* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bio Honors Review Packet
Survey
Document related concepts
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
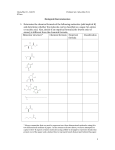
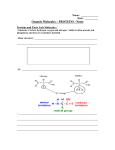
Biochemistry Review Sheet Honors Name: Correctly complete the following statements. 1. Fatty acids containing at least one double or triple covalent bonds between its carbons is called a(n) fatty acid. 2. The structure of a protein describes the overall shape formed by several polypeptide chains which compose the protein. 3. The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide chain best describes the structure of the polypeptide chains. 4. The monomer of polysaccharide is called a(n) . 5. The monomer of a protein is called a(n) . 6. The polysaccharide is also known as animal starch. 7. The polysaccharide is a component of plant cell walls. 8. The ratio between the elements hydrogen and oxygen in a lipid is 9. The hydrolytic breakdown products of a protein hydrolysis are 10. A(n) monomer units. is any long chain molecule formed from repeating 11. One of the reason carbon can form so many compounds is because it has valence electrons. Modified True-False Section **If the statement is true, write true. If it is false, change the underlined word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. The tendency of phospholipids to lie at the interface between nonpolar and aqueous polar environments make them important components to cell membranes. 2. Fatty acids and amino acids are acids because each has a carboxyl group that can lose hydroxide ions in water. 3. Strong bases have a pH of 11-14. . . 4. If the pH changes from a pH of 3 to a pH of 2, the concentration of hydrogen ions increases by 100x. 5. Hydrolysis reactions involve the removal of water to join two simpler molecules to form a more complex molecule. 6. The beta structure of a protein is a pleated sheet type of kind of structure. 7. The section of an enzyme that a attaches to the molecule the enzyme is working on it called the substrate. 8. The attraction between 2 water molecules is an example of cohesion. Multiple Choice Section: Choose the statement which best answer the question or complete the statement. 1. Which of the following molecules is the smallest? a) sucrose b) glucose c) glycogen d) starch 2. Which element is not required in order for a compound to be organic? A) carbon b) oxygen c) hydrogen d) all must be present 3. Which element is usually found in proteins but not in triglyerides? A) calcium b) phosphorus c) nitrogen d) oxygen 4. Structurally lipids are a very diverse group but they are all placed in one group because of what property? a) They are composed of glycerol and amino acids b) They are all relatively insoluble in water c) they all contain 4 interlocking rings d) They all are important as energy storage molecules e) None of the answers in correct 5. In the digestive process, the macromolecules are broken down into small molecules that can cross cell membranes. This process is called a) hydrolysis b) dehydration synthesis c) cellular respiration d) protein synthesis 6. The functional group(s) associated with amino acids is/are a) hydroxyl b) carboxyl c) phosphate d)amino e)both amino and carboxyl 7. The following equation (G = glucose) G + G + G G-G-G + 2H20, is an example of a) ionic bond formation b) peptide bond formation c) dehydration synthesis d) hydrolysis 8. All of the following reaction involve dehydration synthesis except a) the formation of a disaccharide b) production of a polypeptide c) formation of a fat d) digestion of a polysaccharide e) production of a protein 9. Which term is the most inclusive? A) glucose d) carbohydrate e) monosaccharide b) amylose c) sucrose 10) Which pH has an equal concentration of H+ and OH- ions? a) 3 b) 5 c) 7 d) 9 e) 11 11) All of the following are true concerning lipids except a) their monomers consist of a glycerol and 3 fatty acids b) they are used for protection of vital organs c) plants may contain fats in their seeds d) saturated fats have many double bonds between their carbons e) examples of lipids are oils, waxes, and fats 12) Which statement is true? a) Proteins are made of amino acids held together by ester bonds. b) A polysaccharide is a complex lipid needed for storage and structure c) The primary protein structure is based on the order of amino acids d) Steroids are complex proteins needed to control the body’s chemistry. 13) All the following molecules contain more than one ring except: a) cholesterol b) glucose c) sucrose d) chitin 14) Adhesion and cohesion are bonds between water molecules. Those bonds are: a) covalent bonds b) ionic bonds c) VanDer Waals forces d) hydrogen bonds 15) All the following are proteins except: a) hemoglobin b) keratin c) enzymes d) antibodies e) glycogen 16) The main difference between the secondary and quarternary structure of a protein is: a) bond angles between amino acids b) sequence of amino acids c) number of polypeptides in the molecule d) the folding pattern of the molecule 17) The primary structure of a protein refers to a) coiling due to hydrogen bonding between amino acids b) number and sequence of amino acids c) the alpha-helix, or pleated sheets d) the weak interaction between two or more polypeptides 18) A fatty acid containing at least two double bonds is called a) cholesterol b) saturated c) polyunsaturated d) monounsaturated 19) Which is not a function of carbohydrates? a) Immediate energy b) structural support c) Energy storage d) Enzymatic catalysis 20) Most biopolymers are formed by what type of reaction? a) Hydrophobic b) Hydrolysis c) Dehydration synthesis d) none of the above 21) Which is a true statement comparing phospholipids and triglyerides (fats and oils)? a) both molecules contain a phosphate group b) All phospholipids are saturated. c) Phospholipids are primarily used for energy storage d) phospholipids form rings, triglycerides form straight lines e) triglycerides are non-polar, and phospholipids have a polar head and nonpolar tail 22) are the subunits of proteins, and subunits of fats and oils. a) Amino acids…..fatty acids and glycerol b) Amino acids…..monosaccharides c) Nucleic acids….monosaccharides d) Glutamic acids…. carboxylic acids e) Nucleic acids….fatty acids are the 23) A hydrophobic amino acid R group would be found where in a protein? a) forming a peptide bond with the next amino acid in the chain b) on the outside of the folded chain, in the water c) on the inside of the folded chain, away from water d) forming hydrogen bonds with other R groups 24) The building blocks of nucleic acids are called a) polysaccharides b) amino acids c) fatty acids . d) nucleotides Use the molecule below and your knowledge of biochemistry to answer the following question. 25) The molecules above contains numerous bonds between carbon and hydrogen. These bonds are bonds. a) covalent bonds b) James c) hydrogen bonds d) ionic bonds 26) This compound would be a(n) a) glycerol b) fatty acid c) amino acid Use the pictured reaction below and your knowledge of biochemistry to answer the following questions. 27) Identify functional group #1 on the compound A. 28) Identify functional group #2 on the compound A. 29) Identify the monomer represented by compound A. 30) Identify compound B. 31) Identify the reaction occurring here. 32) Identify the specific type of polar covalent bond being formed at the arrow above. 33) Identify the specific class of carbohydrate. 34) What are the monomers of this compound? 35) Identify the monosaccharide and write out the molecular formula. 36) What are the pH ranges for acids, bases, and neutral? 37) What makes something organic? 38) Write next to each formula write either carbohydrate, lipid, protein, nucleic acid. C32H87O6 C32H87O6N4 C12H22O11 C32H87O6N3P18 39) Complete the table for each indicator below. Indicator Color it is originally Clear What color it changes to pink Blue black It is an indicator for Monosaccharides Bromothymol blue