* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
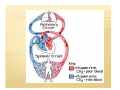
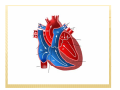
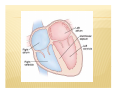
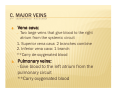
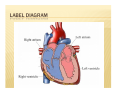
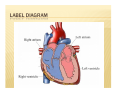
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM BELLWORK ´ How much blood do you think is pumped throughout the body each day? « 7,000 ´ Liters How many times does your heart beat in a lifetime? « 2.5 billion times I. FUNCTION: A. B. Pump fluid throughout the body for gas exchange Circulation allows tissues to receive oxygen and nutrients and to remove wastes II. STRUCTURE: A. B. C. Blood- fluid that delivers gas between alveoli and tissues Heart- Pumps blood through two circuits Blood vessels- Distributes blood to alveoli and tissues C. BLOOD VESSELS a) Veins: deliver oxygen depleted blood from tissues to the heart b) Arteries: deliver oxygen rich blood from the heart to the tissues c) Capillaries: small tubules that are the site of nutrient, electrolyte, gas, and waste exchange D. CIRCUITS The cardiovascular system is made of two circuits: 1) Pulmonary circuit: sends deoxygenated blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen and unload carbon dioxide 2) Systemic circuit: sends oxygenated blood and nutrients to all body cells and removes wastes • VIDEO CLIPS School House Rock Do the Circulation ´ http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D3ZDJgFDd k0&feature=related circulatory system ´ CIRCULATION AND HEART ANATOMY PULMONARY CIRCULATION 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Deoxygenated blood begins in the right side of the heart. Heart pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs via (pulmonary) arteries. Blood releases CO2 and picks up O2 at the alveoli of lungs. Gas exchange occurs at capillaries. Blood is now oxygenated. Oxygenated blood returns to the left side of the heart via (pulmonary) veins. SYSTEMIC CIRCULATION 6. 7. 8. 9. Heart pumps oxygenated blood to body tissues via arteries (aorta). Blood releases O2 and picks up CO2 at the body tissues. Gas exchange occurs at capillaries. Blood is now deoxygenated. Deoxygenated blood returns to the right side of the heart via veins (superior and inferior vena cava). ANATOMY OF THE HEART A. B. C. D. E. F. Four chambers Septum Major veins Major arteries Valves Covering & Wall of Heart A. FOUR CHAMBERS ´ Heart is divided into four hollow chambers- two on the left, two on the right « Atria: Upper chambers; thin walls. *Receive blood returning to heart from veins. « Ventricles: Lower chambers. *Receive blood from atria. *Contract to force blood out of the heart and into arteries. ´ Label the four chambers on your sheet. B. SEPTUM ´ A solid wall-like barrier that separates the left atrium & ventricle from the right atrium & ventricle ´ Label diagram C. MAJOR VEINS a. Vena cava: Two large veins that give blood to the right atrium from the systemic circuit 1. Superior vena cava: 2 branches combine 2. Inferior vena cava: 1 branch **Carry de-oxygenated blood – b. Pulmonary veins: - Give blood to the left atrium from the pulmonary circuit **Carry oxygenated blood LABEL DIAGRAM D. MAJOR ARTERIES a. Pulmonary trunk: branches into 2 pulmonary arteries that bring de-oxygenated blood to the lungs from the right ventricle b. Aorta: large artery that brings blood from left ventricle to the tissues of the systemic circuit. Divides into three branches. LABEL DIAGRAM E. VALVES ´ In the heart we have valves which connect different parts of the heart. For example: RA & RV « What would the purpose of this valve be? E. VALVES A valve allows the one-way flow of blood between two parts of the heart. (Similar to a sphincter) ´ A cusp is a tapered projection on the valve ´ Draw bicuspid vs. tricuspid: ´ E. VALVES 1. Atrioventricular (A-V) valves: separate the atria from the ventricles i. ii. 2. 3. Mitral (bicuspid) valve: left side of heart Tricuspid valve: right side of heart, prevents backflow Pulmonary valve: at the base of the pulmonary trunk. Three cusps. Aortic valve: found at the base of the atria. Three cusps. F. COVERING & WALL OF HEART Pericardium: tissue layers which enclose the heart & proximal ends of veins & arteries ´ 3 parts of wall help to protect and supply nutrients, nerves, capillaries ´ Draw 3 layers of wall ´ PAIR WORK WORKSHEET ´ Label major parts of heart & flow of blood ALSO… ´ Label the 4 major arteries/veins ´ Label the 4 major valves ´ Mark where blood is oxygenated & where blood is deoxygenated