* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic molecules - Napa Valley College
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
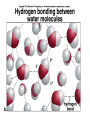
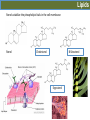
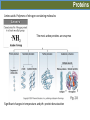
Organic molecules Organic molecules Organic molecules are formed for a few elements ü Carbohydrates ü Lipids ü Proteins ü Nucleic acids Organic molecules The have a reactive part. They always react in the same way. They can be hydrophilic or hydrophobic. monomers=1, dimers= 2, polymers= several Polymeriza5on is the stepwise linking of monomers into polymers Carbohydrates Sucrose is the source of energy for plants Carbohydrates Amylose. Linear molecule Amylopec2n. Branched molecule Carbohydrates Storage polysaccharide in prokaryotes, fungi and animals Fructans: polymers of fructose Stored in higher concentrations that starch Carbohydrates Hypermastigida Termite symbiont * Silverfish Carbohydrates Chi2n Lipids • Hydrophobic molecules • Insoluble in water • Energy and structural molecules • Storage molecules ü Fat triglycerides ü Oil ü Phospholipids ü waxes Coconut oil Safflower oil Palm oil Peanut oil Palm kernel oil Corn oil Lipids Sterols stabilize the phospholipid tails in the cell membrane Sterol Cholesterol Β-‐Sitosterol Ergosterol Lipids Cu2n and suberin form a matrix with embedded waxes Carnauba wax palm (Copernicia cerifera) Wax myrtle (Myrica cerifera) Proteins Amino acids: Polymers of nitrogen-‐containing molecules The most ac2ve proteins are enzymes Significant changes in temperature and pH= protein denatura2on Proteins The most active proteins are enzymes Energy molecule To obtain energy to do cellular work, the cell hydrolizes the ATP, releasing the stored energy and forming ADP and phosphate once again. The energy can then be used to drive an endergonic reaction. Attendance 1. What is a trans fat? 2. What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fat? 3. How many bonds does a carbon atom form? a) one bond b) four bonds c) six bonds 4. What are the characteristics of a functional group or Rgroup? 5. Which organic molecules have the defining characteristic that they do not dissolve readily in water? a) lipids b) carbohydrates c) sugars 6. The outer membrane of the cell is largely made up of a) phospholipids. b) steroids. c) carbohydrates. 7. What is the difference between condensation synthesis and hydrolysis?