* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Characteristics of Stars
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
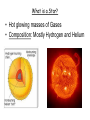
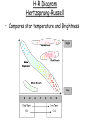
Characteristics of Stars 4-2 Constellations • Today we use constellations to find stars in the night sky. Classifying Stars • • • • • Color Temperature Size Composition Brightness Star Temperature • Surface Temperature = Color Blue-white Hottest White yellow *Sun orange red coolest Compare the sizes of Stars • Our Sun is a medium sized Star What is a Star? • Hot glowing masses of Gases • Composition: Mostly Hydrogen and Helium What makes a Star Shine? • The fusion of Atoms Hydrogen atoms fusing to form Helium releasing Heat, Light and energy • Astronomers use a Spectroscope to determine the composition of a Star Star Brightness (magnitude) • Absolute Magnitude: the “Real” brightness of the star. How much light it really gives off.(Need to know the distance to the Star) • Apparent Magnitude: How bright the star appears to be. Star Distance • Measured in Light-Years • Light-Year: The distance light travels in a year. (9.5 million million Kilometers) 5.87849981 × 1012 miles (6 trillion miles) • Speed of light: 186,000 Miles/second 300,000 Kilometers/Second Finding the Distance to Stars • Parallax: The “apparent “ Shift that a star has over a period of Time • The closer the object, the more it will shift position in the sky * Background Star H-R Diagram Hertzsprung-Russell • Compares star temperature and Brightness Star Types