* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protists and Fungi
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of phycology wikipedia , lookup
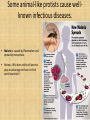
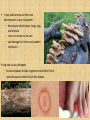
Protists and Fungi Chapter 19 •Kingdom Protista – Most diverse of all the kingdoms because its organisms are different from one another. Difficult to classify because some protists are not closely related. – Nicknamed the “odds and ends” kingdom – It is predicted that Protista classification will change as scientists find out more about the molecular evidence of these mysterious organisms. – Most unicellular, some multicellular – Some autotrophs, some heterotrophs – Cell walls of cellulose – Protists are eukaryotes that are not animals, plants, or fungi, but Protists can be animal-like, plantlike, or funguslike. Animal-like protists consume other organisms and can move. • Heterotrophs • Single-celled • Animal-like protists are often called protozoa. • Move in various ways: —Cilia help protists swim and capture food —Flagella help zooflagellates swim —Pseudopod (“False Foot”) changes shape as they move Some animal-like protists cause wellknown infectious diseases. • Malaria is caused by Plasmodium and spread by mosquitoes. • Review: Why does sickle cell anemia play an advantage to those in third world countries? Plantlike protists are photosynthetic and are called algae. – single-celled, colonial, or multicellular – no roots, stems, or leaves – 3 types of algae: Green, Red, and Brown Euglenoids are a large group of plantlike protists –mostly photosynthetic – some heterotrophic – single-celled – one or two flagella Dinoflagellates are mostly marine plantlike protists. –can cause red tide, which is toxic and causes fish kill. Diatoms are plantlike protists with glasslike shells. –shells made of silica. Used in toothpaste to help polish teeth. –Provides Earth with oxygen. Dinoflagellates • Some algae produce sexually and asexually. – Some species alternate generations, which means they can do both types of reproduction. –Sexual reproduction can be triggered by environmental stress. Funguslike protists decompose dead organisms and organic matter. – – – – heterotrophs that absorb their food can move like animals, whereas fungi (mushrooms) cannot can be parasites of plants or fish Examples: – Slime mold that grows on trees and on forest floor. It can ooze its way around. – Water molds are freshwater, funguslike protists. One type of water mold caused The Great Potato Famine of Ireland in the 1800’s •Kingdom Fungi – Fungi are multicellular organisms, with the exception of yeasts. – Eukaryotes – Heterotrophs because absorb their food from the environment through hyphae – Cell walls of chitin – decomposers and pathogens • Fungi and bacteria are the main decomposers in any ecosystem. – decompose dead leaves, twigs, logs, and animals – return nutrients to the soil – can damage fruit trees and wooden structures •Fungi can act as pathogens. –human diseases include ringworm and athlete’s foot – plant diseases include Dutch elm disease • Fungi can act as mutualists. They can form beneficial relationships with other organisms. – Examples: – Lichens: Algae feed fungus through photosynthesis, and fungal mycelium provides habitat for algae. Can grow anywhere because they are highly adaptive. – Mycorrhizae: Hyphae of fungus colonize plant roots to boost plant growth by absorbing nutrients. Plants give fungus sugar from photosynthesis. – Fungal gardens and insects: Leafcutter ants carry leaves back to nests to provide food for fungi. The ants eat the growing fungi mycelium.