* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EKG
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
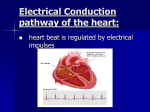
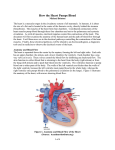
EKG • 4 chambers of the heartupper called atria and bottom called ventricles • Blood pathway through structures of the heart Electrical Conduction • Electrical impulses in the heart control the the contraction of the heart muscles • Electrical impulses begin in the SA (sinoatrial) node located in the right atrium; impulse causes the muscles of the atria to contract • Impulse then travels to the AV (atrioventricular) node through a band of fibers called the Bundle of His then through the right and left bundle branches to the final branches called the Purkinje fibers • Purkinje fibers distribute the impulses to the muscles of the right and left ventricles causing them to contract • Movement of these electrical impulses are recorded by an EKG (electrocardiograph) machine as a series of waves called a PQRST complex What does PQRST mean? • P wave= impulse in SA node and travels through the atria • QRS wave= movement of the impulse through the AV node, bundle of His, bundle branches and Purkinje fibers • T wave= represents the period of recovery (repolarization) of the ventricles before heart contracts again • Pattern of electrical current in the heart is recorded by an electrocardiograph machine= EKG/ECG • Each pattern represents the electrical activity that occurs with each contraction of the heart • So, each PQRST complex represents 1 heartbeat • If an abnormal electrical impulse occurs it will show on the EKG= we use EKG to dx disease or damage to the muscles of the heart • Electrical activity is recorded from different angles called leads • The different leads give MD a more complete picture of the heart • MD will note any abnormal electrical activity in the leads to help determine which part of the heart may be malfunctioning A complete EKG consists of 12 leads • Electrodes are placed at specific locations; Connections between the various electrodes create various leads • Leads are labeled 1(I), 2(II), 3(III), aVR, aVL, aVF, V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, V6 • Leads are classified as standard/limb leads, augmented, and chest leads • RA- right arm • LA- left arm • RL- right leg • LL-left leg • C or V for chest- placed at 6 different locations on chest • Explain procedure to pt- “not painful” • Position pt comfortably; pt needs to relax • Pt needs to avoid moving around during EKGcauses electrical interference and will show on EKG recording • After all EKG leads have be recorded, a section of each recorded lead is mounted onto a firmer backing using self stick tape (depends on machine you have) Label mount with pt’s name, address, MD name, date, time, and any pertinent info