* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Back
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
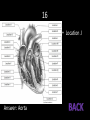
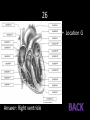
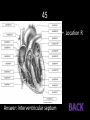
Bell Work 1. 2. What is the good and bad cholesterol called? What is a wave of pressure which forces blood through the arteries which can be felt at certain points of the body? 3. What is recommended to help prevent the changing of the walls of blood vessels? 4. What causes the “lub-dub” sound of the heart? 5. During a heart transplant, the heart is washed in a special fluid. Besides cleaning the heart, what else does it do to the heart? 6. What is considered to be the normal blood pressure reading? 7. This occurs when the arteries that supply the heart are narrowed or blocked reducing the oxygen levels to part of the heart. 8. This occurs when part of the heart is starved of oxygen which results in damaged cells that cannot work properly and stop. 9. This occurs when part of the heart muscle dies due to low oxygen levels. 10. Fully describe how the heart circulates the blood through the body. Make sure to include how the blood enters the heart, how the four chambers of the heart are involved, and where the blood goes upon leaving the heart’s different chambers 1. 2. 3. Good – HDL-C; Bad – LDL-C Pulse Changing your diet to eat less animal fat, avoid stress, eliminate smoking, exercise more 4. The valves of the heart closing 5. It paralyzes it so it doesn’t start beating too early 6. 120/80 7. Coronary Artery Disease 8. Heart Attack 9. Acute Myocardial Infarction 10. The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve and travels to the lungs via the pulmonary arteries. From the lungs, the blood uses the pulmonary vein to return to the left atrium, where it passes the bicuspid valve to the left ventricle. It finally leaves the heart after passing through the aortic semilunar valve to the aorta to the body. (enters right atrium from body --> right ventricle --> lungs -> left atrium --> left ventricle --> body) 1 8 15 22 29 36 43 2 9 16 23 30 37 44 Game Board 3 4 5 10 11 12 17 18 19 24 25 26 31 32 33 38 39 40 45 46 47 6 13 20 27 34 41 48 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 1 • This part of the blood helps the blood to fight diseases. Answer: leukocytes 2 • This blood type is known as the universal donor Answer: O- 3 • This is also known as good cholestrol. Answer: HDL-C 4 • This wave of an ECG is the result of ventricular depolarization. Answer: QRS complex 5 • This genetic condition results in cells that are deformed and sharp and it causes extreme pain. Answer: Sickle Cell Anemia 6 • What type of cells does Leukemia affect? Answer: White Blood Cells 7 • This is a wave of pressure which forces blood through the arteries which can be felt at certain points of the body. Answer: pulse 8 • This is due to the blood not having enough clotting factor and results in a body that cannot stop itself from bleeding. Answer: Hemophilia 9 • What temperature should donated blood be stored? Answer: 4 °C or 39.2 °F 10 • build up of fatty deposits on the inner wall of arteries Answer: Atherosclerosis 11 • weak spots that dilate in the body which have the potential of rupturing Answer: Aneurysms 12 • a condition of excessive fluid build up in the lungs or other organs because of inadequate pumping of the heart or a failure of the lungs to function properly. Answer: Congestive Heart Failure 13 • This is a thin, glistening sheet of endothelium that lines the heart chambers. Answer: endocardium 14 • This chamber of the heart pumps the blood to the body. Answer: left ventricle 15 • occurs when part of the heart muscle dies due to low oxygen levels Answer: Acute Myocardial Infarction 16 • Location J Answer: Aorta 17 • occurs when part of the heart is starved of oxygen which results in damaged cells that cannot work properly and stop. Answer: Heart Attack 18 • occurs when the arteries that supply the heart are narrowed or blocked reducing the oxygen levels to part of the heart. Answer: Coronary Artery Disease 19 • This is used by a fetus for all nutrient, excretory, and gas exchanges. Answer: the placenta 20 • This chamber is responsible for pumping blood to the lungs. Answer: right ventricle 21 • What type of blood could the children of a Type A+ mother and a A- father have? Answer: Type A+, A-, O+, O- 22 • stiffing or hardening of arteries due to calcium deposits which results in arteries that aren’t as elastic Answer: Arteriosclerosis 23 • What type of blood could the children of a Type O- mother and a AB- father have? Answer: Type A- or B- 24 • The cause of this disorder is not known but it results from bone marrow cancer and results in the overproduction of cells that cannot perform their duties properly. Answer: Leukemia 25 • What chamber does blood enter when it enters the heart after returning from the body? Answer: right atrium 26 • Location G Answer: Right ventricle 27 • This is the type of cell that is affected by Polycythemia. Answer: Red Blood Cells 28 • This part of the blood helps the blood to clot. Answer: platelets 29 • This is the result of too many cells being produced that results in too much oxygen in the blood. It makes the hands cold and tends to affect middle aged men. Answer: Polycythemia 30 • This chamber of the heart receives blood from the lungs. Answer: left atrium 31 • What type of cell is affected by Thrombocytopenia? Answer: Platelets 32 • This valve is located between the left atrium and ventricle. Answer: bicuspid valve 33 • This is the name of the tip of the heart. Answer: apex 34 • This valve prevents blood from flowing back into the right ventricle Answer: pulmonary semilunar valve 35 • What type of cell is affected by Hemophilia? Answer: Clotting Factors 36 • This is considered to be the normal blood pressure reading Answer: 120/80 37 • This type of exchange of nutrients in the capillary beds refers to the passage of lipid insoluble substances enter or leaving the blood via tiny capsules Answer: vesicle transportation 38 • This disorder causes heavy bleeding and petechiae (purple blotches on the skin) and is common during later stages of pregnancy. Answer: Thrombocytopenia 39 • This is the layer of a blood vessel that lines the inside of the vessel and forms a slick and smooth surface for blood movement Answer: tunica intima 40 • This is a double sac of serous membrane that covers and protects the heart. Answer: pericardium 41 • This refers to an abnormally fast heart beat (>100 beats per minute) Answer: tachycardia 42 • What is the biggest concern if the wrong blood type is given to a patient? Answer: kidney failure 43 • What type of blood antibodies would people with Type O have in their blood stream? Answer: both A and B antibodies 44 • When measuring a patient’s blood pressure, this is placed in the ear and allows the examiner to hear a patient’s pulse. Answer: stethoscope 45 • Location R Answer: Interventricular septum 46 • This disorder is caused by low levels of a certain element in the blood and it results in pale skin, shortness of breath, weakness, and irritability. Answer: Iron Deficiency Anemia 47 • When measuring blood pressure, this is the top number given to a patient. Answer: systolic 48 • What vein drains the terminal part of the large intestine. Answer: inferior mesenteric vein 49 • This vein drains the spleen, pancreas, and the left side of the stomach. Answer: splenic vein