* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download hGH - ISpatula
Bovine somatotropin wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal contraception wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Cryptorchidism wikipedia , lookup
Glycemic index wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
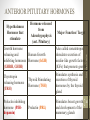
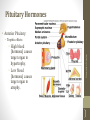
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
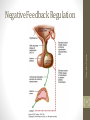
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
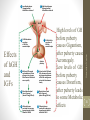
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Adrenal gland wikipedia , lookup
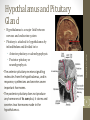
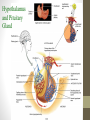
Endocrine System Tortora Chapter 18, edition 13 Ebaa M Alzayadneh, DDS, PhD Integrative Physiology and Pharmacology • Regulated by • Signals from nervous system • Chemical changes in the blood • Other hormones • Most hormonal regulation by negative feedback • Few examples of positive feedback University of Jordan Endocrine System Overview 3 • Hypothalamus is a major link between nervous and endocrine system • Pituitary is attached to hypothalamus by infundibulum and divided in to: • Anterior pituitary or adenohypophysis • Posterior pituitary or neurohypophysis • The anterior pituitary receives signalling molecules from the hypothalamus, and in response, synthesizes and secretes seven important hormones. • The posterior pituitary does not produce any hormones of its own,but, it stores and secretes two hormones made in the hypothalamus. University of Jordan Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland 4 Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland • Release of hormones is stimulated by hypothalamus releasing hormones (factors). • Regulated by negative feedback • Hypothalamic hormones made by neurosecretory cells transported by hypophyseal portal system to ant. pituitary. • Anterior pituitary hormones that act on other endocrine systems called tropic hormones, synthesizing cells are called trophs cells. University of Jordan Anterior pituitary 6 Anterior pituitary To memorize ant. Pituitary hormones F: Follicle Stimulating Hormone L: Luteinizing Hormone A: ACTH : Adrenocorticotropic hormone G: Growth Hormone T: Thyroid Stimulating Hormone O: MSH - melanOcyte stimulating hormone P: Prolactin University of Jordan "FLAGTOP" 7 • Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) by gonadotrophs cells • Ovaries initiates development of oocytes, testes stimulates testosterone production • Luteinizing hormone (LH) by gonadotrophs cells • Ovaries stimulates ovulation, testes stimulates testosterone production • Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) or corticotropin • Released by corticotrophs cells • Stimulates glucocorticoid secretion by adrenal cortex • Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) or thyrotropin by thyrotrophs • Stimulates synthesis and secretion of thyroid hormones by thyroid University of Jordan Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary (FLAG TOP) 8 • Prolactin (PRL):released by lactotrophs • Promotes milk secretion by mammary glands • Melanocyte-stimulating Hormone (MSH) • Unknown role in humans • Human growth hormone (hGH) or somatotropin released by somatotrophs • Stimulates secretion of insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) that promote growth, protein synthesis University of Jordan Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary 9 ANTERIOR PITUITARY HORMONES Hypothalamus Hormone that stimulate Hormone released from Adenohypophysis (ant. Pituitary) Major Function/ Target Also called somatotropin, stimulates secretion of insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) that promote growth Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Stimulates synthesis and secretion of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland Prolactin (PRL) Stimulates breast growth, 10 and development of the mammary glands Prolactin inhibiting hormone (PIHdopamin) University of Jordan Growth hormone releasing and Human Growth inhibiting hormones Hormone (hGH) (GHRH, GHIH) ANTERIOR PITUITARY HORMONES Gonadotropic releasing hormone (GnRH) Gonadotropic releasing hormone (GnRH) Hormone released from Adenohypophysis Major Function/ Target Follicle Stimulating hormone (FSH) Ovaries initiate development of oocytes; testes initiate development of spermatozoa Luteinizing hormone (LH) Ovaries stimulate ovulation; testes stimulate testosterone production University of Jordan Hypothalamus Hormone 11 ANTERIOR PITUITARY HORMONES Corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) Corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) Hormone released from Adenohypophysis Major Function/ Target Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) Stimulates release of mineralocorticoid, glucocorticoid, and androgen hormones from the adrenal cortex Melanocyte Stimulating hormone (MSH) Stimulate the production and release of melanin by melanocytes in skin and hair. 12 MSH signals to the brain have effects on appetite and sexual arousal University of Jordan Hypothalamus Hormone University of Jordan Negative Feedback Regulation 13 Pituitary Hormones • Anterior Pituitary: • Trophic effects: University of Jordan • High blood [hormone] causes target organ to hypertrophy. • Low blood [hormone] causes target organ to atrophy. 14 1 Low blood1glucose Low blood glucose 6 High blood6 glucose High blood glucose (hypoglycemia) (hyperglycemia) (hypoglycemia) (hyperglycemia) stimulates release of release of stimulates release of release of stimulates stimulates GHIH GHRH 2 GHRH stimulates 2 GHRH stimulates secretion secretion of hGH by of hGH by somatotrophssomatotrophs Effects of hGH and IGFs hGH GHIH High levels of GH before puberty causes Gigantism, after puberty causes Acromegaly. Low levels of GH before puberty causes Dwarfism, after puberty leads to some Metabolic 15 effects 7 GHIH inhibits 7 GHIH inhibits secretion of secretion of hGH by hGH by somatotrophssomatotrophs hGH Anterior pituitary Anterior pituitary 3 hGH 8 ofAhGH and IGFs speed low and level of hGH and 3 hGH and IGFs 8 A low level speed upofbreakdown of liver IGFs the rate up breakdown liver IGFs decreases thedecreases rate of glycogen breakdown glycogen intoglycogen glucose, into glucose, of glycogen breakdown enters the blood in the liver and glucose which enterswhich the blood in the liver and glucose enters the blood more more rapidly more rapidly enters the blood more slowly slowly 4 Blood 9 Blood level glucose level level glucose level 4 Blood glucose 9 Blood glucose rises to normal falls to normal rises to normal falls to normal (aboutmL) 90 mg/100 mL) (aboutmL) 90 mg/100 mL) (about 90 mg/100 (about 90 mg/100 5 If blood glucose10 If blood glucose 5 If blood glucose continues to continues increase, to increase, continues to decrease, hyperglycemia inhibits hyperglycemia inhibits hypoglycemia inhibits release of GHRH release of GHIH release of GHRH University of Jordan GHRH