* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory System
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
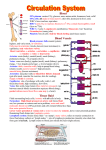
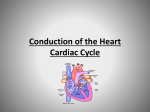
The Circulatory System Lesson #2 Heart Beat and the Cardiac Cycle - the events of each heartbeat are called the cardiac cycle - the heart is highly coordinated so that both atria contract together and then both ventricles contract together - then all of the chambers relax - the term systole refers to the contraction of heart muscle - the term diastole refers to the relaxation of heart muscle - normal heart rate at rest is about 60-80 beats per minute 2 - the familiar “lub-dup” heart sounds are produced by turbulence and tissue vibration as valves close heartbeat sounds: "lub”: - atrioventricular valves close after atria contract, then ventricles relax & fill with blood "dub": - semi-lunar valves close after ventricles contract, meanwhile atria relax & fill with blood Heart Murmurs: - problems with valves closing 1 - Atrial Systole 5 - Late Ventricular Diastole 4 - Early Ventricular Diastole 2 - Early Ventricular Systole 3 - Late Ventricular Systole • Atrial Systole • • Early • Ventricular • Systole • atria contract AV valves open semi-lunar valves closed atria relax; ventricles contract AV valves forced closed semi-lunar valves still closed Late Ventricular Systole • atria relax; ventricles contract • AV valves remain closed • semi-lunar valves forced open Early Ventricular Diastole • atria relax; ventricles relax • AV valves and semi-lunar valves close • atria fill with blood Late Ventricular Diastole • • • • atria relax; ventricles relax atria continue to fill with blood AV valves open semi-lunar valves closed Intrinsic Control of Heartbeat *not under conscious control – it is involuntary and automatic Nodal Tissue: nerve/muscle characteristics SA (sinoatrial) node (pacemaker): sends out signal from upper back wall of right atrium to make atria contract automatically every 0.85 s AV (atrioventricular) node: - SA signal received at base of right atrium near septum - another signal sent to ventricles via Purkinje fibres (conducting fibers) causing ventricular contractions that move up like a wave 7 The Normal Conduction Pathway 1. The SA node in the right atrium initiates an electrical signal (called an action potential). 2. The action potential spreads throughout atrial muscles. 3. The action potential is conducted to the AV node which slows the impulse slightly before sending it to the AV bundle. 4. The AV bundle conducts the impulse down through the septum and branches into many small Purkinje fibers that distributes the impulse throughout both ventricles ventricle Extrinsic Control of Heartbeat Medulla Oblongata: - contains cardiac control center that can alter heart rate (HR) via autonomic nervous system Adrenal medulla (on top of kidneys): - releases protein hormones epinephrine/norepinephrine to ↑HR in response to stress (fight or flight!!) Stimuli: - cause HR to change (pH/CO2 /O2 /blood pressure levels) R Electrocardiogram (ECG): - record of electrical activity of heart P wave: - atria contract QRS wave: - ventricles contract T wave: - ventricles relax T P 9 Q S Circulatory System Review - Matching 1. signals atria to contract 2. signals ventricles to contract 3. strengthens ventricular contraction signal 4. contraction of heart muscle “lub“ “dub“ diastole systole AV node 5. relaxation of heart muscle SA node 6. atrioventricular valves closing Purkinje fibres 7. semilunar valves closing heart murmur 8. problem with valves closing 11 Circulatory System Review – Labelling ventricular systole + atrial diastole ventricular diastole atrial systole R T P Q S 12