* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Coordination complex wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Surface properties of transition metal oxides wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
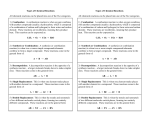
Identifying the Reactions Notes Types of Chemical Reactions Chemists classify chemical reactions into 5 main types This helps to recognize patterns and predict the products 5 Types: Synthesis Decomposition Combustion Single Displacement Double Displacement Synthesis Reactions Definition: Two or more substances react to form a single substance SIMPLER substances combine to form one COMPLEX substance General Equation: A + B AB To Identify: Has one product (a compound) Example: 2 Ca + O2 2 CaO Synthesis Examples Two elements react to form one compound. 2 Mg+ O2 2 MgO Two compounds react to form one compound. CaO + H2O Ca(OH)2 One compound and an element react to form one compound. 2 SO2 + O2 2 SO3 Synthesis Analogy It is like a relationship or marriage Decomposition Reactions Definition: A single compound breaks down into two more simpler substances The reverse of a synthesis reaction General Equation: AB A + B To Identify: Has one reactant (a compound) Example: H2CO3 H2O + CO2 Decomposition Examples Metal carbonates produce metal oxides and carbon dioxide 1. Na2CO3-->Na2O + CO2 Metal hydroxides produce metal oxides and water 2. Ca(OH)2-->CaO + H2O Metal chlorates produce metal chlorides and oxygen gas 3. KClO3-->KCl + O2 Oxyacids produce water and a nonmetal oxide gas 4. 2HNO3-->H2O + N2O5 Metal oxides produce metals and oxygen gas 5. Au2O3--> O2 + Au Water can produce oxygen gas and hydrogen gas 6. H2O--> H2 + O2 Decomposition Analogy It is like a breakup or divorce Combustion Reactions Definition: A hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen to produce water and carbon dioxide General Equation: CxHy +O2 CO2 + H2O To Identify: O2 in reactants, CO2 and H2O in products Example: CH4 + 2 O2 CO2 + 2 H2O Single Displacement Reactions Definition: One element replaces a second element in a compound General Equation: A + BC AC + B To Identify: On each side of the equation, you will see one element and one compound Example: Cu + 2AgNO3 Cu(NO3)2 + 2Ag Single Displacement Examples Types of SR Reactions Metal replaces another metal Mg + CuCl2 MgCl2 + Cu Metal replaces hydrogen 2 Li + H2O H2 + Li2O Nonmetal replaces nonmetal F2 + 2NaBr 2NaF + Br2 Single Displacement Reactions Whether displacement will occur depends on reactivity of elements Use activity series The more reactive element can replace the less reactive element If a less reactive element tries to replace a more reactive element then no reaction Single Displacement Analogy It is like getting divorced and finding a new spouse OR breaking up and finding a new girlfriend/boyfriend Dancing analogy Double Displacement Reactions Definition: Involves an exchange of negative ions between two compounds Often take place in aqueous solutions and produce a precipitate A solid that is produced from liquid solution General Equation: AB + CD AD + CB To Identify: On each side of the equation, you will see two compounds Example: 2 NaOH + CuCl2 2 NaCl + Cu(OH)2 Double Displacement Analogy Dancing with two couples and you switch partners Reactions Summary Table Type of Reaction Reactants Probable Products Generic Equation Synthesis 2 or more substances One compound A + B AB Decomposition One compound 2 or more substances AB A + B Combustion Hydrocarbon & oxygen CO2 + H2O CxHy + O2 CO2 + H2O •Metal & compound •New compound & replaced metal A + BX AX + B •Nonmetal & compound •New compound & replaced nonmetal Single Replacement Double Replacement Two compounds Two different compounds AX + BY AY + BX