* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Preliminary Discussion Questions
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
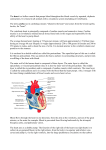
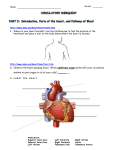
Heart Dissection Ventral side of sheep's heart Preliminary Discussion Questions 1) What is the heart's surface like? 2) How does the heart muscle itself receive oxygen for respiration? 3) Where is the muscle of the heart strongest, how can you tell ? 4) Which of the blood vessels need to be; strongest, largest? 5) How does the heart prevent blood flowing in the wrong direction ? Method First, work out which is the dorsal (back) and ventral (front) side of the heart. The ventral side is the most convex (rounded). The thick walled arteries come from this side too. Identify the parts of the heart shown in the diagram below: The side shown in this diagram is the ventral side (rounded side). Don't cut it yet. Aorta The two vena cava go into the right atrium on the other side (dorsal side) Pulmonary artery The pulmonary vein goes into the left atrium on the dorsal side. Coronary artery and vein When you need to see inside the right ventricle, cut here. When you want to open the left ventricle cut here. 6 Identify the arteries and veins which come out of the heart. Measure the diameter of the arteries and the thickness of the walls. Describe what the arteries look like? (colour, texture, etc) ______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ 7 Carefully put a rubber tube into part of the vena cave, close off any other holes in the vena cava and gently turn on the tap. From which blood vessel does water come out of the heart? This is the pulmonary artery Repeat the last step with the pulmonary vein. The water should flow out of the Aorta. 8 Look carefully at the surface of the heart. Describe the pericardium membrane ? Why is it shiny and slippery? ______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ 9 Can you find any coronary arteries or veins. Where are they found? What is their function? ______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ 10 Cut open the left ventricle following the lines on the diagram. Turn the heart upside down and run water into the ventricle. Can you see the flaps of the bicuspid valve? Draw a sketch of one valve with the suspensory ligaments on the A4 paper. 11 Cut the aorta leaving about 3cm above the heart. Run water into the Aorta from the top of the heart. What structure can you see inside which might stop the water? Why are they called "semi-lunar valves"? ______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ 12 Cut open the right ventricle by following the lines on the diagram. Describe how this is different from the left ventricle in term of volume and muscle thickness. Measure the thickness of the muscle. ______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ 13 Cut into the atria and measure the muscle thickness. Is the muscle wall thicker or thinner than the ventricles? Explain why this is the case. ______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ 14 Finally, what can you say about the size (volume) of each of the chambers? Are they different sizes, which is the largest? ______________________________________________ _______________________________________________