* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download thyroid gland - Uplift Education
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac physiology wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
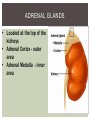
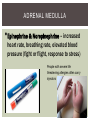
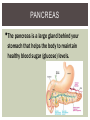
DO NOW 2/18/15 1. A blood test shows that the 35 year old male patient has heightened levels of follicle -stimulating hormone. What ef fects would you expect for this to have on the body? 2. A pregnant woman is prescribed oxytocin to increase her levels of oxytocin. What ef fects would you expect to see? 3. Which hormone released by the pituitary gland regulates water levels? 4. Which hormones released by the pituitary gland activate other endocrine glands? 5. Where is the pituitary gland located? THYROID GLAND • Thyroid hormones control metabolism • Metabolism = the body's ability to break down food and store it as energy, then utilize energy as needed THYROID HORMONES •Thyroxin - increase the rate at which cells release energy from carbohydrates - partly made from iodine • BMR – basal metabolic rate : how many calories the body must consume to maintain life PARATHYROID GLANDS • Located behind the thyroid • Four tiny glands PARATHYROID HORMONE Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) - takes calcium from the bones to make it available in the blood ADRENAL GLANDS • Located at the top of the kidneys • Adrenal Cortex - outer area • Adrenal Medulla - inner area ADRENAL MEDULLA •Epinephrine & Norepinephrine – increased heart rate, breathing rate, elevated blood pressure (fight or flight, response to stress) People with severe life threatening allergies often carry injectors ADRENAL CORTEX •Aldosterone – a mineralcorticoid, helps kidneys conserve sodium and excrete potassium, maintaining blood pressure •Cortisol – glucocortoid, keeps blood glucose and blood pressure levels stable, the “stress” hormone PANCREAS •The pancreas is a large gland behind your stomach that helps the body to maintain healthy blood sugar (glucose) levels. •Insulin – decreases blood sugar concentrations, affects the uptake of glucose by cells OTHER ENDOCRINE GLANDS •Pineal Gland – located between the • cerebral hemispheres, secretes melatonin, important for maintaining Circadian rhythms (light and dark activity) Reproductive Glands – testes and ovaries – testosterone, progesterone, estrogen STEROIDS Anabolic steroids are artificially produced hormones that are the same as, or similar to, androgens, the male-type sex hormones in the body. There are more than 100 variations of anabolic steroids. The most powerful androgen is testosterone. EFFECTS OF STEROIDS Enhanced athletic performance Serious effects on the liver Decreased production of LH and FSH hormones Breast formation, increased sexual desire, increased frequency of erectile dysfunction in males Increased sexual desire, irregular menstrual cycle, hair loss, lowering of voice, increased facial hair growth, decreased breast size in females Most changes are irreversible STRESS Bodies perceive stress extra energy is needed to overcome stressors Eustress – good stress that motivates you to keep working Distress – bad stress that results when the good stress becomes to much to bear or cope with and tension builds Cortisol is produced in response to stress RELEASE OF CORTISOL Increased blood sugar levels Increased heart rate Increased breathing rate NO energy spent on body repair Decreased production of white blood cells immune system weakened EXTENDED STRESS When cortisol levels remain high for extended periods of time, the body takes a long time to repair and the immune system remains weak Easier to get sick MANAGING STRESS LEVELS 1. 2. 3. 4. Exercise regularly (20 -30 minutes a day) Meditation Reduce caf feine Express self creatively (art, music, writing, etc.) STRESS LOG Record stress levels twice a day (once in the morning/afternoon, once at night) for a week On a scale of 1 to 5 where 1 is experiencing no stress and 5 is experiencing extreme stress, rank how stressed you currently feel. Each day, complete an activity to lower cortisol levels and document a description of what you did. Stress Log due Tuesday, 2/24