* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nutrition and Digestion
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
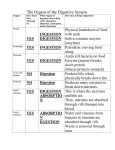
Nutrition and Digestion Vitamin A and Learning In The News Nutrients • Raw materials – Growth – Repair – Maintenance – Reproduction • Energy Classes of Nutrients • • • • • • Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Macronutrients • Carbon-containing compounds • Energy and raw material • Includes carbohydrates, lipids, & proteins • Body needs substantial amounts Carbohydrates • Should supply 45-65% of daily energy • Includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains • more low glycemic than high glycemic Proteins • Should supply 10-35% of daily energy • Proteins made of 20 amino acids • Essential amino acids must come from diet Fats • Should supply 20-35% of daily energy • Types of fats – Monosaturated (good) – Polyunsaturated (good) – Saturated (bad) – Trans fats (bad) Vitamins • • • • • • Play vital role in body function Most are derived from diet Required in small amounts Excess of some can be toxic fat soluble: vitamins A,D,E,and K water soluble: the other nine vitamins Minerals • Inorganic substances • Transported as ions by bloodstream • Variety of uses Water • No set amount daily • Body must maintain normal hydration Digestion • Breaking of food particles into molecules • Unnecessary in autotrophs, (self feeders) • Two types of digestion – Intracellular – Extracellular Organisms with Intracellular Digestion Organisms with Intracellular & Extracellular Digestion Extracellular Digestion Fungi Extracellular Digestion Most Animals Extracellular Digestion • In organisms with & without a digestive system – Fungi – no digestive system – Most animals – digestive system • Relies on enzymes (chemical digestion) • Mechanical digestion may also be present Human Digestion • Mechanical Digestion – Oral cavity by teeth – Stomach churning • Chemical digestion – Hydrochloric acid-denatures proteins, softens connective tissue, converts pepsinogen to pepsin & kills most bacteria – Bile salts emulsify lipids – Enzymes cleave chemical bonds (see table 27.3) • proteases, amylases, lipases Digestion in the Mouth • Salivary glands – Produces saliva • Mostly water • Some enzymes – Salivary amylase • Starch breakdown – Bacteria killing enzymes – mucus Digestion in the Mouth • Teeth – Mechanical digestion – Different teeth • Different functions • Fit omnivore diet Swallowing • Food is formed into a bolus – Chewed & moistened – Formed by tongue • Bolus is pushed into upper pharynx • Soft palate seals off nasopharynx Epiglottis • Folds over opening to larynx • Directs food into esophagus • Esophagus moves food toward stomach – Peristalsis = slow rhythmic squeezing – Gravity helps movement Peristalsis Stomach • Muscular sac – Churns & mixes food • Gastric glands – Produce gastric juice • Pepsinogen to pepsin • hydrochloric acid – Gastrin • Hormone • Controls gastric juices – Hydrochloric acid – Mucus-protection Structure of Stomach Food in the Stomach • Mixed with gastric juices (hydrochloric acid & pepsinogen) • Churned by muscles (3 layers of smooth muscles) • Leaves as paste (chyme) • Process takes 2-6 hours Small Intestine • Site of most digestion • Site of nutrient absorption • Area of association with accessory organs – Liver – Pancreas – Gall bladder Pancreas • Secretes many enzymes (proteases, amylase, lipase) • Empties into duodenum • Alkaline solution to help neutralize acids (sodium bicarbonate) Liver • Secretes bile (stored in gall bladder) • Components: Bile salts & bile pigments • Emulsifies fats Gall Bladder • Stores bile • Releases bile into duodenum Digestion in Small Intestine • Pancreatic amylase – Carbohydrates to maltose • Pancreatic proteases – Chymotrypsin – Trypsin – Carboxypeptidase • Pancreatic lipase – Fats • Disaccharidases (sm. Int.) – Further breaks down sugars • Peptidases (sm. intestine) Absorption in Small Intestine • Villi & microvilli Projections to increase surface area • Infoldings – increase surface area • Energy helps nutrients cross membranes • Nutrients diffuse into capillaries – Blood capillaries for all but lipids – Lacteals pick up lipids Hormones Control Digestive Enzymes Large Intestine • Areas of Colon – Cecum – Rectum – Terminates at anus Large Intestine Function • Concentration & elimination of solids • No digestive function • Absorption of water & sodium ions • Home for bacteria that produce vitamin K Overweight & Obesity • Risk factors for many medical conditions End chapter 27