* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How Powerful is the Sun?
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Bruno Pontecorvo wikipedia , lookup
Weakly-interacting massive particles wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz-violating neutrino oscillations wikipedia , lookup
Neutrino oscillation wikipedia , lookup
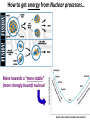
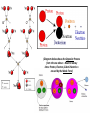
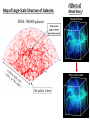
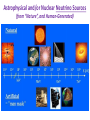
How Powerful is the Sun? PSun ~ 𝟒 × 𝟏𝟎𝟐𝟔 joules/sec = 400,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 watts (= 400 Trillion, Trillion watts!) And this will continue for the Sun’s ~10-Billion-Year Lifetime! Q: What can the Sun do to us from 93,000,000 Miles away? A: Quite a lot! The “Solar Constant” ≈ 1400 Watts per Square Meter! Q: What could the Sun’s Power Source be? A?: • Not Chemical Energy (i.e., “Oxidation/Combustion”… e.g., “Burning” wood, coal, etc…) • Not Gravitational Energy from “Kelvin-Helmholtz” Contraction… • Only one Power Source sufficient… => Nuclear Fusion! Where Nuclear Energy actually comes from… How to get energy from Nuclear processes… Move towards a “more stable” (more strongly bound) nucleus! But a Nucleus is full of Positively-Charged Protons… (…what Fundamental Force of Physics could be Strong enough to hold Nuclei together against the Repulsion of “Like Charges”…?) Yes, that’s right… It’s the “Strong Force”! And YES, the particles carrying the Strong Force are called “Gluons” (No joke!) Fusion in the Core of the Sun: What it takes… No“Cold Fusion”! The key reaction of Solar Fusion: The “Proton-Proton Chain” The 1st Step: (…but what are these “ingredients”?) All the Steps… Q1: What is “Antimatter”? Q2: What happens when “Matter” & “Antimatter” meet? (Diagram below shows the Opposite Process from the one above – Neutron Decay into a Proton, Electron, & Anti-Neutrino – caused by the Weak Force) The Particles that make up our Universe… The “Standard Model of Particle Physics” The most elusive sub-atomic particle… the Neutrino… Neutrinos DON’T “feel” the Strong (Nuclear Binding) or Electromagnetic (Charge) Forces! They just feel the Weak (Radioactive Decay) Force! (…& a tiny bit of Gravity!) Why Care about Neutrinos…? They helped Shape the Universe that we live in! And the tremendous penetrating power of Neutrinos helps us Study the Universe, today! Map of Large-Scale Structure of Galaxies: (Effects of Neutrinos:) Where do Neutrinos come from? • The Big Bang! (the “Cosmic Neutrino Background”) • The Sun (produced by nuclear fusion reactions) • The Earth's atmosphere (produced by cosmic rays) • Supernovae within our galaxy (produced by scattering reactions) • The Earth's crust (produced by uranium and thorium decays) • Cosmic accelerators (produced by pion and kaon decays) • Nuclear power plants (produced by nuclear fission reactions) • Neutrino superbeams (produced by pion and kaon decays) • Neutrino factories (produced by muon decays) Astrophysical and/or Nuclear Neutrino Sources (from “Nature”, and Human-Generated) Many Neutrinos from the Sun’s core… Where on Earth is best to look for them…? Some Neutrino Detectors… Super-Kamiokande Borexino The Unusual Behaviors of Neutrinos can explain some key mysteries of our Universe! (e.g.: The “Solar Neutrino Problem”, Baryogenesis, (Some) Dark Matter…)