* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Balancing Equations
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
California Green Chemistry Initiative wikipedia , lookup
Al-Shifa pharmaceutical factory wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon proliferation wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Double layer forces wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
Determination of equilibrium constants wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
VX (nerve agent) wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
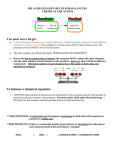
Polyatomic Ions • Polyatomic ions- a unit of more than one atom • Ways to identify polyatomic ions…. 1. If you see elements in parentheses, these are the poly atomics Ca(OH)2 Be(NO3)2 (NH4)2S 2. If you find the polyatomic ion on your polyatomic ions sheet! Balancing Equations Subscripts Coefficient PRODUCTS REACTANTS YIELD SYMBOL Subscripts Subscripts Coefficient 2CU + Zn(NO3)2 2CuNO3 + Zn Chemical Reaction Vocabulary • Chemical Reaction: One or more reactants change into one or more products • Reactant: A substance present at the start of a reaction • Product: A substance produced in a chemical reaction • Chemical Equation: An expression representing a chemical reaction; the formulas of the reactants (on the left) are connected by an arrow with the formulas for the products (on the right). • Example: Reactants Products Law of Conservation of Mass In a chemical reaction mass is conserved. •Mass cannot be created or destroyed •It can only change forms • Solid to liquid to gas • Change into another substance Example • Before Which one has the greater mass? • After change Law of Conservation of Mass —Mass is never created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. • • • When material is burned, residue is less massive than original material Ash, smoke, and gases escaped into the air—(they are still considered matter.) Their mass was not lost, only relocated due to the law of conservation of mass. Law of Conservation of Mass We learned how to count atoms in a chemical formula, now we have to make sure we have the same amount of atoms on each side of the reaction. Balancing Chemical Equations A chemical equation in which mass is conserved; each side of the equation has the same number of atoms of each element Is this equation balanced? Fe + O2 Fe2O2 How many….on the reactants side? On the products side Fe Fe O O The iron is not balanced to conserve mass. We have 1 on the left and 2 on the right, so we need to at a coefficient (small whole number that are placed in front of the formulas in an equation in order to balance it). So the equation would look like this: 2Fe + O2 Fe2O2 Balancing Steps 1. Write the unbalanced equation. 2. Count atoms on each side. 3. Add coefficients as needed to make #s equal on both sides of the equation. Coefficient subscript = # of atoms 4. Reduce coefficients to lowest possible ratio, if necessary. 5. Double check atom balance!!! Helpful Tips • Balance one element at a time. • Update ALL atom counts after adding a coefficient. • If an element appears more than once per side, balance it last. • Balance polyatomic ions as single units. • Common poly atomics: SO4,PO4,CO3,OH • Example: “1 SO4” instead of “1 S” and “4 O”