* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EARTH LANDFORMS OF GEORGIA (Constructive and Destructive
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
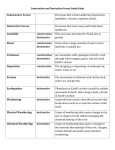
IMPORTANT CONCEPTS YOUR STUDENT SHOULD KNOW AND ACTIVITIES TO DO AT HOME EARTH LANDFORMS OF GEORGIA (Constructive and Destructive Forces) DESCRIPTION In this unit, students will become familiar with landforms around the world! They will learn about the constructive and destructive processes that are continuously shaping our ever changing Earth. Students will explore places like where glaciers are found, the Ring of Fire, the San Andreas Fault, and the ocean floor. In this unit of study, the students will explain what constructive and destructive forces are at work, how those forces impact the environment, and how humans have used technology and/or interventions in attempts to control the effects of these constructive and destructive processes that shape our earth. KEY WORDS TO KNOW Constructive: the process of building up Destructive: the process of breaking down Topography: the arrangement of physical features of an area Plate: Continent-sized slab of Earth's crust and upper mantle Crust: The solid outside layer of the Earth Mantle: The middle layer of the Earth Core: The center of the Earth; The dense center of Earth; a ball made mostly of two metals, iron and nickel Lithosphere: The cool, solid portion of Earth that includes all of the crust and part of the upper mantle Continental Drift: A theory of how Earth's continents move over its surface Magma: Melted rock inside Earth Plate Boundary: Place where two pieces of Earth’s crust meet Earthquake: The shaking of Earth's surface caused by movement of the crust and mantle Volcano: An opening in Earth's surface from which lava flows Lava: A melted rock that reaches Earth's surface AT HOME VOCABULRY STRATEGIES 1. Read aloud with your child. 2. Use vocabulary words in daily conversations. 3. Build a word wall or window. 4. Play simple vocabulary games. 5. Relate words to real life experiences. Page 1 of 3 Children’s Literature (Available at your local public library or Amazon). Islands, by Catherine Chambers, ISBN 1-57572-523-1 (NSTA Recommends) Into the Volcano: A Volcano Researcher at Work, by Donna O’Meara 1553376927 (NSTA Recommends) Forces of Nature: The Awesome Power of Volcanoes, Earthquakes, & Tornadoes, by Catherine O’Neil Grace 0-7922-6328-6 (Outstanding Science Trade Books 2005) Tsumanis by Rochelle Baltzer (eBook on MyBackpack) The creation of canyons by Amy Sterling Casil (eBook on MyBackpack) EARTH LANDFORMS OF GEORGIA (Constructive and Destructive Forces) Important Concepts Addressed in this Unit Sample Problems S5E1. Students will identify surface features of the Earth caused by constructive and destructive processes. 1. Name the layers of the Earth. 2. What is each of the layers of Earth made of? a. b. Identify surface features caused by constructive processes. Deposition (Deltas, sand dunes, etc.) Earthquakes Volcanoes Faults Identify and find examples of surface features caused be destructive processes. Erosion (water --- rivers and oceans, wind) Weathering Impact of organisms How You Can Help Your Child Interactive Learning Games Structure of Earth http://www.bbc.co.uk/science/earth/surface_a nd_interior/inside_the_earth Plate Tectonics http://www.geography4kids.com/files/earth_tecton ics.html Plate Tectonics http://www.kidsgeo.com/geology-for-kids/0043plate-tectonics.php Page 2 of 3 c. Earthquake Volcano Relate the role of technology and human intervention in the control of constructive and destructive processes. Examples include but are not limited to Seismological studies, Flood control, (dams, levees, storm drain management, etc.) 3. What evidence exists to support the theory of continental drift? Beach reclamation (Georgia coastal islands) Page 3 of 3