* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Magnetism and Electromagnetism
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Loading coil wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
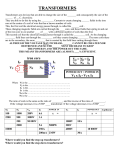
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Ignition system wikipedia , lookup
Transformer types wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
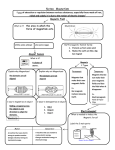
Magnetism and Electromagnetism – ‘I Can’ Statements I Can: 1. State that Bar magnets are permanent magnets. This means that their magnetism is there all the time and cannot be turned on or off. 2. State that they have two poles: north pole (or north-seeking pole) and south pole (or southseeking pole). 3. State that the north pole is normally shown as N and the south pole as S. 4. State that magnets are made from magnetic materials. These are metals that can be magnetised or will be attracted to a magnet. Most materials are not magnetic, but iron, cobalt and nickel are magnetic. Steel is mostly iron, so steel is magnetic too. 5. Attract and repel State that: If you bring two bar magnets together, there are two things that can happen: if you bring a north pole and a south pole together, they attract and the magnets may stick together if you bring two north poles together or two south poles together, they repel and the magnets push each other away. We say that unlike poles attract, and like poles repel. 6. Explain that magnets create magnetic fields. These cannot be seen. They fill the space around a magnet where the magnetic forces work, where they can attract or repel magnetic materials. 7. In the diagram, note that: the field lines have arrows on them the field lines come out of N and go into S the field lines are more concentrated at the poles 8. Electromagnets Explain that when an electric current flows in a wire it creates a magnetic field around the wire. By winding the wire into a coil we can strengthen the magnetic field. Electromagnets are made from coils like this. 9. Explain how to make an electromagnet stronger We can make an electromagnet stronger by doing these things: wrapping the coil around an iron core adding more turns to the coil increasing the current flowing through the coil. 10. Describe how an electric bell works. Electric bells like the ones used in most schools also contain an electromagnet. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. When the current flows through the circuit, the electromagnet makes a magnetic field. The electromagnet attracts the springy metal arm. The arm hits the gong, which makes a sound. The circuit is broken now the arm is out of position. The electromagnet is turned off and the springy metal arm moves back. The circuit is complete again. The cycle repeats as long as the switch is closed. 11. Describe how a relay and circuit breaker works. 12. Describe how an electric motor works i) if a current carrying conductor is in a magnetic field, the conductor will experience a force and will move if it is free to do so. The movement, magnetic field and the current are all at right angles to each other. ii) to reverse the direction of an electric motor we can either reverse the current through the coils or reverse the direction of the magnetic field. 14) Describe the parts of a commercial electric motor. Commercial motors. A commercial motor has carbon brushes for good electrical contact with the commutator and also so that when the brushes wear away, they can easily be replaced. Carbon brushes do not wear away as quickly as metal brushes 15. A commercial motor has a multi-section commutator - two sections for each of several rotating coils wound in different planes. Although only one of these coils carries a current at any one time, having a lot of them makes the rotation far smoother. 16 a). A commercial motor uses field coils not a permanent magnet. These coils become magnetised when a current is passed through them. Field coils give a stronger, more easily shaped magnetic field than permanent magnets. 16 b). Explain how electricity produced. Inducing a voltage is produced when a magnet moves into a coil of wire. This principle is used in generators to produce electricity - either a coil of wire rotates in a magnetic field, or a magnet rotates in a coil of wire. 17. State that one simple example of a generator is the bicycle dynamo. 18. Explain how to Increase the induced voltage To increase the induced voltage: move the magnet faster use a stronger magnet increase the number of turns on the coil increase the area of the coil 19. Explain the function of Transformers A transformer is an electrical device that changes the voltage of an ac supply. A transformer changes a high-voltage supply into a low-voltage one, or vice versa. A transformer that increases the voltage is called a step-up transformer. A transformer that decreases the voltage is called a step-down transformer. Step-down transformers are used in mains adapters and rechargers for mobile phones and CD players. Transformers do not work with dc supplies. Step-up transformers have more turns on the secondary coil than they do on the primary coil. Step-down transformers have fewer turns on the secondary coil than they do on the primary coil. 20. Calculating voltages The ratio between the voltages in the coils is the same as the ratio of the number of turns in the coils. primary voltage / secondary voltage = turns on primary / turns on secondary This can also be written as: Vs /Vp = Ns/Np 21. Explain how a conventional power station works and the energy transfers. Conventional power stations About three-quarters of the electricity which is generated in the UK comes from power stations operated by fossil fuels. There are four main stages: 1. fuel is burned to boil water to make steam. Chemical energy to heat energy. 2. steam makes a turbine spin 3. spinning turbine turns a generator which produces electricity. Kinetic energy to electrical energy. 4. electricity goes to the transformers to produce the correct voltage. 22. State examples of renewable and non-renewable energy resources. 23. State the meaning of a ‘renewable energy resource’. Renewable energy sources quickly replenish themselves and can be used again and again. For this reason they are sometimes called infinite energy resources. 24. Explain the advantages and disadvantages of Renewable and Non-Renewable energy resources. Renewable resources: Solar, Tidal, Hydroelectric, Wave, Geothermal, Wind, Biomass. Non-Renewable resources: Coal, oil, natural gas.