* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Knee Anatomy PowerPoint
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
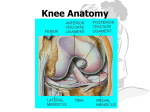
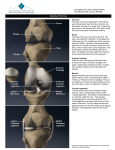
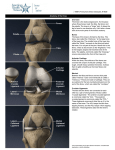
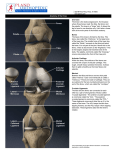
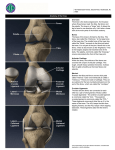
Anatomy of the Knee Bony Femur The longest bone in the body The only bone of the thigh Distal end articulates with the tibia to form the knee Proximal end articulates with the pelvis to form the hip Patella Largest sesmoid bone in the body Embedded in the patellar tendon Gives Quadriceps a mechanical advantage by providing a fulcrum Tibia and Fibula The proximal end of the fibula serves as an attachment point for ligaments of the knee, but has nothing to do with the acutal mechanics of the knee The proximal end of the tibia (tibial plateau) articulates with the femur to form the knee joint MUSCULAR Quadriceps Group of four muscles on the anterior aspect of the thigh All four of them act to extend the knee The rectus femoris also acts to flex the hip All join to form the patellar tendon Sartorius Longest muscle in the body Acts to flex and externally rotate the thigh and to flex and and medially rotate the knee “tailor’s muscle” Hamstrings Group of three muscles on the posterior aspect of the thigh All of them act to flex the knee Two of them also extend the hip Medial thigh muscles The adductors or groin muscles Act to adduct the thigh The knee has four main ligaments The two collateral ligaments sit on the medial and lateral aspects of the knee joint The two cruciate ligaments sit inside the knee joint and form a cross Collateral Ligaments The medial collateral ligament (MCL) runs from the femur to the tibia on the medial aspect of the knee Prevents excessive valgus forces on the knee Collateral Ligaments The lateral collateral ligament (LCL) runs from the femur to the fibula on the lateral aspect of the knee Prevents excessive varus forces on the knee Cruciate Ligaments Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) runs from the anterior tiba to the posterior femur Prevents the the anterior displacement of the tibia on the femur Cruciate Ligaments Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) runs from the posterior tiba to the anterior femur Prevents the posterior displacement of the tibia on the femur Menisci Two semi-circle pieces of cartilage that sit on the tibial plateau In cross section they are pie-shaped They act to deepen the articulating surface between the femur and tibia, as shock absorbers & evenly distribute the synovial fluid