* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download valve - INAYA Medical College
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Pericardial heart valves wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
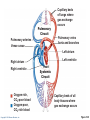
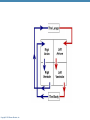
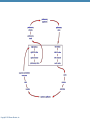
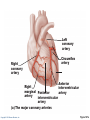
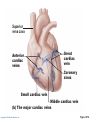
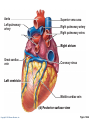
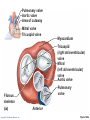
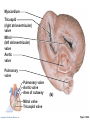
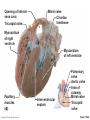
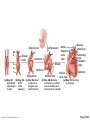
CHAPTER 18 The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Part B Learning Objectives At the end of the discussion students should be able to : Recognize the pathway of the blood through the heart Name and recognize the coronary circulation of the heart Identify and enlist the types of the heart valves Explain the development of the heart Lecture Outline Pathway of Blood Coronary circulation Heart valves Development of the heart Pathway of Blood Through the Heart • The heart is two side-by-side pumps • Right side is the pump for the pulmonary circuit • Vessels that carry blood to and from the lungs • Left side is the pump for the systemic circuit • Vessels that carry the blood to and from all body tissues Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Pulmonary Circuit Pulmonary arteries Venae cavae Capillary beds of lungs where gas exchange occurs Pulmonary veins Aorta and branches Left atrium Left ventricle Right atrium Right ventricle Oxygen-rich, CO2-poor blood Oxygen-poor, CO2-rich blood Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Heart Systemic Circuit Capillary beds of all body tissues where gas exchange occurs Figure 18.5 Pathway of Blood Through the Heart • Right atrium tricuspid valve right ventricle • Right ventricle pulmonary semilunar valve pulmonary trunk pulmonary arteries lungs Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Pathway of Blood Through the Heart • Lungs pulmonary veins left atrium • Left atrium bicuspid valve left ventricle • Left ventricle aortic semilunar valve aorta • Aorta systemic circulation Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Cardiac muscles need the blood too!!!! It’s a living tissue Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Coronary Circulation • The functional blood supply to the heart muscle itself • Collateral routes provide additional routes for blood delivery Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Coronary Circulation Arteries • Right and left coronary arteries (in atrioventricular groove), • Marginal artery • Circumflex artery • Anterior interventricular arteries Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Left coronary artery Right coronary artery Right marginal Posterior artery interventricular artery (a) The major coronary arteries Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Circumflex artery Anterior interventricular artery Figure 18.7a Coronary Circulation Veins • Small cardiac • Anterior cardiac • Middle cardiac veins • Coronary sinus • Great cardiac veins Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Superior vena cava Anterior cardiac veins Great cardiac vein Coronary sinus Small cardiac vein Middle cardiac vein (b) The major cardiac veins Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 18.7b Aorta Left pulmonary artery Superior vena cava Right pulmonary artery Right pulmonary veins Right atrium Great cardiac vein Coronary sinus Left ventricle Middle cardiac vein (d) Posterior surface view Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 18.4d Heart Valves Ensure unidirectional blood flow through the heart Types • Atrioventricular (AV) valves • Semilunar valves Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Heart Valves Atrioventricular (AV) valves • Prevent backflow into the atria when ventricles contract • Tricuspid valve (right) • Mitral valve (left) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Heart Valves Semilunar (SL) valves • Prevent backflow into the ventricles when ventricles relax • Aortic semilunar valve • Pulmonary semilunar valve Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Myocardium Pulmonary valve Aortic valve Tricuspid Area of cutaway (right atrioventricular) Mitral valve valve Tricuspid valve Mitral (left atrioventricular) valve Aortic valve Myocardium Tricuspid (right atrioventricular) valve Mitral (left atrioventricular) valve Aortic valve Pulmonary valve Fibrous skeleton (a) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Pulmonary valve Aortic valve Area of cutaway (b) Pulmonary valve Mitral valve Tricuspid valve Anterior Figure 18.8a Myocardium Tricuspid (right atrioventricular) valve Mitral (left atrioventricular) valve Aortic valve Pulmonary valve Pulmonary valve Aortic valve Area of cutaway (b) Mitral valve Tricuspid valve Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 18.8b Opening of inferior vena cava Tricuspid valve Mitral valve Chordae tendineae Myocardium of right ventricle Myocardium of left ventricle Papillary muscles (d) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Interventricular septum Pulmonary valve Aortic valve Area of cutaway Mitral valve Tricuspid valve Figure 18.8d Developmental Aspects of the Heart • Development of heart occurs from 4th week – 6th week from mesoderm. • Right and left endocardial tubes fuse by Day 22 of development to form heart tube Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Developmental Aspects of the Heart • Folding and rotation of heart tube results in the formation of cardiac chambers Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Arterial end 4a 4 3 2 1 Tubular heart Arterial end Ventricle Atrium Ventricle Venous end (a) Day 20: (b) Day 22: (c) Day 24: Heart Endothelial Heart continues to tubes begin starts elongate and to fuse. pumping. starts to bend. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Aorta Superior vena cava Venous end Inferior vena cava (d) Day 28: Bending continues as ventricle moves caudally and atrium moves cranially. Ductus arteriosus Pulmonary trunk Foramen ovale Ventricle (e) Day 35: Bending is complete. Figure 18.23 KEY POINTS Pathway of Blood -Right side is the pump for the pulmonary circuit -Left side is the pump for the systemic circuit Right atrium tricuspid valve right ventricle Right ventricle pulmonary semilunar valve pulmonary trunk pulmonary arteries lungs Lungs pulmonary veins left atrium Left atrium bicuspid valve left ventricle Left ventricle aortic semilunar valve aorta Aorta systemic circulation Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. KEY POINTS • Coronary circulation Arteries – right coronary, left coronary, marginal, circumflex, and anterior interventricular arteries Veins – small, anterior and great cardiac veins • Heart valves Atrioventricular (AV) valves – Tricuspid (right) – Mitral ( left) Semilunar (SL) valves – Aortic valve – Pulmonary valve Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. KEY POINTS • Development of the heart - Develops from the mesoderm between 4th -6th week - Right and left endocardial tubes fuse - Folding and rotation of heart tube results in the formation of cardiac chambers Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.