaCl is completely dissociated. 9. Predict the Boiling point of solution prepared by dissolving 25.0g of urea and 25.0 g of thiourea in 100 gram of water. Given for water Kb= 0.52 K Kg mol-1 and Boiling point of pure water is 373.15 K. 10. Predict the Boiling point of solution prepared by dissolving 3.42g of sugarcane in 100 gram of water. Given for water Kb= 0.52 K Kg mol-1and Boiling point of pure water is 373.15 K.Ans. ANSWER KEY FOR 3 MARK Ans.1 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 106 Ans.2 Observed Tb = 100.083 - 100 =0.083 0C Ans.3 The semi permeable membrane is very importantin the phenomenon of osmosis because they only permit the movement of solvent molecules through them. Two solutions having similar osmotic pressure at a given temperature are called isotonic solutions. If the given solution has less osmotic pressure it is called hypo tonic and it is hyper tonic if its osmotic pressure is higher than the the solution on the other side of semi permeable membrane. Osmosis takes place only in hypo tonic and hypertonic solutions. Ans.4 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 107 Molar concentration of both the solutions is same. KCl ionizes into K+ and Cl– where as CH3COOH does not ionize Osmotic pressure is colligative property Its value depend on number of particles. Since, KCl produces more ions so, osmotic pressure of KCl will be more than that of CH3COOH. Ans.5 Scuba divers cylinder has a mixture of helium, nitrogen and oxygen ,as they go down at high pressure which increases the solubility of these gases in the blood when they come up pressure decreases and nitrogen is released as the solubility decreases and the bubbles of nitrogen gas can block capillaries causing condition called bends which is both painful and dangerous. In order to avoid formation of bends in blood the divers are subjected to decompression chambers where pressure is lowered down gradually releasing the gas from blood slowly. Ans6.For solution A V= n RT 4.98 x 1L = 18/180 x R x T For solution B V= n RT 1.52 x 1L = n x R x T 1.52 x 1L/ n = 4.98 x 1L / 0.1 1.52 / n = 4.98 / 0.1 n = 1.52 x 0.1 / 4.98 = 0.035moles c= 0.035 mol L-1 Na++ Cl-) in aqueous solution. The concentration of solute particles in this case becomes approximately 0.2 M which is twice the concentration of glucose solution. Consequently, freezing point depression of NaCl solution is also approximately twice that of glucose solution. Ans7. Sodium chloride being ionic compound ionizes as (NaCl Ans.8 Mass of water = density x volume= 1 x 1000 = 1000g = 1Kg. ΔTf = i Kf m 2 = (2 x 1.86 x z / 58.5 x 1000) x 100 z = 58.5/1.86= 31.45g ans.9 No of moles of urea= mass of urea / molar mass of urea. = 25/ 60 =0.42 No of moles of thiourea= mass of thiourea / molar mass of thiourea. = 25/76 = 0.33 molality of solution= moles of solute / mass of solvent in Kg molality of solution= (moles of solute / mass of solvent in g) x 1000 molality of solution= (0.33+0.42/ 100) x 1000 molality of solution= 1.50m ΔTb =0.52 x 1.50= 5.44K Tb (solution) - Tb (solvent) = 5.44K Tb (solution) = 5.44K + 373.15 =378.59K Ans.10.ΔTb = Kb x m ΔTb = (0.52 x 3.42g/342g mol-1 x 100 } x 1000 ΔTb = 0.052 x100 /1000 = 0.0052 K Tb (solution) - Tb (solvent) = 0.0052K Tb (solution) = 0.0052K + 373.15= 373.1552K ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 108 QUESTIONS FOR 5 MARK SOLUTION Q1 (a) Difference between molarity and molality for a solution. How does a change in temperature influence their values? (b) Calculate the freezing point of an aqueous solution containing 10.50 g of MgBr2 in 200 g of water. (Molar mass of MgBr2 =184 g) (Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol-1) OR (a) Define the terms osmosis and pressure. Is the osmotic pressure of a solution a colligative property? Explain. (b) Calculate the boiling point of a solution prepared by adding 15.00 g of NaCl to 250.0 g of water.(K b for water = 0.512 K kg mol-1), Molar mass of NaCl = 58.44 g. Q.2 Q.3 A solution is prepared by dissolving 30g of non-volatile non-electrolyte solute in 90g water. The vapour pressure of solution was 2.8 K Pa at 298K. When 18g of water was further added to it, the vapour pressure became 2.9 k Pa at 298K. Calculate molar mass of solute. Q4 Question 1 a. Define the following terms: i. Mole fraction ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 109 ii. Van't Hoff factor b. 100 mg of a protein is dissolved in enough water to make 10.0 mL of a solution. If this solution has an osmotic pressure of 13.3 mmHg at 25° C, what is the molar mass of protein? (R=0.0821 L atm mol -1 K-1and 760 mmHg = 1 atm) or a. What is meant by: i. Colligative properties ii. Molality of a solution b. What concentration of nitrogen should be present in a glass of water at room temperature? Assume a temperature of 25°C, a total pressure of 1 atmosphere and mole fraction of nitrogen in air of 0.78. [KH for nitrogen = 8.42 x 10-7 M/mm Hg]Ans. Q5(a) weak electrolyte AB is 5% dissociated in aqueous solution. What is the freezing point of a 0.100 molal aqueous solution of AB? For water Kf = 1.86 K (b)0.02molal solution of acetic acid is 3% dissociated at 25 oC calculate the Osmotic pressure of the solution.Ans. ANSWER FOR 5 MARKS Ans 1 (a) Molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute dissolved per litre of solution. (b) Mathematically M = (c) Molality of a solution is defined as the number of moles of solute (d) dissolved in 1000 grams of solvent. (e) Mathematically, m = (f) While molarity decreases with an increase in temperature, molality is independent of temperature. This happens because molality (g) involves mass, which deos not change with a change in temperature, while molarity involves volume, which is temperature dependent. (h) (b) Given w2 = 10.50 g (i) w1 = 200g (j) Molar mass of MgBr2 (M2) = 184 g (k) Using the formula, (l) = ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 110 (m) = (n) = = 0.53 (o) Now, Tf = To (p) = 273 – 0.53 = 272.47 K OR (a) Osmosis : The process of flow of solvent molecules from pure solvent to solution or from solution of lower concentration of solution (b) of higher concentration through a semi – permeable membrane is called osmosis. (c) Osmotic pressure : The pressure required to just stop the flow of solvent due to osmosis is called osmotic pressure (d) Yes, the osmotic pressure of a solution is colligative property. The osmotic pressure is expressed as. (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) (k) (l) (m) (n) (o) (p) Where, = osmotic pressure n = number of moles of solute V = volume of solution T = temperature From the equation, it is clear that osmotic pressure depends upon the number of moles of solute 'n' irrespective of the nature of the solute. Hence, osmotic pressure is a colligative property. (b) Given, Kb = 0.512 k kg mol-1 w2 = 15.00 g w1 = 250.0 g M2 = 58.44 g Using the formula, (q) (r) = (s) = = 0.52 (t) Now, Tb = To + (u) = 373 + 0.53 = 373.53 K ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 111 ANS.2 ANS.3 ANS4(i) Mole fraction of a component is the ratio of number of moles of the component to the total number of moles of all the components. (a) (ii) Van't Hoff factor is the ratio of normal molar mass to the abnormal molar mass. (b) Van't Hoff factor is the ratio of observed value of colligative property to calculated value of colligative property assuming no association or dissociation. (c) (b) Mass of protein = 100 mg = 0.1 g (d) V= 10 Ml ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 112 (e) (f) Or (g) (i) All the properties which depend on the number of solute particles irrespective of their nature relative to the total number of particles present in the solution are known as colligative properties. (h) (ii) Molality of solution is the number of moles of solute present in 1 kilogram of solvent.(b) Ans..5 ( a) AB 1 0 1-α α α = 5/100 = 0.05 concentration= m x (1+ α) = 0.100 x (1 + 0.05) concentration= 0.100 x (1 + 0.05) = 0.105m ΔTf = Kf x m = 1.86 x 0.105= 0.1953 Tf (solution) = 273.15K- 0.1953K= 272.95 K B- + A+ 0 α (b) = i CRT Calculation of Van't Hoff factor CH3COOH CH3COO- + H+ ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 113 1 0 0 1-α α α i = 1+ α /1 = 1+ 0.03 / 1= 1.003 = i CRT = 1.003 x 0.0821 x 300 x 0.02 = 0.494atm Prepared by: Bhubaneswar Region ELECTROCHEMISTRY ONE Mark Each 1. The difference between the electrode potentials of two electrodes when no current is drawn through the cell is called ___________. 2. Under what condition an electrochemical cell can behave like an electrolytic cell ? 3. What is the quantity of charge in faraday is required to obtain one mole of aluminum from Al2O3 ? 4. How the cell constant of a conductivity cell changes with change of electrolyte, concentration and temperature? 5. What will happen at anode during the electrolysis of aqueous solution of CuSO4 in the presence of Cu electrodes? 6. Under what condition is ECell = 0 or ΔrG = 0 ? OR Give the condition for Daniell Cell in which there is no flow of electrons or current. 7. Why is alternating current used for measuring resistance of an electrolytic solution? 8. How will the pH of brine (aq. NaCl solution) be affected when it is electrolyzed ? 9. Unlike dry cell, the mercury cell has a constant cell potential throughout its useful life. Why? 10. Mention the purpose of salt-bridge placed between two half-cells of a galvanic cell? 11. Two metals A and B have electrode potential values of – 0.25V and 0.80V respectively. Which of these will liberate hydrogen gas from dilute H2SO4 ? 12. What is the effect of temperature on molar conductivity? 13. What is the role of ZnCl2 in the dry cell ? 14. Why is the equilibrium constant K, related to only E° cell and not Ecell ? 15.Rusting of iron is quicker in saline water than in ordinary water. Why is it so? 16. Why rusting of iron prevented in alkaline medium? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 114 17.Which will have greater molar conductivity and why? 1 mole KCl dissolved in 200 cc of the solution OR 1 mole KCl dissolved in 500 cc of the solution. storage battery as a secondary cell can be recharged? 19.Write the name of a chemical substance which is used to prevent corrosion. 18.Why Lead 20.Write the unit of Faraday constant. Answer of one mark 1. Cell emf 2. When Eext> Ecell 3. 3F 4. Remain unchanged for a cell 5. Copper will dissolve at anode 6. When the cell reaction reaches equilibrium 7. Alternating current is used to prevent electrolysis so that concentration of ions in the solution remains constant. Otherwise if DC is used the ions will get discharged and electrolysis will occur 8. The pH of the solution will rise as NaOH is formed in the electrolytic cell.) 9. Ions are not involved in the overall cell reaction of mercury cells. 10. Neutralize the two half cell. 11. Metal - A 12. Molar conductivity of an electrolyte increases with increase in temperature. 13. ZnCl2 absorbs ammonia produced in the reaction by forming a complex [Zn(NH3)4]2+ 14. This is because E cell is zero at equilibrium. 15.Due to presence of ions in saline water conductivity is more than the ordinary water. Hence in miniature electrochemical cell flow of electrons will increase, consequently rusting of iron is increased. 16. In alkaline medium, atmospheric oxygen is unable to take electron which is given by the oxidation of Fe. 17. 1 mole KCl dissolved in 500 cc of the solution, Due to more mobility of ions and more degree of dissociation. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 115 18. Recharging is possible in this case because PbSO4 formed during discharging is a sticky solid which sticks to the electrode. Therefore it can either take up or give up electrons during recharge. 19. Bisphenol 20. Coulomb/ mol ELECTROCHEMISTRY TWO Marks Each 1.Solutions of two electrolytes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are diluted. The Λm of ‘B’ increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Justify your answer. 2. When acidulated water (dil.H2SO4 solution) is electrolysed, will the pH of the solution be affected? Justify your answer. 3. What advantage do the fuel cells have over primary and secondary batteries? 4. How does the density of the electrolyte change when the lead storage battery is discharged ? 5. Why on dilution the Λm of CH3COOH increases drastically, while that of CH3COONa increases gradually? 6. What is the relationship between Gibbs free energy of the cell reaction in a galvanic cell and the emf of the cell? When will the maximum work be obtained from a galvanic cell? 7.Define corrosion. Write chemical formula of rust. 8.Can you store copper sulphate solutions in a zinc pot? 9.Write the cell reaction which occur in the lead storage battery (a) when the battery is in use (b) when the battery is on charging. 10.Write the product of electrolysis of aqueous copper sulphate by using platinum electrode. Answer 1.Electrolyte ‘B’ is strong as on dilution the number of ions remains the same, only interionic attraction decreases therefore increase in ∧ is small. 2.pH of the solution will not be affected as[ H+] remains constant. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 116 At anode: 2 H2O At cathode: 4H + O2 + + 4H 4 e- + + 4 e- 2 H2 3.Primary batteries contain a limited amount of reactants and are discharged when the reactants have been consumed. Secondary batteries can be recharged but take a long time to recharge. Fuel cell runs continuously as long as the reactants are supplied to it and products are removed continuously. 4.Density of electrolyte decreases as water is formed and sulphuric acid is consumed as the product during discharge of the battery. Pb + + PbO2 2 H2SO4 + 2 PbSO4 2 H2O 5.In the case of CH3 COOH, which is a weak electrolyte, the number of ions increase on dilution due to an increase in degree of dissociation. In the case of strong electrolyte the number of ions remains the same but the inter ionic attraction decreases. 6.∆rG = – nFE(cell)If the concentration of all the reacting species is unit. 7.Corrosion is a process of formation sulphides, oxides, carbonates, hydroxides, etc. of metal on its surface as a result of its reaction with air and water, surrounding it. Formula of rust- Fe2O3.XH2O 8.No, We cannot store CuSO4 solution in zinc pot, because electrode potential of zinc is less than copper,so Cu2+ ions get replaced by Zn2+ ions in solution . Zn is more reactive metals than Cu . (Displacement reaction) 9. (a) When battery is in use Oxd n React n Pb Red n React n Cell React n SO24 2- PbSO4 + 2 e- + + SO4 + 4 H + 2 e- PbSO4 + PbO2 + 2 SO42- + 4 H+ 2 PbSO4 + 2 H2O 2SO4 4H PbO2 Pb + + 2 H2O (b) When the battery is on charging Red n React n Oxd n React n Cell React n + 2 ePbSO4 + 2 H2O 2 PbSO4 + 2 H2O PbSO4 Pb + 2SO4 PbO2 Pb + + PbO2 + +2 + + 2 e- 2SO4 + 4H + 10. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 117 Electrolysis of aqueous CuSO4 using Pt electrode 2+ CuSO4 Cu Anode [ SO4 2- Cathode [ Cu 2+ HO + H - SO4 2- + ] 4 HO ] Cu 2+ - 2 H2O + + H2O + O2 + H + - HO 4e- Cu 2e- ELECTROCHEMISTRY THREE Marks Each 1.Calculate the EMF of the cell in which the following reaction take place: 2.If a current of 05 ampere flows through a metallic wire for 2 hours, then how many electrons flow through the wire 3.Calculate the potential of hydrogen electrode in contact with a solution whose PH is 10. 4.The molar conductivity of 0025 mol L1 methanoic acid is 461 S cm2 mol1. Calculate its degree of dissociation and dissociation constant. Given 0H = 3466 S cm2 mol1 and 0HCOO = 546 S cm2 mol1 5.If a current of 05 ampere flows through a metallic wire for 2 hours, then how many electrons flow through the wire ? 6. Calculate om for CaCl2 and MgSO4 from the data given in the table of Book. 7.The Conductivity of 0001028 mol L1 acetic acid dissociation constant if 0 for acetic acid is 3905 S cm2 mol1. is 495 × 105 S cm1. Calculate its 8. A solution of CuSO4 is electrolysed for 10 minutes with a current of 15 amperes. What is the mass of copper deposited at the cathode ? 9.The conductivity of 020 M solution of KCI at 298 K is 00248 S cm1. Calculate its molar conductivity. 10. Write the Nernst equation and find emf of the following cells at 298 K: Mg(s) Mg2+ (0001 M) Cu2+ (00001 M) Cu(s) Answer 1.Ni + 2 Ag+ (0002M) Ni2+ (0160 M) + 2 Ag ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 118 0 Given that ECell 1 05 V (According to Nernst equation : E Cell E 0Cell 1 05 0 059 Ni2 log 2 n Ag 0 059 0 160 log 0 9143V 2 0 0022 2.Quantity of electricity (Q) = Current (ampere) × time (second) = 05 × 2 × 60 × 60 = 3600 C (Coulombs) A flow of 69487 C of electricity 6022 × 1023 electrons 6 022 1023 3600 2 246 1022 electrons 96487 3600 C of electricity = 3.PH = 10 means [H+] = 10-10 M Now for the electrode; H+ E H H E 0H 2 H2 - (Here n = 1) 1 0 059 1 log = 0 0059 log 10 = 0059 log 1010 = 0059 × 10 = 059 v 10 n H 4.C = 461 S cm2 mol1 0HCOO 0H 1 H2 2 e + C = 0025 mol L1 + 0HCOO = 349.6 + 546 = 4042 S cm2 mol1 Degree of dissociation C 46 1 0 114 0 404 2 Dissociation constant K a c 2 0 025 0 114 0 0003667 3 67 104 1 1 0 114 2 5.Quantity of electricity (Q) = Current (ampere) × time (second) = 05 × 2 × 60 × 60 = 3600 C (Coulombs) A flow of 69487 C of electricity 6022 × 1023 electrons 6 022 1023 3600 2 246 1022 electrons 96487 3600 C of electricity = o o 2 6. om Cacl2 Ca mol -1 2 2 - 119 0 2 76 3 119 0 152 6 271 6 S cm cl o 2 -1 om MgSO4 oMg 2 SO 2- 106 0 160 0 266 S cm mol 4 7. m k 1000 4 95 10-5 1000 = 4815 cm2 mol1 C 0 001028 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 119 m 48 15 0 1233 om 390 0 C 2 0 001028 0 1233 Dissociation constant (Ka) = 1 78 105 1- 1 0 1233 2 8.Quantity of electricity (Q) = Current time = 15 10 60 = 900 C According to the reaction : Cu2+ + 2e Cu We required 2 F or 2 96487 C of electricity to deposit 1 mol or 63 g of Cu 900 C electricity will deposit = 63 900 = 02938 g of Cu at the cathode 2 96487 9.02 M 02 moles KCI present in 1 litre i.e. 1000 cm3 of solution 1 mole KCI present in 1000 cm3of solution 02 K = 00248 S cm1 Conductance of 1 cm3 solution = 00248 S Conductance of 1000 1000 cm3 solution = 00248 × = 124 S cm2 mol1 02 02 So Molar conductivity () = 124 S cm2 mol1 10. Oxidation Half Reduction Half Mg2+ Mg + Cu2+ + 2e 2e Cu ---------------------------------------------------------------------Cell Reaction Mg + Cu2+ Mg2+ + Cu Here number of moles of electrons (n) = 2 Eocell EoCu2 Cu EoMg 2 Mg = 034 ( 237) = 271 V The Nernst equation for the cell : E cell E Ecell 2 71 o cell 0 059 [Mg2 ] log 2 [Cu 2 ] 0 59 0 001 = 271 00295 log 10 = 271 00295 = 26805 V log 2 0 0001 FIVE Marks Each ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 120 1. (a) A Leclanche cell is also called dry cell. Why? (b)Why is the voltage of a mercury cell constant during its working? (c)Name two metals that can be used for cathodic protection of iron? (d)What do you mean by primary and secondary battery? [1+1+1+2] 2. (a)What do you understand by strong and weak electrolytes? [1+2+2 ] (b)State Faraday’s Laws of electrolysis? (c)Silver is deposited on a metallic vessel by passing a current of 0.2 amps. for 3 hrs. Calculate the weight of silver deposited. (At mass of silver = 108 amu, F = 96500 C? 3. (a)Define the term resistivity and give its SI unit . [1+2+2] (b) What are the factors on which conductivity of an electrolyte depend? (c) The molar conductivity of 0.1M CH3COOH solution is 4.6 cm2 mol-1. What is the conductivity and resistivity of the solution? 4.(a) State the factors that affect the value of electrode potential? [1+2+2] (b) Write Nernst equation for a Al-ZnSO4 cell? (c) write the chemistry of rusting of iron 5.(a) Can an electrochemical cell act as electrolytic cell? How? [1+2+2] (b) Explain construction and working of standard Hydrogen electrode? (c) What is an electrochemical series? How does it predict the feasibility of a certain redox reaction? Answer 1. (a) Leclanche cell consists of zinc anode (container) and carbon cathode. The electrolyte isa moist paste of MnO2, ZnCl2, NH4Cl and carbon black. Because there is no free liquid inthe cell, it is called dry cell. (b)As all the products and reactants are either in solid or liquid state, their concentration does not change with the use of the cell. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 121 (c)Names of the metals are –Zinc and Magnesium. (d)In the primary batteries, the reaction occurs only once and after the use over a period of time battery becomes dead and cannot be reused again. A secondary battery , after used,can be recharged by passing current through it in the opposite direction so that it can beused again. 2. (a)An electrolyte that ionizes completely in solution is a strong electrolyte eg. NaCl , CaCl2 etc and an electrolyte that ionizes partially in solution is weak electrolyte eg CH3COOH , NH4OH etc. (b) Faraday’s Laws of electrolysis First Law: The amount of chemical reaction which occurs at any electrode during electrolysis by a current is proportional to the quantity of electricity passed through the electrolyte. Second Law: The amount of different substances liberated by the same quantity of electricity passing through the electrolytic solution is proportional to their chemical equivalent weights. (c) 2.417 g of silver. 3. (a) The resistivity of a substance is its resistance when it is one meter long and its area of Section is one m2. Unit: ohm .meter (b) The conductivity of an electrolyte depends upon i) The nature of electrolyte ii) Size of the ions produced iii) Nature of solvent and its viscosity. iv) Concentration of electrolyte. v) Temperature (c) 4.(a) Factors affecting electrode potential values are – a) Concentration of electrolyte b) Temperature. (b) TheNernst equation for a Al-ZnSO4 cell: ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com cross 122 The Cell is : Al | Al 3+ || Al 3+ Anode reaction : Al Cathode reaction : Zn 2+ + Cell reaction : 2 Al 0 E=E - 0.059 6 Zn 2+ | Zn + 3e- ] x 2 + 2e- Zn ] x 3 3 Zn 2+ 2 Al 3+ + 3 Zn [Al3+]2 log [Zn2+]3 (c) The chemistry of rusting of iron [1]Creation of Acidic medium: Atmospheric carbon dioxide and water vapour combine to form . carbonic acid. + CO 2 H2O H2CO 3 [2] Iron will oxidise [ Anode- Oxidation half ] 2+ Fe + Fe 2 e- X 2 [3] In another spot, oxygen of air will take the two electrons with help of H+ ion and will be . reduced to H2O [ Cathode - Reduction half ] Cell React n O2 + 4H 2 Fe + O2 + + + 2 H2O 4 e4H + 2+ 2 Fe + 2 H2O In alkaline medium, atmospheric oxygen is unable to take electron which is given by the oxidation of Fe . [4] Atmospheric oxygen further oxidises ferrous ion into ferric oxide. 2+ 2 Fe + 2 H2O + 1 2 O2 Fe 2O 3 + 4H + [5] Ferric oxide will hydrolyse with water to form rust. Fe 2O 3 + x H 2O Fe 2O 3 . x H2O [ Rust ] --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------5.(a) Yes, An electrochemical cell can be converted into electrolytic cell by applying anexternal opposite potential greater than its own electrical potential.} (b) Standard Hydrogen electrode: ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 123 The Standard Hydrogen Electrode consists of a platinum electrode coated with platinum black. The electrode is dipped in an acidic solution and pure hydrogen gas is bubbled through it. The concentration of both the reduced and oxidised forms of hydrogen is maintained at unity. This implies that the pressure of hydrogen gas is one bar and the concentration of hydrogen ion in the solution is one molar. + Anode - H2 Cathode - 2H 2H + + If it act as cathode 2 e- + 2 eH2 E 2 H+ | H2 = 0 H2 gas at 1 bar Finely divided platinum coated on platinum foil The maximum bubbling of hydrogen gas from the solution will evolve . If it act as anode The minimum bubbling of hydrogen gas from the solution will evolve (c) The arrangement of metals and ions in increasing order of their electrode potential values is known as electrochemical series. The reduction half reaction for which the reduction potential is lower than the other will act as anode and one with greater value will act as cathode .Reverse reaction willnot occur. Prepared by: Bhubaneswar Region CHAPTER --4:- --.CHEMICAL KINETICS (1 MARK QUESTIONS) 1.What do you understand by the rate determining step of a reaction? 2.Find the molecularity of following reaction. RCOOR’ + H2O --------H+ RCOOH + R’OH 3. The rate constant of a reaction is 5.0 X 10-5 L mol-1 min-1. What is the order of the reaction? 4. Why rate of the reaction does not remain constant throughout? 5. What is the order of reaction whose rate constant has the same units as the rate of reaction? 6. Write Arrhenius equation. 7. Define rate constant or specific reaction rate. 8. The reaction A + 3B ---- 2C obeys the rate equation.Rate = k [A]1/2 [B]3/2. What is the order of this reaction? 9. What are the units of rate constant for a first order reaction? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 124 10. Give one example of a reaction where order and molecularity are equal. 11. What do you understand by half-life period of a reaction? 12. Hydrolysis of ethyl acetate withNaOH is a reaction of second order while with HCl, it is of firstorder. Why? 13. What is the effect of adding catalyst on the free energy (∆G) change of a reaction? 14. The rate of a reaction whose rate law is Rate = k [B]nbecomesdouble on doubling the concentration of B. Find the value n. 15. A reaction is 50% complete in 2 hrs. And 75% complete in 4 hrs. What is the order of reaction? 16. Give one example of a first order reaction. 17. Define threshold energy. 18. The reaction A+B -- C has zero order. What is the rate equation? 19. Which reactions proceed with constant rate?. 20. How does catalyst affect rate of reaction? ANSWERS TO 1 MARK QUESTION 1. The slowest step in a reaction is known as rate determining step. 2. Molecularity of reaction = 2 (there are two reactant molecules in balanced equation) 3. The order of reaction is 2. 4. Rate of reaction depends upon concentration of reactants which keep on decreasing with time. Hence, rate of reaction does not remain constant throughout. 5. Zero order. 6. Ae-Ea/RT Where,k = Rate constant Ea = Activation energy A = Arrhenius factor 7. When the molar concentration of each reactant is unity, the rate of reaction is called specific reaction rate. 8. Order =(1/2) + (3/2) = 2 9. s-1 10. For elementary reaction, order and molecularity are same. These reactions are carried out only in one step . 2HI --H2 + I2. 11. The time taken for half of the reaction to complete is known as half–life period of that reaction. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 125 12. Rate of hydrolysis of ethyl acetate with NaOH depends upon concentration of both CH3COOC2H5 and NaOH while with HCl it depends only upon the concentration of ethyl acetate. 13. Free energy of the reactants and products remains the same. Hence, there is no change in ∆ G on adding catalyst. 14. n = 1 15. First order 17. Threshold energy is minimum energy which the colliding molecules must possess so that the collision between them may be effective. Threshold energy = Activation energy + energy possessed by reactant molecules. 18. Rate =k [A]o [B]o 19. Zero order reactions. 20. A catalyst can increase rate of reaction by lowering down the activation energy. It gives alternate path to the reaction. (2 MARKS QUESTIONS) 1. What is (i) Rate law expression? (ii) Rate determining step? 2. (i) This reaction is of first order and rate constant of reaction is 5.7 X 10-3 S-1. Find the value of t1/2. 3. Define (i) Activation energy (ii) Collision freq 4. For a reaction A--- B, the rate of reaction doubles when concentration of A is increased by 4. What is the order of reaction? 5. Time required to decompose SO2Cl2 to half of its initial amount is 1 hour. If the decomposition is a first order reaction, calculate the rate constant of the reaction. 6. The conversion of molecules from A to B follows second order kinetics. If the concentration of A is increased to five times, how will it affect the rate of formation of B? 7.The rate of decomposition of N2O5 is 2.4 x 10-4mol L-1s-1 when [N2O5] is 0.36 M. What is the rate law and value of k for this first order reaction? 8. In a first order reaction, 75% of reactants disappeared in 1.386 hrs. Calculate the rate constant of the reaction. 9.Rate of formation of product for second order reaction is 9.5 x 10-5mol L-1 s-1. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 126 The initial concentration of reactant was found to be 0.01 mol/L. a) Write rate law for second order reaction. b) Calculate the rate constant for the given second order reaction. 10. What do you understand by effective collision? What are the factors affecting the effectivecollision? (THREE MARKS QUESTIONS) 1. (i) Define half life period. (ii)The half-life period of reaction is 10 minutes. How long it will take for concentration of reactant to be reduced to 10% of original? 2. Explain the term Activation energy and threshold energy? How temperature affects the rate of reaction? 3. What do you understand by integrated rate equation? Deduce the integrated rate equation for first order reaction? 4.A chemical reaction is of second order w.r.t. a reactant. How will the rate of reaction be affected if the concentration of this reactants : (a) Doubled; (b) Reduced to 1/8th. 5.From the following data for a chemical reaction between A and B at 300 K [A] mol/L [B] mol/L Initial rate (mol L–1 sec–1) 2.5 × 10–4 3 × 10–5 5 × 10–4 2.5 × 10–4 6 × 10–5 4 × 10–3 1 × 10–3 6 × 10–5 1.6 × 10–2 Calculate (i) the order of reaction with respect to A and with respect to B.(ii) the rate constant 300K 6. (i) Distinguish between elementary and complex reaction? (ii) What are the factors affecting the rate of chemical reaction? 7.The decomposition of phosphine4PH3(g)----P4(g) + 6H2(g) has rate law; Rate = k [PH3]. The rate constant is 6.0 × 10–4 s–1 at 300K and activation energy is 3.05 × 105 J mol–1. Calculate the value of the rate constant at 310K. (R = 8.314 J k–1mol–1). 8.The decomposition of hydrocarbon follows the equation k = (4.5 × 1011 s–1)e–28000 K/T. Calculate Ea . ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 127 9. Show that for a first order reaction, time required for 99% completion is twice for the time required for the completion of 90% of reaction. 10. The rate of reaction triples when the temperature changes from 20°C to50°C. Calculate the energy of activation. [R = 8.314 J k–1mol–1, log 3 =0.48] 5 MARKS QUESTIONS 1. (a) For a reaction A + B Products, the rate law is given by r = k [A]1/2 [B]2 What is the order of reaction? (b) The conversion of molecules X to Y follows second order kinetics. If concentration of X is increased to three times how will it affect the rate of formation of Y? ( c) Write two points of difference between order and molecularity of a reaction. 2. a)Define (i) Activation energy (ii) Collision frequency b) The rate constants of a reaction at 500k& 700k are 0.02s-1& 0.07s-1 respectively. Calculate thevalue of Ea& A. 3. (i) A reaction is first order in A & second order in B. a) Write differential rate equation. b) How is the rate affected on increasing the concentration of B three times? c) How is the rate affected when conc of both A&B is doubled? ( ii) Name the factors which affect the rate of reaction. 4. a) Deduce the expression of half-life for zero order reaction. b) Show that time required for 99.9% completion of the first order reaction is 10 times of t1/2 for first order chemical reaction. 5. a) For a reaction A + B Products, the rate law is given by r = k [A]1/2 [B]2. What is the order of reaction? (b) T he conversion of molecules X to Y follows second order kinetics. If concentration of X is increased to three times how will it affect the rate of formation of Y? Prepared by : Bhubaneswar Region FAQ - Chapter 5 SURFACE CHEMISTRY 1 Mark Questions:1.Bleeding caused by a nick from a razor during shaving can be stopped by rubbing with alum. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com Why? 128 Ans: Blood is a negatively charged colloidal solution. When alum is rubbed the positively charged Al 3+ ions from alum neutralizes the charge on the particles and makes it coagulate to form a clot. 2. In which of the following does adsorption take place and why? (i) Silica gets placed in the atmosphere saturated with water. (ii) Anhydrous CaCl2 placed in the atmosphere saturated with water. Ans: Water vapour gets adsorbed on the surface of silica since it is a good adsorbent. 3. Action of soap is due to emulsification and micelle formation. Comment. Ans: Soap molecules adsorb on to the dirt surface and try to emulsify it by forming micelles. Soap micelles thus make the insoluble dirt(greasy materials) into colloidal form such that it gets washed away by water. 4. What is the use of ZSM-5? Ans: It converts alcohols directly into gasoline (petrol) by dehydrating them to give a mixture of hydrocarbons. 5. Give one example for each (i) sol (ii) gel. Ans: (i) paints (ii)Butter or any other correct options. 6. What is collodion? Ans: It is a 4% solution of nitrocellulose in a mixture of alcohol and ether. 7. Can we form a colloid with two gaseous components?Comment. Ans: No. a gas mixed with another gas forms a homogeneous mixture which does not come under a colloidal system. 8. What are the physical states of the dispersion medium and dispersed phase in froth? Ans: In froth, the dispersed phase is a gas while dispersion medium is a liquid. 9. Write the equation for the preparation of colloidalsulphur ? Ans: SO2 + 2H2S 3S(sol) + 2H2O 10. Why does physisorption decrease with increase of temperature? Ans: Adsorption is an exothermic phenomenon. The increase in temperature will favour the reverse process i.e. desorption according to Le Chatlier’s principle. Therefore physisorption decreases with increase in temperature. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 129 11.What is CMC (Critical Micelle Concentration) Ans:-It is a particular concentration above which the particles aggregate to form micelles or associated colloids. 12.Why are powdered substances more effective adsorbents as compared to their crystalline forms? Ans:- Powdered form has more surface area than crystalline form. 13.Why is it necessary to remove CO when ammonia is obtained by Haber’s process? Ans:-In Haber’s process iron is used as catalyst .If CO is present ,it acts as catalytic poison. 14.What is electrophoresis due to ? Ans:- It is due to existence of positive or negative charge on colloidal particles. 15. Mention two ways by which lyophilic colloids can be coagulated. (C.B.S.E-2008) Ans:- 1) By adding en electrolyte. 2) By adding a suitable solvent. 16.What is Kraft temperature? (C.B.S.E Foreign 2004) Ans:-It is the temperature above which the formation of micelle takes place. 17. What is Brownian movement due to? (C.B.S.E -1999) Ans:- It is due to unbalance bombardment of the colloidal particles by the molecules of dispersion medium. 18. Name two industrial processes in which heterogeneous catalysts are employed.(C.B.S.E-2008) Ans: (i).Manufacture of ammonia by Haber’s process. (ii) manufacture of sulphuric acid by contact process. 19. What is an emulsion? (C.B.S.E Foreign 2009) Ans:-Emulsion is a colloidal solution of two immiscible liquids of which one is the dispersion medium and the other is dispersed phase. 20. What is Zeta potential? Ans:- The potential difference between the fixed layer and diffused layer of opposite charges around the colloidal particles. 2 Marks Questions 1. Explain why lyophilic sol are more stable than lyophobic sols? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 130 Ans; Lyophilic colloids have great affinity for the dispersion medium i.e. dispersed phase particles are solvated to a greater extent in case of Lyophilic colloids. Hence Lyophilic sols are relatively more stable than lyophobic sols. 2. State two features of chemical adsorption which is not found with physical adsorption. Ans: (i) Chemical adsorption has high enthalpy of heat. (ii) It is highly specific. 3. Describe the following types of colloids giving one example for each? (i)Multi molecular colloids (ii) Macro molecular colloids (C.B.S.E 2007) Ans(i) Multi molecular colloids consist of aggregates of atoms or small molecules with diameter less than 1 nm. The colloidal particles are held by weak van der Waal’s forces, e.g. sols of S8. (ii) Macromolecular colloids are those in which molecules of dispersed phase are of colloidal dimensions 1-1000nm. These have very high molecular mass, e.g. sols of proteins. 4. Explain the process of Ultra filtration. Ans:- Ultra filtration is the process of separating the colloidal particles from the solvent and soluble solutes present in the colloidal solution by specially prepared filters which are permeable to all substances except the colloidal particles. These filter papers are prepared by impregnating ordinary filter paper with collodion solution and hardening by formaldehyde. 5.What is shape selective catalysis? (C.B.S.E -2003 , Foreign-2004) Ans:-A catalyst whose catalytic action depends upon its pore structure and molecular sizes of the reactants as well as the products is known as shape selective catalysis and the catalytic action is called shape selective catalysis. For example, Zeolites act as shape selective catalysts. Recently ZSM-5 has been used in producing gasoline from alcohol. 6.(a) Adsorption of a gas on the surface of solid is generally accompanied by a decrease in entropy. Still it is a spontaneous process .Explain. (b)How does an increase in temperature affect both physical as well as chemical adsorption? Ans: (a) During adsorption there is a decrease in energy. It is exothermic, i.e. ΔH=-ve. During adsorption, freedom of molecules becomes restricted, ΔS=-ve. But ΔG becomes negative. Hence, the reaction is spontaneous. (b) Extent of physical adsorption decreases with increase in temperature whereas the extent of chemical adsorption first increases and then decreases as the temperature increases. 7. What is an adsorption isotherm? Describe Freundlich adsorption isotherm. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 131 Ans:-The graph drawn betweenthe amount of gas adsorbed per unit mass of adsorbent x/m and pressure of the gas at a constant temperature is known as adsorption isotherm. After saturation pressure there is no more adsorption on the surface. Freundlich adsorption isotherm can be expressed by x/m =kp1/n (n>1) log x/m =log k +1/n logp (Graphs for both expression can be drawn) 8. What is the difference between dialysis and osmosis? Ans:The two processes appear to be the same since both involve the diffusion through semi permeable membrane .However in osmosis ,only the solvent and not the solute particles can pass through the membrane ,but in dialysis even small ions of electrolyte can pass through the membrane and colloidal particles which are comparatively big in size cannot pass. 9. DescribeBredig’s Arc method for preparation of gold sol? Ans:-An electric arc is struck between electrodes made of gold immersed in dispersion medium water. The intense heat produced vapourises the metal which then condenses to form particles of colloidal gold.(Label diagram to be drawn). 10. Name four different ways by which coagulation of lyophobic sols can be carried out? Ans :- (i) By electrophoresis (ii) By boiling (iii) By mixing two oppositely charged sols (iv) by addition of electrolytes. 3 Marks Questions 1. What are emulsions? What are their different types? Give example of each type. Ans: Emulsions are the colloidal solutions of two immiscible liquids in which dispersed phase as well as the dispersion medium are liquids. Since the two do not mix well, the emulsion is generally unstable and is stabilized by adding a suitable reagent called emulsifier, e.g. gum, soap, etc. Types of emulsions: These are of two types: (i)Oil in water emulsions in which oil acts as the dispersed phase while water acts as the dispersion medium. For example, milk is an emulsion of fats in water and here casein acts as an emulsifier. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 132 (ii) Water in oil emulsions. In this case, water acts as the dispersed phase while the oil acts as the dispersion medium. For example, butter, cold cream. 2. Explain what is observed when (i) a beam of light is passed through a colloidal sol (ii) an electrolyte, say NaCl is added to hydrated ferric oxide sol (iii) electric current is passed through a colloidal sol? Ans: (i) When a beam of light is passed through a colloidal sol placed in a dark room the beam of light is scattered by the colloidal particles and the path of the beam becomes visible. The phenomenon is called Tyndall effect. (ii) When NaCl is added to hydrated ferric oxide sol, the Cl- ions of NaCl neutralizes the positive charge on ferric hydroxide sol particles, and coagulation of sol occurs. (iii) When electric current is passed through a colloidal sol, the dispersed phase moves towards oppositely charged electrodes. On reaching the electrode, they lose their charge and get coagulated. 3. Write a short note on (i) Activity (ii) Selectivity and give examples? Ans:- (i) Activity:- the activity of a catalyst depends upon the strength of chemisorptions to a large extent. The reactants must get adsorbed strongly on to the surface of catalyst to become active. Ex:2 H2 (g) + O2 (g) Pd 2 H2O (l) (ii)Selectivity:-It is the ability of the catalyst to direct a reaction to yield a particular product. For example starting with H2 and CO2and using different catalysts,we get different products. (i) CO (g) + 3 H2 (g) Ni CH4(g) +H2O (g) (ii) CO (g) + 2 H2 (g) Cu/Zno-Cr2O3 CH3OH(g) 4. Name& explain three methods of purification of colloids. Ans:-Dialysis:-Separation of electrolytes and colloidal solution uses a semi-permeable membrane. Electro-dialysis:- When dialysis is carried out with an electric field around the membrane, the purification process is enhanced. Ultra-filtration:- Use of special filters, which are permeable to all substances except colloidal particles. 5. What is Hardy Schulze rule? Explain with examples? “The greater the valence of the flocculating ion the greater is its power to cause coagulation”. Ex: In the coagulation of a negative sol the flocculating power is in the order Al3+> Ba2+>Na+. In the case of a positive sol the flocculating power is in the order [Fe(CN)6]4->PO43->Cl6. What is Tyndall effect,under what conditions it is observed? Ans:- The scattering of light by colloidal particles is called Tyndall effect. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 133 The required conditions to observe this effect are (i) The diameter of the dispersed particles is not much smaller than the wavelength of the light used,and (iii) The refractive indices of the dispersed phase and the the dispersion medium differ greatly in magnitude. 7. Explain mechanism of enzyme catalyzed reaction? Ans:-E + S [E- S] E+ P Thus the enzyme-catalysed reactions may be considered to proceed in two steps. Step 1: Binding of enzyme to substrate to form an activated complex. E + S ES* Step 2: Decomposition of the activated complex to form product. ES * * E +P 8.Differentiatebetween homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis . Give one example of each. Homogeneous catalysis:- In which the catalyst and reactants are in the same phase (i:e liquid or gas). Ex:- Oxidation of sulphur dioxide into sulphur trioxide with catalyst as NO(g). All are in the gaseous state. Heterogeneous catalysis:- A process in which the reactants and catalyst are in different phases.Ex. 2 V O (s) SO2 (g)+ O2 2 SO3 (g) 2 5 9. Write short notes on (a) multimolecular (b) macromolucular (c) associated colloids Ans:- (a) It has many molecules aggregated together. Ex :-sulphur sol (b) Consists of macromolecules in a suitable solvent Ex: dispersion of cellulose in a suitable solvent. © Substances at low concentrations behave as electrolyte while at high concentrations they behave as colloids. Ex: Soap solution 10. Account for the following (i) Delta is formed when river meets sea water (ii) For water purification alum is added (iii) Cottrell smoke precipitator is used to reduce pollution. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 134 Ans:-(i) Electrolytes of sea water coagulate colloidal clay particles of river water. (ii)Alum coagulates the suspended colloidal impurities. (iii)In Cottrell smoke precipitator colloidal smoke particles lose their charge as they pass through it and coagulate. Prepared by : Bhubaneswar Region Chapter 6 General principles and processes of isolation of elements One mark Questions 1.Differentiate between a mineral and an ore. Ans: the naturally occurring chemical substances present in the earth’s crust which can be obtained by mining are called minerals while minerals from which metals can be extracted economically are called ores. 2. Why is it that only sulphide ores are concentrated by froth floatation process. Ans: This is because sulphide ores particles are wetted by oil and gangue particles are wetted by water. 3. Name one acidic flux and one basic flux. Ans: silica and lime 4. Name the chief ore of silver. Ans: argentite or silver glance 5. Name a reagent used during leaching of bauxite ore. Ans : NaOH (sodium hydroxide) 6. Why is silica added to sulphide ore of copper in the reverberatory furnace? Ans : in order to remove the iron impurity as slag 7. What is the role of flux in metallurgical processes? Ans : flux is used for making the molten mass more conducting. 8. What is the thermodynamic relation between Gibbs free energy and emf of the cell. Ans: ∆G0= —nFE0 9. What is the relation between gibbs free energy and equilibrium constant? Ans: ∆G0= —RTlnK 10. Give the expression for Gibbs Helmholtz equation. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 135 Ans : ∆G= ∆H—T∆S 11. Name one chemical which can be used to concentrate galena selectively by froth floatation process. Ans: sodium cyanide (NaCN) 12. What type of ores are roasted? Ans : sulphide ores 13. Out of C and CO which is a better reducing agent for ZnO? Ans : the free energy of formation of CO from C becomes lower at temp. above 1120K whereas that of CO2 from C becomes lower above 1323K than free energy of formation of ZnO. The free energy of formation of CO2 from CO is always higher than that of ZnO. Therefore, C can reduce ZnO to Zn better than CO. 14. What is the chemical principle on which chromatography separation based on? Ans : Adsorption 15. What are the products obtained during the electrolysis of brine solution? Also write the name of this process. Ans : chlorine, hydrogen and sodium hydroxide. The process is popularly known as chlor-alkali process. 16. What is roasting? Ans : The preliminary treatment of the concentrated ore in which the ore is heated in excess of air below its melting point. 17. What is calcination? Ans: The process of heating the concentrated ore in absence/ limited supply of air below its melting point. 18. What is smelting? Ans: Reduction of metal oxide into metal in the presence of carbon or carbon monoxide. 19. What is blister copper/ copper matte? Ans: The copper obtained after extraction has blistered appearance due to the evolution of SO 2. It is called blistered copper/ copper matte. 20.What is meant by beneficiation process? Ans: The process of removal of unwanted earthy and silicious impurities form the ore is called beneficiation process. 2marks questions 1. Write down the reactions taking place in blast furnace related to the metallurgy of iron. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 136 Ans : 3Fe2O3 + CO 2Fe3O4 +CO2 Fe3O4 + 4CO 3Fe + 4CO2 Fe2O3 +CO 2FeO + CO2 2. Describe with chemical equation the extraction of silver from its ore. Ans : argentite ore is treated with dilute solution of NaCN in presence of oxygen to form complex. 2Ag2S + 8CN- + O2+2H2O 4 [Ag(CN)2]-+2S +4OHZn acts as reducing agent and displaces silver from the complex. 2[Ag(CN)2]- + Zn [Zn(CN)4]2- + 2Ag The crude silver obtained is refined by fusion with borax or by electrolysis. 3. Describe the role of the following. (a) NaCN in the extraction of silver from a silver ore (b) Cryolite in the extraction of aluminium from pure alumina. Ans : (a) 2Ag+ 8NaCN + O2+2H2O 4 Na[Ag(CN)2]+2S +4NaOH OR Ag2S + 4 NaCN 2Na[Ag(CN)2] + Na2S (b) i. it lowers the melting point of the mixture ii. it increase the electrical conductivity of the mixture. 4. Explain the role of carbon monoxide in the purification of nickel and iodine in zirconium. Ans : When nickel is heated carbon monoxide forms a volatile complex nickel tetracarbonyl which on further heating at higher temperature decomposes to give pure nickel. 330-350K 450-470K Ni + 4CO [Ni(CO)4 ] Ni + 4 CO Impure zirconium is heated with iodine to form volatile compound ZrI 4 which on further heating over tungsten filament decomposes to give pure zirconium. 870K2075K Zr + 2 I2 ZrI4 Zr + 2 I2 5. (a) Name the method used for refining of (i) nickel (ii) zirconium (b)The extraction of gold by leaching with NaCN involves both oxidation and reduction. Justify equations. Ans : (a) (i)Mond’s process giving (ii) van arkel method (b)4 Au + 8CN- + O2+2H2O 4 [Au (CN)2]- +4OH2[Au(CN)2]- + Zn [Zn(CN)4]2- + 2Au In the first reaction Au changes into Au+ i.e. oxidation takes place. In the second case Au+ changes to Au i.e. reduction takes place. 6. What criterion is followed for selection of the stationary phase in chromatography? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 137 Ans : the stationary phase is selected in such a way that the impurities are more strongly adsorbed or are more soluble in the stationary phase than element to be purified. Under these conditions, when the column is extracted the impurities will be retained by the stationary phase and the pure component is easily eluted. 7. Explain electrolytic refining of copper with thermodynamic principle involve in the process. Ans : in this method impure metal is made to act as anode. A strip of same metal in pure form is used as cathode. They are put in an electrolytic bath containing soluble salt of the same metal. On passing electric current metal ions from the electrolyte solution are deposited at the cathode while an equivalent amount of metal dissolves from the anode and goes into the solution. At Cathode: Cu2+(aq) + 2eCu (s) 2+ At anode: Cu (s) Cu (aq) + 2eThe thermodynamic principle involve during the process can be explained by the following expression ∆G0= —nFE0. 8. What are the limitations of Ellingham diagram? Ans: (i) Ellingham diagram simply indicates whether a reaction is possible or not. It does not say about the kinetics of the reduction process. (ii) the interpretation of ∆G0 is based on K , thus it is presumed that the reactant and products are in equilibrium which is not always true. 9. What is the role of depressant in froth floatation process? Ans: in froth floatation process the role of the depressant is to prevent certain type of particles from forming the froth with the air bubbles. Example NaCN is used as a depressant to separate PbS from ZnS. NaCN forms a zinc complex Na2[Zn (CN)4] on the surface of ZnS preventing it from the formation of froth. 10. How are metals used as semiconductors refined? What is the principle of the method used? Ans : Semiconductors metals is produced by zone refining method which is based on the principle that the impurities are more soluble in melt than in the solid state of metals. 3marks questions: 1. Describe how the following changes are brought about : (i) Pig iron into steel (ii) Zinc oxide into metallic zinc (iii) Impure titanium into pure titanium Ans : (i) pig iron is converted into steel by heating in a converter. A blast of oxygen diluted with carbon dioxide is blown through the converter. Oxygen reacts with impurities and raised the temperature to 2173K. carbon gets oxidized to CO which burns of at the mouth of the converter. Oxides of silicon and magnesium form slag. When the flame is stopped, slag is tapped out and other metals like Mn, Cr, Ni, W may be added in the end. (ii) the reduction of zinc oxide is done using coke as a reducing agent. For the purpose of heating, the oxide is made into brickettes with coke and clay. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 138 ZnO + C Zn + CO The metal is distilled off and collected by rapid chilling. (iii) Impure titanium is heated with iodine to form volatile TiI4 which decomposes on tungsten filament at higher temperature to give pure titanium. Ti + 2 I2 TiI4 Ti + 2 I2 2. Describe the role of (a) NaCN in the extraction of gold from gold ore. (b) SiO2 in the extraction of copper from copper matte. (c) Iodine in the refining of zirconium Ans : (a) 4 Au + 8CN- + O2+2H2O 4 [Au (CN)2]- +4OH(b) the role of SiO2 is to convert FeS, FeO present in the matte into slag. 2FeS + 3O2 2FeO + 2SO2 FeO + SiO2 FeSiO3 (c) Impure zirconium is heated with iodine to form volatile compound ZrI 4 which on further heating over tungsten filament decomposes to give pure zirconium. 870K2075K Zr + 2 I2 ZrI4 Zr + 2 I2 3. Describe how the following changes are brought about : (i) Pig iron into steel (ii) Bauxite into pure alumina (iii) Impure copper into pure copper Ans (i) pig iron is converted into steel by heating in a converter. A blast of oxygen diluted with carbon dioxide is blown through the converter. Oxygen reacts with impurities and raised the temperature to 2173K. carbon gets oxidized to CO which burns of at the mouth of the converter. Oxides of silicon and magnesium form slag. When the flame is stopped, slag is tapped out and other metals like Mn, Cr, Ni, W may be added in the end. (ii) Finely powdered bauxite is digested with an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide . Al2O3 is leached out as sodium aluminate leaving impurities behind . Al2O3+ 2NaOH + 3H2O 2Na[Al(OH)4] The aluminate is neutralised by passing CO2 and hydrated Al2O 3 is precipitated. The solution is seeded with freshly prepared hydrated Al2O3 which induced the precipitation. 2Na[Al(OH)4] + CO2 Al2O3∙x H2O + 2NaHCO3 The sodium bicarbonate remains in the solution and hydrated alumina is filtered, dried and heated to get back pure Al2O3. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 139 Al2O3∙x H2O Al2O3 + x H2O (iii)In this method impure metal is made to act as anode. A strip of same metal in pure form is used as cathode. They are put in an electrolytic bath containing soluble salt of the same metal. On passing electric current metal ions from the electrolyte solution are deposited at the cathode while an equivalent amount of metal dissolves from the anode and goes into the solution. At Cathode: Cu2+(aq) + 2eCu (s) 2+ At anode: Cu (s) Cu (aq) + 2e4. Describe the principle behind each of the following process. (i) Vapour phase refining of a metal (ii) Electrolytic refining of a metal (iii) Recovery of silver after silver ore was leached with NaCN Ans : (i) in this method the metal is converted into its volatile compound and collected. It is then decomposed to give the pure metal . (ii) in this method impure metal is made to act as anode. A strip of same metal in pure form is used as cathode. They are put in an electrolytic bath containing soluble salt of the same metal. On passing electric current metal ions from the electrolyte solution are deposited at the cathode while an equivalent amount of metal dissolves from the anode and goes into the solution. At Cathode: Cu2+(aq) + 2eCu (s) 2+ At anode: Cu (s) Cu (aq) + 2e(iii) During leaching Ag is oxidized to Ag+ which then combines with CN- to form soluble complex. Silver is then recovered from the complex by displacement method using more electro positive metal. Zn acts as reducing agent and displaces silver from the complex. 2[Ag(CN)2]- + Zn [Zn(CN)4]2- + 2Ag 5. Write the reaction involved in the following process (i) Leaching of bauxite ore to prepare pure alumina (ii) Refining of zirconium by Van Arkel method (iii) Recovery of gold after gold ore has been leached with NaCN Ans (i)Al2O3+ 2NaOH + 3H2O 2Na [Al(OH)4] + CO2 Al2O3∙x H2O 2Na[Al(OH)4] Al2O3∙x H2O + 2NaHCO3 Al2O3 + x H2O (ii) 870K2075K Zr + 2 I2 ZrI4 Zr + 2 I2 (iii) 4 Au + 8CN + O2+2H2O 4 [Au (CN)2] +4OH2[Au(CN)2]- + Zn [Zn(CN)4]2- + 2Au 6. Write the reactions involved in the following process: (i) Mond’s process ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 140 (ii) Mac Arthur forest cyanide process (iii) Hall heroult’s process Ans (i)330-350K 450-470K Ni + 4CO [Ni(CO)4 ] Ni + 4 CO (ii)4 M + 8CN + O2+2H2O 4 [M (CN)2]- +4OH2[M(CN)2]- + Zn [Zn(CN)4]2- + 2M where M=Ag or Au (iii) Al2O3 2Al3+ + 3 O2Cathode: Al3+ +3eAl 2Anode: C + O CO + 2 eC + 2O2CO2 + 4 eOverall reaction 2Al2O3+ 3C 4Al + 3CO2 7. Account for the following facts : (a) Reduction of a metal oxide is easier if the metal formed is in the liquid state at the temperature of reduction (b) The reduction of Cr2O3 with aluminium is thermodynamically feasible, yet it does not occur at room temperature (c) Pine oil is used in froth floatation method Ans : (a) in liquid state entropy is higher than the solid form. This makes ∆G more negative. (b) by increasing temperature fraction of activated molecule increases which help in crossing over the energy barriers. (c) pine oil enhances non wetting property of the ore particles and acts as a collector. 8. (a) (b) (c) State briefly the principles which serve as basis for the following operation in metallurgy . Froth floatation process Zone refining Refining by liquation Ans : (a) sulphide ore particle are preferentially wetted by pine oil whereas the gangue particles are wetted by water. (b)the impurities are more soluble in the melt than in the solid state of the metal . (c)the impurities whose melting points are higher than the metal are left behind on melting the impure metal. Hence pure metal separates out. 9. Explain the basic principles of the following metallurgical operations (a) Zone refining (b) Vapour phase refining (c) Electrolytic refining Ans: (a) the impurities are more soluble in the melt than in the solid state of the metal. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 141 (b)in this method the metal is converted into its volatile compound and collected. It is then decomposed to give the pure metal . (c)In this method impure metal is made to act as anode. A strip of same metal in pure form is used as cathode. They are put in an electrolytic bath containing soluble salt of the same metal. On passing electric current metal ions from the electrolyte solution are deposited at the cathode while an equivalent amount of metal dissolves from the anode and goes into the solution. 10. Complete the following reactions: (i)Al2O3+ NaOH + H2O (ii) Au + CN- + O2+H2O 450-470K (iii) [Ni(CO)4 ] Ans : (i) Al2O3+ 2NaOH + 3H2O (ii) 4 Au + 8CN- + O2+2H2O (iii)[Ni(CO)4 ] Ni + 4 CO 2Na[Al(OH)4] 4 [Au (CN)2]- +4OH- 5 marks questions 1. Describe the principle behind each of the following process. (i) Vapour phase refining (ii) Electrolytic refining of the metal (iii) Recovery of silver after silver ore was leached with NaCN (iv) Preparation of cast iron from pig iron (v) Preparation of pure alumina from bauxite Ans (i) in this method the metal is converted into its volatile compound and collected. It is then decomposed to give the pure metal . for example mond’s process. When nickel is heated carbon monoxide forms a volatile complex nickel tetracarbonyl which on further heating at higher temperature decomposes to give pure nickel. 330-350K 450-470K Ni + 4CO [Ni(CO)4 ] Ni + 4 CO (ii) in this method impure metal is made to act as anode. A strip of same metal in pure form is used as cathode. They are put in an electrolytic bath containing soluble salt of the same metal. On passing electric current metal ions from the electrolyte solution are deposited at the cathode while an equivalent amount of metal dissolves from the anode and goes into the solution. (iii)During leaching Ag is oxidized to Ag+ which then combines with CN- to form soluble complex. Silver is then recovered from the complex by displacement method using more electro positive metal. Zn acts as reducing agent and displaces silver from the complex. 2[Ag(CN)2]- + Zn [Zn(CN)4]2- + 2Ag ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 142 (iv)pig iron is melted with scrap iron and coke using hot air blast. Due to this impurities such as carbon, sulphur and phosphorus present in the pig iron are removed as CO2 , SO2 and P2O5 and carbon content is reduced to about 3%. (v) bauxite is soluble in concentrated NaOH solution whereas impurities are not. 2. Explain the role of each of the following in the extraction of metals from their ores : (i) CO in the extraction of nickel (ii) Zinc in the extraction of silver (iii) Silica in the extraction of copper (iv) Iodine in the extraction of titanium (v) Cryolite in the extraction of aluminium Ans (i) in this method the metal is converted into its volatile compound and collected. It is then decomposed to give the pure metal . for example mond’s process. When nickel is heated carbon monoxide forms a volatile complex nickel tetracarbonyl which on further heating at higher temperature decomposes to give pure nickel. 330-350K 450-470K Ni + 4CO [Ni(CO)4 ] Ni + 4 CO (ii) Zn acts as reducing agent and displaces silver from the complex. 2[Ag(CN)2]- + Zn [Zn(CN)4]2- + 2Ag (iii)the role of SiO2 is to convert FeS, FeO present in the matte into slag. 2FeS + 3O2 2FeO + 2SO2 FeO + SiO2 FeSiO3 (iv)impure titanium is heated with iodine to form volatile TiI4 which decomposes on tungsten filament at higher temperature to give pure titanium. Ti + 2 I2 TiI4 Ti + 2 I2 \ (v)i. it lowers the melting point of the mixture ii. it increase the electrical conductivity of the mixture 3. Explain the following (a) Generally sulphide ores are converted into oxides before reduction (b) Carbon and hydrogen are not used as reducing agent at high temperature (c) Silica is added to sulphide ore of copper in the reverberatory furnace (d) NaCN acts as a depressant in preventing ZnS from forming the froth (e) Role of cryolite in the metallurgy of aluminium Ans : (a) because sulphide ores are not reduced easily but oxide ores are easily reduced. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 143 (b) because at high temp. carbon and hydrogen react with metals to form carbides and hydrides respectively. (c)the role of SiO2 is to convert FeS, FeO present in the matte into slag. 2FeS + 3O2 2FeO + 2SO2 FeO + SiO2 FeSiO3 (d) in froth floatation process the role of the depressant is to prevent certain type of particles from forming the froth with the air bubbles. Example NaCN is used as a depressant to separate PbS from ZnS. NaCN forms a zinc complex Na2[Zn (CN)4] on the surface of ZnS preventing it from the formation of froth. (e) i. it lowers the melting point of the mixture ii. It increase the electrical conductivity of the mixture 4. (a) Describe the principle of froth floatation process. What is the role of depressant? Give an example. (b) Define leaching. How is this process used in the benefaction of silver and gold ores? (f) Ans : (a) sulphide ore particle are preferentially wetted by pine oil whereas the gangue particles are wetted by water.In froth floatation process the role of the depressant is to prevent certain type of particles from forming the froth with the air bubbles. Example NaCN is used as a depressant to separate PbS from ZnS. NaCN forms a zinc complex Na2[Zn (CN)4] on the surface of ZnS preventing it from the formation of froth. (b)Leaching consist of treating the powdered ore with a suitable reagent which can selectively dissolved ore but not the impurity . for leaching silver and gold, the powdered ore is treated with sodium cyanide. As a result a dissolved complex is obtained which is further treated with zinc metal which displaces the less active metals from the complex. This can be represented by following reaction. 4 M + 8CN- + O2+2H2O 4 [M (CN)2]- +4OH2[M(CN)2]- + Zn [Zn(CN)4]2- + 2M where M=Ag or Au 5. Write the chemical reaction which takes place in the following operations: (a) Electrolytic reduction of Alumina (b) Mond’s process (c) Van Arkel method (d) Mac Arthur forest cynide process (e) Electrolysis of brine Ans (a) Al2O3 Cathode: Al3+ +3eAnode: C + O2C + 2O2Overall reaction 2Al2O3+ 3C 2Al3+ + 3 O2Al CO + 2 eCO2 + 4 e4Al + 3CO2 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 144 (b)330-350K 450-470K Ni + 4CO (c) Ti + 2 I2 (d) 4 M + 8CN- + O2+2H2O 2[M(CN)2]- + Zn (e) 2NaCl +2H2O [Ni(CO)4 ] TiI4 Ni + 4 CO Ti + 2 I2 4 [M (CN)2]- +4OH[Zn(CN)4]2- + 2M where M=Ag or Au 2NaOH + H2 + Cl2 Prepared By GUWAHATI REGION The p- block elements : TYPE- MLL One Mark questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Why is H3PO3 diprotic? Nitrogen does not form pentahalide like phosphorous,why? H2O is a liquid while H2s is a gas ,why? Arrange NH3 PH3 AsH3 BiH3 SbH3 in the increasing order of basic strength. Oxygen is a gas while sulphur is a solid,why? Write the formula of hyponitros acid. Why does Al not react with conc.nitricacid? Can PCl5 act as an oxidising agent and reducing agent? Why does NO2 readily dimerise? Why is BiH3 the strongest reducing agent amongst all the hydrides of nitrogen family? Write the chemical formula of peroxodisulphuric acid. Why does NH3 act as a Lewis base /complexing agent? What is the basicity of H3PO4? Why does R3P = O exist but R3N = O does not (R = alkyl group)? Why does the reactivity of nitrogen differ from phosphorus? Why is white phosphorous highly reactive? Why group 16 members are called chalcogens? OF4 is not known but SF4 is known .Explain Solid PCl5 exists as an ionic solid,Why? Bismuth is a strong oxidizing agent in pentavalentstate,why? Two Marks questions 21. 22. Draw the shapes of SF4, BrF3 on the basis of VSEPR theory. (a) Why is atomic radius of Argon more than that of Chlorine ? (b) Why is ionization enthalpy of Nitrogen more than oxygen? 23. (a) Arrange F2,Cl2,Br2,I2 in the increasing order of bond dissociation energy. (b) Arrange HOClO,HOClO2,HOClO3 in the increasing order of acidic strength. 24.Explain giving suitable reasons: (i) NH3 has higher boiling point than PH3 (ii) SbF5 is known but BiF5 is unknown. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 145 25.Explain giving suitable reasons: (i) SF6 is well known but SH6 is not known. (ii) Proton affinity of NH3 is more than PH3. 26. Explain giving suitable reasons. (i) Sulphur in vapour form is paramagnetic in nature. (ii) Catenation properties of Phosphorous is more than Nitrogen. 27. Give chemical equations ,when : (a). Ammonium dichromate is heated ? (b). Sodium azide is heated? 28. Complete the following equations: (i) HgCl2 + PH3 (ii) P4 + NaOH + H2O 29. Write main differences between the properties of white phosphorus and red phosphorus. 30. Arrange H2O,H2S,H2Se, H2Te in the increasing order of (i) Acidic Character (ii) Thermal stability . Three Marks questions 31. (i) Why is ICl more reactive than I2? (ii) Interhalogen compounds are strong Oxidizing agents ,why? (iii) Bleaching of flowers by Cl2 is permanent while SO2 is temporary,why? 32. Give Reasons: (a) Iodine is more soluble in KI solution than in water . (b) HF is stored in wax -coated bottle . © HCl is not used to make the medium acidic in titrations involving KMnO 4 . 33. Explain giving suitable reasons: (i) SbF5 is known but BiF5 is unknown. (ii) CN− ion is known but CP− is not . (iii) Compounds of Noble gases are known with Xe and fluorine. 34. Explain giving suitable reasons: (i) PH3 has lower boiling point than NH3. (ii) Nitric oxide becomes brown when released in air. (iii) When HCl reacts with finely powered iron, it forms ferrous chloride and not ferric chloride. 35. (i)Which Xe compound has distorted octahedral shape? (ii)How does Chlorine react with hot and concentrated NaOH ? (iii) Write the chemical reaction involved in the ring test. 36. (a) Are all the bonds in PCl5 equivalent in length? (b) On the basis of structure show that H3PO2 is a good reducing agent. © How many P-OH bonds are present in Pyrophosphoric acid? 37. Complete the following equations: P4 + SOCl2 NH3 + CuSO4(aq) XeF4 + H2O ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 146 38. (i) Arrange M-F,M-Cl,M-Br,M-I in the increasing order of ionic character. (ii) Arrange HF,HCl,HBr,HI in the increasing order of reducing behavior. (iii) Arrange F2,Cl2,Br2,I2 in the increasing order of bond dissociation energy. 39. Starting from sulphur ,how would you manufacture H2SO4 by contact process. 40.Write the reaction involved in formation of ammonia by Habers process?State the favorable conditions for good yield of ammonia . Five Marks questions 41.A gas “X” is soluble in water . Its aq. Solution turns red litmus blue with excess of aq. CuSO 4 solution it gives deep blue colour and with FeCl3 solution a brownish ppt. soluble in HNO3 is obtained. Identify gas”X” and write reactions for changes observed . 42. Write the reaction involved in formation of Nitric acid by Osrwald ,s process? State the favorable conditions for good yield of Nitric oxide. 43. Complete the following equations: (I ) XeF4 + H2O (ii)XeF6 + PF5 (iii)Cl2 + F2 (excess) (iv)HgCl2 + PH3 (v)SO3 + H2SO4 44.A translucent white waxy solid ‘A’ on heating in an inert atmosphere is converted in to its allotropic form (B). Allotrope ‘A’ on reaction with very dilute aqueous KOH liberates a highly poisonous gas ‘C’ having rotten fish smell. With excess of chlorine ‘A’ forms ‘D’ which hydrolysis to compound ‘E’. Identify compounds ‘A’ to ‘E’ . 45. What happens when Concentrated H2SO4 is added to/ Give the reactions of H2SO4 with(i) calcium fluoride (ii) KCl, (iii) Sugar (iv) Cu turnings.(v) Sulphur ANSWER KEY The p-block elements Type : MLL Q.N. Answer 1 Two ionisable hydrogen 2 Absence of d-orbitals in nitrogen. 3 H-bonding in H2O 4 NH3>PH3>AsH3>SbH3>BiH3 5 Absence of pπ- pπ bonding in oxygen. 6 HNO2 7 Formation of passive oxide film 8 No, can act as oxidizing agent only. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 147 9 To pair up odd electron. 10 Low bond dissociation enthalpy. 11 H2S2O8 12 It can donate lone pair of electrons very easily. 13 3 14 Presence of d-orbitals in phosphorous. 15 Absence of d-orbitals ,H-bonding, tendency to form multiple bond. 16 Strained structure. 17 Ore forming nature. 18 Absence of d-orbitals in oxygen. 19 It exists as [PCl4]+[PCl6]- in solid state. 20 Inert pair effect. 21 SF4 (See saw) BrF3 ( T-shape) Draw yourself 22 (a) Ar (Vander waal’s radius) Cl( Covalent radius) The magnitude of Vr> Cr . (b) Half-filled configuration shown by nitrogen. 23 (a) Cl2> Br2> F2>I2 (b) HOClO3>HOClO2>HOClO 24 (a) H- bonding in ammonia (b) Inert pair effect shown by Bi. 25 (a) The enthalpy of atomization of H—H is very high as compared to F—F . High enthalpy of dissociation cannot be compensated by energy released during bond formation . (b) High electronegativity of nitrogen. 26 27 28 29 (a) In vapour form sulphur behaves like O2. (b) Phosphorous is unable to form multiple bonds. (a) (NH4)2Cr2O7 N2 + Cr2O3 + 4 H2O (b) 2NaN3 2Na + 3N2 (a) 3HgCl2 + 2PH3 Hg3P2 + 6HCl (b) P4 + 3 NaOH + 3H2O PH3 + 3NaH2PO2 White Phosphorous: Stained structure, Highly reactive, Insoluble in water Red Phosphorous : Stable structure, Less reactive, soluble in water 30 Acidic Character : H2O < H2S < H2Se < H2Te ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 148 Thermal stability : H2Te < H2Se< H2S< H2O 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 (a) (b) (c) (a) (b) (c) (a) (b) (c) (a) (b) (c) (a) (b) (c) (a) (b) (c) I-Cl bond is more polar than I-I bond . Low bond dissociation enthalpy of X-Y bond. Cl2 bleach the colour by oxidation while SO2 by Reduction. Formation of KI3 complex. HF reacts with silica frequently. HCl can oxidise into Cl2. Due to Inert pair effect BiF5 is not known. Phosphorous is unable to form multiple bonds. Low ionisation enthalpy of Xe and high electronegativity of F. Absence of hydrogen bonding in PH3. Due to formation of NO2. Fe on reaction with HCl forms H2 which hinder the formation of FeCl3. XeF6 3Cl2 + Hot and Conc. 6NaOH NaClO3 +5 NaCl + 3H2O 2+ NO3 + Fe + 5 H2O [Fe(H2O)5NO]2+ No,axial bonds are slightly longer than equatorial bonds. H3PO2has one P-H bond . 4 (a) P4 + 8SOCl2 (b) 4NH3 + CuSO4(aq) (c) 6XeF4 + 12H2O (a) M-I <M-Br< M-Cl< M-F (b) HF<HCl<HBr<HI (c) I2<F2< Br2<Cl2 4SO2 +4 PCl3+ 2S2Cl2 [Cu(NH3)4]SO4 2XeO3 + 24HF + 4Xe + O2 (a) S + O2 SO2(g) (b) 2SO2+ O2 2SO3 [In presence of V2O5catalyst] (c) SO3 + H2SO4 H2S2O7 (d) H2S2O7 + H2O 2 H2SO4 N2 + 3H2 2NH3(g)[ In presence of Fe/Mo] Low temperature ,High Pressure X = NH3 4NH3 + CuSO4(aq) [Cu(NH3)4]SO4 3NH3 + 3H2O + FeCl3 Fe(OH)3 + 3NH4Cl Brown ppt 42 4NH3 + 5O2 2NO + O2 3NO2 + H2O 4 NO + 6H2O 2NO2 2HNO3 + NO ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 149 43 (a) 6XeF4 + 12H2O (b) XeF6 + PF5 © Cl2 + 3F2 (excess) (d) 3HgCl2 + 2PH3 (e) SO3 + H2SO4 44 2XeO3 + 24HF + 4Xe + O2 [XeF5]+[PF6]2ClF3 Hg3P2 + 6 HCl H2S2O7 A=White P4 B= Red P4 C= PH3 D=PCl5 E= H3PO4 45 CaF2 + Conc. H2SO4 2KCl+ Conc. H2SO4 C12H22O11 + Conc. H2SO4 Cu + Conc. 2 H2SO4 3S + Conc. 2 H2SO4 CaSO4 + 2HF 2HCl + K2SO4 12 C + 11H2O CuSO4 + SO2 + 2H2O 3SO2 + 2H2O Prepared By: Guwahati Region Chapter: d and f- block elements Type : MLL One mark questions Explain Why ? / How would you account for the following: [1 mark each] 1. Transition metals are less reactive, high melting point and enthalpy of atomization. 2. Transition metals have high enthalpy of hydration. 3. Transition metals show several oxidation states. 4. Transition metals form coloured complexes. 5. Transition metals take part in catalytic reactions. 6. Why does vanadium pentaoxide act as a catalyst? 7. Transition metals are paramagnetic in nature. 8. Transition metals form complexes. 9. Transition metals have irregular E0 values. 10. The E0M2+/M for copper is positive (0.34v) .Copper is the only metal in first series of transition elements showing this behavior, why? 11. Transition metals form alloys. 12. Transition metals form interstitial compounds. 13.Cu+ is unstable in aqueous solution. 14.Cu2+ is stable in aqueous solution. 15. Zr and Hf exhibit almost same radii and properties. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 150 16. The d1 configuration is generally unstable in ions. 17. There is a in general increase in density of element from titanium(Z=22) to copper ( Z=29). 18. The lowest oxides of transition metals is basic, the highest is amphoteric or acidic. 19. Anhydrous CuSO4 is white while hydrated Copper sulphate is blue. 20.Co2+ is easily oxidized to Co3+ in presence of strong ligand. Two marks questions 21. (a) Why HCl cannot be used in place of sulphuric acid to acidify KMnO4 solution in volumetric analysis ? (b) Potassium dichromate is a good oxidising agent in acidic medium, why? 22. Write the balanced ionic equations for reacting ions to represent the acidified potassium dichromate solution with : (i) Potassium iodide solution (ii) Acidified ferrous sulphate solution. 23. List some applications of d block elements. 24. Describe giving reasons which one of the following pairs has the properties indicated? (a) Fe or Cu has higher melting point. (b) Co2+Or Ni2+ has lower magnetic moment. 25. Calculate the magnetic moment of a trivalent ion in aqueous solution whose atomic no. is 25. 26 Define transition elements. Explain why is Zn not considered as transition element while Cu does? 27. What happens when Cu2+ is added to I-?Write the balanced chemical equation . 28 Write the electronic configuration of24 Cr and 26Fe2+ . 29 Compare non transition and transition elements on the basis of their Variability of oxidation states (ii) stability of oxidation states. 30 (a) Name a transition element which does not exhibit variable oxidation state. (b) Name three elements of d block which are not regarded as transition element. Three Marks questions 31. Give chemical reactions for the following observations: (i) Potassium permanganate is a good oxidising agent in basic medium. (ii) Inter convertibility of chromate ion and dichromate ion in aqueous solution depends Upon pH of the solution. (iii) Potassium permanganate is thermally unstable at 513K. 32. Define lanthanoid Contraction. Ce4+ is a good oxidizing agent whereas Eu2+, Sm2+ is a good reducing agent, why ? 33.(a)From element to element the actinoid contraction is greater than lanthanoidcontraction,why? (b) Name the lanthanoid element which forms tetra positive ions in the aqueous solution. © The chemistry of actinoids is not as smooth as lanthanoids, why? 34. Balance the following equations: (i) MnO4- + S2O32( Basic medium) 2(ii) MnO4 + S2O3 + H2O (iii) MnO4- + I( in neutral or alkaline medium) ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 151 35 (a)The enthalpies of atomization of transition metals of 3d series do not follow a regular trend throughout the series. (b) The enthalpy of atomization of zinc is lowest. © Zn Cd Hg are soft and have low melting points. 36. Explain: (a) The E° value for Ce4+/Ce3+ is 1.74 Volt. (b)K2Cr2O7 is used as Primary Standard in volumetric analysis. © The third ionization energy of manganese (z=25) is exceptionally high. 37.Explain: (a)Although Cu+ has configuration 3 d10 4 s0 (stable) and Cu2+ has configuration 3 d9 (unstable configuration) still Cu2+ compounds are more stable than Cu+. (b) Titanium (IV) is more stable than Ti (III) or Ti (II). © The greatest number of oxidation states are exhibited by the members in the middle of a transition series. 38 (a) Highest manganese flouride is MnF4 whereas the highest oxide is Mn2O7, why? (b) Copper can notlibrate H2 from dilacids,why? (c )Which of the 3d- series of transition metals exhibits largest number of oxidation states and why? 39.(a)O.S. of first transition series initially increase up to Mn and then decrease to Zn , why? (b) Why is Cr2+ reducing and Mn3+ oxidizingwhile both have d4 configuration. © Ti achieves tetrahalides while chromium forms heaxhalide, why? 40.(a)Which form of Cu is paramagnetic and why? (b) What is the oxidation no. of Cr in Cr2O72-? 41 Complete the following reaction equations: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) MnO2 + KOH (aq) + O2 Fe2+ + MnO4- + H+ MnO4- + C2O4 2- (aq) + H+ Cr2O72- + H2S + H+ Cr2O72- + I- + H + 42. Describe the preparation of potassium dichromate from iron chromite ore. What is the effect of increasing PH on a solution of potassium dichromate or Explain how the colour of K 2Cr2O7 solution depends on PH of the solution? 43.(a)Describe the preparation of potassium permanganate. (b) How does the acidifiedpermanganate solution react with (i) iron(II) ions (ii) SO2 and (iii) oxalic acid?Write the ionic equations for the reactions. 44.Describe the oxidising action of potassium dichromate and write the ionic equations for its reaction with: iodide (ii) iron(II) solution and (iii) H2S 45.When a chrromite ore A is fused with sodium carbonate in free excess of air and the product is dissolved in water , a yellow solution of compound B is obtained .After treatment of this yellow solution ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 152 with sulphuric acid compound C can be crystallize from the solution .When compound C is treated with KCl orange crystals of compound D is crystallizes out. Identify A to D and wtite the reaction from A to B. Answer Key Chapter: d and f- block elements Type : MLL 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Strong metallic bonding and d-d overlapping. Small size Comparable energies of (n-1)d and ns electrons. d-d transition. Can pass from one oxidation state to another very easily. Can pass from one oxidation state to another very easily. Unparied electrons Have vacant d orbitals to accept electrons. Irregualr trend in IE, sublimation energy and hydration energy. Sum of enthalpies of sublimation and ionization ( enthalpy of atomization ) > hydration energy. Almost same size. Can accommodate small atoms in void position. Low hydration enthalpy and property to show disproportionation reaction. High hydration enthalpy. Lanthanoid contraction Hydration energy > Ionization energy. It is due to increase in mass per unit volume with increase in atomic no. Lower oxides are ionic while higher oxides are covalent. No d-d transition in the absence of ligand. Crystal field stabilisation energy of Co+3 ion is higher than Co2+ ion. (a) HCl can be oxidized into Cl2. (b) It evolve nascent oxygen . (a) Cr2O72- + 6I- + 14 H + 2 Cr3+ + 3I2 + 7H2O (b) Cr2O72- + 6Fe2+ + 14 H + 6Fe3+ + 2 Cr3+ + 7H2O Ni , Fe, V2O5 are used as catalyst in various industrial process. AgBr is used in photography. Pt compound are used in anticancer drug. MnO2 is used as OA in dry cells. Fe Ni2+ 4 unpaired electrons M.M = [4(4+2)]1/2 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 153 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 Transition elements are those whose neutral atom or stable ion has partly filled dorbitals. Cu2+ has partly filled d-orbitals which are absent in Zn or Zn2+. 2CU2+ + 4ICu2I2 + I2 5 1 Cr= [Ar] 3d 4s Cu[Ar]3d104s1 Oxidation states of transition elements differ from each other by unity. In non transitionelements oxidation states normally differ by a unit of two. (a) Sc (b) Zn, Cd, Hg (i) 2MnO4- + 2H2O + 3 e2MnO2 + 4OH(ii) CrO42- ======= Cr2O72( if PH > 4 the CrO42- ion will exist and if PH < 4 then Cr2O72- will exist ) ie. 2 CrO42- + 2H+ Cr2O72- + H2O Cr2O72- + 2OH2 CrO42- + H2O (iii) 2 KMnO4 K2MnO4 + MnO2 + O2 + 513 K (a) Decrease in atomic or ionic radii with increase in atomic number. (b) For lanthanoids common oxidation state is +3 . to acquire +3 oxidation state Ce 4+ undergoes reduction and hence acts as oxidizing agent ,while Eu 2+ undergoes oxidation and hence acts as reducing agent. (a) It is due to poor shielding by 4f and 5f electrons. (b) Ce ( Ce4+) © Actinoids are radioactive in nature. i) & (ii) 8MnO4- + 3S2O32- + H2O 8MnO2 + 2 OH- + 6 SO42(iii) 2MnO4- + I+ H2O 2OH- + 2MnO2 + IO3(a) Bec. enthalpy of atomisation depends upon no. of unpaired electrons . (b) No unpaired electrons . © Absence of d-d overlapping and poor metallic bonding. (a) Ce4+ is strong oxidant, being Lanthanoid it reverts to Ce3+ as + 3 is most stable. (b) K2Cr2O7 is not much soluble in cold water. However, it is obtained in pure state and is not Hygroscopic in nature. © Mn3+,extra stable due to half filled d5 configuration. (a) It is due to much more negative Hydration enthalpy of Cu2+ (aq) than Cu+ (b) TiIV is more stable due to d0 configuration. (c) Maximum no. of unpaired electrons are in middle. (a) The ability of oxygen to form multiple bonds to metals, explain its superiority to show higher oxidation state with metal. (b) Positive E° value (+ O . 34 Volt) accounts for its inability to liberate H2 from acids. (c)Mn, Maximum no. of unpaired electrons. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 154 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 (a) Number of unpaired electrons increases up to Mn and then decreases up to Zn. (b) To acquire +3 O.S. Cr2+ has a tendency to lose the electron while Mn3+ has a tendency to accept an electron . (c) To acquire d0 configuration. (a) Cu2+, One unpaired electron. (b) +6 MnO2 + 2 KOH (aq) + O2 K2MnO4 + H2O 2+ + 2+ 5 Fe + MnO4 + 8 H Mn + 4H2O + 5Fe3+ 2MnO4- + 5C2O4 2- (aq) +16 H+ 2 Mn2+ + 8H2O + 10 CO2 Cr2O72- + H2S + H+ Do yourself 2+ Cr2O7 + I + H Do yourself (a) 4FeCr2O4 + 8Na2CO3 + 7 O2 8Na2CrO4+ 2Fe2O3 + 8CO2 2Na2CrO4 + 2H+ Na2Cr2O7 + 2Na+ + H2O Na2Cr2O7 + 2 KCl K2Cr2O7 + 2 NaCl 22(b) CrO4 ======= Cr2O7 ) ( if PH > 4 the CrO42- ion (yellow) will exist and if PH < 4 then Cr2O72- ion(orange) will exist (a) 2MnO2 + 4KOH (aq) + O2 2K2MnO4 + 2H2O MnO42- ----electrolysis- MnO45 Fe2+ + MnO4- + 8 H+ Mn2+ + 4H2O + 5Fe3+ 5 SO2 + 2MnO4- + 2H2O 2Mn2+ + 4H+ + 5SO422MnO4- + 5C2O4 2- (aq) +16 H+ 2 Mn2+ + 8H2O + 10 CO2 (a) Ch3CH2OH-----K2Cr2O7/H+-CH3COOH (b) (b)Cr2O72- + 6I- + 14H + 2Cr3+ +3I2+ 7 H2O Cr2O72- + 6 Fe2++ 14 H+ 2Cr3+ + 6Fe3+ + 7 H2O Cr2O72- + 3S2- + 14 H+ 2Cr3+ + 3S+ 7 H2O A= FeCr2O4 B= Na2CrO4 C= Na2Cr2O7 D = K2 Cr2O74 FeCr2O4 + 8Na2CO3 + 7 O2 8Na2CrO4+ 2Fe2O3 + 8CO2 Prepared By: Guwahati Region CHAPTER 9 COORDINATION COMPOUNDS ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 155 1 mark questions 1. Explain coordination entity with example. Ans: it constitute a central metal atom or ions bonded to a fixed number of molecules or ions ( ligands) .eg. [Co(NH3)3Cl3]. 2. What do you understand by coordination compounds? Ans: coordination compounds are the compounds which contains complex ions. These compounds contain a central metal atom or cation which is attached with a fixed number of anions or molecules called ligands through coordinate bonds. eg. [Co(NH3)3Cl3] 3. What is coordination number? Ans: the coordination number of a metal ion in a complex may be defined as the total number of ligand donor atoms to which the metal ion is directly bonded. Eg. In the complex ion [Co(NH3)6]3+ has 6 coordination number. 4. Name the different types of isomerisms in coordination compounds. Ans: structural isomerism and stereoisomerism. 5. Draw the structure of xenon difluoride. Ans: structure :trigonalbipyramidal Shape: linear 6. What is spectrochemical series? Ans: the series in which ligands are arranged in the order of increasing field strength is called spectrochemical series. The order is : I-<Br-<SCN-<Cl-<S2-<F-<OH-<C2O42-<H2O<NCS-<EDTA4-<NH3<en<CN-<CO 7. What do you understand by denticity of a ligand? Ans: the number of coordinating groups present in ligand is called denticity of ligand. Eg.Bidentateligand ethane-1,2-diamine has 2 donor nitrogen atoms which can link to central metal atom. 8. Why is CO a stronger ligand than Cl-? Ans: because CO has π bonds. 9. Why are low spin tetrahedral complexes not formed? Ans : because for tetrahedral complexes, the crystal field stabilisation energy is lower than pairing energy. 10. Square planar complexes with coordination number 4 exhibit geometrical isomerism whereas tetrahedral complexes do not. Why? Ans: tetrahedral complexes do not show geometrical isomerism because the relative positions of the ligands attached to the central metal atom are same with respect to each other. 11. What are crystal fields? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 156 Ans: the ligands has around them negatively charged field because of which they are called crystal fields. 12. What is meant by chelate effect? Give an example . Ans: when a didentate or polydentate ligand contains donor atoms positioned in such a way that when they coordinate with the central metal atom, a 5 or 6 membered ring is formed , the effect is called chelate effect. Eg. [PtCl2(en)] 13. What do you understand by ambidentate ligand? Ans: a ligand which contains two donor atoms but only one of them forms a coordinate bond at a time with central metal atom or ion is called an ambidentate ligand. Eg.nitrito-N and nitrito-O. 14. What is the difference between homoleptic and heteroleptic complexes? Ans: in homoleptic complexes the central metal atom is bound to only one kind of donor groups whereas in heteroleptic complexes the central metal atom is bound to more than one type of donor atoms. 15. Give one limitation for crystal field theory. Ans: i) as the ligands are considered as point charges, the anionic ligands should exert greater splitting effect. However the anionic ligands are found at the low end of the spectrochemical series. ii) it does not take into account the covalent character of metal ligand bond. ( any one ) 16. How many ions are produced from the complex: [Co(NH3)6]Cl2 Ans: 3 ions 17. The oxidation number of cobalt in K[Co(CO)4] Ans: -1 18. Which compound is used to estimate the hardness of water volumetrically? Ans: EDTA 19. Magnetic moment of [MnCl4]2- is 5.92B.M explain with reason. Ans: the magnetic moment of 5.9 B.M. corresponds to the presence of 5 unpaired electrons in the dorbitals of Mn2+ ion. As a result the hybridisation involved is sp3 rather than dsp2. Thus tetrahedral structure of [MnCl4]2- complex will show 5.92 B.M magnetic moment value. 20. How many donor atoms are present in EDTA ligand? Ans: 6 2 marks questions 1. Give the electronic configuration of the following complexes on the basis of crystal field splitting theory. i) [CoF6]3ii) [Fe(CN)6]4Ans: i) Co3+ (d6) t2g4eg2 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 157 iii) Fe2+ d6t2g6eg0 2. Explain the following with examples: i) Linkage isomerism ii) Outer orbital complex Ans: i) this type of isomerism arises due to the presence of ambidentate ligand in a coordination compound. Eg. [Co(NH3)5NO2]Cl2 and [Co(NH3)5ONO]Cl2 iii) When ns, np and nd orbitals are involved in hybridisation , outer orbital complex is formed. Eg. [CoF6]2- in which cobalt is sp3d2 hybridised. 3. i)Low spin octahedral complexes of nickel are not found . Explain why? ii)theπ complexes are known for transition elements only.explain. Ans: i) nickel in its atomic or ionic state cannot afford 2 vacant 3d orbitals and hence d2sp3 hybridisation is not possible. ii) transition metals have vacant d orbitals in their atoms or ions into which the electron pairs can be donated by ligands containing πelectrons.eg. benzene, ethylene etc. thus dπ-pπ bonding is possible. 4. How would you account for the following: i) [Ti(H2O)6]3+ is coloured while [Sc(H2O)6]3+ is colourless. ii) [Ni(CO)4] possess tetrahedral geometry whereas [Ni(CN)4]2- is square planar. Ans: i) due to the presence of 1 electron in 3d subshell in [Ti(H2O)6]3+ complex d-d transition takes place by the absorption of visible light. Hence the complex appears coloured. On the other hand, [Sc(H2O)6]3+ does not possess any unpaired electron .Hence d-d transition is not possible (which is responsible for colour) in this complex is not possible, therefore it is colourless. ii) Ni in [Ni(CO)4] is sp3 hybridised. Hence it is tetrahedral. Whereas for [Ni(CN)4]2- is dsp2 hybridised hence it has square planar geometry. 5. State reasons for each of the following: i) All the P—Cl bonds in PCl5 molecule are not equivalent. ii) S has greater tendency for catenation than O. Ans: i) in P Cl5 the 2 axial bonds are longer than 3 equatorial bonds. This is due to the fact that the axial bond pairs suffers more repulsion as compared to equatorial bond pairs. ii) The property of catenation depends upon the bond strength of the element. As S—S bond is much stronger (213kJ / mole) than O—O bond (138 kJ/mole), S has greater tendency for catenation than O. 6. Give the stereochemistry and the magnetic behaviour of the following complexes: i) [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2 ii) K2[Ni(CN)4] ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 158 Ans: i) d2sp3 hybridisation, structure and shape = octahedral Magnetic behaviour- diamagnetic ii) dsp2 hybridisation, structure and shape = square planar magnetic behaviour- diamagnetic 7. Draw the structures of isomers if any and write the names of the following complexes: i) [Cr(NH3)4Cl2]+ ii) [Co(en)3]3+ Ans: i) tetraamminedichloridochromium(III) ion ii) tris(ethane-1,2-diammine)cobalt(III)ion 8. State reasons for each of the following: i) The N—O bond in NO2- is shorter than the N—O bond in NO3ii) SF6 is kinetically an inert substance. Ans: i) this is because the N—O bone in NO2- is an average of a single bond and a double bond whereas N—O bond in NO3- is an average of 2 single bonds and a double bond. iii) In SF6 the S atom is sterically protected by 6 fluorine atoms and does not allow water molecules to attack the S atom. Further F atoms does not contain d orbitals to accept the electrons denoted by water molecules. Due to these reasons , SF6 is kinetically an inert substance. 9. Hydrated copper sulphate is blue in colour whereas anhydrous copper sulphate is colourless. Why? Ans: because water molecules act as ligands which splits the d orbital of the Cu2+ metal ion. This result in d-d transition in which t2g6eg3 excited to t2g5eg4 and this impart blue colour to the crystal. Whereas when we talk about anhydrous copper sulphate it does not contain any ligand which could split the d orbital to have CFSE effect. 10. Calculate the magnetic moment of the metal ions present in the following complexes: i) [Cu(NH3)4]SO4 ii) [Ni(CN)4]2Ans: i)electronicconfig. t2g6eg3, n=1, µs= √n(n+2) = 1.732 B.M ii) electronicconfig. t2g6eg2 , n=2, µs= √n(n+2)=2.828 B.M 3 marks questions 1. (a) What is a ligand? Give an example of a bidentate ligand. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 159 (b) explain as to how the 2 complexes of nickel,[Ni(CN)4]2- and Ni(CO)4 have different structures but donot differ in their magnetic behaviour.( Ni=28) Ans: (a) the ion , atom or molecule bound to the central atom or ion in the coordination entity is called ligand. A ligand should have lone pair of electrons in their valence orbital which can be donated to central metal atom or ion. Eg.Bidentate ligandethylenediammine (b)dsp2, square planar, diamagnetic (n=0) Sp3 hybridisation , tetrahedral geometry, diamagnetic (n=0) 2. Nomenclate the following complexes: i) [Co(NH3)5(CO3)]Cl ii)[COCl2(en)2]Cl iii) Fe4[Fe(CN) 6] Ans: i) pentaamminecarbonatocobalt(III)chloride ii) dichloridobis(ethane-1,2-diamine)cobalt(III)chloride iii)iron(III)hexacyanidoferrate(II) 3. (a)why do compounds with similar geometry have different magnetic moment? (b)what is the relationship between the observed colour and wavelength of light absorbed by the complex? Ans: (a) it is due to the presence of weak and strong ligands in complexes, if CFSE is high the complex will show low value of magnetic moment and if it is low the value of magnetic moment is high. Eg. [CoF6]3- and [Co(NH3)6]3+ , the former is paramagnetic and the latter is diamagnetic. (b) higher the CFS lower will be the wavelength of absorbed light. Colour of the complex is obtained from the wavelength of the leftover light. 4. Explain the following terms giving a suitable example. (a) ambident ligand (b) denticity of a ligand (c) crystal field splitting in an octahedral field ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 160 Ans (a) Aligand which contains two donor atoms but only one of them forms a coordinate bond at a time with central metal atom or ion is called an ambidentate ligand. Eg.nitrito-N and nitrito-O. (b)The number of coordinating groups present in ligand is called denticity of ligand. Eg.Bidentateligand ethane-1,2-diamine has 2 donor nitrogen atoms which can link to central metal atom. (c) the splitting of the degenerated d orbital into 3 orbitals of lower energy t2g and 2 orbitals of higher energy eg due to presence of a ligand in a octahedral crystal field is known as crystal field splitting in an octahedral complex. 5. (a) Copper sulphate pentahydrate is blue in colour while anhydrous copper sulphate is colourless. Why? (b) Sulphur has greater tendency for catenation than oxygen.Why? Ans : (a)because water molecules act as ligands which splits the d orbital of the Cu2+ metal ion. This result in d-d transition in which t2g6eg3 excited to t2g5eg4 and this impart blue colour to the crystal. Whereas when we talk about anhydrous copper sulphate it does not contain any ligand which could split the d orbital to have CFSE effect. (b)The property of catenation depends upon the bond strength of the element. As S—S bond is much stronger (213kJ / mole) than O—O bond (138 kJ/mole), S has greater tendency for catenation than O. 6. draw structures of geometrical isomers of the following complexes: (a) [Fe(NH3)2(CN)4]- (b)[CrCl2(ox)2]3- (c)[Co(en)3]Cl3 7. write the state of hybridisation, the shape and the magnetic behaviour of the following complexes: (i) [Co(en)3]Cl3 (II) K2[Ni(CN)4] (III)[Fe(CN)6]38. how would you account for the following: (i) [Ti(H2O)6]3+is coloured while [Sc(H2O)6]3+ is colourless . (II) [ Fe(CN)6]3- is weakly paramagnetic while [ Fe(CN)6]4- is diamagnetic. (III) Ni(CO)4 possess tetrahedral geometry while [Ni (CN)4]2- is square planar. Ansi) due to the presence of 1 electron in 3d subshell in [Ti(H2O)6]3+ complex d-d transition takes place by the absorption of visible light. Hence the complex appears coloured. On the other hand, [Sc(H2O)6]3+ does not possess any unpaired electron .Hence d-d transition is not possible (which is responsible for colour) in this complex is not possible, therefore it is colourless. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 161 (ii) paramagnetism is attributed to the presence o f unpaired electrons. Greater the number of unpaired electron greater is the paramagnetism. Due to the presence of one electron in the 3d subshell in [ Fe(CN)6]3it is weakly paramagnetic. On the other hand [ Fe(CN)6]4- is diamagnetic because all electrons are paired. iii) Ni in [Ni(CO)4] is sp3 hybridised. Hence it is tetrahedral. Whereas for [Ni(CN)4]2- is dsp2 hybridised hence it has square planar geometry. 9. Explain the following :: (i) low spin octahedral complexes of Ni are not known. (ii) The pi – complexes are known for the transition elements only. (iii) CO is a stronger ligand than NH3 for many metals Ans. i) nickel in its atomic or ionic state cannot afford 2 vacant 3d orbitals and hence d2sp3 hybridisation is not possible. ii) transition metals have vacant d orbitals in their atoms or ions into which the electron pairs can be donated by ligands containing πelectrons.eg. benzene, ethylene etc. thus dπ-pπ bonding is possible. (iii) because in case of CO back bonding takes place in which the central atom uses its filled d orbitals with empty anti bonding π*molecular orbital of CO. 10. What is meant by stability of a coordination compounds in solutions? State the factors which govern the stability of complexes. Ans : the stability of a complex in solution refers to the degree of association between the two species involved in the state of equilibrium. The magnitude of the equilibrium constant for the association expresses the stability . M +4L ML4 4 K = [ML4]/[M][L] Factors on which stability of complex depends (i) charge on central metal ion (ii) nature of the metal ion (iii) basic nature of the ligand (iv) presence of the chelate ring (v) effect of multidentate cyclic ligand . 5 marks questions 1. Draw the structures of the following molecules: (a) [Fe(NH3)2(CN)4]- (b)[CrCl2(ox)2]3- (c)[Co(en)3]Cl3(d) [Co(en)3]Cl3(e)[Fe(CN)6]3- 2. What is crystal field theory for octahedral complexes? Also write the limitations of this theory. Ans : 3. Write the state of hybridisation the shape and the magnetic behaviour of the following complex entities: (i) [Cr(NH3)4Cl2]Cl ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 162 (ii) [Co(en)3]Cl3 (iii) K2[NiCl4] (iv) [Fe(H2O)6]2+ (v) [NiCl4]24. Using valence bond theory explain the following questions in relation to [Co(NH3)6]3+. (i) Nomenclature (ii) Type of hybridisation (iii) Inner or outer orbital complex (iv) Magnetic behaviour (v) Spin only magnetic moment 5. Compare the following complexes with respect to structural shape of units, magnetic behaviour and hybrid orbitals involved in units: [Co(NH3)6]3+, [Cr(NH3)6]3+,[ Ni(CO)4] Prepared By: Guwahati Region Chapter: 10 (Halo alkanes and Haloarene) One Mark Questions: 1. Give IUPAC name of the following organic compound: CH3-CH=C- CH-CH3 CH3 Br 2. Write the structural formulae of 4-Chloropent-2-ene. Q3.Arrange the following halides in order of increasing SN2 reactivity CH3Cl,CH3Br,CH3CH2Cl, (CH3)2CHCl Q5.What is the order of reactivity of different alkyl halides in nucleophilic substitution reaction? Q4.An alkyl halide C4H9Cl is optically active. What is its structure? Q7.Which type of solvents aregenerally used to carry out SN 1 reaction? Q8.Identify the chiral and achiral molecules in following pair of compounds? A:CH3CHCH2CH3 B :CH3CH2CH2CH2Br ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 163 Br Q9.Give two uses of iodoform (CHI3)? Q10.Write a chemical reaction in which iodide ion displaces diazonium group from a diazonium salt? Q11.How you will convert 2-Bromopropane to 1-bromopropane? Q12.In following pairs of halogen compound which compound undergoes faster SN1 reaction? A) Cl i) Cl iii) Cl iv) ii) B) Q13.How you will convert aniline into cholobenzene? Q14.Name the iodine containing hormone, the deficiency of which causes goiter? Q15.Name the synthetic halogen compound which is used in treatment of malaria? Q16.Which isomer of C4H9Br will have lowest boiling point? Q17.Write the IUPAC name of DDT? Q18.Why sulphuric acid is not used during reaction of alcohol with KI? Q19.Out of CH3Br and CH3Cl which will have higher boiling point and why? Q20.Which one of following has highest dipole moment? (i) CH2Cl2 (ii) CHCl3 (iii) CCl4 Two marks questions: Q1.Define the following terms: (i) Ambidient nucleophile (ii) Chirality Q2.Write short note on sandmeyer reaction? Q3.Write the structures of main products: (i).Chlorination of benzene in presence of UV light. (ii).Propene is treated with HBr in presence of benzoyl peroxide. Q4.Complete the following reactions: ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com Cl 164 (i).C6H5N2Cl +KI (ii) CH2=CH2 +Br2 ? CCl4 ? Q5.Explain why haloarenes are much less reactive than haloalkanes towards nucleophilic substitution reaction? Q6.Write short note on: (i).Wurtz reaction (ii).Wurtz-Fittig reaction. Q7.How you will convert: (i).Ethyl chloride into ethyl alcohol. (ii).Ethyl chloride to ethane Q8.Alkyl halides are insoluble in water though they contain polar C-X bond? Q9.Give one test to distinguish between: (i).Chloroform and carbontetrachloride (ii).Methanol and ethanol. Q10.Write short note on : (i).Finkelstein reaction (ii).Hundsdiecker reaction Three Marks Questions: 1.Explain why: (a).Dipole moment of cholorobenzene is lower than cyclohexyl chloride. (b).Grignard reagent should be prepared under anhydrous conditions? (c).Chloroform is stored in dark Brown bottles? Q2.What happens when: ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 165 (a).Chloroform is heated with silver power. (b).Ethyl chloride treated with alcoholic KOH (c).Alcohol reacts with thionyl chloride? Q3.How you will conert: (a).Chlorobenzene into toluene (b).Chlorobenzene to phenol (c).Ethyl bromide to diethyl ether. Q4.Complete the following reactions: (a).CHCl3 +CH3COCH3 ? (b).CH3CH2CH2Br +KOH(alc.) (c).CHCl3 +HNO3 Heat ? ? Q5.Give the chemical test to distinguish between following pair of compounds: (i) Cl and Cl (ii) Ethyl chloride and ethyl bromide (iii) Chlorobenzene and benyl chloride Q6.Give reasons: (i).Boiling point of alkyl bromide is higher than alkyl chloride. (ii).Alkyl halides are better solvents than aryl halides. (iii).Haloalkanesare used as solvent in industry are choloro compounds rather than bromo compounds. Q7.Answer the following: (i).What effect should the following resonance of vinyl chloride has on its dipole moment. CH2=CH-Cl -CH2—CH=Cl+ (ii).Iodoform is obtained by the reactions of acetone with hypoiodite but not with iodide ion. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 166 (iii).Vinyl chloride is hydrolysed more slowly than ethyl chloride. Q8.Write the structure of major organic product in each of following reactions: (i).CH3-CH2-CH2-Cl +NaI Acetone (ii).CH3-CH2-CH2OH +SOCl2 (iii).CH3CH2CH=CH2 +HBr Peroxide Q9.Give uses of following: (i) (ii) (iii) CCl4 DDT Choloroform Q10.Distinguish between SN1 and SN2 reactions? Five Marks Question 1.Identify A,B,C,D,E,R,R’ in the following: Br +Mg dry ether R-Br+Mg dry ether A C D2O H2O CH3CHCH3 CH3 CH3 CH3-C-C-CH3 Na/ether R’-X B D Mg D H2O E CH3 CH3 2.What happens when: (a).n-butyl chloride is treated with alcoholic KOH (b).Bromonenzene is teated with Mg in presence of dry ether (c).ethyl chloride is treated with aquous KOH (d).Ethyl bromide is Na in presence of dry ether. (e).Methyl chloride is treated with KCN ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 167 Q3.Primary alkyl halide A C4H9Br reacted with alcoholic KOH give compound B.Compound B is reacted with HBr to give C which ia an isomer of A.When A was reacted with Na metal it give a compound (D) C8H18 that was different than the compound when n-butyl bromide reacted with sodium .Give the strural formulae for A and write the equations for all the reactions? Q4.Write short note on: (i).Fittig reaction (ii).Friedal Craft Alkylation (iii).Friedal Craft Acylation (iv).Gatterman reaction (v).Carbylaaminereation Q5.Give reasons: (i).Benzyl chloride undergoes SN1 reactions faster than cyclohexy methyl chloride. (ii).p-Dichlorobenzene has higher melting point than ortho-dichlorobenzene. (iii).Out of chlorobenzene and choloromethane ,which is more reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction? (iv). Thionyl chloride is preffered for preparing alkyl chlorides from alcohols. (V).Iodide ion is a better nucleophile than bromide ion? Answer key One Mark Question: 1.Ans:4-Bromo-3-methylpent-2-ene. 2.Ans:CH3-CH=CH-CH2-CH3 Cl 3.Ans:( CH3)2CHCl<CH3CH2Cl,CH3Cl<CH3Br 4.Ans: H CH3- C*-CH2-CH3 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 168 Cl 5.Ans.RI>RBr>RCl 6.Ans:No 7.Ans: Polar protic solvents. 8.Ans: CH3CHCH2CH3 Br 9.Ans: 1.As antiseptic 10.Ans: C6H5-N+2Cl- +KI 11.Ans: 2.As photosensitizer in emulsion of AgBr to make photographic film. C6H5I +KCl +N2 Br CH3-CH-CH3 (Alc.KOH) CH3-CH=CH2HBr/Peroxide CH3-CH2-CH2Br 12.Ans:A (i) B (iii) 13.Ans: N2+Cl- +H20 NH2 +HNO2 +HCl NaNO2 +HCl CuCl/HCl Cl +N2 14.Ans.Thyroxine 15.Ans:Chloroquine. 16.Ans: CH3 CH3-C-Br :tert-Butyl bromide CH3 17.Ans:2-(1,1-Dicholoro diphenyl)-1,1,1-tricholoroethane. 18.Ans:Because it first converts KI to HI and then oxidises it to I2. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 169 19.Ans:CH3Br.More the molecular mass, more the boiling point. 20.Ans:CH2Cl2 Two marks questions: 1.(i)Ans:The nucleophiles having two nucleophiliccentres.For example Cyanide group. -C N :C=N- ii).An object which is not superimposable on its mirror image is said to be chiral.The property of being chiral is known as chirality. 2.Ans:NaNO2 +HCl 273-278K NaCl +HNO2 N2+Cl- +2H2O -NH2 +HNO2 +HCl 273-278K C6H5N2+Cl- CuCl/HCl C6H5Cl+N2 3.Ans: i) ClCl +3Cl2U.V.Light Cl Cl Cl ii).CH3-CH=CH2 +HBr Peroxide 4.Ans : i) C6H5N2Cl +KI (ii).CH2=CH2 +Br2 CCl4 Cl CH3-CH2-CH2-Br C6H5I +KCl +N 2(g) CH2BrCH2Br 5.Ans:1.Due to resonace C-Cl bond aquires double bond charcter . ii.Inhaloarenes Carbon bearing halogen is sp2 hybirdised.So C-X bond is shorter and stronger. 6.Ans.(i) RX +2Na +X-R Dry Ether R-R +2NaX (ii).R-X +2Na + X 7.Ans (i).C2H5Cl +KOH (aq) Dry ether R + 2NaX. C2H5OH +KCl ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 170 (ii).C2H5Cl +2[H] Zn-Cu/C2H5OH C2H6 +HCl 8.Ans:Because haloalkanes cannot form hydrogen bond with water molecules and at the same time they cannot break the hydrogen bonds present in water molecule. 9.Ans: (a). Chloroform when heated with aniline and alc.KOH offensive smeel of isocyanide is produced. C6H5NH2 +CHCl3 +3KOH (alc.) heat C6H5NC +3KCl +3H2O (b).By iodoform test In case of methanol no yellow ppt.But in case of ethanol yellow ppt are formed. CH3CH2OH +4NaOI NaOH +I2 CH3OH +NaOI NaOH+I2 CHI3+HCOONa +NaI+H2O No yellow ppt 10.Ans. (a). CH3-CH2-Cl +NaI Acetone (b). RCOOAg +Br2 CCl4,350K CH3-CH2-I +NaCl R-Br+AgBr+CO2(g) Three Marks question: 1.Ans. (a).Electronegativity of carbon is less than Chlorine so slight negative charge develops on chlorine atom and positive charge on carbon atom.Lower dipole moment of cholobenzene is due to (i) Resonace (ii).different hybirdisation states of C- atom (b).Grignard reagent are very reactive.These are readily decomposed by compounds containing acidic hydrogen as follows RMgX + H2O RH +Mg(OH)X (c).Because it reacts with oxygen in prsesnce of sunlight to form phosgene gas. CHCl3 + ½ O2 Sunlight COCl2 +HCl 2Ans. (a).CHCl3 +6Ag +CHCl3 6AgCl +CH≡CH (b).C2H5Cl +KOH (alc) CH2=CH2 +H2O +KCl (c).R-OH +SOCl2 R-Cl+HCl+SO2 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 171 3Ans.How you will conert: (a).C6H5Cl +2Na+Ch3Cl dry ether C6H5CH3 +2NaCl (b). ONa H2O/H+ Cl NaOH,623K (c).2C2H5Br+Ag2O(dry) OH C2H5-O-C2H5 +2AgBr Ans4.OH (a).CHCl3 +CH3COCH3 CH3-C-CH3 CH3 (b).CH3CH2CH2Br +KOH(alc.) (c).CHCl3 +HNO3 Heat CH3-CH=CH2 +KBr +H2O Cl3C-NO2 +H2O Ans5.Give the chemical test to distinguish between following pair of compounds: Cl +KOH(ag)+ OH - I) KCl+AgNO3 +KCl AgCl (White ppt)+KNO3 Cl +KOH(ag) No Reaction ii) C2H5Cl+KOH(aq) KCl+AgNO3 C2H5Br+KOH(aq) KBr+AgNO3 C2H5OH +KCl AgCl (White ppt)+KNO3 (soluble in NH4OH) C2H5OH +KBr AgBr (pale yellow ppt)+KNO3 ( partially soluble in NH4OH) iii) C6H5CH2Cl +KOH(aq) KCl+AgNO 3 C6H5Cl+KOH(aq) C6H5CH2OH +KCl AgCl (White ppt)+KNO3 (soluble in NH4OH) No reaction Ans6.Give reasons: (i).Beacuse of higher magnitude of Vander Waal’s forces in alkyl bromide than alkyl halide. (ii).Due to greater polarity of alkyl halides. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 172 (iii).C-Cl bond is more polar than C-Br bond. So a better solvent than alkyl bromide. Ans7.Answer the following: i) CH2=CH-Cl- CH2—CH=Cl+ It will decrease the dipole moment of vinyl chloride relative to ethyl chloride. (ii).To prepare Iodoform from acetone I+ is required. As I+ can only be supplied IO- not by I-,therefore hypoiodite is used to convert acetone into iodoform. (iii).Due to resonace there is double bond character between Carbon and chlorine. Ans8. (i).CH3-CH2-CH2-Cl +NaI Acetone CH3-CH2-CH2-I +NaCl (ii).CH3-CH2-CH2OH +SOCl2 CH3-CH2-CH2Cl +SO2 +HCl (iii).CH3CH2CH=CH2 +HBr Peroxide CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2Br Ans.9.Give uses of following: i) ii) iii) CCl4:Used as solvent. DDT:Used as insecticide Chloroform:Used as anesthesia in surgery. Ans10.Distinguish between SN1 and SN2 reactions? Five Marks Question Ans 1. A= MgBr: B= : C=RMgBr R=CH3CHCH3 R’=C(CH3)3: D=C(CH3)3MgX E=HC(CH3)3 Ans2.What happens when: (a).CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-Cl +KOH (alc) (b).C6H5Br +Mg dry ether CH3-CH2-CH=CH2 +KCl +H2O C6H5MgBr ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 173 (c).C2H5Cl+KOH(aq) (d).2C2H5Br+2Na C2H5OH+KCl dry ether CH3-CH2-CH2-CH3 +2NaBr (e).CH3Cl +KCN(alc) CH3CN +HCl Ans 3.A) CH3-CH(CH3)-CH2Br 1-Bromo-2-methylpropane. B) CH3-C(CH3)=CH2 2-Methylprop-1-ene. C) CH3-C(CH3)(Br)-CH3 2-Bromo-2-methylpropane D) CH3-CH(CH3)-CH2-CH2-CH(CH3)-CH3 2,5-Dimethylhexane Equations for reaction: A alc.KOH B B+HBr C 2A+2Na D +2NaBr 4.Ans. i).C6H5Cl +2Na +C6H5Cl C6H5-C6H5 + 2Nacl (ii).C6H6 +CH3Cl (Anhyd)AlCl3C6H5CH3 +HCl iii).C6H5Cl +CH3COCl Anhyd AlCl3C6H5 COCH3 iv) v) C6H5N2Cl Cu/HCl C6H5Cl +N2 CH3CH2NH2 +CHCl3 +KOH(alc.) CH3CH2NC +3KCl+3H2O A ns: 5. (i).Because in case of benzyl chloride the carbocation is formed after the loss of Cl- stabilized by resonance. (ii).It is due to symmetry of p-Dichlorobenzene which fits in crystal lattice better than orthodichlorobenzene. (iii).Chloromethane is more reactive being an alkyl halide (iv). Thebyproducts of the reaction i.e.SO2 and HCl being gases escape into the atmosphere leaving behind the alkyl chloride in almost pure state. (V).Because of bigger size and lower electronegativity. Prepared By Guwahati Region ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 174 Chapter 11 to 16 ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS. Q.1 Give the IUPAC name of the following. CH3-C (CH3) =CH-CH2OH Ans:-3-Methyl But-2-en 1-ol Q.2 Phenols are much more acidic than alcohols. Why Ans:-Due to electron with drowning nature of ph-group. Q3 Give the IUPAC name of the following compound: . Solution : 2 − Bromo-3-methyl-but-2-ene-1-ol. Q.4 What happen when phenol is treated with excess of bromine(aq). Ans It gives 2,4,6-tribromo phenol. Q.5 Write chemical equation Williamson synthesis. Ans- R-X+R- O- Na --------- R-O-R + NaCl Q.6 Mention one uses of methanol. Ans – (i) As a denaturant for ethanol Q.7 The boiling point of ethanol is higher than that methoxy methane. Ans-Ethanol has inter molecular hydrogen bonding, methoxymehane does not have H-bonding. Q.8 Name a substance that can be used as an antiseptic as well as a disinfectant. Ans: Phenol can be used as an antiseptic as well as a disinfectant. 0.1% Soln of phenol is used as an antiseptic & 1% Soln of phenol is used as a disinfectant. Q.9 Write the IUPAC name. (CH3)3 C-OH Ans- 2-methyl-2-propanol Q.10 What is Nucleophiles. Ans- The species which has high electrons density. Q.11 Which catalyst are used in Friedel craft reaction? Ans- Anh.AlCl3. Q.12 Write a test to distinguish between primary, secondary and alcohols? Ans Lucas test. Q13 Write the IUPAC name of CH3OH? Ans- Methanol. Q.14 Write the IUPAC name of CH3-O-CH3? Ans- Methoxy methane. Q.15.Write the IUPAC name of CH3 CH2-O-CH3? Ans- Ethoxy methane. Short answers questions (2marks) ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 175 Q.1 Phenols are as a smaller dipole moment than methanol. Ans:- Due to electron with drowning nature of ph-group-O bond is less polar.in case of methanol methyl group is electron releasing group So C-O bond is more polar. Q.2 Explain why Phenol do not undergo substitution of OH group like alcohol. Ans-C-O bond in phenol has some double bond characters due to resonance an hence cannot be easily replaced by Nu. In contrast the C-O bond in alcohol is pure single bond an hence can be easily released by Nu. Q.3 Give a test to distinguish between phenol and Benzyl alcohol. Ans- Phenols give violet colour with ferric chloride while benzyl alcohol does not give this coloure. Q.4 Give a test to distinguish ethanol and phenol. Ans- phenol turns blue litmus red,but Ethanol donot have effect on litmus paper. Q.5Write theWilliamson synthesis reaction Ans:- R-X +R-ONa----------R-O-R +NaX 3marks questions Q1. Write the reaction of phenol with Zn. Ans: ph-OH +Zn-----------------------C6H6 +ZnO Q2.Write the kolbes reaction? Ans:Ph-oh +NaOH ------ph-oNa +H2O ---- ( CO2) - O- Hydroxy benzoic acid Q3.(i) Explain the mechanism of Addition of Grignard’s reagent to the carbonyl group of a compound forming an adduct followed by hydrolysis. (ii) Explain the mechanism of Acid catalysed dehydration of an alcohol forming an alkene. (iii)Explain the mechanism of Acid catalysed hydration of an alkene forming an alcohol. Ans: (i) Grignard’s reagent is an alkyl magnesium halide. The alkyl group has a partial negative charge, whereas the magnesium group has a partial positive charge. The alkyl group attacks the carbon of the carbonyl group to form an addition compound. Grignard’s reagent acts as a nucleophilic agent & attacks electrophilic carbon atoms to yield a carbon − carbon bond. The addition to the nucleophile is an irreversible process due to the high pka value of the alkyl group. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 176 (ii) When heated with concentrated sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid or boric acid, alcohols undergo dehydration to form alkenes. The mechanism of this reaction involves the protonation of alcohol, followed by loss of a water molecule & a proton. (a) (b) (c) During the dehydration of alcohol, the intermediate carbocation may undergo re-arrangement, resulting in the formation of a stable carbocation. (iii) Some reactive alkenes like 2 − methyl propene undergo direct hydration in the presence of mineral acids which act as catalysts. The addition of water to the double bond takes place in accordance with Markonikoff’s rule. Q.4(i) The bp. of ethanol is higher than that of methoxy methane. (ii) Phenol is more acidic than ethanol. (iii) O & p nitrophenol are more acidic than phenol. Ans:-(i) Due to presence of a hydrogen attached to oxygen atom. As a result ethanol exists as associated molecules & hence it has higher bp. than methoxy methane which does not form hydrogen bond. (ii) Because the phenoxide ion left after the release proton is stabilized by resonance but ethoxide. Moreover ethoxide ion is destabilized by +1 effect of ethyl group. (iii) Due to I-effect or R-effect of NO2 gp. The resulting phenolate ion is more destabilized by +1 effect of ethyl gp. Q.5How are the following conversions carried out? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 177 (i) Benzyl chloride to benzyl alcohol, (ii) Methyl magnesium bromide to 2-methylpropan-2-ol Ans: 5marks questions Q.1 (a) An Organic compound ‘ A’ with molecular formula C8H8O gives positive DNP and iodoform test. It does not reduces Tollens or Fehling reagent and doesnotdecolourisesBr2/H2O also.On oxidation with chromic acid gives a carboxylic acid (B) with molecular formula C7H6O2.Determine the structure of ‘A’ and ‘B’. AnsA = Acetophenone B = Benzoic acid (b) Complete the following reactions by identifying A ,B and C: (I) A +H2(g )------ Pd/BaSO4-------------- (CH3)2 CHCHO (II) (CH3)3C-CO-CH3 + NaOI ---------- B + C Ans- (i) A= (CH3)2 CHCOCl B= (CH3)3C-CO-Na + C = CHI3 Iodoform Q.2 An Organic compound ‘ A’ with molecular formula C3H6 on treatment with aq.H2SO4 gives ‘B’ which on treatment with HCI/Zncl2 gives ‘C’. Thecompound ‘ C’ on treatment with ethanolic KOH gives back the compound ’A’ .Identify the compound A, B and C . Ans: A=Propene, B=Propan-2-ol ,C=2-Chloropropane. Aq.H2SO4 HCI/Zncl2 ethanolickoH CH3-CH=CH2---------CH3-CH-CH3------------------CH3-CH-CH2------------------ CH3-CH=CH2 Hydration propan-2-ol Hydration ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com propene 178 Prepared by: Kolkatta Region ALDEHYDES,KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS SECTION-A (Onemark Questions) 1. Name one distinguishing test between aldehydes and ketones? Ans. Aldehydes and ketones can be distinguished by Tollen’s test. Aldehydes give a silver mirror on reacting with Tollen’s reagent whereas ketones will not react. 2. Give reason why Formaldehyde does not undergo aldol condensation? Ans. Formaldehyde does not have any α -hydrogen and therefore it cannot show aldol condensation. 3. Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than alcohols of same no. of carbon atoms? Ans. Carboxylic acids have more extensive association of molecules through intermolecular hydrogen bonding than alcohols. 4. Write IUPAC name .of CH3COCH2COCH3. Ans.Pentane-2,4-dione. 5.What product is obtained when Ethylbenzene is oxidized with alkaline KMnO4? Ans. Benzoic acid is formed. 6Give chemical test to distinguish between acetaldehyde and benzaldehyde. Ans.Acetaldehyde will respond to Iodoform test where asbenzaldehyde does not. 7.Write one chemical to distinguish between Formic acid and Acetic acid . Ans.Formic acid gives silver mirror when treated with Tollen,’s reagent where as acetic acid does not. 8.Give two important uses of formalin. Ans.Used as a preservative. Used for the preparation of Bakelite. 9.How is formalin and trioxane related to methanal? Ans.Formalin is 40%aqeous solution of methanalwhere astrioxane is trimer of methanal. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 179 10.Complete the following reactionand give the name of the major product. HCHO+ CH3MgX ----------------------------- ? Ans. HCHO +CH3MgX ---------CH3CH2OH + Mg(OH)X CH3CH2OH- Ethanol 11. Draw the structural formula of Hex-2-en4-yn-oic acid. Ans. CH3-C C-CH=CHCOOH 12. Arrange the following in the increasing order of acidic character. HCOOH, ClCH2COOH,CF3COOH,Cl3CCOOH Ans. CF3COOH>CCl3COOH>ClCH2COOH>HCOOH 13. Complete the reaction:RCONH2+4NaOH+Br2 -------- Ans.RCONH2+4NaOH+Br2------- RNH2+ 2NaBr+ Na2CO3+2H2O. 14. Give one chemical test to distinguish between Phenol and benzoic acid. Ans. On treatment with neutral FeCl3 solution Phenol gives a violet color whereas Benzoic acid does not. 15. Most of the aromatic acids are solids while acetic acids and others of this series are liquids. Why? Ans. Aromatic acids have higher molecular weights. Therefore more Vanderwaal’s force of attraction as compared to aliphatic acids and hence they are solids . SECTION –B (2 Mark Questions.) 1. Would you expect benzaldehyde to be more or less reactive in nucleophilic addition reaction than Propanal? Explain your answer. Ans. The carbon atom of the carbonyl group of benzaldehyde is less electrophilic than carbon atom of the carbonyl group present in propanal. The polarity of the carbonyl group is reduced in benzaldehyde due to resonance and hence is less reactive. 2. Describe the Transesterification reaction giving an example. Ans. When an ester reacts with alcohol to form another ester and another alcohol, the process is called transesterification. CH3COOC2H5 +CH3OH ---------- CH3COOC2H5 + C2H5OH ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 180 3.Explain Hell- Volhard –Zelinsky reaction with an example. Ans. Carboxylic acids having an a α hydrogen atom are halogenated at the α position on treatment with chlorine or bromine in the presence of small amount of red phosphorous to give α- halocarboxylic acids (i)X2/P(Red) RCH2COOH --------------RCH(X)COOH. (ii) H2O/H+ 4.Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between :(i) (ii) Pentan-2-one and Pentane-3-one Ethanal and propanal Ans. (i) Pentan-2-one gives Iodoform test on treatment with I2/NaOHwhere as Pentane -3-one does not. (ii)Ethanal gives Iodoform test whereas Propanal does not. 5.AlthoughPhenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than Carboxylate ion, Carboxylic acids are more acidic than Phenol .Why? Ans. In carboxylate ion (-)ve charge is delocalised over two oxygen atoms whereas in phenoxide ion (-)ve charge is delocalised over one oxygen atom .Therefore carboxylate ion is more stable than phenoxide ion .That is why Carboxylic acics are more acidic than Phenol. 6. Why is there a large difference in the boiling points of butanal and butan-1-ol? Ans:-Butan-1-ol has higher boiling point due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding 7.Name the electrophile produced in the reaction of benzene with benzoyl chloridein the presence of anhydrous AlCl3. Name the reaction also. Ans: benzoyliumcation or . Friedel Craft’s acylation reaction. 8. Arrange the following in decreasing order of their acidic strength and give reason for your answer. CH3CH2OH, CH3COOH, ClCH2COOH, FCH2COOH, C6H5CH2COOH Ans: FCH2COOH > ClCH2COOH > C6H5CH2COOH > CH3COOH >CH3CH2OH Due to +ve and –Ve inductive effects 9. Write the names associated with the following reactions:(i) ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 181 (ii) Ans:- (i) Rosenmund Reduction (ii)Stephens Reaction 10. Ans: SECTION- C (THREE MARKS QUESTIONS) 1. What happens when :- (i) an aqueous solution of Sodium acetate is electrolysed (ii) Calcium acetate is dry distilled (iii) Sodium benzoate is heated with Sodalime Ans. (i) 2CH3COONa +2H2O --------- C2H6 +2CO2+2NaOH+H2. (ii)CH3COO)2Ca ----------------CH3COCH3+CaCO3 (iii)C6H5COONa +NaOH(CaO) ---------C6H6 +Na2CO3 2. Write IUPAC names of the following Compounds:(i)CH3CO(CH2)4CH3 (ii) Ph-CH=CH-CHO (iii)OHC Ans. (i) Heptane -2-one (ii) 3-Phenylprop-2-en-1-al.(iii) Cyclopentanecarbaldehyde. 3.Complete the following equations:(i) CH3CONH2P2O5-/heat-(ii) 2CH3CHO ? dil .NaOH ? (iii)C6H5COOH HNO3/H2SO4-Ans. (i)CH3CONH2P2O5-/heat-(ii) 2CH3CHO dil .NaOH ? CH3CN + H2O CH3CH(OH)CH2CHO ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 182 (iii)C6H5COOH HNO3/H2SO4—m-O2N-C6H4-COOH 4.Explain the following:(i)Gatterman-Koch reaction (ii) Clemensen reduction (iii)Wolf-Kishner Reduction Ans(i) When benzene or its derivative is treated with carbon monoxide and hydrogen chloride in the presence of anhydrous aluminiumchloride or cuprous chloride, it gives benzaldehyde or substituted benzaldehyde.This reaction is known as Gatterman-Kochreaction. (ii)The carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones is reduced to CH2 group on treatment with zincamalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid called Clemensen Reduction. (ii)The carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones is reduced to CH2 group on treatment with hydrazine followed by heating with sodium or potassium hydroxide in high boiling solvent such as ethyleneglycolcalled Wolff-Kishner reduction 5. Predict the products of the following reactions ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 183 Ans: (6).An alkene ‘A’ (Mol. formula C5H10) on ozonolysis gives a mixture of two compounds ‘B’ and ‘C’. Compound ‘B’ gives positive Fehling’s test and also forms iodoform on treatment with I2 and NaOH. Compound ‘C’ does not give Fehling’s test but forms iodoform. Identify the compounds A, B and C. Write the reaction for ozonolysis and formation of iodoform from B and C Ans: SECTION- D (FIVE MARKS QUESTIONS) ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 184 1.An organic compound (A) with molecular formula C8H8O forms an orange-red precipitate with 2,4-DNP reagent and gives yellow precipitate on heating with iodine in the presence of sodium hydroxide. It neither reduces Tollens’ or Fehlings’ reagent, nor does it decolourise bromine water or Baeyer’s reagent. On drastic oxidation with chromic acid, it gives a carboxylic acid (B) having molecular formula C7H6O2. Identify the compounds (A) and (B) and explain the reactions involved. Ans:-(A) forms 2,4-DNP derivative. Therefore, it is an aldehyde or a ketone. Since it does not reduce Tollens’ or Fehling reagent, (A) must be a ketone. (A) responds to iodoform test. Therefore, it should be a methyl ketone. The molecular formula of (A) indicates high degree of unsaturation, yet it does not decolourise bromine water or Baeyer’s reagent. This indicates the presence of unsaturation due to an aromatic ring. Compound (B), being an oxidation product of a ketone should be a carboxylic acid. The molecular formula of (B) indicates that it should be benzoic acid and compound (A) should, therefore, be a monosubstituted aromatic methyl ketone. The molecular formula of (A) indicates that it should be phenyl methyl ketone (acetophenone). Reactions are as follows: 2 Write chemical reactions to affect the following transformations: (i) Butan-1-ol to butanoic acid (ii) Benzyl alcohol to phenylethanoic acid (iii) 3-Nitrobromobenzene to 3-nitrobenzoic acid (iv) 4-Methylacetophenone to benzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid (v) Cyclohexene to hexane-1,6-dioic acid Ans:- ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 185 3. An organic compound contains 69.77% carbon, 11.63% hydrogen and rest oxygen. The molecular mass of the compound is 86. It does not reduce Tollens’ reagent but forms an addition compound with sodium hydrogensulphite and give positive iodoform test. On vigorous oxidation it gives ethanoic and propanoic acid. Write the possible structure of the compound. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 186 Element % At. Wt. C H O 69.77 11.63 18.60 12 1 16 Relative atoms 5.81 11.63 1.16 no. of Divide by least 5.81/1.16=5 11.63/1.16=10 1.16/1.16=1 Empirical formula is C5H10O Empirical formula mass = 86 N=86/86=1 Molecular formula is C5H10O Since hydrogen atoms are double than carbon atoms, therefore, it is likely to be aldehyde or ketone. It does not reduce Tollen’s reagent so it is a ketone.It reacts with NaHSO3 and gives Iodoform test .Therefore it is Methylketone.On vigorous oxidation it gives ethanoic acid and propanoicacid . The compound is Pentane-2-one.CH3COCH2CH2CH3 4.An organic compound (A) molecular formula C8H16O2 was hydrolysed with dil. H2SO4 to give a carboxylic acid (B) and alcohol (C) . Oxidation of (C) with chromic acid produced (B).(C) on dehydration gives but-1-ene. Write equations for the reactions involved. Ans. CH3CH2CH2COOCH2CH2CH2CH3+ H2O Dil H2SO4 (A) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH CrO3- CH3CH2CH2COOH+ CH3CH2CH2CH2OH (B) (C) CH3CH2CH2COOH (C) CH3CH2CH2CH2OHConc H2SO4 CH3CH2CH=CH2 (C) 5.What is meant by the following terms:(a) Cyanohydrin (b) Semicarbazone (c)Hemiacetal (d)Ketal (d)2,4 –DNP derivative Ans: (a).(a) When –CN and –OH groups are attached to the same carbon atom it is called cyanohydrin.e.g. CH3CH(OH)(CN). ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 187 (b) When aldehyde or ketone react with semicarbazide the product formed is semicarbazone. E.g. H3C-CH=NNHCONH2 (c) When aldehyde reacts with one mole of alcohol in presence HCl gas Hemiacetal is formed. E.g. H 3C-CH(OH)OCH3 (d) When ketones react with two moles of alcohol /; Ethylene glycol in presence of HCl gas Ketal is formed.e.g. (e)When aldehyde or ketone reacts with 2,4-DNP orange precipitate is formed.e.g. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 188 Prepared by: Kolkatta Region AMINES Q.1Give the IUPAC name of H2N − CH2 − CH2 − CH = CH2. Soln: 4-amino-but-1-ene Q.2 Write structure of methyl amine? Ans- CH3-NH2 Q.3 Write the structure of methyl isocyanides? Ans-CH3NC Q.4 Name the tests for Primary amine. Ans- Carbylamines test Q.5 Primary amines have higher b.p than tertiary amines. Ans- Due to inter molecular hydrogen bonding. Q.6 Why is alkyl amine more basic than ammonia? Ans Due to +I effect of alkyl group. Q.7 why do amine react as nucleophile. Ans-due to lone pair of electron on nitrogen. Q.8 Why are aqueous solution of amine basic in nature? Ans- Because of high electron density on nitrogen it gains H+ from water. Q.9 Name one test to distinguish between ethyl cynide and ethyl isocynide. Ans- ethyl cynide on hydrolysis with acids form propionic acid, whereas ethyl isocynide with dilute HCl forms ethylamine and formic acid. Q10.Identify A and B NaNO2/HCL CuBr C6H5NH2----------------------A------------------------B ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 189 Q11.Name the reaction in which amide directly converted into amines. Ans:Hofmann’sbromamide reaction. Q12.Complete the following: RNH2 + CHCI3+ 3KOH------------------ ? Q13. .Complete the following: RCONH2 + Br2 + 4 NaOH------------------ ? Q14.Write the formula of hinsberg’s reagent. Ans:Benzoyl chloride. Q15.What is meant by diazotization? Ans:Conversion of primary aromatic amines into diazonium salts. 2marks questions Q.1 In an increasing order of basic strength: C6H5NH2,C6H5 N (CH3)2, (C2H5)2 NH & CH3NH2 Ans: Basic strength: Aliphatic amines are stronger bases than aromatic amines due to the presence of lone pair of e- on nitrogen atom. In case of aromatic amines the lone pair gets delocalised by resonance. Diethyl amine has greater + I effect. Hence, edensity over the nitrogen atom is more in this case. Similarly N, N − dimethyl aniline has greater + I effect than aniline. Q.2 In a decreasing order of basic strength: Aniline, p-nitroaniline& p-toluidine Ans- ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 190 Methyl (−CH3) is an e- donating group. It increases the e- density on the ring. Therefore, the lone pair of nitrogen is available for donation. Hence, it is most basic. On the other h& nitro (−NO2) is an e- withdrawing group. It decreases the e- density of the ring. Therefore, the lone pair is more delocalized in this case & is less available for donation. Thus, it will be least basic among the three. Q.3 In an increasing order of pKb values: C2H5NH2, C6H5 NHCH3, (C2H5)2 NH & C6H5NH2 Ans- Stronger the base is lesser is the pKb value. (C2H5)2NH is the strongest base due to two e- releasing group followed by C2H5NH2 which has only one e- releasing group. C6H5NHCH3 is the next stronger base because of the presence of one e- releasing alkyl group & e- delocalising phenyl group. C6H5NH2 is the least basic wherein the e- get delocalised by resonance. Q.4.Write a chemical reaction in which the iodide ion replaces the diazonium group in a diazonium salt. Ans-: Q.5Why is an alkylamine more basic than ammonia? Ans: An alkylamine is more basic than ammonia because of inductive effect (+I effect). Alkyl group or ‘R’ has an e-releasing effect, which increases e- density over nitrogen atom. This increases its basicity. 3marks questions Q.1Describe the Hofmann’s bromamidereaction Ans: ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 191 Hofmann’s bromamidereaction: It involves the reaction of bromine with an acid amide in the presence of an alkali. It results in the formation of a primary amine with one carbon less than the parent compound. Here, the alkyl group migrates from carbonyl, with the elimination of CO2. For example: Q.2Describe the Gattermanreaction Ans- Gattermanreaction: This is a modification of S&meyer reaction in which benzenediazonium chloride is treated with copper powder & halogen acid to form aryl halides. Q.3Describe the couplingreaction Ans Coupling reaction: It is the reaction of diazonium salts with phenols & aromatic amines to form azo compounds of the general formula Ar − N = N − Ar. The coupling of phenol takes place in a mildly alkaline medium. Q.4pKb for aniline is more than that for methylamine. Ans: In aniline, the lone pair of e- on the N atom is delocalised over the benzene ring. As a result, the e- density on the nitrogen atom decreases. In contrast, in CH3NH2, the +I effect of CH3increases the e- density on the N atom. Therefore, aniline is a weaker base than methylamine. Hence, its pKb value is higher than that of methylamine. Q.5 Methylamine Soln in water reacts with ferric chloride Soln to give a precipitate of ferric hydroxide. Ans- Being more basic than water, methylamine accepts a proton from water-liberating OH− ions. These OH− ions combine with Fe3+ ions present in H2O to form a brown precipitate of hydrated ferric oxide. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 192 5marks questions Q1.An aromatic compound ‘ A’ on treatment with aqueous ammonia and heating forms compound ‘B ‘ which on heatiog with Br2 and KOH forms a compound ‘ C’ of molecular formula C6H7N. Write the structures and IUPAC names of compounds A, B andC. Ans:-((A) Benzoic acid (B) Benzamide (c) Aniline Q2.Complete the following reactions: (i)C6H5NH2 +CHCI3 +alc.KOH--------- (II)C6H5N2Cl +H3PO2 +H2O---------------- (III)C6H5NH2 +H2SO4(CONC)--------------- (IV)C6H5N2Cl +C2H5OH------------------------ (V)C6H5NO2 + Fe/HCI---------------------------- Ans:- (i)C6H5NH2 +CHCI3 +alc.KOH-------------C6H5NC +3KCl +3H2O (II)C6H5N2Cl +H3PO2 +H2O----------------C6H6 +H3PO3 +N2 +HCl (III)C6H5NH2 +H2SO4(CONC)-----------------------NH2-Ph-SO3H +H20 (IV)C6H5N2Cl +C2H5OH------------------------------C6H6 +N2+CH3CHO +HCI (V)C6H5NO2 + Fe/HCI-------------------------------C6H5NH2 Prepared by: Kolkatta Region Chapter 14. Biomolecules Section A (One Mark Question) ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 193 1.Name the sugar present in milk. A: Lactose, 2.How many monosaccharide units are present in it? A: two monosaccharide units are present. 3. What are such oligosaccharides called? A: Such oligosaccharides are called disaccharides 4. How do you explain the presence of all the six carbon atoms in glucose in a straight chain? A: On prolonged heating with HI, glucose gives n-hexane. 4. Name the linkage connecting monosaccharide units in polysaccharides. A: Glycosidic linkage. 5. Under what conditions glucose is converted to gluconic and saccharic acid? A: Glucose is converted to gluconic acid by bromine water and to saccharic acid by conc. HNO3. 6. Which sugar is called invert sugar? A: Sucrose. 7. During curdling of milk, what happens to sugar present in it? A: It converts into Lactic acid. 8. . Monosaccharide contain carbonyl group hence are classified, as aldose or ketose. The number of carbon atoms present in the monosaccharide moleculeare also considered for classification. In which class of monosaccharide willyou place fructose? A:Fructose is a ketohexose. 9. The letters ‘D’ or ‘L’ before the name of a stereoisomer of a compound indicate the correlation of configuration of that particular stereoisomer. This refers to their relation with one of the isomers of glyceraldehyde. Predict whether the following compound has ‘D’ or ‘L’ configuration. A: ‘L’ configuration 10. What are constituents of Starch? A: Amylose and Amylopectin 11. What D N A & R N A Stand for? A: Deoxyribonuclic acid and Ribonuclic acid. 12. What are Zwitter ions? A: A Zwitter ion is a dipolar ion formed by neutralisation of acidic and basic centers present within the molecule . 13. .What is non reducing sugar? Give example. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 194 A: The groups like CHO, - C= O, which are not freely available in the molecule do not answer tollens or fehlings test are called non reducing sugar. E.g. maltose and lactose 14. Define mutarotation? Give example. A: The anomers of glucose i. e. alpha and beta are having specific rotation of + 111 0Cand + 19.20Crespectively. The mixtures of these two have a rotation of +52.40 C. this is called a mutarotation. 15. Amino acids are amphoteric in behavior? Explain. A: they form zwitterion(dipolar ion) and behave as neutral molecule at pH 7(isoelectric point). SECTION –B (2 Mark Questions.) 1.Define native state and denaturation of protein. What happens when: a. Protein is cooled to zero degree C? b. Protein is heated to 800 C A: protein in the native state has definite configuration and biological activity. The higher structure of protein is affected without disturbing the primary structure is called denaturation. a. no change b.the coagulation of the protein takes place. 2. Which forces are responsible for stability of alpha Helix of protein? Why it is called 3.613 helix? A: Hbonding. It has 3.6 amino acids in one single turn,and a 13 member ring is formed by H bonding. 3. What are essential amino acids? Give example and what happens when it is polymerized? A: amino acids required by the body and cannot be synthesized in our body are called essential amino acids. e.g. Lysine. When it is polymerized polypeptide chains are formed. 4. Glucose and sucrose are soluble in water but Cyclohexane and benzene are not soluble. Why? A : Glucose and sucrose form H bonding with water 5.(i) Write the sequence of base on mRNA molecule synthesized on the following strand of DNA: A: AUAGAUGGACCU (ii)Name a powerful antioxidant which is a water soluble vitamin. A: Vitamin C TATCTACCTGGA SECTION- C (THREE MARKS QUESTIONS) 1. (i)Protein found in a biological system with a unique three-dimensional structureand biological activity is called a native protein. When a protein in its native form,is subjected to a physical change like change in temperature or a chemical changelike, change in pH, denaturation of protein takes place. Explain the cause. (ii) Structures of glycine and alanine are given below. Show the peptide linkage in glycylalanine. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 195 Ans: A(i) Due to physical or chemical change, hydrogen bonds in proteins are disturbed, globules unfold and helix gets uncoiled therefore protein loses its biological activity. This is called denaturation of proteins. (ii) 2. (i) What are the expected products of hydrolysis of lactose? (ii) How do you explain the absence of aldehyde group in the pentaacetate of D-glucose? A(i)It is composed of β-D-galactose and β-D-glucose. The linkage is between C1 of galactose and C4 of glucose. (ii) The pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine indicating the absence of free —CHO group. 3. (i) What products would be formed when a nucleotide from DNA containing thymine is hydrolysed? (ii)How will you distinguish 1° and 2° hydroxyl groups present in glucose? A(i)Complete hydrolysis of DNA yields a pentose sugar, phosphoric acid and thymine (ii)On oxidation with nitric acid, glucose as well as gluconic acid both yield a dicarboxylic acid, saccharic acid. This indicates the presence of a primary alcoholic (–OH) group in glucose. 4. Write the reactions of D-glucose which can’t be explained by its open-chain structure. How can cyclic structure of glucose explain these reactions? Ans: The following reactions and facts could not be explained by this structure. 1. Despite having the aldehyde group, glucose does not give Schiff’s test and it does not form the hydrogensulphite addition product with NaHSO3. 2. The pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine indicating the absence of free —CHO group. 3. Glucose is found to exist in two different crystalline forms which are named as α and β. The α-form of glucose (m.p. 419 K) is obtained by crystallisation from concentrated solution of glucose at 303 K while the β-form (m.p. 423 K) is obtained by crystallisation from hot and saturated aqueous solution at 371 K. 5. Write the evidences for the following on the basis open chain structure of Glucose.(I) all the six carbon atoms are linked in a straight chain. (ii)the presence of a carbonyl group (>C = O) in glucose. (iii)five –OH groups are attached to different carbon atoms. Ans: (i) ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 196 (ii) (iii) 6.Explain the terms primary structure of proteins. Ans:- Primary structure of proteins: Proteins may have one or more polypeptide chains. Each polypeptide in a protein has amino acids linked with each other in a specific sequence and it is this sequence of amino acids that is said to be the primary structure of that protein. Any change in this primary structure i.e., the sequence of amino acids creates a different protein. 7. Explain the terms secondary structure of proteins. What is the difference between α-helix and β-pleated sheet structure of proteins? Ans: Secondary structure of proteins: The secondarystructure of protein refers to the shape in which a long polypeptide chain can exist. They are found to exist in two different types of structures viz. α-helix and β-pleated sheet structure. These structures arise due to the regular folding of the backbone of the polypeptide chain due to hydrogen bonding between-CO- and –NH– groups of the peptide bond. α-Helix is one of the most common ways in which a polypeptide chain forms all possible hydrogen bonds by twisting into a right handed screw (helix) with the –NH group of each amino acid residue hydrogen bonded to the C O of an adjacent turn of the helix. In β-structure all peptide chains are stretched out to nearly maximum extension and then laid side by side which are held together by intermolecular hydrogen bonds. The structure resembles the pleated folds of drapery and therefore is known as β-pleated sheet. 8. Explain tertiary structure of Protein. Ans: Tertiary structure of proteins: The tertiary structure of proteins represents overall folding of the polypeptide chains i.e., further folding of the secondary structure. It gives rise to two major molecular shapes viz. fibrous and globular. The main forces which stabilise the 2° and 3° structures of proteins are hydrogen bonds, disulphide linkages, van der Waals and electrostatic forces of attraction. 9. What are structural difference between Cellulose and Starch ? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 197 Ans:-Starch is a polymer of α-glucose and consists of two components— Amylose and Amylopectin. Amylose is water soluble component which constitutes about 15-20% of starch. Chemically amylose is a long unbranched chain with 200-1000 α-D-(+)-glucose units held by C1– C4 glycosidic linkage. Cellulose is a straight chain polysaccharide composed only of β-D-glucose units which are joined by glycosidic linkage between C1 of one glucose unit and C4 of the next glucose unit. Prepared by: Kolkatta Region CHAPTER-15(Polymer) (one mark questions Q1 to Q20) Q1.Give the name and structure of reagent usedfor initiating a free radicalchainreaction . Ans: Name- benzoylperoxide ,C6H5-CO-O-O-CO-H5C6 Q2.Classify them as addition and condensation polymers:Nylon-66,Buna-s,polythene,terylene ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 198 Ans:Additionpolymer:Polythene and Buna-s,Condensationpolymer:Nylon-66,terylene Q3.Give name and structure of monomer present in natural rubber. Ans:Name:Isoprene(2-Methyl1,3-Butadiene),Structure:CH2=C(CH3)CH=CH2 Q4.What is biodegradeablepolymers?Give one example Ans:PHBV Q5.What is polymers? Ans:Polymers are high molecularmass substances consisting of large no of repeating structural units. Q6.How are the polymer classified on the basis of structure: Ans:a) Linear Polymer b)Branched chain polymers c)Cross linked polymers Q7Writes the names of monomer of the following (-CO-(CH2)5-NH-)n Ans:Caprolactum Q8.Arrange the following polymers in increasing order of their intermolecular forces: Nylon6,Neoprene,polyvinyl chloride. Ans:Neoprene<Polyvinyl chloride<Nylon-6 Q9.Is (-NH-CHR-Co-)n is a homopolymer or copolymer? Ans: Homopolymer Q10.What is vulcanized rubber? Ans:process of heating a mixture of natural rubber with sulphur is called vulcanized rubber. Q11.Write the monomer of Bakelite. Ans: Phenol and formaldehyde Q12.Menton two uses of Bakelite. Ans: It is used for making combs,electrical switches and handle of various utensils Q13Explain the term copolymer and give two examples. Ans:Polymer which are made up of two different monomer unit are called copolymers: eg.Buna-N,Buna-S (CH-15) Q14.Mention one use of melamine? Ans: It is used in the manufacture of unbreakable crockery. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 199 Q15.How can natural rubber be made more tough? Ans: By the process of vulcanization with sulphur. Q16.What is natural rubber? Ans: It is a cis 1,4-polyisoprene. Q17.How do you explain functionality of monomer? AnS:No of bonding sites in monomers. Q18.What are natural polymers? Ans:Those polymers which are obtained mostly from plants and animals are called natural polymers eg Natural rubber,cellulose Q19.What is synthetic polymers? Ans:Those polymer which are obtained from chemical compound are called synthetic polymer Q20.What is monomer of Nylon-2-Nylon-6? Ans: Glycine,6-Aminocaproic acid. (Two marks questions on polymer) Q1.Explain the difference between Buna-N and Buna-s. Ans:Buna-Nis a polymer of 1,3-Butadiene and andacrylonitrile and buna-s is a polymer of 1,3-Butadiene and styrene. Q2.Distinguish between homopolymer and copolymer? (For two marks,polymer) Q2.Ans:Homopolymer is made up of only one type of monomer unit eg. PVC. Where as co-polymer is made up of two different monomer units eg Buna-s. Q3.What are polyamides and polyesters?Give one example of each. Ans:Polymers having amide linkage in the chain are called polyamides eg Nylon-6.Polymers having ester linkage in the chain are called polyesters eg. Terylene. Q4Dicuss the main purpose of vulcanization. Ans:Natural rubberbecome soft at high temperature,Brittle at low temperature.And show higher water absorption capacity. It is nonresistant to attack by oxidizing agent .In order to improve these properties a process of vulcanization is carried out. Q5.In which classes, the polymers are classified on the basis of molecular forces? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 200 Ans: Elastomer, fibre ,thermoplastics and thermosetting polymers. Q6. Write names of monomers of the following polymers. a)(-CF2-CF2-)n b)(CH2-CH(cl)-)n. Ans:a)Tetrafluoroethene b)Vinyl chloride . Q7.what are monomeric repeating units of nylon-6 and nylon-6,6 ? Ans ;Caprolactam , Hexamethylenediamine and Adipic acid Q.8 Arrange the following polymers in increasing order of their intermolecular forces. a) nylon-6 ,6 ,Buna-S , Polythene b) Neoprene, Nylon-6, PVC Ans.a) BUNA-S< Polythene <Nylon-6,6 b)Neoprene < PVC < nylon-6 Q9.Classify the following as Addition and condensation polymers: Bakelite,melamine,PVC,Buna-S,Buna-N,Nylon-6,6 Ans:Additionpolymers:Buna-N,Buna-S,PVC Condensation polymer:Nylon-6,6,Bakelite melamine, Q10.How is novolac converted into bakelite? Ans: Novolac on heating with formaldehyde undergoes crosslinking to form an infusible solid mass called Bakelite. Q11.Differentiate between Addition and condensation polymers. Ans:Addition polymer:1)It takes place in unsaturated monomers. 2)Loss of small molecule like water and ammonia does not take place. (Two marks questions,Polymer) Condensation polymer: 1)It takes place in monomers having multi functional groups .2)Loss of small molecules like water and ammonia takes place. Q12.Differentiate between thermoplastic and thermosetting polymer. Ans:. Those polymers which are remoulded into our desire shape on heating and cooling are called thermoplastic.eg.PVC,Teflon ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 201 Those polymers which are not re mouded into our desire shape on heating and cooling are called thermoplastic.eg.Bakelite,Melamine. Q13.How is Dacron obtained? Ans:Dacron is obtained by the condensation of ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. Q14. Give the synthesis of a)Neoprene b)Teflon. Ans:(a)n CH2=C (cl)-CH=CH2 -------(CH2-C(cl)=CH-CH2)n (b) n(CF2=CF2)--------------(-CF2-CF2)n Q15.What do you mean by nylon-6,6? Ans: Nylon6,6 is a condensation polymer and is made up of two different monomer units ie,hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid. (Three marks questions on polymer) Q1.How does the presence of double bond in rubber molecule influence their structure and reactivity? Ans: The natural rubber is a linear1,4-polyisoprene.Double bonds are located between C-2 and C-3 of isoprene units.This configuration about double bond do not allow the chains to come closer for effective attraction due to weak intermolecular forces of attraction.That is why natural rubber has a coiled structure and shows elasticity. Q2.Arrange the following polymers in increasing order of their nter molecular forces. a)PVC,Naturalrubber,Terylene, b)Nylon-6,6,Neoprene,PVC c)Nylon6,Buna-N,Teflon Ans:a)Natural rubber<PVC<Terylene b)Neoprene<PVC<Nylon6,6 c)Buna-N<Teflon<nylon6 Q3.Write the names of monomers used f0r getting the following polymers. a)PVC b)Teflon c)bakelite d)Neoprene e)Polyacrylonitrile f)Buna-S Ans:a) Vinyl chloride b)Tetrafluoroethene c)Phenol and formaldehyde d) 2-chloro 1,3-butadiene,e)Acrylonitrile,f)1,3 Butadiene and styrene Q4.Classify the following as addition and condensation polymer:PHBV,Dacron,Teflon,neoprene,PVC,Bakelite Ans: Addition polymer:Teflon,PVC,Neoprene Condensation polymer:PHBV,Bakelite,Dacron Q5.Discuss and classify the polymers on the basis of inter molecular forces. Ans1)Elastomer: Weakest intermolecular forces eg.Buna-N,Buna-S 2.Fibre; Strong intermolecular force like hydrogen bond eg Nylon-66 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 202 3. Thermoplastic;No cross linkage eg PVC 4. Thermosetting Polymer; numerous cross linkage egBakelite Prepared By Kolkatta Region Chapter 16. Chemistry in everyday life Section A (One Mark Question) 1. Name a drug which is an analgesic and antipyretic? A:aspirin 2. Elucidate the structural differences between biodegradable and non- bio degradable detergent? A:Biodegradable detergents have straight chains Eg:sodium dodecyl benzene sulphonate.Nonbiodegradable detergents have branched chains Eg:sodium(1,3,5,7- tetramethyloctyl)benzene sulphonate. 3. Why are ranitidine and cimetidine better antacids than sodium bicarbonate? A:Sodium bicarbonate if taken in excess makes the stomach alkaline and thus more HCl is released which causes ulcers. Whereas ranitidine prevent the interaction of histamineinthe stomach wall and thus lesser release of HCl. 4. Though saccharin is 550 times sweeter than sugar it is used as a sweetening agent by diabetic patient. Why? A:as it is eliminated in urine and provide less calorie. 5. Distinguish between drugs and medicine. A:Drugs have addictive action but medicine is not addictive in nature. 6. If water contains (CaHCO3)2,out of soap and detergent which one will you choose for cleaning clothes.? A:Calcium ion forms scum, hence detergents are preferred. 7. Why cationic detergent has limited use? A:they are quarternary ammonium salts of amines with acetates, chlorides, bromides. As they have germicidal properties and are expensive so are of limited use. 8. While antacids and antiallergic drugs interfere with the function of histamine. Why do not interfere with the function of each other?Explain. A:As they work on different receptors .eg release of histamine causes allergy and also causes acidity due to release of HCl.But antihistamine removes allergy while antacids remove acidic. 9. Aspirin helps in prevention of heart attack. A:Dueto its anti-blood clotting action. 10. Give One example of drugs used as antiseptics and disinfectants.? A: 0.2% solution of phenol is an antiseptic while its one % solution disinfectant. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 203 FAQ SOLID STATE 1.What is photovoltaic cell? 2.What do you mean by the term Doping? 3.What the term 12 – 16 compounds stand for? 4. What is the number of tetrahedral voids in a ccp structure of solid? 5.Crystalline solids are anisotropic in nature.comment on this statement. 6. What is the percentage efficiency of a solid whose particles are having ccp structure? 7.LiCl crystal appears to be pink in colour .Why? 8.WhenGe is doped with slight amount of In,what type of semiconductor will be formed? 9.Metal deficiency defect with extra anions in interstitial sites can’t be produced in solids.Why? 10. The electrical conductivity of semiconductors increases with increase in temperature but in case of metals conductivity decreases with rise in temp. Why? 11.The window panes seem to be thicker at the bottom in case of old buildings.what can be the reason? 12.Assign the relationship between edge length (a,b,c) and values of α,β and ϒ for tetragonal unit cell. 13.Give an example of solid which can exhibit schottky defect as well as frenkel defect. 14.Atoms of element A are occupying all the octrahedral voids while atoms of B are in 1/4thtetrahedral voids and atoms of C are arranged in hexagonal arrays .what will be the formula of the compound? 15.What is the co-ordination number of a particle in ccp structure? 16.What happens when Na vapours is passed over crystalline NaCl? 17.Ferromagnetic and ferrimagneetic solids on heating converted into paramagnetic in nature.justify the reason. 18.Gjass is assumed to be supercooledliquid.why? 19.Give an example of solid which has its structure as fluorite type structure. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 204 20.Copper is conducting as such while copper sulphate is conducting only in aqueous solution .why? Ans. 1 device which converts sunlight into electrical energy. 2 Introduction of defects in solid by incorporating foreign particles. 3 compounds formed by combination of group 12 elements and group 16 elements.e.gZnS 4 2N or 8 5 a single property differs in different direction in solids. 6 74% 7 presence of F – centre . 8 p – type semiconductor 9 usually anions are larger in size and hence donot fit into interstitial sites 10 kernels makesxibration and creates obstacles in the motion of electrons in case of metals. 11 Glass is supercooled liquid and has floed under the influence of gravity. 12 a = b ≠ c, α =β =ϒ =900 13 AgBr. 14 A2BC2 15 12 16 Appears yellow due to creation of F – centre. 17 Due to randomization of electrons. 18 Flowing tendency under influence of gravity. 19 CaF2 20 Copper is electronic conductor but copper sulphate is ionic conductor so ions are free only in molten or in aqueous state. Prepared by: Ranchi Region ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 205 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. Can you store CuSO4 solution in Zn pot ? 2. Write the name of electrolyte used in mercury cell. 3. What does the negative value of E0cell indicate? 4. What fiows in the internal circuit of the Galvanic cell? 5. What is the EMF of the cell when the cell reaction attains equilibrium ? 6. Why does an aqueous solution of NaCl in electrolysis give H2 gas at cathode not sodium metal? 7. Which type of metal can be used in cathodicprotection of iron against rusting? 8. Why does the conductivity of solution decreases on dilution ? 9.Except hydrogen, write the name of two chemical species which are used in fuel cell. 10.How many coulombs are required for conversion of 1 molFeO into Fe2O3? 11.State the factors which influences the value of cell potential. 12.What is the relationship between the free energy change and EMF of the cell? 13. What are the products of electrolysis of molten NaCl and aqueous solution of NaCl? 14.What is the role of ZnCl2 in dry cell? 15.Rusting of iron is quicker in saline than ordinary water.why? 16.Write one use of Kohlrausch’s law. 17.What is cell constant ? 18.What is the relationship between Molar conductivity of electrolytic solution to its degree of dissociation ? 19.Which type of cell is used in wrist watch? 20.Which acid doesnot react with rust? Ans. 1. No, Zn is more reactive thanCu . ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 206 2. ZnO and KOH 3. Negative value shows reaction is non- spontaneous 4. Ions. 5. E0cell = 0 6. Electrode potential of hydrogen is greater than Na. 7. More reactive metals than Fe. Such as Zn,Mg. 8. Due to less no. of ions oer unit volume. 9. Methane and methanol. 10. 1 faraday 11. Concentration of electrolyte and no. of electron exchanged 12. ∆G0 = -nFE0 13. Na , Cl2 and H2,Cl2 14. Zn2+ ions combines with NH3 to form complex [Zn(NH3)2]2+ 15. Due to presence of salt in saline water. 16. To find the limiting molar conductivity of weak electrolyte 17. The ratio of l/a 18. α =Λcm/Λ0m 19. Mercury cell or Button cell 20. Organic acid. Two marks question:1. Consider the standard electrode potential k+/K = - 2.93 V, Ag+/Ag= 0.80V, Hg2+ /Hg = 0.79V Cr3+/Cr = -0.74V. arrange these metals in their increasing order of reducing power. 2. The conductivity of 0.20M soiution of HCl at 298K is 0.0248 SCm-1.Calculate molar conductivity. 3. How much charge will be required for 1 mol Cu2+ to Cu and for 1 mol MnO4- to Mn2+? 4. Write the Variation of conductivity and Molar conductivity with dilution. 5. Λ0m for NaCl ,HCl and NaAc are 126.4,425.9 and 91.0 SCm2/mol respectively .Calculate Λ0m for acetic acid. 6. A solution of Ni(NO3)2is electrolyzed between Pt electrode using current of 5 amp. For 20 min. What mass of Ni will be deposited at cathode ? 7. State and explain Faraday laws of electrolysis. 8. Write the cell reaction of Lead storage battery. 9. Which cell is more efficient than others.why? 10. Discuss the mechanism of protection of water supply of underground pipe line system. Ans. 1.Ag< Hg<Cr<K 2. Λ0m = K x 1000/M , 124SCm2/mol ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 207 3.Cu2+ + 2e- -- Cu , 2F MnO4- + 8H+5e-Mn2++8H2O, 5F 4. With increase in dilution, conductivity decreases but molar conductivity increases. 5.Λ0m (HAc) =λ0H++λ0Ac =λ0H+ +λ0cl- +λ0Ac- +λ0Na+ - λ0cl- - λ0Na+ = (425.9 +91.0 – 126.4) SCm2/mol = 390.5SCm2/mol 6. Q = IT, 6000C. 58.7 x6000/2 x 96500 = 1.825 gm. 7. Statement and mathematical derivation. 8. at anode Pbso4 +2H2O PbO2 + SO42- + 4H+ 2eAt cathode PbSO4 + 2e-Pb + SO429. Fuel cell, as it has high efficiency and continuous source of energy .pollution free working. 10. More reactive metal is used to follow the principle of sacrificial protection. Three marks question:1. Explain construction and working of standard Hydrogen electrode? 2. What is an electrochemical series? How does it predict the feasibility of a certain redox reaction? 3.The conductivity of an aqueous solution of NaCl in a cell is 92 1 -1 cm resistance offered by this cell is 247.8 . Calculate the cell constant? 4.The measured resistance of a cell containing 7.5 x 10-3 M solution of KCl at 250C was 1005 calculate (a) Specific conductance and (b) Molar conductance of the solution. Cell Constant = 1.25 cm-1 5.Enlist the factors affecting corrosion? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com the 208 Prepared by Ranchi Region SURFACE CHEM. (QUESTION) 1 MARKS 1.What are the physical states of dispersed phase and dispersion medium of froth? 2.What is the cause of Brownian movement among colloidal particles? 3.Arrange the solutions: True solution, colloidal solution, suspension in decreasing order of their particles size? 4.Give an example of micelles system? 5.Why is it necessary to remove CO when ammonia is obtained by Haber’s process? 6.How is adsorption of a gas related to its critical temperature? 7.What is meant by Shape Selective Catalyst? 8.Of the physiorption&chemisorptions, which type of adsorption has higher enthalpy of adsorption? 9.Write down the Example of Positive Sol? 10.Write down the Example of Negative Sol? 2 marks question. 1.(Q.) Define hardy-Schulze rule? 2.(Q.) Define flocculation value? 3.(Q.) What is the difference between a sol and a gel? 4.Q.) What are macromolecular and multimolecular colloids? How are they different from associated colloids? 5Q.)Give any two reasons for the origin of electrical charge on the colloidal particles. 6.(Q.) Differentiate between electrophoresis and electro-osmosis? 7.(Q.) Why lyophilic colloids are called reversible sols while lyophobic sols are called irreversible sols? Give on example of each. 8.(Q.) Explain cleansing action of soap. 9.(Q.) Differentiate between chemisorption and physisorption. 10.(Q.) Why is adsorption always exothermic? Ans. 1 marks. 1.Ans - Dispersed phase is gas, dispersion medium is liquid. 2.Ans - Due to collision between particles 3.Ans – Suspension > colloidal > true solution 4.Ans – Sodium stearate (C17 H35 COO- Na+) 5.Ans- CO acts as poison catalyst for Haber’s process therefore it will lower the activity of solution therefore it is necessary to remove when NH3 obtained by Haber’s process. 6.Ans- Higher the critical temperature of the gas. Greater is the ease of liquefaction. i.e. greater Vander walls forces of attraction and hence large adsorption will occur 7.Ans – On the Shape Selective Catalyst, the rate depends upon pore size of the catalyst and the shape & size of the reactant and products molecules 8.Ans - chemisorptions. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 209 9.Ans – Ferric hydro-oxide sol 10.Ans – Arsenic sulphide. Ans. 2 marks 1.It is the capacity of an electrolyte to cause coagulation of a sol depends upon the number of charges on the ion having charge opposite to that possessed by the sol particles, but is independent of the charges on the ion having similar charge. 2.The number of milli moles of an electrolyte required to bring about the coagulation of one litre of a colloidal solution is called its flocculation value. 3.In a sol, dispersed medium is liquid and dispersed phase is solid. On the other hand, in a gel, dispersion medium is solid and dispersed phase is liquid. 4.Macromolecular colloids:-i)They are molecules of large size. ii) They have lyophobic property. Multimolecular colloids:-i) They are formed by the aggregation of large number of atoms or molecules which have diameter less than 1nm.ii) They have lyophilic property.Associated colloids:-i) they are formed by the aggregation of large number of ions in concentrated solutionii) They contain both lyophilic and lyophobic groups 5.The two reasons are: i) Due to electron capture by sol particles during electro dispersion of metals, due to preferential adsorption of ions from solution ii) Dissociation of colloidal sols. 6.Electrophoresis is the movement of colloidal particles under the influence of an electrical field.Electroosmosis is the movement of dispersion medium molecules under the influence of electric field when colloidal particles are not allowed to move 7.In the lyophilic colloids if the dispersed medium is separated from the dispersion medium the sol can beprepared again by simply remixing with the dispersion medium. So they are called reversible sols. Example: Starch. In lyophobic sols if small amount of electrolyte is added, the sols are readily precipitated and do not give back the colloid by simple addition of the dispersion medium. So they are called irreversible sols. Example: metal sulphides. 8.Action of soap is due to emulsification and micelle formation. Soaps are sodium salt of higher fatty acids like sodium stearate, C17H35COO-Na+ ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 210 The anionic head of stearate ion (COO-) is hydrophobic in nature and has great affinity for water, while the hydrocarbon part (C17H35) is hydrophilic in nature and great affinity for oil,greaseetc.When soap is used in water, the anions (C17H35COO-) form micelle and encapsulate oil or grease inside. These micelle are removed by rinsing with water; while free dirt (from oil or grease) either settle down or are washed away by water. Thus the main function of a soap is to entrap oil or grease with the micelles through emulsification, thereby freeing dirt from grease and oil. 9.Physisorotion.(a)The forces operating are weak van der Waal’s forces. b)The heat of adsorption is low. c)Does not require any activation energy. d)Formsmultimoleculerlayer.Chemisorption: a)Forces acting are similar to those of chemical bonds. b)The heat of adsorption is high. c)Requires activation energy. d)Forms unimolecular layer. 10.Adsorption occurs because of attraction between adsorbate and adsorbent molecules and therefore, energy is always released during adsorption. Hence adsorption is an exothermic process. Prepared by Ranchi Region CHEMICAL KINETICS 1.. For a chemical reaction represented by R→ P the rate of reaction is denoted by –d [R]/dt or +d[P]/dt . State the significance of plus and minus sign. 2. Express the rate of reaction in terms of disappearance of hydrogen and appearance of ammonia in the given reaction. N2(g) + 3 H2 (g) → 2NH3 (g) 3. Why rate of reaction does not remain constant throughout? 4. Write the unit of first order rate constant of a gaseous reaction if the partial pressure of gaseous reactant is given in bar. 5. What will be the order of reaction, if the rate of reaction does not depend on the concentration of any of the reactant. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 211 6. For the elementary step of a chemical reaction : H2 + I2 →2HI rate of reaction →[H2] [I2] What is the (i) molecularity and (ii) order of the reaction. 7.For a chemical reaction A→ B. The rate of the reaction is given as Rate = k [A]n the rate of the above reaction quadruples when the concentration of A is doubled. What is the value of n? 8.Mention one example of zero order reaction. 9. What is the value of the order of reaction of radioactive decay? 10. Express the relation between the half life period of a reactant and initial concentration for a reaction of nth order. 11. A reaction is 50% complete in 2 hours and 75% complete in 4 hours. What is the order of reaction? 12. Suggest an appropriate reason for the observation : “On increasing temperature of the reacting system by 10 degrees, the rate of reaction almost doubles or even sometimes becomes five folds.” 13. For a chemical reaction, activation energy is zero and at 300K rate constant is 5.9 × 10-5s–1, what will be the rate constant at 400K? 14. Two reactions occuring at the same temperature have identical values of Ea. Does this ensure that also they will have the same rate constant? Explain. 15. The rate constant of a reaction is given by the expression k = Ae–Ea/RT Which factor in this expression should register a decrease so that the reaction proceeds rapidly? 16. For a chemical reaction rate constant k = 5.3 × 10-4mol L–1 s–1, what will be the order of reaction? 17.. Write the rate law and order for the following reaction : AB2 + C2→AB2C + C (slow) AB2 + C→AB2C (Fast)] 18.The conversion of molecules X to Y follows second order kinetics.If concentration of Xis increased to 3 times how will it affect the rate of formation of Y. 19.When rate of reaction becomes equal to specific reaction rate. 20.87.5% of the substance disintegrated in 45 minutes(first order reaction) .What is its Half life. Answer 1.(–) sign represents decrease in concentration with time while (+) sign represetns increase in concentration. 2.Rate= -1/3d[H2]/dt rate=+1/2d[NH3]/dt 3.It is because concentration of reactants goes on decreasing with time. 4.s-1 5.. zero order 6. .i)2 ii) 1 7. n=2 8.2NH3 (g)→N2 (g) +3H2(g) (at1130K and Pt as catalyst) 9. First order ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 212 10.t1/2 α 1/[R]0n-1 where n is order of reaction. 11.First order 12.Increasing the temperature of the substance increases the fraction of molecules which collide with energy greater than Ea. 13..5.9 × 10–5 s–1 14No,because the Rate depends on the nature and concentrations of reactants and also pre-exponential factor. 15.Ea should. Deacrease. : Rate = k [AB2] [C2]; Order = 1 + 1 = 2] 16.zero order reaction 17.Rate = k [AB2] [C2]; Order = 1 + 1 = 2] 18.The rate will increase 9 times. 19.When the concentration of reactant is Unity. 20.15 Minutes. Prepared by Ranchi Region Principles and processes of isolation of elements. (1x20) 1. Name chief ore of Iron and Aluminium. 2. At what temperature CO is better reducing agent than carbon? 3. What is meant by gangue? 4. Name the impurities associated with bauxite. 5. What is the basis of zone refining? 6. What is the basis of vapour phase refining? 7. Name the refining method used for high degree of purity of metal. 8. How is copper extracted from low grade copper ore? 9. What is the role of collectors in froth floatation process? 10. Name two metals that occur in nature as oxides. 11. Out of C and CO which is better reducing agent for ZnO? 12. What is the role of cryolite in electrometallurgy of aluminum? 13. Why is Bauxite not heated to remove the impurities of water associated with it? 14. Copper can be extracted by hydrometallurgy but not Zn. Why? 15. What is the role of CaF2 in electrometallurgy of aluminum? 16. Why is CaCO3 added to blast furnace during reduction of Haematite? 17. Though thermodynamically feasible below given reaction, does not happen at room temperature? 3TiO2 +4 Al -------------- 3Ti + 2Al2O3 , ΔG0 = - ve 18. What is the role of graphite rods in electrometallurgy of aluminum? 19. Why is it not advisable to reduce MgO with carbon? 20. What is the % of carbon in cast and pig iron? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 213 Answer: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Haematite (Fe2O3) and Bauxite(Al2O3.2H2O) 673K and Above temperature. Unwanted impurities associated with the ores. SiO2 ,TiO2 and Fe2O3 Impurities are more soluble in melt than the metal. Metal should form volatile compound and it should be easily decomposable. Zone refining. Hydrometallurgy Cu2+ + H2 --------------- 2H+ + Cu 9. Collects lighter sulphide ore in it. 10. Iron and Aluminium. 11. C 12. Reduces the melting point of Alumina. 13. Because aluminium has low melting point and water is chemically associated, so heating causes loss of metal. 14. The E0 of Zn is lower than that of Cu thus Zn can displace Cu2+ ion from its solution. On other hand side to displace Zn from Zn2+ ion, we need a more reactive metal than it. 15. Increases conductivity. 16. Provides flux on decomposition (CaO) 17. Requires activation energy. 18. Acts as anode. 19. Requires very high temperature thus it is not economical. 20. Cast Iron: about 3% pig iron: About 4% (2x10) Q.1 Describe the method of refining of Titanium. Q.2- What is Zone Refining? Explain with example. Q.3 Write the principal of electro-refining. Q.4- Write difference between calcinations and roasting . Q.5- Describe the method of refining of Zirconium. Q.6- Out of C & CO, which is better reducing agent for ZnO? Q.7- The value of Δf G0 for Cr2O3 is -540kJ/mole & that of Al2O3 is -827kJ/mole. Is the reduction of Cr2O3 possible with aluminium? Q.8:- Why copper matte is put in silica lined converter? Q.9- What is meant by term chromatography? Q.10-Why is reduction of metal oxide easier if metal formed is in liquid state at temperature of reduction. Answer: ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 214 A.1- In the Van- Arkel Process, Ti is heated in a stream of I2 forming a volatile complex, which then decomposes at higher temperature to giveTi. Ti + 2I2 → TiI 4 TiI4 → Ti + 2I2 A.2- Zone refining is a method of obtaining a metal in very pure state. It is based on the principal that impurities are more soluble in molten state of metal than solidified state. In this method, a rod of impure metal is moved slowly over circular heater. The portion of the metal being heated melts & forms the molten zone. As this portion of the rod moves out of heater, it solidified while the impurities pass into molten zone. The process is repeated to obtain ultrapure metal and end of rod containing impure metal cutoff. A.3- In this method of purification impure metal is made Anode and pure metal is made the cathode. On passing electricity, pure metal is deposited at the cathode while the impurities dissolve dissolve in solution as anode mud. E.g. electro- refining of copper:At Cathode: - Cu2+ + 2e → Cu At Anode: - Cu → Cu2+ + 2e A.4 (1) Calcination: it carried out in limited/no supply of air but roasting is carried in the presence of air. (2) In roasting sulphide ore is converted to its oxide while in calcination hydroxide, hydrates, carbonates are converted to oxides. A.5- Van Arkel process is used for obtaining ultrapure metal. The impure metal is converted into volatile compound, which then decomposes electrically to get pure metal. At 850K: - Zr impure) + 2 I2 → ZnI4 At 2075K:- ZnI4 → Zr (pure) + 2 I2 A.6- Since free energy of formation of CO from C is lower at temperature above 1120K while that of CO 2 from carbon is lower above 1323K than free energy of formation 0f ZnO. However, the free energy of formation of CO2 from CO is always higher than that of ZnO. Hence, C is better reducing agent of ZnO. A.7- The desired conversion is 4 Al + 2Cr2O3 → 2Al2O3 + 4Cr It is obtained by addition of following two reactions:4Al + 3O2 → 2 Al2O3 Δf G0=-827kJ/mole 2Cr2O3 → 4Cr + 3O2 Δf G0==+ 540 kJ/mole Therefore, Δ G0 for desired reaction is -827+540=-287, as a result reduction is possible. A.8:- Copper matte consists of Cu2S and FeS. When blast of air is passed through molten matte in silica-lined converter, FeS present in matte is oxidized to FeO, which combines with silica to form slag. (i) 2FeS + 3O2→2FeO +2 SO2, (ii) FeO + SiO2 →FeSiO3 (slag), (III) 2Cu2S + 3O2 →2Cu2O+2SO2, (IV) 2Cu2O+2Cu2S→ 6Cu + SO2 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 215 A.9-Chromato means Colour and graphy means writing because the method was first used for separation of coloured substance. It is based on selective distribution of various constituents of a mixture between two phases, a stationary phase and a moving phase. The stationary phase can be either solid or liquid on solid support. A.10- The entropy of a substance is higher in liquid state than solid state. In the reduction of metal oxide, the entropy change will be positive if metal formed is in liquid state. Thus, the value of Δ G0 becomes negative and reduction occurs easily. (3x10) Q.1- Explain the following:(i) Zinc but not copper is used for recovery of Ag from the complex [Ag(CN)2]-. (ii) Partial roasting of sulphide ore is done in the metallurgy of copper. (iii) Extraction of Cu from pyrites is difficult than that from its oxide ore through reduction. The reduction of metal sulphide does not have large negative value. Q.2- Explain the role of each of the following in the extraction of metals from their ores. (1) CO in the extraction of Nickel (2) Zn in the extraction of Ag (3)Silica in the extraction of Copper. A.3- Describe the principle behind each of the following processes(A)Vapour phase refining of a metal (B) Electrolytic refining (C) Froth floatation process Q.4- Describe the principles of extraction of Zinc from zinc blende . Q.5- Predict the modes of occurrence of the following three types of metals: (1) Highly reactive metals (2) Moderately metals (3) Noble metals Q6. What happens when: (a) Cinnabar is roasted (b) Silver sulphide is shaken with a dilute solution of NaCN (c) HgO is heated Q7. What is Ellingham’s diagram? What is its use? Q8. What is the role of depressant in froth floatation process? Q9. Define following terms: (a)Roasting (B) Calcination (C) Smelting Q10. How are metals used as semiconductors refined? What is the principle of method used? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 216 Answer: A.1- (i) Zn is more powerful reducing agent in comparison to copper.Zn is also cheaper than Cu. (ii) Partial roasting of sulphide ore forms some oxide. This oxide then reacts with remaining sulphide ore to give copper i.e. self-reduction occurs. 2Cu2S + 3O2 →2Cu2O+2SO2, 2Cu2O+2Cu2S→ 6Cu + SO2 . (iii) Though carbon is good reducing agent for oxide but it is poor reducing agent for sulphides. A2. (1) Forms volatile compound with Ni i.e. Ni(CO)4 (2) Leaching of the Ag. (3) Acts as flux and reacts with FeO to form FeSiO3(Slag) A3. (A) Metal should form volatile compound and it should be easily decomposable. (B) Less reactive metals undergo reduction at cathode when electricity is passed in the aqueous solution of their salts making impure metal as anode and pure metal as cathode. A4. Chief ore of Zinc: ZnS 1. Enrichment: froth floatation process 2. Roasting: 2ZnS + 3O2 ---- 2ZnO + 2SO2 3. Reduction: ZnO + C ----- Zn + CO 4. Refining: Distillation A.5 (1) Highly reactive metals- oxides and halides (2) Moderately metals- Sulphide and oxides and carbonates (3) Noble metals- pure form/Native state A6. (a) 2HgS + 3O2 ---- 2HgO + 2SO2 (b) Ag2S +NaCN ------ Na [Ag(CN)2] (c) 2HgO ------------- 2Hg + O2 A.7 The plots between ΔG0 of formation of oxides of elements against temperature are called Ellingham’s diagram. They are useful in deciding the suitable reducing agent in the metallurgical processes. A.8 They are used to separate two sulphide ores. For example PbS and ZnS are separated by NaCN as depressant.NaCN selectively prevents ZnS from coming to the froth. A9. (a)Roasting : Heating of Sulphide ores in the presence of air to obtain its oxide ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 217 (B) Calcination : Heating of metal carbonates/hydroxides/hydrates to obtain oxides in absence/limited supply of air (C) Smelting : Reduction of metal oxide to its metal using carbon as reducing agent. A10. Zone refining. Impurities are more soluble in melt than the metal. 5- marks Q.1- Explain the method for obtaining pig iron from magnetite. A.1- Extraction of iron from Magnetite takes place in following steps:(i) Concentration of ore: - It is done by Gravity separation followed by magnetic separation process. (ii) Calcination: - It involve heating when the volatile matter escapes leaving behind metal oxide. Fe2O3.xH2O→ Fe2O3 + xH2O . (iii) Roasting: - It involves heating of ore in presence of air, thus moisture,CO2,SO2, As2O3 removed And FeO oxidized to Fe2O3. (iv) Smelting of roasted ore: - A mixture of ore, coke & CaCO3 is smelted in long BLAST FURNACE. Following reaction takes place at different temperature zones:(i) Zone of reduction: - Temperature range 250oC-700oC Fe2O3+3CO 2FeO+3CO2 Fe3O4+4CO 3FeO+ 4CO2 FeO +CO Fe+ CO2 (ii) Zone of slag formation:- Temperature range 800oC-1000oC CaCO3CaO+CO2 CaO+SiO2 CaSiO3, P4O10+10C4P+10CO, SiO2+2C Si+2CO, MnO2+2C Mn+2CO (iii) Zone of fusion:- Temperature range 1150oC-1350oC CO2 + C 2CO (iv) Zone of fusion:- Temperature range 1450oC-1950oC C +O2CO2 Thus, Pig iron is obtained from Blast Furnace. Q.2- Name the principle ore of aluminium and describe how Al is extracted from its ore. Ans2Step:-1 Bauxite is treated with NaOH .Following reaction takes place:Al2O3 +2NaOH + 3 H2O2 Na [Al(OH)4] and impurities of Fe2O3,TiO2&SiO2 are removed . Na [Al(OH)4] ,then reacts with CO2 then pure Alumina is obtained. Na [Al(OH)4] + 2CO2 → Al2O3.xH2O + 2NaHCO3 Step:-2 Electrolytic reduction of pure alumina takes place in iron box (cathode) with cryolite (Na3AlF6) & fluorspar CaF2.Graphide rods act as anode. Following reactions take place:At cathode:- Al3+ + 3e→ Al, At Anode:- 2O2- →O2 + By this process 98.8% pure Aluminum is obtained. Q.3-Given is the Ellingham diagram. With the help of this diagram answer the following questions. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 218 Q1. Which of Al and Mg is better reducing agent below and above 1673K? A: Below 1673 K – Mg and above 1673 K – Al Q2. Which of C and CO can reduce MgOat 2000K temperature? A: CO Q3.Suggest a condition under which magnesium could reduce alumina. A: Below the temperature 1600K P - BLOCK ELEMENTS 1.Q.Why does NO2 dimerise? 2.Q.Give chemical reactions involved in brown ring test to confirm nitrates. 3. Q.Give the structure of nitric acid. 4. Q.Give equations in each step of oswald's process 5.Q.Give flow chart for preparation of ammonia by Haber's process. 6.Q.Explain preparation of nitrogen. 7.Q. Why do chromium and aluminium not react with the most oxidizing agent? 8.Q. Name the oxides of nitrogen and give oxidation number of each oxide. 9.Q. Give conditions which favors formation of ammonia as it is a reversible reaction. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 219 10.Q. Draw the structures of white phosphorus and red phosphorus. Which one of these two types of phosphorus is more reactive and why? 11.Q.Whichoxoacids of phosphorus are reducing in nature? 12.Q.Why is phosphorus acid diprotic and phosphoric acid triproticinpite 3 hydrogens in both? 13.Q.Give the structure of oxy acids of phosphorus and list the anions formed. 14.Q.Why does PCl3 fume in moisture? 15 Q.Show that PH3 is basic in nature. 16 Q.Give reason that NCl5 is not formed but PCl5 is formed. .17.Show that hydrogen peroxide behaves both as an oxidizing and reducing agent. 18.Q.What is oleum? Draw its structure. 19.Q.What happens when sulphur is passed through conc. H2SO4 solution and SO2 is passed through an aqueous solution of Fe(III) salt? 20. Q.Whyare halogens coloured? P – BLOCK ANS. 1.NO2 contains odd number of valence electrons. It behaves as an odd electron molecule and therefore undergoes dimerisation to form stable N2O4 molecule with even number of electrons. 2. 3 . 4. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 220 5. 6.Air is liquefied, and the oxygen which is about 20.9% gets boiled off at -183oC, leaving liquid nitrogen behind, which boils at -196oC .This process is known as Fractional distillation. Nitrogen can also be made by heating NaN3 to 300 degrees C. Annual worldwide production is around 44,000,000 tons. 7.These elements form a passive layer of oxide on the surface and prevent the metal to react with nitric acid. 8.The common oxides of nitrogen include examples of nitrogen with every oxidation number from +1 to +5 N as +1: N2O N as +2: NO N as +3: N2O3 N as +4: NO2 N as +5: N2O5 9.The reaction is reversible. Only about 15-20 % of the reactants are converted into products.The forward reaction) is exothermic. Amount of product or yield from a reversible reaction depends on temperature, pressure and catalyst Decreasing the temperature favors exothermic reactions. Increasing the pressure favors smaller volume. Using a catalyst gives the equilibrium conditions more quickly. 10. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 221 White phosphorus is less stable and therefore, more reactive than the red phosphorus under normal conditions because of angular strain in the P4 molecule where the angles are 60° only. 11. (1x20) 1. Which of NH3 and H3O+ has higher bond angle and why? 2. Which of PH4I and PH4Cl is more stable and why? 3. What is the basicity of H3PO3 and H3PO4? 4. NH3 is easily liquefiable than PH3? 5. Which of NH3 and PH3 is stronger Lewis base and why? 6. Why does NO2 dimerise? 7. N2O4 is colourless but NO2 is brown in colour? 8. Write the products of hydrolysis of ClF3. 9. Why is S2 paramagnetic? 10. Why does not SO3 disproportionate? 11. Why Cl2 bleaches permanently but SO2 temporarily? 12. Why is He used in observation balloons? 13. Why is SF6 resistant to hydrolysis? 14. What is the geometry and shape of ClF5? 15. Why is ICl more reactive than I2? 16. Arrange following in increasing order of their reactivity. IF, F2 and I2 17. Xe is more reactive than He. Why? 18. Does the hydrolysis of XeF6 lead to a redox reaction? Why? 19. H2S is less soluble in water than H2Se .Why? 20. Trimethylamine is more basic than tri silylamine. Why? Answer:(20x1) 1. H3O+because central atom has higher electronegativity thus it pulls bond pairs of electrons towards itself and bp-bp repulsion increases. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 222 2. PH4 I is more stable PH4+ is bigger cation and I- is bigger anion so offers effective crystal packing and has larger lattice enthalpy. 3. 2 and 3 4. Due to intermolecular H- bonding in NH3. 5. NH3 because of its smaller size it has greater charge density on nitrogen. 6. In NO2, there is an odd electron. 7. In N2O4 there is no unpaired electron. 8. ClF3 + 2H2O ----- 3HF + HClO2 9. Due to presence of unpaired electrons on anti-bonding orbitals. 10. Sulphur is in highest oxidation state. 11. Cl2 bleaches by oxidation but SO2 bleaches by reduction. 12. He is very light. 13. SF6 if sterically protected. 14. Geometry-Octahedral and shape: square pyramidal 15. ICl has low bond dissociation enthalpy. 16. I2> F2>IF 17. Less I.E. 18. No, because the oxidation state of Xe does not change. 19. H2Se has stronger Vander wall’s forces with water. 20. Due to presence of vacant of d- orbitals in Si, the pair of electron lying on N disperses via dπ-pπ back bonding. (10x2) 1.Give reason for the following(A) Phosphorus is reactive but Nitrogen is much stable. (B) Nitrogen is linear but Phosphorus is tetrahedral. 2. Explain why? (A)Nitrogen has stronger tendency of multiple bonding than that of Phosphorus. (B)NCl5 does not exist but PCl5 exists. 3. Explain the chemistry of ring test of nitrate ion. 4. Draw the structures of following using VSEPR Model XeO2F2 and XeO3 5. Complete the following reactions: (A) Ca3P2 + H2O------- (B) Cu + Conc. HNO3 ------- 6. Give reason for the following: (a)NO2 has net dipole moment but N2O4 does not have? (b)Phosphorus has greater catenation tendency than Nitrogen? 7. Explain following: ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 223 (1)Interhalogens are covalent, diamagnetic. (2)I2 is soluble in aqueous KI. 8. Arrange following according to the property shown against each: (a) HClO, HClO3, HClO4, HClO2 ------ Increasing order of acidity (b)PH3, NH3, SbH3, AsH3, BiH3 ------- Decreasing order of basicity 9. Arrange following according to the property shown against each: (a) I2, F2, Cl2, Br2 ---------Increasing order ease of liquefaction (b)ClO, Cl2O3, Cl2O5, Cl2O7 ------------ Increasing acidity strength 10. Complete the following reactions: (1)P4 + NaOH + H2O --------- (2)NaCl+ MnO2 + H2SO4 ---------- Answer (10x2) 1. (A)N2 has much higher bond enthalpy.. (B)In N2, N is sp-hybridized but in P4, P is sp3- hybridized. 2. (A)N- has three unpaired electrons in p-orbital, has high effective nuclear charge and small atomic size to undergo greater overlapping of the orbitals. (B)N does not have d- orbitals. 3. 3Fe2+ + NO3-1 + 4H+ ----------- 3Fe3+ + NO + 2H2O [Fe (H2O) 6]2+ + NO ---------[ Fe(H2O)5(NO)]2+ + H2O (brown ring) 4. Each correct structure one mark 5. (A) Ca3P2 + 6H2O-------3Ca(OH)2 + 2PH3 (B) Cu + 4HNO3 -------Cu(NO3)2 + 2NO2 + 2H2O 6. (a)In NO2 there is an odd electron on nitrogen. (b)P-P bond is stronger than N-N bond. 7. (1)Because they have high electronegativity and paired electrons. (2)It forms KI3 8. (a) HClO, HClO2, HClO3, HClO4 (b)NH3, PH3, AsH3, SbH3, BiH3 9. Arrange following according to the property shown against each: (a) F2, Cl2, Br2, I2 (b)ClO, Cl2O3, Cl2O5, Cl2O7 10. Complete the following reactions: (1)P4 + 3NaOH + 3H2O --------- PH3 + 3NaH2PO2 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 224 (2)4NaCl + MnO2 + 4H2SO4 ---------- MnCl2 + 4NaHSO4 + Cl2 + 2H2O (10x3) 1. Give reason for the followingi) NO2 is acidic oxide but NO is neutral? ii) NH3 has greater tendency of complex formation than PH3? iii) PH3 dissolves in HI. Why? 2. Explain for the followinga) H3PO3 shows disproportionation reactions? b) PCl5 in solid state exists as an ionic compound? c) BiCl5 is a strong oxidizing agent? 3. Explain the structure of the following compounds using VSEPR theory a) PCl6-1 b) SF4 c) ICl2-1 4.Give the comparative account of the chemistry of carbon and silicon with regard to their: [i] property of catenation [ii] stability of hydrides and oxides 5.Account for the following: [i] Ammonia has higher boiling point than phosphine [ii] Trimethyl ammine is pyramidal and trisilyl ammine is planar. [iii] Ammonia is stronger base than phosphine. 6.Describe the following about halogen family: [i] Oxidising power [ii] Relative acidic strength of their hydrides [iii] Relative reducing strength of their hydrides. 7.Give reason for the following observations. [i] Noble gases are mostly chemicallly inert [ii] Nitrogen does not form pentahalide [iii] Bismuth is a strong oxidising agent in pentavalent state 8. Arrange following according to the property shown against each: a)NO2, P2O3, N2O5, P2O5, As2O3, Bi2O3 --- Increasing acidity strength b)PH3, NH3, SbH3, AsH3, BiH3 ----- Decreasing order of thermal stability c)Xe, He, Ne, Kr, Ar, ---------Increasing order ease of liquefaction 9. Complete following reactions: 1)NH3 + AgCl --------- 2)XeF2 + H2O ---------- 3)NaNO2 + NH4Cl ------- 10. How does ozone reacts with following i) NO ii) PbS iii) Aq. KI ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 225 Answer(10x3) 1. i) More oxygen contents in NO2 than NO. ii) NH3 is stronger Lewis base iii) PH3 is a base and HI is acid so gives PH4I 2. a) The O.S. of P is +3 so it can undergo oxidation as well as reduction. b) It exists as [PCl4]+[PCl6]c) Bi is in +5 oxidation state but its stable O.S. is +3 3. correct structure 4. [i] P- has greater catenation tendency than N [ii] The oxides and hydrides of N are more stable than that of P 5. [i] Due to inter molecular H- bonding [ii] presence of d- orbitals in Si can allow dπ-pπ back bonding thereby dispersing lone pair. [iii] The lone pair lying on N in NH3 can be easily donated due to greater charge density on nitrogen.. 6. [i] F2> Cl2> Br2> I2 [ii] HI>HBr>HCl>HF [iii] HI>HBr>HCl>HF 7.Give reason for the following observations. [i] They have very high I.E. and completed octet [ii] Absence of d- orbitals [iii] Inert pair effect 8. a) N2O5,NO2, P2O5,P2O3, As2O3, Bi2O3 b)NH3,PH3,AsH3, SbH3, BiH3 c), He, Ne, Ar, Kr,Xe 9. 1) 2NH3 +AgCl --------- [Ag(NH3)2]Cl 2)2XeF2 + 2H2O ----------2 Xe + 4HF + O2 3)NaNO2 + NH4Cl -------NaCl + N2+ 2H2O 10. How does ozone reacts with following i) NO + O3 ------- NO2 + O2 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 226 ii) PbS +4 O3 ------- PbSO4+ 4O2 iii) Aq. 2KI + O3+ H2O----- 2KOH + I2 +O2 (5x5) 1. A white coloured salt (A) on treatment with conc. H2SO4 gives a pungent smelling gas (B) which turns moist blue litmus to red. The gas (B) oxidizes in presence of MnO2 to yield a greenish yellow gas (C). The gas (C) is used in disinfecting drinking water and decolourising the wood pulp in paper industries. Identify A , B and C and write necessary equations. 2 .Give reason for the following observations. a) HF is weakest acid and HI is strongest. b)Fluorides of Xe undergo hydrolysis readily c)Oxygen is diatomic but S is octatomic? d)Reaction of NaBr and H2SO4 does not form HBr but it forms Br2 gas. e)HF is liquid but HCl is a gas. 3 .Arrange following according to the property shown against each: a) HClO, HClO3, HClO4, HClO2 ------ Increasing order of acidity b) HClO, HBrO, HIO, HFO -------Increasing order of acidity c) F2, O2, Cl2, Br2 ------- ------------ Increasing order of oxidizing tendency d) PH3, NH3, SbH3, AsH3, BiH3 -------- Decreasing order of bond angle e) I2, F2, Cl2, Br2 ---------Increasing order of b.p. 4. A element (X) on heating with Conc. NaOH yields a poisonous gas(Y) and spontaneously catches fire. The gas (Y) reacts with Aq.HgCl2 to form precipitate (Z). Identify X , Y and Z and write necessary equations. 5 . Draw the structure of the following compounds using VSEPR theory. XeF6,XeOF4, XeO3,PCl3,White Phosphorus (P4) Answer: 5 Marks 1. (A)=NaCl (B)=HCl (C)= Cl2 4NaCl (A)+ 4H2SO4 ---------- NaHSO4 + HCl(B) 4HCl + MnO2----- MnCl2+ 2H20 + Cl2(C) 2 . a) Bond dissociation enthalpy of HF is more than HI b)Presence of vacant d- orbitals in Xe c)O=O is stronger than S=S d)Because H2SO4 oxidisesHBr to Br2 e)Presence of intermolecular H- bonding in HF. 3. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 227 a) HClO, HClO2, HClO3, HClO4 b) HFO,HClO,HBrO, HIO c) Cl2, Br2 ,O2,F2 d) NH3,PH3, AsH3, SbH3,BiH3 e) F2, Cl2, Br2,I2 4 X= P4 Y= PH3 Z= Hg3P2 P4 + 3NaOH + 3H2O --------- PH3 + 3NaH2PO2 2 PH3 + 3 HgCl2 -----------Hg3P2 + 6 HCl 5. Structures 12. 13. OXYACID OXYANION ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 228 14. 15.PH3 has a lone pair of electron and readily reacts with acids like HI and forms. 16.Nitrogen does not have usable d orbitals and cannot expand its octet. Phosphorus can expand its valence shell to hold more than eight electrons, but nitrogen cannot. PH3+ HI →PH4I. 17.It produces oxygen and acts as a oxidizing agent in both acid and basic medium: Mn2+ + H2O2→ Mn4+ + 2OHAs a reducing agent HOCl + H2O2→ H2O + Cl- + O2 18.Oleum is a oxoacid of sulphur and is a pyrosulphuric acid.- H2S2O7 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 229 19. 20.Absorption of radiations in visible region by halogen atoms, results in the excitation of outer electrons to higher energy level. By absorbing radiation of different wavelength, they display different colours. For example, F2 has yellow, Cl2 has greenish yellow colour, Br2 has red colour and I2 has violet colour. Prepared By : Silchar Region d &f BLOCK ELEMENTS 1 MARK QUESTIONS (1-20) 1. Zn, Cd & Hg are not treated as true transition elements. Why? 2. Cu & Ag are transition metals although they have completely filled d-orbitals. Why? 3. Why some d-block elements have irregular (exceptional) electronic configuration? 4. Atomic size does not change appreciably in a row of transition metals. Why? 5. Transition elements have variable oxidation states. Why? 6. Transition metals have high melting and boiling points. Why? 7. Transition metals have high enthalpy of atomization. Why? 8. Transition metals show catalytic properties .Why? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 230 9. Transition metals and their salts are generally colored .Why? 10. Why transition metals form coordination compounds? 11. Why transition metals form alloys? 12. Transition metals form interstial compounds. Why? 13. Zn, Cd & Hg have low boiling points and Hg is liquid. Why? 14. Transition metals and many of their compounds show paramagnetic behavior .Why? 15. d1 configuration is very unstable in ions .Why? 16. Cr2+ is strongly reducing while Mn3+ is strongly oxidizing. Why? 17. Cobalt(II) is stable in aqueous solution but in presence of complexing agents it gets oxidized. Why? 18. Mn2+ compounds are more stable than Fe2+ .Why? 19. Fe3+ is stable compared to Fe2+.Why? 20. Transition metals exhibit highest oxidation states in oxides and fluorides. Why? 2 Mark Questions (21-30) 21`.The highest oxidation state of transition metal is exhibited in oxoanions For the first row transition metals the Eo values are: Eo V Cr Mn Fe (M2+/M) –1.18 – 0.91 –1.18 – 0.44 Co – 0.28 Ni – 0.25 Cu +0.34 Explain the irregularity in the above values.? 22. Why is the E0 value for the Mn3+/Mn2+ couple much more positive than that for Cr3+/Cr2+ or Fe3+/Fe2+? Explain.? 23. In the series Sc (Z = 21) to Zn (Z = 30), the enthalpy of atomization of zinc is the lowest.Why? 24. Explain why Cu+ ion is not stable in aqueous solutions? 25 Actinoid contractions are greater from element to element than lanthanoid contraction.Why? 26. K2PtCl6 is well known compound and corresponding Ni4+ Salt isunknown . Whereas Ni+2 is more stable than Pt+2. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 231 27. Why KMnO4 is bright in colour ? 28. CrO is basic but Cr2O3 is amphoteric? 29. In the titration of Fe2+ ions with KMnO4 in acidic medium, why dil. H2SO4 is used and not dilHCl. 30. K2Cr2O7 is used as Primary Standard in volumetric analysis.Why? 3 MARKS QUESTIONS(31-40) 31. (a) Although Cu+ has configuration 3 d10 4 s0 (stable) and Cu2+ has configuration 3 d9 (unstable configuration) still Cu2+ compounds are more stable than Cu+. (b) Titanium (IV) is more stable than Ti (III) or Ti (II). 32. The actinoids exhibit more number of oxidation states and give their common oxidation states. 33. (a) Give reason CrO3 is an acid anhydride. (b) Give the structure of CrO5. 34. Why is Cr2+ reducing and Mn3+ oxidising when both have d4 configuration ? 35. .(a) In MnO4– ion all the bonds formed between Mn and Oxygen are covalent. Give reason. (b) Beside + 3 oxidation state Terbium Tb also shows + 4 oxidation state. (Atomic no. = 65) 36. (a) Highest manganese flouride is MnF4 whereas the highest oxide is Mn2O7. (b) Copper can not librate H2 from dil acids : Note : Although only oxidising acids (HNO3 and hot conc. H2SO4) react with Cu light. 37. A metal which is strongly attracted by a magnet is attacked slowly by the HCl liberating a gas and producing a blue solution. The addition of water to this solution causes it to turn pink, the metal is 38.Comment on the statement that elements of the first transition series possess many properties different from those of heavier transition metal ? 39. The paramagnetic character in 3d-transition series elements increases upto Mn and then decreases. Explain why? 40.Why are Mn2+ compounds more stable than Fe2+ compounds towards oxidation to +3 state? 5 MARK QUESTIONS(41-45) 41.A wellknown orange crystalline compound (A) when burnt impart violet colour to flame. (A) on treating (B) and conc. H2SO4 gives red gas (C) which gives red yellow solution (D) with alkaline water. (D) on treating with acetic acid and lead acetate gives yellow p. pt. (E). (B) sublimes on heating. Also on heating (B) with NaOH gas (F) is formed which gives white fumes with HCl. What are (A) to (F) ? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 232 42. Give reasons for the following: (a) Among the lanthanoids, Ce(III) is easily oxidised to Ce(IV). (b) Fe3+ / Fe2+ redox couple has less positive electrode potential than Mn3+ / Mn2+couple. (c) The second and third transition series elements have almost similar atomic radii. (d) Transition metals and many of their compounds show paramagnetic behaviour. (e) KMnO4 titration is not carried out using HCl as acid medium. (iii) The transition metals generally form coloured compounds. 43. a) A Complex having scandium in +3 oxidation-state was found colorless why? b) Show the splitting of d, orbitals of Ti in [Ti(H2O)6]+3 c) [Ti(H2O)6]+3 is coloured why? d) Differentiate between. Lanthanides and actinides w.r t. (i) Oxidation state (ii) electronic configuration 44. 1. Mixed oxide of iron and Chromium FeO.Cr2O3 is fused with Sodium Carbonate in the presence of air to form yellow compound (A). On acidification Compound (A) forms an orange coloured compound (B) which is an oxidizing agent i) Identify A and B. ii) Write balanced chemical equation for each 2. Among the lanthanoids, Ce(III) is easily oxidised to Ce(IV). 3.Fe3+ / Fe2+ redox couple has less positive electrode potential than Mn3+ / Mn2+couple. 45. (I) Account for the following : (a) Zirconium & Hafnium exhibit almost similar properties (b) Zinc salts are white while Cu2+ salts are coloured (c) The transition elements have high enthalpies of atomization. (d) Among transition metals, the highest oxidation state is exhibited in oxoanins of a metal. (e) Zn2+ salts are white while Cu2+ salts are blue. D & f BLOCK ELEMENTS ANSWERS 1. Because they have completely filled d-orbitals in their atomic as well as stable ionic state. 2. Cu2+& Ag2+ have (n-1)d9 4s0 configuration. 3. Due to very small energy difference between (n-1) d & ns sub-shell. 4. Along the rows nuclear charge increases but the penultimate d-sub shell has poor shielding effect so atomic and ionic size remain almost same. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 233 5. Due to very small energy difference between (n-1)d & ns sub-shell electrons from both the sub-shell take part in bonding . 6. A large number of unpaired electrons take part in bonding so they have very strong metallic bonds and hence high m.pt & b.pt 7. A large number of unpaired electrons take part in bonding so they have very strong metallic bonds and hence high enthalpy of atomization 8. Because they have variable oxidation states and hence can form different intermediates. They also provide large surface area. 9. Because they have partially filled d-sub shell and hence d-d electron transition takes place when they absorb radiations from visible region and transmit complementary colors. 10. Because they have large number of vacant orbitals in (n-1)d, ns, np & ns sub shells so they can accept electron pairs from ligands 11. They have comparable atomic size and hence can be mixed uniformly. 12. Because small atoms like H, C, N etc can be entrapped in their metallic crystals. 13. They have full filled 3d-orbitals and no electrons from d-orbitals are taking part in metallic bonding so they have weak metallic bonding. Due to larger atomic size Hg is liquid. 14. Because they have unpaired electrons. 15. Because by losing one electron they get extra stability. 16. E0 value for Cr3+/Cr2+ is negative but that of Mn3+/Mn2+ is positive so Cr2+ can lose electron to form Cr3+ while Mn3+ accepts electron to form Mn2+. In case of Cr d4 to d3 occurs for Cr2+ to Cr3+. d3 is stable. 17. Oxidation state changes from +2 to +3 because in presence of ligands d-orbitals split up into t2g and eg having the stable configuration t2g6 eg0. 18. Mn2+ has half-filled d-orbitals i.e 3d5 4s0 configuration. 19. Due to half-filled configuration i.e 3d5 4s0 configuration. 20. Because of small size and high electronegativity oxygen or fluorine can oxidise the metal to its highest oxidation state. 2 Marks(21-30) ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 234 21.The E0 (M2+/M) values are not regular which can be explained from the irregular variation of ionisation enthalpies (Δ i H 1 + Δ i H 2) and also the sublimation enthalpies which are relatively much less for manganese and vanadium. 22. Much larger third ionisation energy of Mn (where the required change is d5 to d4) is mainly responsible for this. This also explains why the +3 state of Mn is of little importance. 23. In the formation of metallic bonds, no electrons from 3d-orbitals are involved in case of zinc, while in all other metals of the 3d series, electrons from the d-orbitals are always involved in the formation of metallic bonds. 24. Cu+ in aqueous solution undergoes disproportionation, i.e., 2Cu+(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + Cu(s) The E0 value for this is favorable. 25. The 5f electrons are more effectively shielded from nuclear charge. In other words the 5f electrons themselves provide poor shielding from element to element in the series. 26. The stability of the compounds depends upon sum of ionization enthalpies: IE1 + IE2< IE1 + IE2 in Ni in Pt Ni2+ is stable than Pt+2. IE1 + IE2 + IE3 + IE4< IE1 + IE2 + IE3 + IE4 in Pt4+ Pt4+ is stable, in Ni4+ K2PtCl6 is well known compound. 27. It is due to charge transfer. In MnO4– an electron is momentarily transferred from O to the metal, thus momentarily O2– is changed to O– and reducing the oxidation state of the metal from Mn (VII) to Mn (VI). 28. CrO Cr2O3 O. N. +2 +3 Higher the oxidation states higher the acidity. In lower oxidation state some of valence e– of the metal atom are not involved in bonding, can donate e– and behave as base. In higher oxidation state e– are involved in bonding and are not available, rather it can accept e– and behave as an acid. 29. KMnO4 produce Cl2 KMnO4 in presence of dil. HCl acts as oxidising agent, Oxygen produced is used up partly for oxidation of HCl : 2 KMnO4 + 3 H2SO4 ——— K2SO4 + 2 MnSO4 + 3 H2O + 5 (O) ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 235 2 KMnO4 + 4 HCl ——— 2 KCl + 2 MnCl2 + 2 H2O + 6 (O) 2 HCl + (O) ——— H2O + Cl2 30. K2Cr2O7 is not much soluble in cold water. However, it is obtained in pure state and is not Hygroscopic in nature. 3 marks questions(31-40) 31.(a) It is due to much more (–) (b) Hydration H– of Cu2+ (aq) than Cu+, which is more than compensates for the II ionization enthalpy of Cu. 22Ti = 3 d² 4 s² TiIII = 3 d¹ TiII = 3 d² TiIV = 3 d° most stable configuration. TiIV is more stable than TiIII and TiII. 32.As the distance between the nucleus and 5 f orbitals (actinoides) is more than the distance between the nucleus and 4 f (lanthanoids) hence the hold of the nucleus on valence electrons decrease in actinoids. For this reason the actinoids exhibit more number of oxidation states in general. Common O. N. exhibited are + 3 (similar to Canthanoids) besides + 3 state, also show + 4, maximum oxidation state in middle of series i. e. Pu and Np. have anoidation state upto + 7. 33. (a) CrO3 + H2O ——— H2CrO4 i. e. CrO3 is formed by less of one H2O molecule from chromic acid : – H2O H2CrO4 ——— CrO3 (b) O O Cr O O O 34.Cr2+ is reducing as its configuration changes from d4 to d3, the d3 has half-filled t2g level. n the other hand, the change from Mn2+ to Mn3+ results in the half filled (dS) configuration which has extra stability. Cr2+ = 3 d4 4 s0 Mn3+ = 3 d4 4 s0 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 236 Mn2+ = 3 d5 4 s0 Cr3+ = 3 d3 4 s0 Cr3+ = 3 d3 4 s0 d5 have half-filled half-filled extra t2g level. stable. 35. (a) In MnO4–, O. N. is + 7, but it is not possible to lose 7 electrons because very high energy is required to remove 7 electrons. Therefore it forms covalent bonds. (b) Tb = 65E. C. is 4 f9 6 s2 Tb4+ = 4 f7 6 s0 half-filled f-orbital stable. after losing 4 e– it attains half-filled orbital. 36. (a) The ability of oxygen to form multiple bonds to metals, explain its superiority to show higher oxidation state with metal. (b) Positive E° value (+ O – 34 Volt) accounts for its inability to liberate H2 from acids. The high energy to transform Cu (s) to Cu2+ (aq) is not balanced by its Hydration enthalpy. Note : For (b) Consult Fig. 8.4 in NCERT 37.The metal is CO CO + 2 HCl ——— COCl2 + H2 blue solution COCl2 in solution is [CO (H2O)6]2+ blue pink 38.The following points justify that the given statement is true:(i) Ionization enthalpies of heavier transition elements are higher than the elements of 3d series. Consequently, heavier transition elements are less reactive in comparison to 3d-elements. (ii) Melting points of heavier transition elements are higher than 3d-elements. (iii) Higher oxidation states of heavier transition elements are stable whereas lower oxidation states are stable in 3d-elements. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 237 39. In the 3d-transition series as we move from Sc (21) to Mn (25) the number of unpaired electrons increases and hence paramagnetic character increases. After Mn, the pairing of electrons in the d-orbital starts and the number of unpaired electrons decreases and hence, paramagnetic character decreases. 40.The electronic configuration of Mn2+ is [Ar] 3d5, i.e. all five d-orbitals are singly occupied. Thus this is stable electronic configuration and further loss of electron requires high energy .on other hand side the electronic configuration of Fe2+is [Ar] 3d6, i.e. Loss of one electron requires low energy. 5 MARK QUESTIONS(41-45) 41.(i) K2Cr2O7 + 4 NH4Cl + 3 H2SO4 ——— K2SO4 +2 Cr2O2Cl2 + 2 (NH4)2SO4 + 3 H2O (A) (B) Sublime Chromyl Chloride red gas(C) (ii) CrO2Cl2 + 4 NaOH ——— Na2CrO4 + 2 NaCl +2 H2O (D) Yellow Soln. (iii) Na2CrO4 + (CH3COO)2 Pb ——— PbCrO4 + 2 CH3COONa Yellow p. pt. (E) 42. (a) vacant (n-2) f subshell in Ce(IV). (b) extra stability of Fe3+ than Mn3+ ion (c) Due to lanthanoid contraction (d)they both will be reacting. (e) unpaired d –electrons and d-d transitions. 43. a) Due to absence of unpaired electron in d orbtal b) Correct splitting of d orbitals in octahesral feild into t2g and eg c) Due to presence of single electron d) lathanoid Actinoid (i) Shows common It shows common oxidation state of +3+4+5 oxidation state +3 (ii) 4 f arefielled 5f are filled 44.(1) A= Na2CrO4 ; B= k2Cr2 O7 4FeCr2O4 + 8 NaCrO4 +7O2 -----8 Na2CrO4 + 2 Fe2O3+8 CO2 2Na2CrO4 + 2 H+ -----------Na2Cr2O7 + 2Na+ +H2O . (2) vacant (n-2) f subshell in Ce(IV). (3) extra stability of Fe3+ than Mn3+ ion 45. 1(a). Because of same size (b). Because Zn+2 ion does not have unpaired electrons while Cu+2 have one unpaired electron ©.Because of many unpaired electrons they have many metallic binds (d) In these oxoanions the oxygen atoms are directly bonded to the transition metal. Since oxygen is highly electronegative, the oxoanions bring out the highest oxidation state of the metal. (e) Zn2+ ion has all its orbitals completely filled whereas in Cu2+ ion there is one half-filled 3d-orbital. It therefore has a tendency to form coloured salts whereas Zn2+ has no such tendency. 1 Prepared By : Silchar Region ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 238 Coordination Compounds ONE MARK QUESTIONS: Q.1Write the formula forTetraamineaquachloridocobalt(III) chloride Q.2 Write the IUPAC name of [Co (NH3)4 Br2]2 [Zn Cl4] Q.3 Which of these cannot act as ligand and why: NH3, H2O, CO, CH4. Give reason? Q.4 How many EDTA (lethylendiamine tetra acetic acid) molecules are required to make an octahedral complex with a Ca2+ ion. Q.5 Why tetrahedral complexes do not exhibit geometrical isomerism ? Q.6 What is the hybridisation of central metal ion and shape of Wilkinson’s catalyst ? Q.7 Specify the oxidation numbers of the metals in the following coordination entities: (i) [Co(H2O)(CN)(en)2]2+ and (ii) [CoBr2(en)2]+ Q.8 Draw the structure of optical isomers of [Co(en)3]3+. Q.9 Name the types of isomerism exhibited by [Co(NH3)5(NO2)](NO3)2 Q.10 Write the formula of Amminebromidochloridonitrito-N-platinate(II) ion Q.11 which one is more stable complex among(i) [Fe(H2O)6]3+ (ii) [Fe(NH3)6]3+(iii) [Fe(C2O4)3]3− Q.12 How many ions are produced from the complex Co(NH3)6Cl2 in solution? Q.13 What do you meant by degenerate d-orbitals? Q.14 Out of the following two coordination entities which is chiral (optically active)? (a) cis-[CrCl2 (ox)2]3- (b) trans-[CrCl2 (ox)2]3Q.15 The spin only magnetic moment of [MnBr4]2- is 5.9 BM. Predict the geometry of the complex ion? Q.16 What is the oxidation state of Ni in [Ni(CO)4]. Q.17 What is the magnetic behavior of [Ni(CN)4]2- . Q.18 Name the metal ion present in vitamin B12. Q.19 Name the isomerism shown by complex K[Cr(H2O)2(C2O4)2] Q.20 Name the compound used for inhibiting the growth of tumours. (cancer treatment) TWO MARK QUESTIONS: Q.1Write the IUPAC names of the following coordination compounds: (i) [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NO2 )] (ii) K3 [Cr(C2O4)3 ] Q.2 A cationic complex has two isomers A & B. Each has one Co3+, five NH3, one Br and one SO42-. A gives a white precipitate with BaCl2 solution while B gives a yellow precipitate with AgNO3 solution. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 239 (a) What are the possible structures of the complexes A and B? (a) Write the name of structural isomerism shown by A and B. Q.3 FeSO4 solution mixed with (NH4)2SO4 solution in 1 : 1 molar ratio gives the test of Fe2+ ion but CuSO4 solution mixed with aqueous ammonia in 1 : 4 molar ratio does not give the test of Cu 2+ ion. Explain why ? Q.4 What is meant by ambidentate ligands? Give two examples. Q.5 [Co(NH3)6]3+ is diamagnetic whereas [Co(F6)]3- is paramagnetic. Give reasons. Q.6 [Cr(NH3)6]3+ is paramagnetic while [Ni(CN)4]2− is diamagnetic. Explain why? Q.7 Draw figure to show the splitting of d orbitals in an octahedral crystal field. How is the magnitude of ∆0 affected by (i) Nature of ligand. (ii) Oxidation State of metal ion. Q.8 Metal carbonyl are much more stable than normal complexes, why? Q.9 Give evidence that [Co(NH3)5Cl]SO4 and [Co(NH3)5SO4]Cl are ionization isomers. Q.10 Write the formulas for the following coordination compounds and name the isomerism shown by them: i. potassium tetracyanonickelate(II) ii. tris(ethane−1,2−diamine) chromium(III) chloride THREE MARK QUESTIONS: Q.1 How many geometrical isomers are possible in the following coordination entities? (i) [Cr(C2O4)3]3− (ii) [Co(NH3)3Cl3] Q.2 (a) Write the IUPAC name of [Ti(H2O)6]+3. (b) [Ti(H2O)6]+3 is coloured why? (c) A Complex having scandium in +3 oxidation-state was found colorless why? Q.3 (a) Write IUPAC name of [Co(en)3]3+ (b) [NiCl4]2- is paramagnetic while [Ni(CO)]4 is diamagnetic though both are tetrahedral. Why? (c) Explain why K3[Fe(CN)6] is more stable than K4[Fe(CN)6]. Q.4 (a) What is the hybridization state of nickel in [Ni(CN)4]2− (b) Draw the structure of [Ni(CN)4]2− (c) A solution of [Ni(H2O)6]2+ is green but a solution of [Ni(CN)4]2− is colourless. Explain. Q.5 Explain [Co(NH3)6]3+ is an inner orbital complex whereas [Ni(NH3)6]2+ is an outer orbital complex. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 240 Q.6 For the complexes (i) [Ni(CN)4]2− (ii) [Ni(Cl)4]2− (iii) [Ni(CO)4] Identify: (a) The oxidation No. of nickel (b) The hybrid orbitals and the shape of the complexes Q.7 Specify the (i) oxidation numbers (ii) coordination numbers and (iii) IUPAC name of the following coordination entities: (a) [Co(H2O)(CN)(en)2]2+ (b) [PtCl4]2− Q.8 Discuss the nature of bonding in the following coordination entities on the basis of valence bond theory: (a) [Fe(CN)6]4− (b) [FeF6]3− Q.9 Dimethyl glyoxime is added to alcoholic solution of NiCl2. When ammonium hydroxide is slowly added to it, a rosy red precipitate of a complex appears. (a) Give the str. of the complex showing hydrogen bond. (b) Give oxidation state and hybridization of central metal ion. (c) Identify whether it is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. Q.10 Draw all the isomers (geometrical and optical) of: (a) [CoCl2(en)2]+ (b) [Co(NH3)Cl(en)2]2+ FIVE MARK QUESTIONS: Q.1 For the complex [Fe(en)2Cl2]Cl identify : (2009) (a) the oxidation No. of Iron. (b) the hybrid orbitals and the shape of the complex. (c) the magnetic behavior of the complex. (d) No. of geometrical isomers. (e) whether there is an optical isomer also (f) name of the complex. Q.2 State a reason for each of the following situations (a) Co2+ ion is easily oxidized to Co3+ in the presence of strong ligand. (2010,12) (b) CO is a stronger complexing reagent than NH3 . (2009,12) (c) The molecular shape of [Ni(CO)4 ] is not the same as that of [Ni(CN)4]2−. (2012) (d) Ni does not form low spin octahedral complexes. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com (2009,10) 241 (e) The complexes are known for the transition metals only. (2009,10) Q.3 Write down the IUPAC name for each of the following complexes and indicate the oxidation state, electronicconfiguration and coordination number. Also give stereochemistry and magnetic moment of the complex: (i)K[Cr(H2O)2(C2O4)2].3H2O (ii) [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2 (iii)CrCl3(py)3 Q.4 (i) Write the IUPAC name and type of isomerism shown by following complex compounds a) [Co(NH3)5(NO2)](NO3)2 b) [Pt(NH3)(H2O)Cl2] (ii) Write all the geometrical isomers of [Pt(NH3)(Br)(Cl)(py)] and how many of these will exhibit optical isomers? Q.5 (i) If to an aqueous solution of CuSO4 in two tubes, we add ammonia solution in one tube and HCl(aq) to the other tube, how the colour of the solutions will change? Explain with the help of reaction. (ii) Write the IUPAC name of complex compounds formed during the process (Answers) UNIT- 09 Coordination Compounds Answers(one mark questions) Ans.1 [Co(NH3)4(H2O)Cl]Cl2 Ans.2 Tetraamminedibromocobalt (III) tetrachlorozincate (II) Ans.3 CH4 can’t act as a ligand due to absence of lone pair of electron. Ans.4 EDTA is a hexadentate ligand therefore only one EDTA molecule is required. Ans.5 Because relative position of ligands attached to central atom are same with respect to one another Ans.6 Wilkinson’s catalyst is (PH3P)3RhCl. In this Rh has dsp² hybridisation and square planar shape. Ans.7 (i) +3 (ii) +3 Ans.8 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 242 Ans 9. It can show linkage isomerism. [Co(NH3)5(NO2)](NO3)2 and [Co(NH3)5(ONO)](NO3)2 It can also show ionization isomerism. [Co(NH3)5(NO2)](NO3)2 and [Co(NH3)5(NO3)](NO3)(NO2) Ans 10.[Pt(NH3)Br Cl (NO2)]Ans 11. [Fe(C2O4)3]3− (due to chelation) Ans 12. The given complex can be written as [Co(NH3)6]Cl2. Thus, [Co(NH3)6]+ along with two Cl− ions are produced. Ans.13 d-orbitals having same energy are called as degenerate d- orbitas. Ans. 14 cis-[CrCl2 (ox)2]3Ans. 15 Tetrahedral (sp3) Ans 16 Zero (0) Ans 17. Diamagnetic Ans 18. Cobalt (Co3+) Ans 19. Both geometrical (cis-, trans-) isomers for K[Cr(H2O)2(C2O4)2]can exist. Also, optical isomers for cis-isomer exist. Ans 20.compounds of platinum (for example, cis-platin) Answers(two mark questions) Ans. 1 (i) [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NO2 )] Diaminechloridonitro(o)platinum(II) (ii) K3 [Cr(C2 O4 )3 ] Potassium trioxalatochromate(III) Ans. 2 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 243 (a) [CO (NH3)5Br]SO4and [CO (NH3)5SO4]Br (b) Ionisation Isomerism Ans. 3 When FeSO4 and (NH4)2SO4 solution are mixed in 1 : 1 molar ratio, a double salt is formed. It has the formula FeSO4 (NH4)2SO4 .6 H2O. In aqueous solution, the salt dissociates in to its constituent ions. When CuSO4 and NH3 are mixed in the molar ratio of 1 : 4 in solution, a complex [Cu (NH3)4] SO4 is formed, which does not dissociates into constituent ions. Ans. 4 Ligands that can attach themselves to the central metal atom through two different atoms are called ambidentate ligands. For example: (a) (The donor atom is N) (The donor atom is oxygen) (b) (The donor atom is S) (The donor atom is N) Ans 5. In [Co(NH3)6]3+, cobalt ion is in + 3 oxidation state and has the electronic configuration 3d6. It undergoes d²sp³ hybridisation. Each hybrid orbital receives 1 pair of electrons from ammonia. Since all electrons are paired it is diamagnetic. In [CoF6]3+, cobalt ion is in + 3 oxidation state and has the electronic configuration 3d6. It undergoes sp³ d² hybridisation. Each hybrid orbital receives a pair of electrons from F-. THe 3d electrons of Co remain unpaired making it paramagnetic. Ans 6. Cr is in the +3 oxidation state i.e., d3 configuration. Also, NH3 is a weak field ligand that does not cause the pairing of the electrons in the 3d orbital. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 244 Cr3+ Therefore, it undergoes d2sp3 hybridization and the electrons in the 3d orbitals remain unpaired. Hence, it is paramagnetic in nature. In [Ni(CN)4]2−, Ni exists in the +2 oxidation state i.e., d8 configuration. Ni2+: CN− is a strong field ligand. It causes the pairing of the 3d orbital electrons. Then, Ni2+ undergoes dsp2 hybridization. As there are no unpaired electrons, it is diamagnetic. Ans 7 The splitting of the d orbitals in an octahedral field takes palce in such a way that , experience a rise in energy and form the eglevel, while dxy, dyzanddzx experience a fall in energy and form the t2g level. (a) (b) Stronger the ligand, more is the splitting. Higher the oxidation state, greater is the magnitude of 0. Ans 8. The metal-carbon bonds in metal carbonyls have both σ and π characters. A σ bond is formed when the carbonyl carbon donates a lone pair of electrons to the vacant orbital of the metal. A π bond is formed by the donation of a pair of electrons from the filled metal d orbital into the vacant anti-bonding π* orbital (also known as back bonding of the carbonyl group). The σ bond strengthens the π bond and vice-versa. Thus, a synergic effect is created due to this metal-ligand bonding. This synergic effect strengthens the bond between CO and the metal. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 245 Ans 9. When ionization isomers are dissolved in water, they ionize to give different ions. These ions then react differently with different reagents to give different products. [Co(NH3)5Cl]SO4 + Ba2+ BaSO4 white precipitate [Co(NH3)5Cl]SO4 + Ag+ No Reaction [Co(NH3)5SO4]Cl + Ag+ AgCl white precipitate [Co(NH3)5SO4]Cl + Ba 2+ No Reaction Ans 10 i. ii. K2[Ni(CN)4] [Cr(en)3]Cl3 No Isomerism shown by it Optical isomerism Answers(three mark questions) Ans 1. (a) For [Cr (C2O4)3]3−, no geometric isomer is possible as it is a bidentate ligand. (b) [Co(NH3)3Cl3] Two geometrical isomers are possible. Ans 2. (a) hexaaquotitanium(III) ion (b) Due to presence of single electron in d orbitals so that d-d transition is possible. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 246 (c) Due to absence of unpaired electron in d orbital Ans. 3 (a) Tris-(1,2-ethanediamine) cobalt (III) ion (b) Though both [NiCl4]2− and [Ni(CO)4] are tetrahedral, their magnetic characters are different. This is due to a difference in the nature of ligands. Cl− is a weak field ligand and it does not cause the pairing of unpaired 3d electrons. Hence, [NiCl4]2− is paramagnetic. In Ni(CO)4, Ni is in the zero oxidation state i.e., it has a configuration of 3d8 4s2. But CO is a strong field ligand. Therefore, it causes the pairing of unpaired 3d electrons. Also, it causes the 4s electrons to shift to the 3d orbital, thereby giving rise to sp3 hybridization. Since no unpaired electrons are present in this case, [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic (c) It is because the stability of complex depends upon the charge density (i. e. charge/radius ratio) on central ion. More is the charge density greater is the stability. Ans 4. (a) dsp2hybridisation (b) Square planer structure (c) In [Ni(H2O)6]2+, H2O is a weak field ligand. Therefore, there are unpaired electrons in Ni 2+. In this complex, the d electrons from the lower energy level can be excited to the higher energy level i.e., the possibility of d−d transition is present. Hence, Ni(H2O)6]2+ is coloured. In [Ni(CN)4]2−, the electrons are all paired as CN- is a strong field ligand. Therefore, d-d transition is not possible in [Ni(CN)4]2−. Hence, it is colourless Ans. 5 [Co(NH3)6]3+ [Ni(NH3)6]2+ Oxidation state of cobalt = +3 Oxidation state of Ni = +2 Electronic configuration of cobalt = d6 Electronic configuration of nickel = d8 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 247 NH3 being a strong field ligand causes the pairing. Therefore, Ni can undergo d2sp3 hybridization. Hence, it is an inner orbital complex. If NH3 causes the pairing, then only one 3d orbital is empty. Thus, it cannot undergo d2sp3 hybridization. Therefore, it undergoes sp3d2 hybridization. Hence, it forms an outer orbital complex Ans. 6 complex Oxidation no. of Ni hybrid orbitals shape (i) [Ni(CN)4]2− +2 dsp2 Square planer (ii) [Ni(Cl)4]2− +2 sp3 Tetrahedral (iii) [Ni(CO)4] Zero (0) sp3 Tetrahedral Ans. 7 (a) [Co(H2O)(CN)(en)2]2+ oxidation numbers = +3; coordination number = 6 IUPAC name = aquacynobis-(ethane 1,2diamine) cobalt (III) ion (b) [PtCl4]2− oxidation numbers = +2; coordination number = 4 IUPAC name = tetachloridoplatinate(II) ion Ans. 8 (a) [Fe(CN)6]4− In the above coordination complex, iron exists in the +2 oxidation state. Fe2+ : Electronic configuration is 3d6 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 248 Orbitals of Fe2+ ion: As CN− is a strong field ligand, it causes the pairing of the unpaired 3d electrons. Since there are six ligands around the central metal ion, the most feasible hybridization is d2sp3. d2sp3hybridized orbitals of Fe2+ are: 6 electron pairs from CN− ions occupy the six hybrid d2sp3orbitals. Then, Hence, the geometry of the complex is octahedral and the complex is diamagnetic (as there are no unpaired electrons). (b) [FeF6]3− In this complex, the oxidation state of Fe is +3. Orbitals of Fe+3ion: There are 6 F− ions. Thus, it will undergo d2sp3 or sp3d2 hybridization. As F− is a weak field ligand, it does not cause the pairing of the electrons in the 3d orbital. Hence, the most feasible hybridization is sp3d2. sp3d2 hybridized orbitals of Fe are: Hence, the geometry of the complex is found to be octahedral. Ans. 9 (a) ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 249 (b) O. S. = + 2 bybridisation = dsp² (c) diamagnetic as no unpaired electron. Ans. 10 (a) [CoCl2(en)2]+ In total, three isomers are possible. (b) [Co(NH3)Cl(en)2]2+ Trans-isomers are optically inactive. Cis-isomers are optically active ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 250 Answers(five mark questions) Ans. 1 (a) the oxidation No. of Iron = +3 (b) the hybrid orbitals = d2sp3 and the shape of the complex = octahedral (c) the magnetic behavior of the complex = Paramagnetic (d) No. of geometrical isomers = Two (cis and trans) (e) cis structure can show an optical isomer also (f) bis-(ethane 1,2diamine)dichloridoplatinum (III) chloride Ans. 2 (a) Co2+ ion is easily oxidized to Co3+ because Co3+ contains t2g6,eg0 (stable) electronic configuration in the presence of strong ligand while Co2+ has t2g6,eg1 (unstable) electronic configuration. (b) CO is a stronger complexing reagent than NH3 due to its capacity to form a synergic (back-bonding or dπ – pπ bonding). (c) The molecular shape of [Ni(CO)4] is not the same as that of [Ni(CN)4]2- due to availability of vacant d orbital for the hybridization. [Ni(CO)4] is tetrahedral in the structure due to sp3 hybridization while [Ni(CN)4]2- is square planer in the structure due to dsp2 hybridization (d) Because of non-availability of inner vacant d-orbital for pairing the electrons. (e) due to availability of vacant d- orbitals to form a bond with a ligand. Ans. 3 (i) Potassium diaquadioxalatochromate (III) trihydrate. Oxidation state of chromium = 3 Electronic configuration: 3d3: t2g3 Coordination number = 6 Shape: octahedral Stereochemistry: ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 251 Magnetic moment, μ 4BM (ii) [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2 IUPAC name: Pentaamminechloridocobalt(III) chloride Oxidation state of Co = +3 Coordination number = 6 Shape: octahedral. Electronic configuration: d6: t2g6. Stereochemistry: Magnetic Moment = 0 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 252 (iii)CrCl3(py)3 IUPAC name: Trichloridotripyridinechromium (III) Oxidation state of chromium = +3 Electronic configuration for d3 = t2g3 Coordination number = 6 Shape: octahedral. Stereochemistry: Both isomers are optically active. Therefore, a total of 4 isomers exist. Magnetic moment, μ ∼4BM Ans. 4 (i) (a) [Co(NH3)5(NO2)](NO3)2 IUPAC Name: pentaamminenitrocobalt(III) nitrate It can show two types of isomerism linkage isomerism. [Co(NH3)5(NO2)](NO3)2 and [Co(NH3)5(ONO)](NO3)2 ionization isomerism. [Co(NH3)5(NO2)](NO3)2 and [Co(NH3)5(NO3)](NO3)(NO2) (b)[Pt(NH3)(H2O)Cl2] IUPAC Name :ammineaquochloridoplatinum(II) Geometrical (cis-, trans-) isomers of [Pt(NH3)(H2O)Cl2]can exist. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 253 (ii) [Pt(NH3)(Br)(Cl)(py) From the above isomers, none will exhibit optical isomers. Tetrahedral complexes rarely show optical isomerization. They do so only in the presence of unsymmetrical chelating agents. Ans. 5 (i) In first case, colour will change from blue to deep blue. [Cu (H2O)4]2+ + 4 NH3 → [Cu (NH3)4]2+ + 4 H2O deep blue While in second case, its colour will change to yellow. [Cu (H2O)4]2+ + 4 Cl- → [CuCl4]2+ + 4 H2O Yellow (ii) (a) [Cu (NH3)]4]2+ = tetraamminecopper(II)ion (b) [CuCl4]2+= tetrachloridocopper(II) ion Prepared By : Silchar Region CHAPTER 9 COORDINATION COMPOUNDS 1 mark questions 21. Explain coordination entity with example. Ans: it constitute a central metal atom or ions bonded to a fixed number of molecules or ions ( ligands) .eg. [Co(NH3)3Cl3]. 22. What do you understand by coordination compounds? Ans: coordination compounds are the compounds which contains complex ions. These compounds contain a central metal atom or cation which is attached with a fixed number of anions or molecules called ligands through coordinate bonds. eg. [Co(NH3)3Cl3] 23. What is coordination number? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 254 Ans: the coordination number of a metal ion in a complex may be defined as the total number of ligand donor atoms to which the metal ion is directly bonded. Eg. In the complex ion [Co(NH3)6]3+ has 6 coordination number. 24. Name the different types of isomerisms in coordination compounds. Ans: structural isomerism and stereoisomerism. 25. Draw the structure of xenon difluoride. Ans: structure :trigonalbipyramidal Shape: linear 26. What is spectrochemical series? Ans: the series in which ligands are arranged in the order of increasing field strength is called spectrochemical series. The order is : I-<Br-<SCN-<Cl-<S2-<F-<OH-<C2O42-<H2O<NCS-<EDTA4-<NH3<en<CN-<CO 27. What do you understand by denticity of a ligand? Ans: the number of coordinating groups present in ligand is called denticity of ligand. Eg.Bidentateligand ethane-1,2-diamine has 2 donor nitrogen atoms which can link to central metal atom. 28. Why is CO a stronger ligand than Cl-? Ans: because CO has π bonds. 29. Why are low spin tetrahedral complexes not formed? Ans : because for tetrahedral complexes, the crystal field stabilisation energy is lower than pairing energy. 30. Square planar complexes with coordination number 4 exhibit geometrical isomerism whereas tetrahedral complexes do not. Why? Ans: tetrahedral complexes do not show geometrical isomerism because the relative positions of the ligands attached to the central metal atom are same with respect to each other. 31. What are crystal fields? Ans: the ligands has around them negatively charged field because of which they are called crystal fields. 32. What is meant by chelate effect? Give an example . Ans: when a didentate or polydentate ligand contains donor atoms positioned in such a way that when they coordinate with the central metal atom, a 5 or 6 membered ring is formed , the effect is called chelate effect. Eg. [PtCl2(en)] 33. What do you understand by ambidentate ligand? Ans: a ligand which contains two donor atoms but only one of them forms a coordinate bond at a time with central metal atom or ion is called an ambidentate ligand. Eg.nitrito-N and nitrito-O. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 255 34. What is the difference between homoleptic and heteroleptic complexes? Ans: in homoleptic complexes the central metal atom is bound to only one kind of donor groups whereas in heteroleptic complexes the central metal atom is bound to more than one type of donor atoms. 35. Give one limitation for crystal field theory. Ans: i) as the ligands are considered as point charges, the anionic ligands should exert greater splitting effect. However the anionic ligands are found at the low end of the spectrochemical series. ii) it does not take into account the covalent character of metal ligand bond. ( any one ) 36. How many ions are produced from the complex: [Co(NH3)6]Cl2 Ans: 3 ions 37. The oxidation number of cobalt in K[Co(CO)4] Ans: -1 38. Which compound is used to estimate the hardness of water volumetrically? Ans: EDTA 39. Magnetic moment of [MnCl4]2- is 5.92B.M explain with reason. Ans: the magnetic moment of 5.9 B.M. corresponds to the presence of 5 unpaired electrons in the dorbitals of Mn2+ ion. As a result the hybridisation involved is sp3 rather than dsp2. Thus tetrahedral structure of [MnCl4]2- complex will show 5.92 B.M magnetic moment value. 40. How many donor atoms are present in EDTA ligand? Ans: 6 2 marks questions 11. Give the electronic configuration of the following complexes on the basis of crystal field splitting theory. iv) [CoF6]3v) [Fe(CN)6]4Ans: i) Co3+ (d6) t2g4eg2 vi) Fe2+ d6t2g6eg0 12. Explain the following with examples: iv) Linkage isomerism v) Outer orbital complex Ans: i) this type of isomerism arises due to the presence of ambidentate ligand in a coordination compound. Eg. [Co(NH3)5NO2]Cl2 and [Co(NH3)5ONO]Cl2 vi) When ns, np and nd orbitals are involved in hybridisation , outer orbital complex is formed. Eg. [CoF6]2- in which cobalt is sp3d2 hybridised. 13. i)Low spin octahedral complexes of nickel are not found . Explain why? ii)theπ complexes are known for transition elements only.explain. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 256 Ans: i) nickel in its atomic or ionic state cannot afford 2 vacant 3d orbitals and hence d2sp3 hybridisation is not possible. ii) transition metals have vacant d orbitals in their atoms or ions into which the electron pairs can be donated by ligands containing πelectrons.eg. benzene, ethylene etc. thus dπ-pπ bonding is possible. 14. How would you account for the following: iii) [Ti(H2O)6]3+ is coloured while [Sc(H2O)6]3+ is colourless. iv) [Ni(CO)4] possess tetrahedral geometry whereas [Ni(CN)4]2- is square planar. Ans: i) due to the presence of 1 electron in 3d subshell in [Ti(H2O)6]3+ complex d-d transition takes place by the absorption of visible light. Hence the complex appears coloured. On the other hand, [Sc(H2O)6]3+ does not possess any unpaired electron .Hence d-d transition is not possible (which is responsible for colour) in this complex is not possible, therefore it is colourless. ii) Ni in [Ni(CO)4] is sp3 hybridised. Hence it is tetrahedral. Whereas for [Ni(CN)4]2- is dsp2 hybridised hence it has square planar geometry. 15. State reasons for each of the following: iii) All the P—Cl bonds in PCl5 molecule are not equivalent. iv) S has greater tendency for catenation than O. Ans: i) in P Cl5 the 2 axial bonds are longer than 3 equatorial bonds. This is due to the fact that the axial bond pairs suffers more repulsion as compared to equatorial bond pairs. ii) The property of catenation depends upon the bond strength of the element. As S—S bond is much stronger (213kJ / mole) than O—O bond (138 kJ/mole), S has greater tendency for catenation than O. 16. Give the stereochemistry and the magnetic behaviour of the following complexes: iii) [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2 iv) K2[Ni(CN)4] Ans: i) d2sp3 hybridisation, structure and shape = octahedral Magnetic behaviour- diamagnetic ii) dsp2 hybridisation, structure and shape = square planar magnetic behaviour- diamagnetic 17. Draw the structures of isomers if any and write the names of the following complexes: iii) [Cr(NH3)4Cl2]+ iv) [Co(en)3]3+ ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 257 Ans: i) tetraamminedichloridochromium(III) ion ii) tris(ethane-1,2-diammine)cobalt(III)ion 18. State reasons for each of the following: iv) The N—O bond in NO2- is shorter than the N—O bond in NO3v) SF6 is kinetically an inert substance. Ans: i) this is because the N—O bone in NO2- is an average of a single bond and a double bond whereas N—O bond in NO3- is an average of 2 single bonds and a double bond. vi) In SF6 the S atom is sterically protected by 6 fluorine atoms and does not allow water molecules to attack the S atom. Further F atoms does not contain d orbitals to accept the electrons denoted by water molecules. Due to these reasons , SF6 is kinetically an inert substance. 19. Hydrated copper sulphate is blue in colour whereas anhydrous copper sulphate is colourless. Why? Ans: because water molecules act as ligands which splits the d orbital of the Cu2+ metal ion. This result in d-d transition in which t2g6eg3 excited to t2g5eg4 and this impart blue colour to the crystal. Whereas when we talk about anhydrous copper sulphate it does not contain any ligand which could split the d orbital to have CFSE effect. 20. Calculate the magnetic moment of the metal ions present in the following complexes: iii) [Cu(NH3)4]SO4 iv) [Ni(CN)4]2Ans: i)electronicconfig. t2g6eg3, n=1, µs= √n(n+2) = 1.732 B.M ii) electronicconfig. t2g6eg2 , n=2, µs= √n(n+2)=2.828 B.M 3 marks questions 2. (a) What is a ligand? Give an example of a bidentate ligand. (b) explain as to how the 2 complexes of nickel,[Ni(CN)4]2- and Ni(CO)4 have different structures but donot differ in their magnetic behaviour.( Ni=28) Ans: (a) the ion , atom or molecule bound to the central atom or ion in the coordination entity is called ligand. A ligand should have lone pair of electrons in their valence orbital which can be donated to central metal atom or ion. Eg.Bidentate ligandethylenediammine (b)dsp2, square planar, diamagnetic (n=0) ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 258 Sp3 hybridisation , tetrahedral geometry, diamagnetic (n=0) 2. Nomenclate the following complexes: i) [Co(NH3)5(CO3)]Cl ii)[COCl2(en)2]Cl iii) Fe4[Fe(CN) 6] Ans: i) pentaamminecarbonatocobalt(III)chloride ii) dichloridobis(ethane-1,2-diamine)cobalt(III)chloride iii)iron(III)hexacyanidoferrate(II) 3. (a)why do compounds with similar geometry have different magnetic moment? (b)what is the relationship between the observed colour and wavelength of light absorbed by the complex? Ans: (a) it is due to the presence of weak and strong ligands in complexes, if CFSE is high the complex will show low value of magnetic moment and if it is low the value of magnetic moment is high. Eg. [CoF6]3- and [Co(NH3)6]3+ , the former is paramagnetic and the latter is diamagnetic. (b) higher the CFS lower will be the wavelength of absorbed light. Colour of the complex is obtained from the wavelength of the leftover light. 4. Explain the following terms giving a suitable example. (a) ambident ligand (b) denticity of a ligand (c) crystal field splitting in an octahedral field Ans (a) Aligand which contains two donor atoms but only one of them forms a coordinate bond at a time with central metal atom or ion is called an ambidentate ligand. Eg.nitrito-N and nitrito-O. (b)The number of coordinating groups present in ligand is called denticity of ligand. Eg.Bidentateligand ethane-1,2-diamine has 2 donor nitrogen atoms which can link to central metal atom. (c) the splitting of the degenerated d orbital into 3 orbitals of lower energy t2g and 2 orbitals of higher energy eg due to presence of a ligand in a octahedral crystal field is known as crystal field splitting in an octahedral complex. 5. (a) Copper sulphate pentahydrate is blue in colour while anhydrous copper sulphate is colourless. Why? (b) Sulphur has greater tendency for catenation than oxygen.Why? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 259 Ans : (a)because water molecules act as ligands which splits the d orbital of the Cu2+ metal ion. This result in d-d transition in which t2g6eg3 excited to t2g5eg4 and this impart blue colour to the crystal. Whereas when we talk about anhydrous copper sulphate it does not contain any ligand which could split the d orbital to have CFSE effect. (b)The property of catenation depends upon the bond strength of the element. As S—S bond is much stronger (213kJ / mole) than O—O bond (138 kJ/mole), S has greater tendency for catenation than O. 6. draw structures of geometrical isomers of the following complexes: (a) [Fe(NH3)2(CN)4]- (b)[CrCl2(ox)2]3- (c)[Co(en)3]Cl3 7. write the state of hybridisation, the shape and the magnetic behaviour of the following complexes: (i) [Co(en)3]Cl3 (II) K2[Ni(CN)4] (III)[Fe(CN)6]38. how would you account for the following: (i) [Ti(H2O)6]3+is coloured while [Sc(H2O)6]3+ is colourless . (II) [ Fe(CN)6]3- is weakly paramagnetic while [ Fe(CN)6]4- is diamagnetic. (III) Ni(CO)4 possess tetrahedral geometry while [Ni (CN)4]2- is square planar. Ansi) due to the presence of 1 electron in 3d subshell in [Ti(H2O)6]3+ complex d-d transition takes place by the absorption of visible light. Hence the complex appears coloured. On the other hand, [Sc(H2O)6]3+ does not possess any unpaired electron .Hence d-d transition is not possible (which is responsible for colour) in this complex is not possible, therefore it is colourless. (ii) paramagnetism is attributed to the presence o f unpaired electrons. Greater the number of unpaired electron greater is the paramagnetism. Due to the presence of one electron in the 3d subshell in [ Fe(CN)6]3it is weakly paramagnetic. On the other hand [ Fe(CN)6]4- is diamagnetic because all electrons are paired. iii) Ni in [Ni(CO)4] is sp3 hybridised. Hence it is tetrahedral. Whereas for [Ni(CN)4]2- is dsp2 hybridised hence it has square planar geometry. 11. Explain the following :: (iv) low spin octahedral complexes of Ni are not known. (v) The pi – complexes are known for the transition elements only. (vi) CO is a stronger ligand than NH3 for many metals ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 260 Ans. i) nickel in its atomic or ionic state cannot afford 2 vacant 3d orbitals and hence d2sp3 hybridisation is not possible. ii) transition metals have vacant d orbitals in their atoms or ions into which the electron pairs can be donated by ligands containing πelectrons.eg. benzene, ethylene etc. thus dπ-pπ bonding is possible. (iii) because in case of CO back bonding takes place in which the central atom uses its filled d orbitals with empty anti bonding π*molecular orbital of CO. 12. What is meant by stability of a coordination compounds in solutions? State the factors which govern the stability of complexes. Ans : the stability of a complex in solution refers to the degree of association between the two species involved in the state of equilibrium. The magnitude of the equilibrium constant for the association expresses the stability . M +4L ML4 4 K = [ML4]/[M][L] Factors on which stability of complex depends (i) charge on central metal ion (ii) nature of the metal ion (iii) basic nature of the ligand (iv) presence of the chelate ring (v) effect of multidentate cyclic ligand . 5 marks questions 6. Draw the structures of the following molecules: (a) [Fe(NH3)2(CN)4]- (b)[CrCl2(ox)2]3- (c)[Co(en)3]Cl3(d) [Co(en)3]Cl3(e)[Fe(CN)6]3- 7. What is crystal field theory for octahedral complexes? Also write the limitations of this theory. Ans : 8. Write the state of hybridisation the shape and the magnetic behaviour of the following complex entities: (vi) [Cr(NH3)4Cl2]Cl (vii) [Co(en)3]Cl3 (viii) K2[NiCl4] (ix) [Fe(H2O)6]2+ (x) [NiCl4]29. Using valence bond theory explain the following questions in relation to [Co(NH3)6]3+. (vi) Nomenclature (vii) Type of hybridisation (viii) Inner or outer orbital complex (ix) Magnetic behaviour (x) Spin only magnetic moment ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 261 10. Compare the following complexes with respect to structural shape of units, magnetic behaviour and hybrid orbitals involved in units: [Co(NH3)6]3+, [Cr(NH3)6]3+,[ Ni(CO)4] Prepared By : Silchar Region HALOALAKANES & HALOARENES 1 MARK QUESTIONS(1-20) 1. What happens when tert-butyl alcohol is treated with Cu / at 573 K.? 2. Arrange the following halides in order of increasing SN² reactivity : CH3 — Cl, CH3 — Br, CH3CH2Cl, (CH3)2 CHCl 3. Alkyl halides, though polar, are immiscible with water. Why? 4. Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions. Why? 5. Which of the following two compounds would react faster by SN² pathway: 1-bromobutane (OR) 2bromobutane. 6. Allyl Chloride is more reactive than n-propyl Chloride towards nucleophilic substitution reactions. Explain. 7. Explain why is Chlorobenzene difficult to hydrolyse than ethyl chloride ? 8. R—Cl is hydrolysed to R—OH slowly but the reaction is rapid if a catalytic amount of KI is added to the reaction mixture.Why? 9. Why haloalkanes are more reactive than haloarenes. 10. Why do haloalkenes undergo nucleophillic substitution whereas haloarenes under go electophillic substitution? 11. Aryl halides cannot be prepared by the action of sodium halide in the presence H2SO4 .Why? 12. Why is Sulphuric acid not used during the reaction of alcohols with KI ? 13. p- dichlorobenzene has highest m.p. than those of ortho and m-isomers.? 14. Although chlorine is an electron- withdrawing group, yet it is ortho and para directing in electrophillic aromatic substitution reactions.Why? 15. Explain why vinyl chloride is unreactive in nucleophillic substitution reaction? 16. Arrange the following compounds according to reactivity towards nucleophillic substitution reaction with reagents mentioned :a. 4- nitro chloro benzene, 2,4 di nitro chloro bemzene, 2,4,6, trinitrochlorobenzene with CH3ONa 17. Arrange in order of boiling points. a. Bromobenzene, Bromoform, chloromethane,Dibromo-methane b. 1-chloropropane, Isopropyle chloride, 1-Chlorobutane. 18. Predict the reactivity in SN1 a. C6H5CH2Br, C6H5CH (C6H5)Br, C6H5CH(CH3)Br, C6H5C(CH3)( C6H5)Br 19. Why is vinyl chloride less reactive than ethyl chloride? 20. Chloroform is stored in dark coloured & sealed bottle. Why? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 262 2 MARK QUESTIONS(21-30) 21. The treatment of alkyl chlorides with aqueous KOH lead to the formation of alcohols but in presence of alcoholic KOH alkenes are major products. Explain? 22. p-Dichlorbenzene has higher melting point and lower solubility than those of o- and m- isomers. Discuss. 23. Haloalkanes react with KCN to form alkyl cyanides as major product while AgCN form isocyanide as the chief product. Explain 24. Explain why is Chlorobenzene difficult to hydrolyse than ethyl chloride ? 25. Which compound will react faster in SN2 reaction with OH---? a. CH3Br and CH3I (SN2) b. (CH3)3C-Cl or CH3Cl (SN2) 26. Alcohols reacts with halogen acids to form haloalkenes but phenol does not form halobenzene. Explain 27. How the following conversions can be carried out? a. Propene to propan-1-ol b. 1-Bromopropane to 2-bromopropane 28. The treatment of alkyl chlorides with aq KOH leads to the formation of alcohols but in presence of alcoholic KOH, alkenes are the major products. Explain. 29. Tert-butyl chloride reacts with aq. NaOH by SN¹ mechanism while n-butyl chloride reacts by SN² mechanism. Why ? 30. Why alkyl halides are generally not prepared in laboratory by free radical halogenation of alkanes ? 3MARK QUESTIONS(31-40) 31. Haloalkanes undego substitutions. nucleophilic substitutions whereas Haloarenes undegoes electrophilic 32. Why alkyl halides are generally not prepared in laboratory by free radical halogenation of alkanes? 33. Why preparation of aryl iodide by electrophilic substitution requires presence of an oxidising agent? Why can aryl flouride not be prepared by this method? 34. Why aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution? 35. (i) (ii) Arrange in order of property indicated : CH3CH2CH2CH2Br, (CH3)3 Br, (CH3)3 CHCH2 Br (Increasing boiling point) CH3F, CH3I, CH3Cl, CH3Br (nucleophilic substitution) 36. Why does 2 bromopentane gives pent-2-ene as major product in elimination reaction ? 37. Complete the reaction : (a) CH3OCH3 + PCl5 ——— (b) C2H5OCH3 + HCl ——— (c) (C2H5)2 O + HCl ——— 38 Distinguish between the following pair of organic compounds i) CCl4 and CHCI3 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 263 ii) Chlorobenzene and Benzyl chloride 39. How are the following conversions carried out? (i) Benzyl chloride → Benzyl alcohol. (ii) Ethyl magnesium chloride → Propan-1-ol. Cu /HCl (iii) C6H5N2Cl ───────→ 40. Write the formula of main product formed in the following chemical reactions. Na (i) (CH3)2 CH-C1 ──────→ Dry ether ∆ (ii) CH3Br + AgF──────→ (iii) Dry acetone CH3CH2Br + Nal ───────→ 5MARKS QUESTIONS(41-45) 41. Identify A, B, C, D, E, R, R¹ in the following : Dry ether H2O (i) Br + Mg ———— A ———— B Dry ether (ii) R — Br + Mg ———— C ———— CH3 — CH — CH3 | D CH3CH3 | | (iii) D2O Na/ether Mg H2 O CH3 — C — C — CH3 ———— R¹X ——— D ——— E | | CH3CH3 42.a) Give the IUPAC name of ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 264 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH2 C C CH2 CH 2 OH Br Br b)Complete the following reactions: (a) C6H5ONa + C2H5Cl --------> (b) CH3CH2CH2OH + SOCl2 -------> (c ) Preparation of haloalkane with Alkane and halogen using U.V light is least Preferred method.Explain? 43.a).p-dichlorobenzene has higher melting point and lower solubility than o- and m-isomer. Explain? b) Which will have a higher boiling point? 1 - Chloro enthane or - 2 methyl -2- chlorobutane Give reasons? c) Chloroform is not used as anesthetic nowadays. Why? 44.(a) p - nitro chlorobenzene undergoes nucleophilic substitution faster than chlorobenzene. Explain giving the resonating structures as well. (b)Allyl chloride is more reactive than n - propyl chloride towards nucleophilic substitution reaction. Explain why? (c) Give IUPAC name of the following organic compound C6H5CH2Cl 45.a) Why do alcohols have higher boiling points than the halo alkanes of the same molecular mass? b) Convert the following: i) Benzene to aniline. ii) Benzene to diphenyl iii) Benzene to p-Chloro toluene. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 265 ANSWERS 1 MARK ANSWERS(1-20) 1.Dehydration reaction will take place. Isobutene will be formed. CH3 | CH2 CU || CH3 — C — OH —————— CH3 — C | 573 K | CH3 – H2 O CH3 2.(CH3)2 CHCl < CH3CH2Cl < CH3Cl < CH3Br. (Hint : As the size of the alkyl group increases SN² reactivity decreases.) 3. Alkyl halides cannot form H-bonds with water molecules and hence are insoluble in water. 4. Because Grignard reagents have a very strong affinity for H+ ions. In presence of water, they abstract H+ ions from water and form alkanes. To prevent this, they should be prepared under anhydrous conditions. 5. The reactivity in SN² reaction depends upon the extent of steric hindrance. i-bromobutane is a 1° alkyl halide and 2-bromobutane is a 2° alkyl halide. Since there will be some steric hindrance in 2° alkyl halide than in 1° alkylhalide, therefore 1°-bromobutane will react faster than 2-bromobutane in SN² reaction. 6. Allyl Chloride readily undergoes ionization to produce resonance stabilized allyl carbocation. Since carbocations are reactive species they readily combine with OH– ions to form allyl alcohol. 7. The lone pair of electrons of Chlorine is Chlorbenzene participates into resonance with the benzene ring.As a result C — Cl bond acquires a partial double bond character. Therefore, this C — Cl bond is stronger than C — Cl bond in ethyl chloride which is a pure single bond. As such the Chlorobenzene is difficult to hydrolyse than ethyl chloride. 8. Iodide ion is a powerful nucleophile and hence reacts rapidly with RCl to form RI. + + I–; R — Cl + I– ——— KI ——— — I + Cl– 9.In haloarenes, there is double bond character b/w carbon and halogen due to resonance effect which makes him less reactive. 10. Due to more electro negative nature of halide atom in haloalkanes carbon atom becomes slightly positive and is easily attacked by nucleophillic reagents. While in haloarenes due to resonance, carbon atom becomes slightly negative and attacked by electrophillic reagents. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 266 11. Due to resonance the carbon- oxygen bond in phenols has partial double bond and it is stronger than carbon oxygen single bond. 12.It is because HI formed will get oxidized to I2 by concentrated Sulphuric acid which is an oxidizing agent. 13. p- dichlorobenzene is symmetrical, fits into crystal lattice more readily and has higher melting point. 14. Ans. Chlorobenzene is resonance hybrid, there is –ve charge at 0 and para positions, electrophillic substitution reaction will take place at 0 and para position due to +R effect. +R effect is dominating over – I effect. . 15. Vinyl chloride is unreactive in nucleophillic substitution reaction because of double bond character between C=CL bond which is difficult to break. 16. 2,4,6, trinitrochlorobenzene > 2,4 dinitrochlorobemzene > 4- nitrochlorobenzene 17. Ans. (a) chloromethane < Bromobenzene < Dibromo-methane < , Bromoform (b) , Isopropyle chloride <1-chloropropane <1-Chlorobutane 30 > 20> 10 (SN1) 18. C6H5C(CH3)(C6H5)Br > C6H5(C6H5)Br > C6H5CH(CH3)Br > C6H5CH2Br (30) (20) (20) (10) 2 19.Due to the sp hybridization and resonance in vinyl chloride. 20.Because it undergoes oxidation and converting to poisonous gas phosgene. 2 mark questions(21-30) 21. In aqueous KOH,OH- is nucleophile which replaces another nucleophile. R-X +KOH R-OH +KX Where as in alcoholic KOH C2H5OH +KOH C2H5O- + K+ CH3CH2-Cl + alcoholic KOH-------- CH2 =CH2 + C2H5OH (C2H5O-) 22.The p-isomer being more symmetrical fits closely in the crystal lattice and thus has stronger intermolecular forces of attraction than those of o- and m- isomers. Since during melting or dissolution, the crystal lattice breaks, therefore a larger amount of energy is needed to melt or dissolve the p- isomer than the corresponding o- and meta isomers. 23. KCN is a ionic compound and provides cyanide ions in solution. Although both carbon and nitrogen atoms are in a position to donate electron pairs, the attack takes place mainly through Carbon atom and not through nitrogen atom since C — C bond is more stable than C — N bond. However AgCN is mainly covalent in nature and nitrogen is free to donate electron pair forming isocyanide as the main product. 24.The lone pair of electrons of Chlorine is Chlorbenzene participates into resonance with the benzene ring. As a result C — Cl bond acquires a partial double bond character. Therefore, this C — Cl bond is ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 267 stronger than C — Cl bond in ethyl chloride which is a pure single bond. As such the Chlorobenzene is difficult to hydrolyse than ethyl chloride. 25.a) CH3I will react faster than CH3Br b) CH3Cl will react faster than 30 halide 26. The C-O bond in phenol acquires partial double bond character due to resonance and hence be cleared by X- ions to form halobenzenes. But in alcohols a pure C — O bond is maintained and can be cleared by X– ions. . 27.a) b) 28.In aq. solution, KOH is almost completely ionised to give OH– ions which being a strong nucleophile brings about a substitution reaction to form alcohols. Further in aq. solution, OH– ions are highly solvated (hydrated). This solution reduces the basic character of OH– ions which fail to abstract a hydrogen from the carbon of the alkyl halide to form an alkene. However an alcoholic solution of KOH contains alkoxide (RO–) ions which being a much stronger base than OH– ions preferentially abstracts a hydrogen from the -carbon of the alkyl halide to form alkene. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 268 29.Tert-butyl chloride reacts via SN¹ mechanism because the heterolytic cleavage of C — Cl bond in tertbutyl chloride gives 3 carbocation which is highly stable and favourable for SN¹ mechanism. Moreover, tert-butyl chloride (3°) bring a bulky molecule has steric hindrance which will not allow SN² mechanism to take place. Hence only SN1 mechanism can occur in tert-butyl chloride. However n-butyl chloride (1°) reacts via SN² because ‘C’ of C — Cl bond is less crowded and favourable for nucleophile to attack from back side results in the formation of transition state. It has less steric hindrance which is a favourable factor for SN² mechanism. 30.It is because : (i) It gives a mixture of isomeric monohalogenated products whose boiling points are so close that they cannot be separated easily. (ii) Polyhalogenation may also take place, thereby making the mixture more complex and hence difficult to separate. 3 MARK QUESTIONS(31-40) 31. Haloalkanes are more polar than haloarenes. -atom carrying the halogen in haloalkanes is mroe e– deficient than that in haloarenes. In haloarenes, the love pair of electrons present on the halogen atom goes into resonance with the aryl ring. The aryl ring being rich in electron density, undergoes electrophilic substitutions. 32.It is because : (i) It gives a mixture of isomeric monohalogenated products whose boiling points are so close that they cannot be separated easily. (ii) Polyhalogenation may also take place, thereby making the mixture more complex and hence difficult to separate. 33.Reactions with I2 are reversible in nature and require presence of oxidising agent (HNO3, etc.) to oxidise HI formed during iodination and promote forward reaction. Fluoro compounds cannot be prepared due to high reactivity of flourine. 34.(i) Resonance effect : Due to resonance C — Cl bond acquires partial double bond character. (ii) Difference in hybridisation of Carbon in C —X bond : in haloarene C-atom attached to halogen in sp² hybrid while sp³ in haloalkane. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 269 C — X bond length in sp² hybrid is shorter and hence stronger and difficult to break. (iii) Instability of phenyl cation (iv) Possible repulsion of nucleophile to approach e– rich arenes. 35.(i) B. P. decreases with increase in branching due to decrease in Van der Waals forces of attraction. (CH3)3 CBr < (CH3)2 CHCH2 Br < CH3CH2CH2CH2Br (ii) Reactivity increases as C — X bond dissociation energy decreases. CH3F < CH3Cl < CH3Br < CH3I 36. Br OH– | OH– CH3 — CH2 = CH = CH2 —> CH3—CH2—CH2—CH—CH2 —> CH3CH2CH2CH = CH2 | H (81%) (Pent-2-ene) (19%) (Pent-1-ene) This is because of Saytzeff’s rule — In dehydrohalogen reactions, the preferred product is that alkene which has the greater number of alkyl groups attached to the doubly bonded carbon atoms. 37. (a) 2 CH3Cl (b) CH3Cl + C2H5OH (c) C2H5Cl + C2H5OH 38. i)Carblamine reaction : chloroform gives offensive smell due to formation isocyanide but CCl4 don’t. ii) Diazotisation test will be given by benzyl chloride. 39.i)Hydrolysis with water. ii) Nucleophillic addition with HCHO followed by hydrolysis. iii) Cu /HCl C6H5N2Cl ───────→C6H5Cl 40 (a) (CH3)2 CH-C1 ──────→ (CH3)2 CH-CH(CH3)2 Dry ether ∆ (b) CH3Br + AgF──────→CH3F (c) Dry acetone CH3CH2Br + Nal ───────→ CH3CH2I ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 270 5 MARK ANSWERS(41-45) dry ether Ans. (i) Br + Mg ———— (A) MgBr——— H2 O + Mg (OH) Br (B) (ii) Dry ether D2O RBr + Mg ———— RMgBr ———— CH3 — CH — CH3 | D Here R = CH3CHCH3 | CH3 CH3 CH3 | | Na/ethe | (iii) CH3 — C — C — CH3 ———— CH3 — C — X | | CH3 CH3 | CH3 CH3 | H2 O CH3 | CH3 — C — H ———— CH3 — C — MgBr | CH3 | CH3 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 271 42. a)3,4-dibromo-3,4-dimethylhexan-1-ol. b) (a) C6H5ONa + C2H5Cl C6H5-O-C2H5 + NaCl (b) CH3CH2CH2OH + SOCl2 CH3CH2CH2Cl + HCl + SO2 c) Due to formation of mixed halides primary, secondary tertiary. 43.a) The p-isomer being more symmetrical fits directly in the crystal lattice and thus has stronger inter molecular forces of attraction than o- and m- isomers.During melting or dissolution, the crystal lattice breaks. Therefore, a large amount of energy is needed to melt or dissolve the p-isomer than the resultant oand m- isomers. b) 1-chloro pentane Surface area and hence Van der Waal’s forces of attraction decreases on branching. c)Due to the formation of poisonous gas during oxidation. 44(a) In this reaction a carbanion intermediate is formed. This is stabilized by Resonance in p-nitrochloro benzene Resonance Structure (b) In allyl chloride, the carbocation formed is stabilised due to resonance while the carbocation formed form n - propyl chloride i.e. is less stable, so allyl chloride is more reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction. (c) Chlorophenylmethane 45 a) Alcohols are capable of forming intermolecular H-bonds . b) i) C6H6 + Cl2 ----------- C6H5Cl + NH3 ---------------C6H5NH2 + HCl FeCl3 Cu2O,Δ ii) C6H6 + Cl2 -----------C6H5Cl + 2Na + C6H5Cl ------------ C6H5-C6H5 + 2NaCl FeCl3 Dry ether iii)C6H6 + CH3Cl ------------ C6H5CH3 + Cl2 ------------------ C6H4CH3Cl + HCl AlCl3 FeCl3 Prepared By : Silchar Region CHAPTER 11 Alcohols And Phenols 1 MARKS QUESTIONS Q1. What is absolute alcohol ? Ans: 100% C2H5OH is known as absolute alcohol. Q2. What is rectified spirit ? Ans:95% C2H5OH is known as rectified spirit. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 272 Q3.Lower alcohols are soluble in water but higher alcohols are not soluble . Why? Ans: Due to large Hydrocarbon part which hydrophobic. Q4. Why ether is insoluble in water ? Ans: Due to absence of HB. Q5. How is alcohol made unfit for drinking purposes ? Ans: By adding CH3OH , CuSO4 and Pyridine Q6. Phenol is an acid but does not react with NaHCO3. Why? Ans: Since Phenol feebly weak in nature. Q7.Diethylether does not react with Na.Why ? Ans: Due to absence of acidic Hydrogen (Active). Q8.Propanol has higher B.P. than that of n-Butane. Why? Ans : In propanol there is HBonding but in n-Butane there is no HBonding. Q9. Mixture of o- &p-Nitrophenol is separated by Steam volatile . Why ? Ans: Due to intramolecular HB in O-Nitrophenol. Q10. Out ofo- &p-Nitrophenol which one is more volatile ? Ans:O-Nitrophenol due to intramolecular HB. Q11. IUPAC Name of Dimethylether is – Ans: Methoxymethane Q12.IUPAC Name of Isobutyl alcohol is— Ans: 2-Methylpropanol Q13.What is anisol ? Ans: Methyl phenyl ether Q14. Give an example of 3o alcohol. Ans: Dimethylethanol Q15.What is phenetol ? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 273 Ans :Ethylphenyl ether(C6H5-O-C2H5) Q16.Phenol gives litmus test but not alcohol. Why? Ans: S.N. 1. Compounds Phenol Alcohol More Acidic due to –I effect Less Acidic due to +I effect Q17.What is Lucas Reagent ? Ans: Anhydrous Zinc Chloride +Conc.HCl Q18.Dimethyl ether is more volatile than ethanol . Why? Ans: Due to absence of HB. Q19.Which product will obtain by dehydration of ethanol ? Ans: Ethene. Q20. Out of But-2-en-1-ol and 2-Butanol which one shows Cis&Trans isomerism ? Ans:But-2-en-1-ol will show Cis&Trans isomerism . By Tinsukia Region CHAPTER 12 1 Marks Questions Q1. Write IUPAC Name of Acetone . Ans: Propanone Q2.Draw the structure of –Isobutyraldehyde. Ans: CH3-CH(CH3)-CH2-CHO Q3.Write the IUPAC Name of Caproic Acid. Ans: Hexanoic Acid. Q4.What is Fehling’s Solution ‘A’? Ans: Aqueous solution of CuSO4. Q5.What is the Tollen’s Reagent? Ans: Ammonical Silver Nitrate Solution . ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 274 Q6.Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their B.P. CH3CHO,CH3CH2OH,CH3OCH3,CH3CH2CH3 Ans:CH3CH2CH3<CH3OCH3<CH3CHO<CH3CH2OH Q7. Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their reactivity in nucleophilic Addition reactionEthanal,Propanal,Propanone,Butanone Ans: Butanone<Propanone<Propanal<Ethanal Q8. Write the structure of 3-Hydroxy butanal. Ans:CH3-CH(OH)-CH3-CHO Q9. B.P. of ketone&aldehyde is higher than that of hydrocarbons of comparable molecular mass why? Ans: Due to dipole-dipole interaction in carbonyl compounds. Q10. What is formalin ? Ans: 40% aqueous solution of HCHO. Q11.What is Vinegar? Ans: 8% solution of acetic acid. Q12. Formic Acid is more acidic than acetic acid why? Ans: Due to +I effect in acetic acid Q13. What is Per-Fluoro acetic acid? Ans: CF3COOH Q14.Acidic nature of carboxylic acid is higher than Phenol Why? Ans : Carboxylate ions are more stable than Phenoxide ions . Q15. Out of Propionaldehyde and Acetone , which more reactive ? Ans: Acetone Q16. What is Schiff’s base ? Ans: RCH=NR’ Q17.Out of CH3CHO&HCHO which compound will give aldol condensation ? Ans: CH3CHO Q18. Out of CH3CHO&HCHO which compound will give Cannizzaro’s Reaction ? Ans: HCHO Q19.Write oxidation product of Propanol. Ans: Propanoic Acid Q20. What is PCC? Ans: PyridiniumChloroChromate By Tinsukia Region CHAPTER 13 1MARKS QUESTIONS Q1. Give an example tertiary amine . Ans: Trimethyl amine Q2. Write the IUPAC Name of ethyl amine Ans: Ethanamine Q3. Which amine is more basic CH3NH2or(CH3)3N in Gaseous Phase ? Ans: (CH3)3N Q4. What is the Zwitterion ? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 275 Ans: Dipolar ion Q4.Give an example of Zwitter ion. Ans: H3N+-CH2-COOQ5. Write the IUPAC Name of CH2=CHCN. Ans: Pro-2-enenitrile Q6.Give one important use of Phenyl isocyanide . Ans : As insecticide Q7. B.P. of 1o Amine is higher than that of secondary amine of comparable molecular mass why? Ans: Due to more Number of HB. Q8. Ethyl amine is soluble in water but Aniline does not why? Ans: Due to HB in Ethyl amine Q9. Which amine gives Carbyl amine test ? Ans: Primary(1o) Amine Q10. Write the IUPAC Name of (CH3)3N. Ans: N,N-Dimethylmethanamine Q11.Arrange the following in the decreasing order of basic strength. C6H5NH2 ,(C2H5)2NH,C2H5NH2,NH3 Ans:(C2H5)2NH>C2H5NH2>NH3>C6H5NH2 Q12. Aniline is less basic than ammonia why? Ans: Due to +R effect in Aniline Q13. Why are aliphatic amines stronger bases than aromatic amines ? Ans: There is +I effect in aliphatic amines and –I effect in aromatic amines. Q14.Write the IUPAC Name of -- Ans: 2-Methylaniline Q15. Which is more basic triethyl amine or Diethyl amine in Gaseous state ? Ans:Diethyl amine Q16. Which of followings have higher Kb , H2O or NH3? Ans: NH3 Q17.Write the structure of Benzenediazonium chloride. Ans: Q18. What is Hinsberg’sReagent ? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 276 Ans: Bezenesulphonyl Chloride (C6H5SO2Cl) Q19. Which of compound CH3NH2 and C2H5NH2 has higher value of PKb ? Ans:CH3NH2 Q20. Write the structure of p- Amino azobenzene. Ans: By Tinsukia Region CHAPTER 14 1 MARK QUESTION Q1. What is invert sugar ? Ans: Mixture of glucose & Fructose Q2. Which disaccharide is present in milk ? Ans: Lactose Q3. Which Polysaccharide is present in Rice ? Ans: Starch Q4. Write hydrolysis product of Lactose. Ans: Glucose &Galactose Q5. Name the carbohydrate which is not digested in human body ? Ans; Cellulose Q6. Which Functional groups are present in glucose ? Ans : -OH & CHO Q7. What are the constituents of Maltose ? Ans: 2 Units of α-D-glucose Q8.What are the constituents of Starch ? Ans: Amylose & Amylopectin Q9. Which Polysaccharide is stored in the Liver of Animals ? Ans: Glycogen Q10.Name two Carbohydrades which act as byfuels? Ans: Starch & Glycogen Q11. Write the water soluble vitamins . Ans: Vitamin B & Vitamin C ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 277 Q12. Give an example of Fibrous Protein . ANS: Keratin Q13.Give two examples of essential amino acids . Ans: Valine&Lycine Q14. Name the Enzymes present in the saliva of Human. Ansd: Amylase Q15. What is Glycogen ? Ans: Polysaccharide Q16. What type of bonding occurs in globular Proteins ? Ans: Van der Waal’s interaction , Dipolar interaction , HB. Q17 Which bio-molecules act as catalyst ? Ans: Enzyme Q18.Name the enzyme which breaks proteins into peptides ? Ans: Pepsin & Trypsin Q19.Name the purines present in DNA > Ans: Adenine and Guanine Q20 Name the base that is found in RNA only . Ans: Uracil By Tinsukia Region CHAPTER 15 1 MARK QUESTIONS Q1. Write the monomers of Bakelite. Ans: Phenol & Formaldehyde Q2. Give the chemical name of Tefflon. Ans: PTFE Q3. What is the main constituent of Babalgum ? Ans: Butadiene &Sytrene Q4.Name a synthetic polymer which is an amide ? Ans: Nylon-66 Q5. Name a polymer used to make cups for hot drinks? Ans: Urea formaldehyde resin Q6.Name one thermosetting & one thermoplastic polymer> Ans: PVC & Bakelite Q7 Name a synthetic polymer which is an ester. Ans: Terrylene Q8. Give an example of Step –Growth Polymer . Ans: Terrylene Q9. Write the monomers of Neoprene Ans: Chloroprene Q10 Write monmers of Nylon-66 Ans; Hexamethylenediamine&Adipic acid Q11. Write the Full form of PMMA. Ans: PolyMethylMethAcrylate ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 278 Q12. What is the volcanisation ? Ans: Heating of natural rubber with sulphur . Q13.What is PHBV? Ans: Poly-β-hydroxybutyrate-Co-β-hydroxyvalerate Q14. Give an example of Bio-degradable polymer ? Ans: PHBV Q15. What do you hy Buna-S ? Ans: Butadiene & Styrene Q16.Arrange the following Polymers in increasing order of intermolecular force. Nylon-66,Buna-S,Polythene Ans:Buna-S<Polythene<Nylon-66 Q17.Name a polymer used in non-stick utensils. Ans: Tefflon Q18. What do you understand for 6&6 in Nylon -66 ? Ans: Both 6 shows number of carbon atoms in monomers. Q19.What do you mean by Bu- , na& N in Buna-N. Ans: Bu-Butadiene ,na-Sodium (Na) and N- Acrylonitrile Q20. Write the monomers of Melamin Formaldehyde Resin. Ans: Melamin& Formaldehyde CHAPTER 16 1MARK QUESTIONS Q1.Name two types of chemical messangers. Ans: Neurotransmitters & Hormones Q2. Name the antibiotic used in typhoid fever. Ans:Chloramphenicol Q3.Name a Broad spectrum Antibiotic. Ans;Chloramphenicol Q4. Name the Medicine which can act as analgesic as well as antipyretic ., Ans: Aspirin Q5. Name the constituents of Dettol. Ans; Chlroxylenol&terpineol Q6. Why is Ethanal added to Soap ? Ans: To make it transparent Q7. Name an ant acid which prevent the formation of acid in the stomach. Ans : Ranitidine Q8. Why is glycerol is added to shaving soap? Ans: To prevent rapid drying. Q9. Give an example of bacteriocidal antibiotic. Ans: Penicillin Q10.Name a drug used in mental depression . Ans: Equanil Q11. Name a few artificial sweatners Ans: Saccharin & Aspartame Q12. What type drugh is phenacetine? ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 279 Ans: Antibiotic Q13.What are pathogens? Ans; Disease causing organisms. Q14.Name two Narcotics which are used as analgesics > Ans: Morphine & Codeine Q15. What is Chemotherapy? Ans: Use of chemical for treatment of disease . Q16. Mention a few drug targets . Ans: Carbohydratyes, Lipids , Proteins & Nucleic Acids . Q17. Define a Tanquilizer. Ans: Drug which act on CNS to help in reducing anxiety. Q18.Define Soap . Ans: Soap is a Sodium or Potassium salt of Fatty Acids Q19.Why are detergents preferred over soaps ? Ans: Unlike soaps detergents can be used even in hard water. Q20.What is a Bacteriostatic drug ? Ans: A drug which inhibit the growth of disease causing organisms. Prepared by Tinsukia Region ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 280 ANION ANALYSIS SALT + Dil H2SO4 Effervescence No Effervescence Could be CO32-, SO32-, S2-, NO2- SALT + Conc H2SO4 + warm Effervescence No Effervescence Could be Cl-, Br-, I-, NO3-, CH3COO- Test using SCE Smell the gas Odourless; could be CO32- Smell of burning hair; could be SO32- Passed the gas through limewate r Passed the gas through 1) acidified K2Cr2O7 Soln2) acidified KMnO4 soln Lime water turns milky confirms CO32- Observe colour of the gas Smell of rotten egg; could be S2- Passed the gas through acidified lead acetate solution Lead acetate soln turnsblack confirms S2- K2Cr2O7 Soln turns green confirms SO32n KMnO4 sol is decolourised confirms SO32- Continued in next page Colourless gas turning brown could be NO2- Colourless gas giving dens white fumes with ammonia , could be chloride Salt +MnO2 + conc H2SO4 + Δ SCE + dil HNO3 + AgNO3 soln Greenish yellow gas could be Cl- White ppt soluble in NH4OH confirms Cl- Reddish Brown gas could be Br-- Black/ violet gas, could be iodide Light brown gas turning dense brown on heating could be NO3- SCE + CHCl3/CCl4 + Cl2 Water Salt + K2Cr2O7 + conc H2SO4. Pass the gas evolved through water. Acidify the water with acetic acid and add lead nitrate Reddish brown gas , turns water yellow, finally yellow ppt soluble in NaOH con firms Cl- in the organic layer --Red/ brown colour confirms Br---violet colour confirms I- Salt + Cu turnings + conc H2SO4+ heat Brown gas and the solution turns blue, could be NO3- SCE + FeSO4 Soln + dil H2SO4 + Conc H2SO4 along the walls of the test tube. Brown ring at the junction of the two layers confirms NO3- ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 281 Salts that do not give effervesence with dil H2SO4/ Conc H2SO4 Preparation of SCE ie Sodium carbonate extract: Salt + same quantity of Na2CO3 + water + boil. Filter. Filtrate is called SCE. SCE + dil HCl + BaCl2 Soln SCE + dil HNO3 + Ammonium Molybdate White ppt insoluble in conc HCl confirms SO42- Cranary yellow ppt confirms PO43- Prepared By: Mrs Hajra Shaikh Resource Person ZIET Bhubaneswar ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 282 ANALYSIS OF CATIONS ORIGINAL SALT SOLUTION + Dil HCl White Ppt No Ppt Pass H2S Could be Pb2+ Black ppt Dissolve in hot water No ppt Could be Pb2+ /Cu2+ Boil off H2S + Dil HNO3+ NH4Cl Solution + NH4OH + Colorless Solution could be Pb2 Ppt Divide into two parts Add K2CrO4 Add KI Dissolve in minimum quantity of 50% HNO3 Blue Soln could be Cu2+ Divide into three parts Yellow ppt soluble in NaOH soln confirms Pb2+ Yellow ppt soluble in hotwater which reappears on cooling as golden yellow spangles confirms Pb2+ Add NH4OH Deep blue colouration Add Pot Ferro Cyanide Chocolate brown ppt no ppt Could be Fe3+,Al3+, Mn2+ Gelatinou s Brown could be Fe3+ Add KI Dirty white ppt Confirms Cu2+ Add Pot Ferro Cyanide soln Gelatinous white could be Al3+ Pass H2S through the above solution Dissolve ppt in minimum amount of HCl Fe3+ Al3+ Divide it into two parts Add NaOH Soln and a drop of litmus Add Pot sulpho Cyanide Soln ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Blood Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India 3+ Fe confirmed redE.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org color Black PPt could be Co2+ and Ni2+ On the next page Disolve ppt in min amount of aqua regia and evaporate to dryness 283 Blue lake floating in a colourless background confirms Al3+ Deep blue color Blue residue could be Ni2+ Yellow residue could be Co2+ From previouspage No Ppt White ppt could be Zn2+ Dissolve in dil HCl. Add NaOH soltion White ppt soluble in excess of NaOH confirms Zn2+ Boil off H2S. add Na2CO3 Soln White Ppt could be Ca2+, Ba2+, Sr2+ Individual test for Na+, K+, Mg2+, NH4+ Dissolve ppt in minimum quantity of acetic acid and divide into three parts Add K2CrO4 soln Add Amm Acetate No ppt Yellow ppt soluble in NaOHcould be Ba2+ Green colour on flame test confirms Ba2+ Add Amm Carbonate no ppt White ppt could be Sr2+ Red colour on flame test comfirms Sr2+ White ppt could be Ca2+ Brick red on flame test confirms Ca2+ Prepared By: Mrs Hajra Shaikh Resource Person ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 284 ZIET Bhubaneswar ORGANIC CHEMISTRY COMPOUNDS CONTAINING NITROGEN Amines PROPERTIES Physical Chemical 3 N sp hybridised Classified as 1o, 2o and 3o depending on no of H atoms replaced by alkyl or aryl groups in NH3. Common name: Alkyl amines IUPAC names Alkane amines and aryl amines Cyanides --Lower aliphatic amines are soluble in water—(H bonding). Solubility inversly proportional to molecular mass. Aromatic amines— insoluble in water --BP of amines 1o>2o>3o amines. BP is α to inter molecular H bonding. Acids> Alcohols> Amines> Hydrocarbons Chemical Common name: Alkyl Cyanides IUPAC name: Alkane Nitriles --Lower members are liquids while higher members are solids. – Solubility in water decreases as number of C atoms increases. -Soluble in Organic solvents. -Due to dipolar association BP is higher than hydrocarbons --Hydrolysis RCN RCOOH --RCN ( LiAlH4 or Na + C2H5OH) RCH2OH --RCN(SnCl2 /HCl + H2O) RCHO (Stephen’s reaction) --RCN + NH3 R—C—NH2 ǁ NH Properties Diazonium salts IUPAC name: Alkyl diazonium salt; Aryl Diazonium Salt --Alkyl salts are more soluble than aryl salts -Readily soluble in water, but Benzene Diazonium floroborate is insoluble in water. --soluble in solution and decomposes in dry state --Basicity 2o>3o>1o ( in aqueous phase). Ethanamine > NH3> Aniline EDG increase basicity EWG decrease Basicity --With alkyl halides alkylation --1o and 2o amines react with acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, esters by neucleophilic substitution -- Carbylamine reaction:1o amines on heating with CHCl3 and KOH form isocyanides with abnoxiuos smell. --1oAliphatic amines + NaNO2 + HCl Alcohol. 1o aromatic amines + NaNO2 Diazonium salts --1o& 2o amines = C6H5SO2Cl(Hinsberge reagent) sulphonamide --electrophilic substitution occurs at –O-, -P-, position --1o& 2o amines + RMgX Alkanes. Chemical Properties --Displacement of N Physical CuCl/HClArCl ArN2+X- CuBr/HBr ArBr KI ArI ArN2+X- HBF4/Δ ArF H2O/Δ H3PO2+ H2O Sandmeyer CH3CH2OH ArH Cu/HCl Cu/HBr CuCN/KCN ArCN Reaction ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar ArOH Kv-3 Campus, ArBr Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India ArCl Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com HBF4ArN2BF4 Δ ArF Diazo group is retained:(COUPLING REACTIONS) From colourless Diazonium salts to brightly coloured azo compounds Ar-N=N-Arusing 285 NITRITES IUPAC Name Alkyl nitrites Containing –O—N=O group, isomeric to nitro alkanes Sn/HClROH + NH2OH R–O—N=O H2O/ H+ NITRO IUPAC Name Nitro alkanes ROH + HNO2 Properties Physical Chemical --colourless and pleasant smelling liquids. --less soluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. --high boiling point --high dipole moment ISOCYANIDES Common name: Alkyl isocyanides IUPAC Name: Alkyl Carbylamines --Highly poisonous and abnoxious smelling liquid --B P lesser than cyanides --insoluble in water --Reduction: RNO2Sn/HClR—NH2 Zn /NH4ClR—NH—OH --Hydrolysis: RCH2NO2 + H2O HCl R—COOH 2R2CHNO2HCl 2R2CO --Halogenation: RCH2NO2Br2/NaOH Di bromo derivative R2CHNO2 Br2/NaOHMono bromo derivative R3CNO2Br2/NaOHNo Reaction Properties Physical Chemical --Hydrolysis: R—NC --Reduction: R—NC H3O+RNH2 ( Primary Amines) LiAlH4RNHCH3 ( Secondary Amines) -- R—NC + HgO R—NCO + Hg ( Alkyl Isocyanate) --R—NC Δ/250oC RCN ( Isomerisation) Prepared By: Mrs Hajra Shaikh Resource Person ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 286 ZIET Bhubaneswar Amines Mind Map ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 287 Benzenediazonium Chloride NaNO 2 + HCl + N2 Cl + NaCl Diazotisation Benzenediazonium chloride Benzenediazonium chloride is stable due to resonance. + Diazonium ion being a weak electrophile,can couple with a strongly activated aromatic system. NH2 HNO 2 Coupling do not occur in strong acidic medium NH3 NH2 H H3PO2 + + H H2O CH 3CH 2OH + H + + H2O + N2 H3PO3 + HCl CH 3CHO + HCl + N2 - OH CuCl / HCl Less activated aromatic system CuBr / HBr - Cl + Br + CN + Cl + O OH N2 N2 - OH H + CuCN / KCN N2 - + N Cl N Cu / HCl N2 + CuCl In strongly alkaline medium, the concentration of diazonium ion ( act as electrophile ) decreases and coupling reaction does not occur. -+ O Na N KI + I N HBF4 + - N2 BF4 NaOH N2 + F KCl + N2 + BF3 OH H2O N + OH N HBF4 + N N H - N2 BF4 NaOH NaNO 2 Cu HO HO HCl NO 2 + N2 + NaBF4 N N OH ( Orange dye ) Coupling reaction H - + OH + - N2 NH2 Coupling reaction N N p-Aminoazobenzene ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com NH2 ( Yellow dye ) 288 CHARACTERS OF AMINES Basic strength in gaseous phase Et3N > Et2 NH > Et NH 2 > NH3 Basic strength in aqueous Basic strength PKb value Et2 NH > Et NH2 > NH3 > PhNH2 p-Toluidine > Et NH2 Basic strength Et2 NH Boiling point > Et2 NH > Et OH C2H5 2o H3C C2 H5 NH CH3 2o H5C2 N H5C2 NH2 3o C2H5 Et NH 2 NH3 1o CH3 H3C 1o NH2 H3C 3o N > PhNH2 > CH3NH2 > Ph N Me 2 > PhNH2 Basic strength in Aqueous medium H5C2 NH > p-Nitroaniline > PhNHCH 3 > Et NH 2 > Et2 NH PhNH 2 Solubility Aniline NH3 CH3 CONTROLLED AMINES ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com > Et2 NH 289 Controlled Bromination O O xx NH2 N H C N H CH3 ( CH 3CO )2O C CH3 - Br2 Pyridine CH 3COOH Controlled Nitration xx NH2 N H Br C Br O O ( CH 3CO )2O N H CH3 C - HNO 3 , H2SO4 , 288 K CONVERSIONS Aliphatic Conversions : For stepping up the series Alcohol Anhydrous ZnCl R 2 alc. KCN X Alkyl halide Primary alcohol Reduction R CH 2 NH2 Primary amine HNO 2 Hydrolysis Hydrocarbon CH 2 OH LiAlH 4 CN Nitrile X2 / UV R R H3O LiAlH 4 H3O + ( NaNO 2 & HCl ) + RCOOH Carboxylic acid R Oxidation + OH / H NO 2 HX NH2 CH3 Pyridine OH + OH / H N-Phenylethanamide ( Acetanilide ) R NH2 CH 2 OH Primary alcohol For stepping down the series ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com NO 2 290 RCOOH Carboxylic acid NH 3 Br 2 RCONH 2 Acid amide Alkaline KMnO4 R HNO 2 R NH 2 Amine KOH ( NaNO 2 & HCl ) Aqueous KOH CH2 OH Primary alcohol R R HX OH Primary alcohol R Anhydrous ZnCl 2 X Alkyl halide CH2 X Alkyl halide Aromatic Conversions When the functional group contains carbon atom Cl OH NaOH , 623 K, 300 atm H OHC CH3 CH 3Cl Zn dust + Anhydrous AlCl3 H2 / Pd , BaSO4 , S Boiling Xylene ClOC SOCl2 HOOC When the functional group does not contain carbon atom ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com Alkaline KMnO4 291 OH Warm H2O I Zn dust H3PO2 H2O KI + N2 BF4- + N2 ClCuCl HCl 2 NO 2 CuBr Sn / HCl HBr Br HCl , NaNO2 F Cu Na NO H2SO4 , 333 K Conc. HNO 3 HBF4 Cl NH2 Prepared By Bhubaneswar Region ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 292 CONCEPT MAPPING COLLOIDS CLASSIFICATION OF COLLOIDS Based on particles of dispersed phase i)Multimolecular ii)Macromolecular iii)Associated Based on nature of interaction i)Lyophilic ii)Lyophobic Based on physical state i)solid in solidi)liquid in solid iii) gas in solid iv)solid in liquid v)liquid in liquid vi)gas in liquid vii) solid in gas viii) liquid in gas PREPARATION OF COLLOIDS Chemical Method Bredig’s Arc Method Peptisation PROPERTIES OF COLLOIDS Tyndall effect Brownian Motion Electrophoresis Colligative Properties Charge on colloidal particle ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 293 Colour Coagulation PURIFICATION Dialysis Electrodialysis Ultra filtration Prepared by Ranchi region ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 294 CONCEPT MAPPING CHAPTER 10 CLASSIFICATION OF HALOALKANES On the basis of No. of Halogen atoms On the basis of Hybridisation Of Carbon atom On the basis of 1 ,2 &3 Carbon atoms o o o Haloderivative Dihaloderivative Trihaloderivative Primary haloalkane Sec. halo Tert. Halo alkane alkane CHX3(Haloforms) CH3-CH2-X CH3-CH(X)-CH3 CHX3 CH2-X CH2-X ogen is bonded to Sp3 Hybridised C CH3CH2CH2-X Allylic halides eg. CH2=CH-CH2-X ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com Vinylic Halides CH2=CH-X 295 PREPARATION OF HALOALKANES From alcohols From hydrocarbons From alkanes By halide exchange CH2=CH2 +HX ZnCl2 R-OH +HX RX +H2O CH3CH2-X Cl2 CH3CH2CH2CH3 UV CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl + CH3CH2CH(Cl)CH3 Finkelstein Reaction RX+NaI Swarts Reaction RI + NaX RX + AgF (X=Cl,Br) +KOH (aq.)NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTION OF HALOALKANES R-OH +KX +NaOR R-X R-O-R +NaX +KCN (alc) R-CN + KX +AgCN R-NC + AgX +KNO2 R-O-N=O ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com RF + AgF 296 Prepared by Silchar Region UNIT11 ALCOHOLS,PHENOLS ÐERS CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF ALCOHOLS Reactions involving the cleavage of involving the cleavage O-H bond well as OH gp With metals 2ROH +2Na With HX ROH +HX Reactions involving the cleavage of C-O bond Esterification 2RONa +H2 RCOOH +R’OH RCOOR’+ H2O RX +H2O ROH + PCl5 With PCl5 RCl + POCl3 + HCl Reactions involving thealkyl as well as OH gp ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com Reactions alkyl as 297 Dehydration 30>20>1010>20>3010>20>30 H2SO4 CH3CH2OH CH2=CH2 +H2O 443K Oxidation Dehydrogenation K Cr O 2 2 7+H2SO4 CH3CH2OH CH3CHO [O] RCH2OH 573k Cu CH3COOH RCHO +H2 Prepared by Tinsukia Region UNIT12 Test for Carboxylic Acids Litmus Test NaHCO 3 Test Turns blue litmus to red Brisk effervescence of CO2 is evolved Classification of Carboxylic Acid ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com Ester Formation Test Fruity smell of ester 298 Monocarboxylic acids Dicarboxylic acids 1-COOH group Tricarboxylic acids 2-COOH group CH3COOH HOOC-CH2-CH2-COOH 3-COOH group HOOC-CH2-CH(COOH)-CH2-COOH Chemical Properties of Aldehydes & Ketones Nucleophilic Addition Reactions 1.By HCN Reduction Oxidation 4.By NH3 2.By NaHSO3 3.By RMgX Prepared by Tinsukia Region ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 299 Oxygen family ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 300 CONCEPT MAPPING d & f BLOCK ELEMENTS d-BLOCK ELEMENTS Special Properties Physical Properties Some important compounds 1.Variation in M.P 2.Variation in atom & KMnO4 :Preparation,structure & its properties. Ionic size. 3.Ionisation Enthalpies. 4.Oxidation state variation 5.Trends in std.electrode K2Cr2O7 : Preparation,structure & its properties Potential. 6. Trends in stability of higher Oxidation states. 1.Variable Oxidation states. 2.Coloured Ions 3.Catalytic properties 4.Complex formation 5.Alloy formation 6.Interstitial compounds. 7.Paramagnetism. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 301 f-Block Elements Lanthanides Actinides Misch Metall(Alloy of lanthanoids contains 95% Ln & 5%Fe.. 5f series(Thorium Lawrencium 4f series(Cerium to Lutetium) Common ox.state:+3 Lanthanoid Contraction:Reg decrease of at.size /ion.size Actinoid contraction:Reg decrease of at.size /ion.size Common ox.state:+3 Extra ox.states:+5,+6,+7 In +2 statereductant; Most are radioactive In +4 stateoxidant Prepared by Silchar Region ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 302 Type Condensation Polymer + Homopolymer Condensation Polymer +Copolymer Polymer Guwahati Region Concept Mapping Polymer in one Page Monomer Nylon 6 Caprolactum Nyon66 HMDA,Adipic acid Stockings Shirts, Ropes Treylene(Dacron) Ethylene glycol ,Terphthalic acid Fabrics Glyptal Ethylene glycol ,Phthalic acid Paints,Binding materials PHBV 3-Hydroxy butanoic acid, Packaging in Medical industry 3-Hydroxy pentanoic acid Addition Polymer + Homopolymer Uses Fibre,Plastic,tyre -cords Nylon2-Nylon6 Glycine & Aminocaproic acid Bakelite Phenol , formaldehyde Elecctric Switch & switch board, Melamine formaldehyde Resin Melamine ,Formaldehyde Unbreakable Crockery Polythene Ethene Pipes, Electrical insulators, Toys Polystyrene Styrene Combs,Plastic handle,Toys Polypropene Propene Carry bags, Plastic goods PVC Vinyl Chloride Rain coat, Electrical insulators PAN(Orlon) Acrlonitrile Fabrics PTFE( TEFLON) Tetrafluroetene Non-stick Remark Thermoplastic Biodegradable Aliphatic Poly ester Biodegradable Polymer ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com Thermosetting Polymer Thermoplastics 303 utensils Addition Polymer + Copolymer Natural Rubber ( Neoprene) Isoprene Football bladder BUNA-S Buta1,3diene,Styrene Tyre cords BUNA-N Buta1,3-diene,PAN Water storage Tank Classification as elastomer, Fibre, Thermoplasic ,Themosetting Polymer Polymer Classification Type Natural Rubber ( Neoprene) Elastomer, BUNA-S BUNA-N Nylon 6 fibre Nyon66 Treylene(Dacron) Polystyrene Thermoplastic Polypropene PVC PAN(Orlon) PTFE( TEFLON) Glyptal PHBV Nylon2-Nylon6 Polythene Bakelite Thermosetting ploymer Melamine formaldehyde Resin ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 304 Guwahati Region Concept Mapping Chemistry in everyday life in one Page THERAPEUTIC ACTION OF DIFFERENT DRUGS Note: All the medicines should be taken under strict medical supervision Drugs Action Example Analgesics Pain Killer AspirinAnalgin, ,Anacine, Analgesics Produces unconsciousness Opium, Heroin , Codeine, Morphine Produced by micro – organism that can inhibit the growth or kill other microorganism. Penicillin G(Narrow Spectrum) (Narcotic ) Antibiotics i).Bacteriostatic (Streptomycin) Streptomycin, Ampicillin , Amoxicillin Chloramphenicol Vancomycin, ofloxacin , (Broad Spectrum) ii).Bactericidal(Penicillin) Antiseptics Disinfectants Prevent the growth of micro-organism or kill them but not harmful to the living tissues. Kills micro-organisms, not safe for living tissues. It is used for toilets, floors , instruments. Dettol(Chloroxylenol +Terpineol), Bithional(in soap) Tincture iodine, 0.2% phenol, Boric Acid, ethanol,Soframycin,furamycin 1% phenol, chlorine (Cl2) , Sulphurdioxide ( SO2) Antacids Reduce or neutralize the acidity. NaHCO 3 Al(OH)3 gel Mg(OH)2 Antihistamines MgCO3 AlPO4 Reduce release of acid. Cimetidine(Tegamet), Ranitidine (Zantac), It is also used to treat allergy Brompheniramine ( Dimetapp) Terfenadine ( Seldane) Tranquilizers Reduce the mental anxiety, stress, emotional disturbance (sleeping pill) Valium, Serotonin, Veronal, Equanil,Amytal,Nembutal,Luminal, Seconal Antipyretics Reduce body temperature Aspirin, Paracetamol, Analgin, Phenacetin. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 305 Antifertility drugs These are the steroids used to control the pregnancy Norethindrone, Ethynylestradiol (novestrol ) CHEMICALS IN FOOD Sweetening Agent Saccharine, Aspartme(for cold foods) Alitame Sucrolose(stable at cooking temp) Food Preservative Salt, sugar, veg. oils, sodium benzoate CLEANSING AGENTS Soap Na / K –salt of long chain fatty acids Not work in hard water becoz with Ca and Mg salt soap produce insoluble scum Anaionic detergen Sodium laurylsulphate Used in household work / in tooth paste Cationic detergent Cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide Hair conditioner / germicidal properties Non ionic detergent Ester of stearic acid and polyethylene glycol Liquid dishwashing Detergents with highly branched hydrocarbon parts are non-biodegradable and hence water pollutants so branching is minimized which are degradable and pollution is prevented. Pr ot ein s CONCEPT MAP –BIO MOLECULES- [Proteins] All the polymers of ἀ amino acids connected to each other by peptide bond or peptide linkage Structure:Classification Based on molecular structure 1.Fibrous :insoluble in water polypeptide chains run parallel held by H and disulphide bonds. Ex:- Keratin 2.Globular :Chains of polypeptides coil around to give spherical shape. Ex: Insulin Primary: Sequence of amino acids. Secondary:shape due to H-bnding. Tertiary:Overall folding of secondary structure. Quarternary:Special arrangement of Essential Amino acids:Which cannot be made in body ,to be supplied through diet. Non-essential:Can be synthesized by body. subunits wrt to each other. ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 306 ἀ Helix :Formed due to intramolecular Hbonds between the C=O of one amino acid residue and the N-H of the 4th amino acid residue in the chain. Ex :Keratin in hair and myosin in muscles ᵝ-Pleated structure:Peptide chains laid side by side,held together by intermolecular Hbonding, resembles pleated folds of drapery ex:silk protein Denaturation:Due to coagulation native shape of the protein is destroyed and biological activity is lost ,[2ᵒ,3ᵒ structure destroyed, 1ᵒ intact.] B.Sreedhar( NSB2) Sushma(NAD) ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com BBSR 307 Solid State (Chapter -1), Concept Mapping Concept- Unit Cell. Edge Contribution (1/4) Corner Contribution (1/8) Face Contribution (1/2) Body center Contribution (1) Unit Cell Crystal lattice Prepared by Kolkata Region ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 308 Types of unit cell 1.No of atoms 1/8X8=1 2.Relation b/n a = 2r Radius of atom(r) & edge length(a) 3. Lattice point 8 4. Co-ordination 6 Number. 5. Packing 52% efficiency 1/8x8 +1=2 √3a=4r 9 1/8x8+1/2x6=4 √2a= 4r 14 8 68% 12 74% Prepared by Kolkata Region ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 309 Topic:- Solution (Chapter -2), Class XII Concept Mapping Concept:- Colligative properties Relative lowering of vapour pressure ∆P/P10= X2 Colligative Properties C.P. α n α 1/GMM Depression in freezing point Elevation in boiling point ∆Tb = Kb m Osmotic Pressure ∆Tf = Kfm ∏ V = nRT Prepared by Kolkata Region ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 310 Concept:- Concentration of Solution (Molarity) Mass% X density X 10 Gram Molecular mass(GMM) Gram per litter Gram Molecular mass(GMM) Mass of Solute(g) X 1000 Gram Molecular mass(GMM) X Volume of Solution Molarity(M) Moles of Solute(n) Volume of Solution (litre ) Normality of Solution (N) X (X=Molecular Mass/ Equivalent mass) Prepared by Kolkata Region ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 311 Concept mapping for Electrochemistry. Topic:- Galvanic cell (A B &C) A=Anod e electrod e B= Salt bridge C= Cathodeelectrode (-)(Oxidation reaction) (+)(Reduction reaction) Zn -----Zn2+ + 2e Cu2+ + 2e -Cu Zn>Cu (As per reactivity series) Over all reaction:Zn + Cu2+ ----Zn2+ + Cu Ezn+2/zn =E0zn+2/zn - RT/nf ln [Zn] /[Zn+2] -------eq-1 Ecu+2/cu =E0cu+2/cu - RT/nf ln [cu] /[cu+2]--------eq-2 Adding eq-1 & eq-2 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 312 Ecell =E0cell - RT/nf ln [Zn+2] /[Cu+2] At Equilibrium, Ecell=0 E0cell = RT/2f ln [Zn+2] /[Cu+2] =2.303RT/2f log [Zn+2] /[Cu+2] = 0.059/2 log Kc r G =-nFEcell Prepared by Kolkata Region ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 313 Prepared by Guwahati Region ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 314 01| 08 | 2013 A work shop on chemistry started on 1st Aug 2013 in the premises of K.V-3 Bhubaneswar, conducted by ZIET Bhubaneswar. Miss Usha Aswath Iyer, Director /DC- ZIET ,BBSR lit the sacred lamp to signal the commencement of the workshop.Then Mrs. Hajra Shaikh PGT Chemistry, ZIET gave a brief idea about the aims and objectives of the three days workshop. In her introductory speech Mrs. Jayalaxmi, Principal K V Srikakulam and Associate course director highlighted the result of chemistry in the year 2013 and the need for improvement for the next session. The Director / DC- ZIET-BBSR Miss Usha Aswath Iyer delivered her presidential speech throwing light on different aspects of successful teaching through motivation, inspiration and encouraging the students. At the end of the session the vote of thanks was extended by Mr. A. Saha PGT Biology, ZIET BBSR. After the inauguration, the class room teaching started with Mrs. Hajra Shaikh PGT: Chemistry ZIET on SWOT. She enlightened beautifully on Strength-Weakness-Opportunity and Threat .Next Mr. Aditya Panda, PGT Chemistry K.V-3 BBSR presented a work sheet on different chapters for clear understanding of all types of students through concept based questions. The teachers were then divided into different groups for preparing worksheets on different chapters as per the schedule made by ZIET BBSR. The afternoon session ended at 5.30 pm with a cup of tea. Report By: Bhubaneswar and Guwahati Region 2nd days ( i.e.on 02.08.2013) report of work shop done by Ranchi and Kolkatta regions jointly The morning assembly was conducted by BBSR and GUWAHATI REGIONS followed by Miss MERRY’S pledge, thought of the day was given by Mr. Sharad Sharma, current news read by Mr. Sridhar and report given by Mr. P ROY. Next, Director Madam advised the importance of morning assembly and body language. She focused on the ways of behaving at public places and maintaining good etiquette. Thereafter Mr.Sahu advised us to concentrate on slow learners and discussed with us various ways to motivate them. One of the ways was application of Maxwell’s law of distribution of energy to use as a tool to motivate slow learners as the success of teachers is determined by the progress of the slow learners. We were assigned class XII chemistry chapters region-wise and then asked to prepare question banks for average and bright students. After that Mr.J.K.Sahu explained how to use computers in chemistry by using specially designed software. After this it was time for lunch and in the meantime question bank was prepared by all the teachers. There was a short tea break and again the same assignment was started. With this the session came to an end at 5.30pm. Report by :KOLKATA & RANCHI REGIONS ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 315 Day 3 The day started with prayer conducted by the team Ranchi, commanded, Pledge, thought read by & the News, special item was a report on this workshop day two. There was a Session on ‘concept mapping’- the technique and uses till tea break at 10:45 am. After tea, teachers prepared a few concept maps. The Compilation of the work done ended by Lunch. After lunch there was a ‘Plenary Session’. The highlight of the day was a presentation by Mr Mr Jayanth Kumar Sahoo,PGT Chemistry, K V DHENKANALshowed the use of an open source software for writing chemistry formulae and reactions. After tea break, in the valedictory function the participants received the certificates and dispersed. Reported By: SILCHAR AND TINSUKIA REGIONS ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 316 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com 317 ZONAL INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING, Bhubaneswar Kv-3 Campus, Mancheswar Rail Colony, Bhubaneswar (Odisha) 751017 India Visit us: www.zietbbsr.org E.mail: zietbbsr.yahoo.com SURESH KUMAR SAHU (PGT CHEMISTRY) K.V.NO 3 BHUBANESWAR Concepts of Class-XI which are very often used in Class-XII ( Which needs to be mastered for better performance in Class-XII) ORGANIC CHEMISTRY -- Some Basic Principles IUPAC Naming and structure – including all functional group , ( some common names ) Isomerism—geometrical , Structural Classification of Organic compounds Fundamental concept of Organic reaction mechanism Homolytic and Heterolytic cleavage ,Nucleophiles and electrophiles .Electron movement in organic reactions Electron Displacement Effect In Covalent Bond— (i) Inductive effect ( +I and –I –effect) (ii) Resonance Structure – Rules while resonance Structure , Predicting the stable resonating structure , Hybrid Structure Resonance Effect ( + R and - R –effect ) Hyperconjugation Reactive Intermediates Stability of carbocation , Carboanion , free radicals , alkenes Types of Organic Reaction and its Mechanism [ Substitution – SN1 and SN2 , Addition Reaction - AdE and and , Elimination Reaction – alpha and beta , Rearrangement , Polymerisation and Condensation Reaction ] Stability of Carboanion Stability of (C –) α –I /+I INDUCTIVE EFFECT ACIDIC STRENGTH Acidic Strength α -I/+I POLARITY OF ORGANIC COMPOUND Stability of Carboanion Stability α No of resonating St RESONANCE EFFECT Reactivity of Benzene Towards electrophilic substitution ACIDC NATURE BASIC NATURE Basic nature α +R, +I/-R, -I Electron density increases by resonance H + attraction capacity More basic & vice-versa REACTION INTERMEDIATE CARBON FREE RADICALS CARBOCATION OR CARBONIUM ION CARNANIONS CARBENES 1- SUBSTITUTION REACTION IN ALKANE 2- WURTZ REACTION, 3- KOLBE SELECTROLYSIS, 4- ALLYLILIC OR BENZYLIC SUBSTUTION BY NBS. 5- SIDE CHAIN HALOGENATION OF ARENES 1- ELECTROPHILIC ADDITION OF ALKENE & ALKYNE 2- ELECTROPHILIC SUBSTITUTION OF BENZENE 3- NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTION OF HALIDES(SN1) 4- ELIMINATION OF HALIDES(E1) 5- ACID CATALIZED DEHYDRATION OF ALCOHOL 1- NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION REACTION OF ALKYNE 2- DECARBOXYLATION OF ACID 3- REDUCTION OF HALIDES BY Zn/HCl 4- ALDOL CONDENSATION 1- CARBYL AMINE REACTION 2- REIMER-TIEMANN REACTION HYDROCARBON Wurtz Reaction , Duma’s Decarboxylation Reaction , Markovnikov Rule , Kharash Effect (Peroxide effect ) Ozonolysis , Polymerization and cyclic Polymerization , Aromatization , Isomerization , bayer’s reagent , lindlar’s catalyst , dehydrohalogenation Reaction—β-elimination of haloalkanes ( Saytzeff Rule) Aromaticity , Resonance and stability of Benzene Electrophilic substitution Reactions-- Friedel Craft Reaction – alkylation and Acylation ,. Nitration And halogenations , Sulphonation Electrophilic addition Reactions-- Markovnikov Rule Free Radical addition Reactions -- Kharash Effect (Peroxide effect ) Directive influence of a functional group in monosubstituted benzene , ring activating and Deactivating group towards electrophile Mechanism of Markovnikov Rule and Kharash Effect Preparation and Properties of Alkane , alkene , Alkyne , Benzene Acidic Character of Alkynes , alkenes and alkanes Effect of branching on the boiling point of isomeric isomeric compounds ( alkanes , alcohols , haloalkanes) Effect of H-bonding on BP of alcohols , Carboxylic acids , Amines etc. Understanding acidic and basic character using resonance and Inductive effect Some Basic concepts of Chemistry (A) Calculation based on Molarity Molality , Mass Percentage , Mole Fraction , ppm , Mole concepts and Molar masses Use in Solution Chapter For solving Numericals Understanding the concept easily Preparation of standard solution In Lab. Used in Titration ( Quantitative – (B) Calculation based on stoichiometry equations Analysis) to determine the molarity Equation; M1V1/a1 = M2V2/a2 STRUCTURE OF ATOM Idea of writing electronic configuration Shape of orbitals & Degenerate orbitals Effective Nuclear Charge screening effect Penetrating power of different orbitals Use in p-block,d-block & f-block elements to determine stability, I.E., E.G.E, magnetic properties, colour compound determination of structure by VBT in coordination compound Use in CFT ( coordination compound ) Use in variation of size of p-block , d -block &f-block element ,concept of lanthanoid contraction Stability of completely filled and half filled subshell stability of different oxidation state in p & d block element CHEMICAL BONDING VSEPR Theory HYBRRIDISATION Resonance and Resonating structures PREDICTING SHAPE AND GEOMETRY OF VARIOUS MOLECULE USED IN P BLOCK ELEMENT TO DETERMINE STRUCTURE OF OXO ACID,INTER HALOGEN COMPOUND,& COMPOUND OF NOBLE GAS VBT IN CORDINATION COMPOUND -- Understanding the conditions of stability of resonating structure ( various application Questions) STRUCTER OF OXO ACID VACANT dORBITAL BOND POLARITY BASIC NATURE OF HYDRIDE ACIDIC NATURE OF OXIDE & OXOACID P∏-P∏BONDING CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS & p-BLOCK ELEMENTS METALLIC PROPERTY B.D.E THERMAL STABILITY REDUCTION CAPACITY OF HYDRIDE AND OXIDE ELECTRONEGATIVITY ELECTRON GAIN ENTHALPY INERT PAIR EFFECT FAJAN’S RULE CATENATION Metallic and non metallic character IE α 1/Metallic property IONISATION ENTHALAPY Stability of oxidation state METALLIC AND NON METALLIC NATURE BOND ENTHALPY ∆EN α 1/BOND LENGTH BOND ENERGY α ELECTRONEGATIVITY DIFFRENCE ACIDIC STRENGTH OF HYDRIDE BOND ENERGY α STABILITY OF MOLECULE REACTIVITY DIFFRENCE IN ELECTRONEGATIVITY α STABILITY α 1/REACTIVITY APPLICATION OF ELECTRONEGATIVITY NATURE OF BOND AND PRCENTAGE OF IONIC CHARECTER NOMENCLATURE OF INORGANIC COMPOUNDS OF2 OXYGEN DIFLORIDE ACIDIC NATURE OF THE OXIDE α ELECTRONEGATIVITY NATURE OF HYDROXIDE Thermodynamics Enthalpies of different types of reactions – Std enthalpy of combustion , Std. enthalpy of formation , Std. enthalpy of reaction Enthalpy of atomization ,Bond Enthalpy , Lattice enthalpy , Hydration Enthalpy , Enthalpy of solution Spontaneity – Enthalpy and entropy , Gibb’s Free Energy of reaction States of Matter Intermolecular forces Isotherm , isobar , isochore Vapour pressure – Boiling point , std. and normal BP evaporation and vaporization Critical Temperature Vapour pressure Vs Temperature Curve Ideal Gas Equation Equilibrium Idea about dynamic equilibrium , Rate law expression , Law of mass action , Relation between Kc and Qc , Kp and Kc Le Chatelier’s Principle and its application Different concepts of Acids and Bases—Lewis , Bronsted , Arrhenius Conjugate Acid –Base pair PH calculation . knowledge about Ka , Kb , Kw Pka , PKb . Pkw , Ksp ( Solubility Product) , common ion effect REDOX REACTIONS Understanding the concept of Redox Reactions ( both oxidation and Reduction half cell reaction) Calculation of Oxidation number ( deal some special cases H2O2 , NaH , Cr2O5 , H2S2O5 , CaOCl2 ) Identification of oxidizing and reducing agent in a given reaction Types of redox reactions – Combination , Decomposition , Displacement, Disproportionation Reactions Competitive electron transfer reactions -- Metal activity or electrochemical series Balancing of redox reactions -- half reaction method ( Ion –electron method ) in acidic and basic medium Redox reactions as the basis for Titrations Redox reactions and electrode processes -- Feasibility of Redox couple , Standard Hydrogen electrode , Standard electrode potential Cell Representation , carriers of current , Sign of electrode , Half cell reaction . TO COMPARE THE RELATIVE ACTIVITIES OF METALS ELECTROCHEMICAL SERIES TO PREDICT THE SPONTANEITY OF REDOX REACTION