* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How your body works? Objectives • To name the major muscles of
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
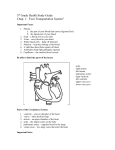
How your body works? Objectives • To name the major muscles of the body • To name the major bones of the body • Know how the heart works • Know the process that happens when we breathe Task 1 Using the following muscle names, can you locate them on the human body Trapezius Latisimus dorsi Deltoids Hamstrings Quadriceps Biceps Triceps Gastronemius Rectus Abdominus Erector Spinae Soleus Task 2 Below are a list of exercise, can you write down in the box provided what muscles are working? Exercise Sit to stand Bicep Curl Kettlebell swings Wall press Boxing Knee lifts Walking Muscles worked Muscles always work in opposite pairs. Each muscle will have a partner or the opposite muscle. So when one contracts the other will relax. Can you think of 3 benefits of resistance exercises? 1. 2. 3. How do we move? • • • Muscles are attached to bones via tendons Bones are held together by ligaments Every time we move our muscles pull on our bones to initiate movement. Human Skeleton What does your skeleton do? Your skeleton has 5 functions, can you name these? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Task 3 Using the following bone names, can you locate them on the skeleton? Cranium Patella Femur Tibia Radius Carpals Fibula Scapula Ulna Tarsals Metacarpals Metatarsals Can you think of 3 benefits of weight bearing exercise? 1. 2. 3. Circulatory system The heart • • • • • • Located in the chest, slightly to the left A pump to maintain circulation Two halves (The right side is deoxygenated, the left side is oxygenated) Four chambers o 2 collecting chambers- The atria o 2 pumping chambers- The ventricles Valves ensure the flow is one way Coronary arteries supply the heart muscle with oxygenated blood How does blood move around your body? • • • • • • • • Blood enters your (right atrium) through the Vena Cava, this is collected from the rest of your body It is then pushed into your right ventricle Your right ventricle pumps blood to your lungs via your pulmonary artery Here it collects oxygen From your lungs it then travels back to your left atrium via your pulmonary vein It is then pushed into your right ventricle From your right ventricle it is then pumped around of the body via the aorta From the rest of your body it travels back to the right atrium via your Vena Cava THE WHOLE CYCLES THENS STARTS AGAIN Arteries, Veins and Capillaries Arteries • Carries blood away from your heart • Thicker muscular walls, deal with blood under high pressure • Carry oxygenated blood with the exception of the pulmonary artery Veins • • • • Carries blood towards your heart Thin walls, no pressure Contain valves to prevent blood flow Carry deoxygenated blood with the exception of the pulmonary vein Capillaries • Arteries become smaller to form arterioles which link to capillaries • Capillaries are one cell thick to allow gaseous exchange • From the capillaries venules take blood into the veins, into the Vena Cava Respiratory System The lungs • The lungs are located in the thorax, protected by the ribs The air we breathe Normal Air Exhaled Air 78% nitrogen 78% nitrogen 21% Oxygen 16% Oxygen 0.04% Carbon dioxide 4% Carbon Dioxide Why do you think we breathe out less Oxygen and more Carbon Dioxide? Breathing There are 3 muscles associated with breathing • Diaphragm The diaphragm is a dome shaped muscled located below the ribs, when it contracts, it flattens increasing the abdominal cavity. • Internal Intercostals The internal intercostal muscles pull the ribs downward and inward, this muscle is used when breathing out • External Intercostals The external intercostal muscles pull the ribs upwards and outward, this helps with breathing in