* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quiz Bowl Study Guide
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
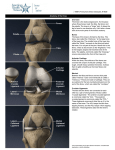
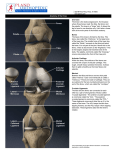
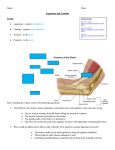
Study Guide for the Lower Anatomy Abbreviations to Remember: A.T.C – Certified Athletic Trainer (National) L.A.T - Licensed Athletic Trainer (State) N.A.T.A – National Athletic Training Association (headquarters in Dallas, TX) S.W.A.T.A – Southwest Athletic Trainers (Texas) GHATS- Greater Houston Athletic Trainers’ Society Advisory Board of Athletic Trainers – responsible for governing/ Licensing of Athletic trainers in Texas Terminology to Review: Abduction – moving away from midline Acute – a new injury Adduction – moving toward the midline Anatomical Position – body is erect with hands at side with palms forward Anterior – front ASIS- Anterior Superior Iliac Spine Bursa – a sac or pouch of synovial fluid located at friction points Chronic – an old injury Contusion - Bruise Cryotherapy – treatment by use of cold or ice Dislocation – displacement of a bone from a joint w/tearing of ligaments & tendons Distal– away from the point of attachment Dorsal-flexion – pulling foot toward head Edema – abnormal accumulation of fluid in tissue Eversion – sole of foot turned outward Hemotoma – a tumor-like mass produced by an accumulation of coagulated blood HIP POINTER - contusion to the iliac spine HOPS= History, Observation, Palpation and Special test Hyperextension – continuation of extension beyond normal Inferior – towards bottom of body or body part Inversion – sole of foot turned inward -Itis – inflammation Inflammation- Local response to cellular injury Lateral – away from the midline Ligament – connects bone to bone Medial - towards the midline Meniscus – crescent (“c”) shaped cartilage in the knee joint Plantar-flexion – pointing the toe Posterior – back Proximal – toward the point of attachment Sprain – injury to ligaments Strain – injury to muscle/tendons Subluxation – partial dislocation Superior - towards the top of body or body part 1 of 6 C. Marr Study Guide for the Lower Anatomy Tendon – connects muscle to bone Thermotherapy – treatment by use of heat Turf Toe – Sprain of the great toe Primary Survey – A= airway B= breathing C= circulation P= Protection R= rest I= ice C= compression E= elevation Secondary Survey – H= history O= observation P= palpation S= stress test *Quadricep muscle – 4 muscles on anterior portion of the femur Rectus femoris Vastus lateralis Vastus Intermedius Vastus Medialis * 4 Ligaments of the knee ACL –Anterior Cruciate PCL – Posterior Cruciate MCL –Medial Collateral LCL – Lateral Collateral *Cruciate ligaments – 2 ligaments that “cross” in middle of the knee ACL – Anterior Cruciate ligament PCL – Posterior Cruciate ligament *4 Bones of knee joint Femur – strongest bone in body Patella – knee cap Tibia – biggest and weight bearing bone in lower leg Fibula – small bone in lower leg, lateral to tibia *3 Bones of ankle joint Tibia Fibula Talus *4 Movements of the ankle Plantar-flexion Dorsi-flexion Inversion Eversion 2 of 6 C. Marr Study Guide for the Lower Anatomy *Bones that make up the foot 5 Tarsals= Cuboid, Navicular, 3 Cuneiforms 5 Metatarsals Phalanges Calcaneous – Heel bone BONES 2 Bones that make up the hip joint 1. Femur (ball) 2. Pelvis (Acetabulum- socket of the pelvis) 4 Bones of knee joint (hinge joint) 1. Femur – strongest bone in body 2. Patella – knee cap 3. Tibia – biggest and weight bearing bone in lower leg 4. Fibula – small bone in lower leg, lateral to tibia Bones of ankle joint 1. Tibia 2. Fibula 3. Talus Bones of the foot 1. 2. 3. 4. Calcaneus – Heel bone Tarsals- Cuboid, Cuneiforms, Navicular MetatarsalsPhalanges- Toes MUSCLES Quadriceps muscle group– 4 muscles on anterior portion of the femur 1. Rectus femoris 2. Vastus lateralis 3. Vastus Medialis 4. Vastus Intermedius Hamstring muscle group- 3 muscles on the posterior aspect/ ischium 1. Semitendinosus 2. Semimembranosus 3. Bicep Femoris LIGAMENTS Ligaments of the Knee 1. ACL –Anterior Cruciate 2. PCL – Posterior Cruciate 3. MCL –Medial Collateral 3 of 6 C. Marr Study Guide for the Lower Anatomy 4. LCL – Lateral Collateral Cruciate ligaments – 2 ligaments that “cross” in middle of the knee Collateral ligaments- 2 ligaments that are on the “outside” (ll) of the knee Ligaments of the Ankle 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Anterior Talor Fibular ATF Posterior Talor Fibular PTF Anterior Tib- Fib Posterior Tib- Fib Calcaneofibular CF Posterior Calcaneofibular PCF Deltoid ACTIONS/ MOVEMENTS/ MOTIONS Hip 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Knee Flexion (primary quadriceps) Extension (primary hamstrings) Adduction Abduction Internal Rotation External Rotation 7. Flexion (primary hamstrings) 8. Extension (primary quadriceps) Ankle (subtalar joint) 1. 2. 3. 4. Plantar-flexion (primary gastrocnemius) Dorsi-flexion (primary anterior compartment muscles) Inversion Eversion *2 Bloodborn pathogens HIV Hepatitis B *2 Bones that make up the hip joint Femur Pelvis – Acetabulum *Largest sesamoid bone in the body Patella 4 of 6 C. Marr Study Guide for the Lower Anatomy *Your HAMSTRINGS flex you leg and extend your hip *The Hamstrings are sometimes referred to as the “NATURAL KNEE BRACE” *The KNEE is the largest joint in the body *The QUADRICEPS are the strongest muscle group in the body *Your quadriceps pull your leg into extension and flex your hip *The ACHILLES TENDON is the strongest tendon in the body *Contusion to the iliac spine is called a HIP POINTER *PLANTER FASCIA is a wide inelastic ligamentous tissue that extends from the anterior portion of the calcaneus to the heads of the metatarsals *DELTOID LIGAMENT – large ligament located on the medial aspect of the ankle. *ANTERIOR TALOFIBULAR – most commonly injured ligament on the lateral surface of the ankle *3 muscles that make up the hamstring Semitendinosus Semimembranosus Bicep Femoris *CHONDROMALACIA –softening or wearing away of the underside of patella *OSGOOD-SCHLATTER DISORDER – patella tendon partially pulls away from the tibia causing am abnormal bony growth *UNHAPPY TRIAD – When the MCL, ACL & medial meniscus are all torn *SARTORIUS Muscle – commonly known as the tailors muscle, Longest muscle *JONES FRACTURE – Avulsion fracture of the fifth metatarsal *There are 28 bones in the foot *3 arches of the foot transverse longitudinal metatarsal 5 of 6 C. Marr Study Guide for the Lower Anatomy *GASTROCNEMIUS – Calf muscle (turns into the ACHILLES TENDON) *Function of the ACL – prevent the tibia from moving forward on the femur *Function of the PCL – prevents the tibia from moving backwards on the femur *Valgus Stress – *Varus Stress*I T Band – * Anterior Compartment Syndrome - 6 of 6 C. Marr