* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IPC T-50 Terms and Definitions
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Printed circuit board wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Overhead power line wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
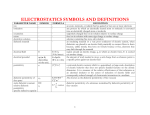
IPC T-50 Terms and Definitions Of Interest to Embedded Passives Subcommittees Capacitance Capacitive Coupling Capacitance Density Characteristic Impedance Dielectric Dielectric Breakdown Dielectric Constant Dielectric Strength Dissipation Factor Effective Permittivity Effective Relative Dielectric Constant Electrical Resistance Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Embedded Component Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) Farad Ground Plane Hipot Test Impedance A measure of the ability of two adjacent conductors separated by an insulator to hold a charge when a voltage is impressed between them. The electrical interaction between two conductors that is caused by the capacitance between them. The amount of capacitance available per unit area. The resistance of a parallel conductor structure to the flow of alternating current (AC), usually applied to high speed circuits, and normally consisting of a constant value over a wide range of frequencies. A material with a high resistance to the flow of direct current, and which is capable of being polarized by an electrical field. The complete failure of a dielectric material that is characterized by a disruptive electrical discharge through the material that is due to deterioration of material or due to an excessive sudden increase in applied voltage. The ratio of the capacitance of a configuration of electrodes with a specific material as the dielectric between them to the capacitance of the same electrode configuration with a vacuum or air as the dielectric. The maximum voltage that a dielectric can withstand under specified conditions without resulting in a voltage breakdown, usually expressed as volts per unit dimension. A parameter used to express the tendency of insulators or dielectrics to absorb some of the energy in an alternating current signal. The parameter is expressed as the ratio of loss current to charging current, and is given by e"/e', where e' and e" are the real and imaginary parts of the permittivity. See "Dielectric Constant." The value of the dielectric constant obtained when experimentally determined in an application as opposed to measured values of sample material. (See Resistance) The instantaneous transfer of charges accumulated on a nonconductor to a grounded conductor. A discrete component that is fabricated as an integral part of a printed board. A loss parameter used to compare two capacitors of equal value in order to determine their relative effectiveness as filters. A unit of electrical capacitance. A conductor layer, or portion thereof, that serves as a common reference for electrical circuit returns, shielding, or heat sinking. (See also "Signal Plane" and "Voltage Plane.") A method in which the unit under test is subjected to a high alternating current (ac) voltage. The resistance to the flow of current, represented by an electrical network of combined resistance, capacitance and inductance reaction, in a conductor as seen by an AC source of varying time voltage.The unit of measure is ohms. Inductance Laminate (n.) Load Capacitance Passive Base Material Passive Component (Element) Permeability Permittivity Permittivity Printed Component Printed Components, Conductive Inks Power Plane Inductance Relative Permittivity (єr) Resistance Resistive Clad Laminate Sheet Capacitance Sheet Resistance Static Relative Permittivity Voltage Plane Compiled by Sidney Cox December 2002. The property of a conductor that allows it to store energy in a magnetic field induced by a current flowing through it.The unit to measure is henry. A product made by bonding together two or more layers of material. The capacitance seen by the output of a logic circuit or other signal source. Base material, that does not exhibit transistance, that serves as the physical support and thermal sink for film circuits. A discrete electronic device whose basic character does not change while it processes an applied signal.(This includes components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors.) A general term used to express various relationships between magnetic induction and magnetizing force. See "Dielectric Constant." The square foot of the ratio of the electromagnetic wave propagation characteristics of free space to that of the dielectric medium. The permittivity, є, of a material is, in general, a complex-valued (has real and imaginary parts) parameter. A part (such as an inductor, resistor, capacitor, or transmission line) that is formed as part of the conductive pattern of a printed board. Component (e.g.printed inductor, resistor, capacitor or transmission line) forming part of the pattern of a printed circuit. The reactive component inductance, in response to AC noise, seen on a DC backplane system. The relative permittivity, єr, is the ratio of the permittivity of a material to that of free space. The restriction to the flow of electrons, determined by Ohms law; the quotient of DC voltage, applied to the extremes of a conductor or insulator, and the current flowing through it. A clad laminate containing resistive material that is used in making planar resistors. The electrical capacitance of a material as measured from one electrode to another, expressed in a unit of capacitance (e.g.farads or microfarads) per unit area. The electrical resistance of a planar film of a resistive material with uniform thickness as measured across opposite sides of a unit square pattern, expressed in ohms per square. The ratio of the capacitance (Cx) of a given configuration of electrodes with a specified dielectric, filling all the region pf electropotential field, to the capacitance (Cv) of the same electrode configuration with a vacuum (or air) as the dielectric. A conductor layer, or portion thereof, that serves as a common voltage source at other than ground potential for an electrical circuit, shielding, or heat sinking.(See also "Ground Plane" and "Signal Plane.")