* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 8- Lesson 1-4 - Mater Academy Lakes High School
Regions of ancient Greece wikipedia , lookup
Greek contributions to Islamic world wikipedia , lookup
Aristotle's biology wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek architecture wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek warfare wikipedia , lookup
Pontic Greeks wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of Greece and the Greek world wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek cuisine wikipedia , lookup
Greek Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
Ancient economic thought wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek medicine wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek religion wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
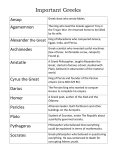
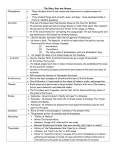
Notes 11 Chapter 8 Comedy, Tragedy, Satire • • • • • • The ancient Greeks loved live theatre. Every town had at least one open air theatre. These theatres attracted crowds of 15,000 people per performance. At first, Greek theaters were not used for plays. They were used for music, songs, and dances in honor of the Greek gods. Songs were sung by a chorus. These songs told stories of the gods. As time went on, some of the chorus began acting out the stories. Greek writers began to write plays for the chorus to sing and act out. There was almost no scenery or backdrops. There were two simple machines used on the stage. One was to lift an actor into the air, who was playing the part of a god. The other machine made a thunder sound, as Zeus was often a character in the play, and the sound of thunder was something Zeus did according to the ancient Greeks. The actors wore masks and were only male. Each town bragged about how wonderful their plays were and how marvelous their actors were. The Greeks were very competitive. They had drama contests between towns. Winners were treated with great respect, nearly as much respect as the Olympic winners. Many Greeks tried to become famous playwrights. The three best-known dramatists who wrote Greek tragedies were Aeschylus, Euripides, and Sophocles. One of the most successful and famous was a Greek named Sophocles. Sophocles wrote 120 plays! The Greek architects built theatres on hillsides. That let them position long benches in rows, one above the other, so that everyone could see what was happening on the stage. The stage was located at the bottom of the hill. They could also hear. Greek theatres had great acoustics by design. The ancient Greeks invented three types of plays. Tragedies always had a sad ending, comedies a happy ending, and satires poked fun at real people and events. (In ancient Greece, it was illegal to poke fun at the gods. Punishment for mocking the gods was death.) Comedies and tragedies entertained, but a well written satire could sway public opinion. Architecture • • • • • • The ancient Greeks excelled in the arts and architecture. They created works that expressed the ideals of reason, balance, and harmony. It was the ancient Greeks who invented 3 beautiful types of columns. These were used all over ancient Greece to hold up buildings and rooftops and temples. The Doric style is the most plain. The Ionic design is famous for its scrolls. The Corinthian style is quite fancy. Classical Greek art set standards of beauty that people still admire today. The Greeks constructed beautiful buildings. Every Greek city-state had a temple dedicated to a god or goddess. Temples such as the Parthenon included a central room that housed statues of the gods. Some famous buildings in Washington, D.C., such as the White House and the Capitol, have Greek columns. Sculpture decorated many Greek temples. The human body was the favorite subject of Greek artists. Greek sculptors tried to show ideal beauty in perfect human forms. The ancient Greeks loved beauty, music, literature, drama, philosophy, politics and art. Their statues always represented perfect looking people, with muscles and perfect noses and eyes spaced just right. Philosophy • • • • • • • • • What is Philosophy? Philosophy is the study of knowledge, reality, and existence. And what does that mean exactly? That's just it - there is no exact in philosophy. Philosophy is the practice of asking really big questions that have no clear answer or that have more than one answer. The word philosophy comes from the Greek words for love and wisdom. Simply, philosophy is the love of wisdom. Philosophers ask questions to open topics of discussion and to get people thinking. Here are five questions a philosopher might ask: 1. Is our government working? 2. What does it mean to be beautiful? 3. What makes something music? 4. Who is the most important person in your classroom? 5. Should asking some questions be against the law? The ancient Greeks thought of philosophy as an art, and philosophers as teachers of the art of asking questions. But some things in ancient Greece could not be questioned. It was against the law to do so. But that did not stop one famous philosopher from asking these questions anyway. He found himself in a lot of trouble because he ignored the law. His name was Socrates. Two other famous Greek philosophers were Plato and Aristotle, both of whom were students of Socrates, and both of whom went on to greatness. All three men wrote many things down, including some of their philosophical questions. Today, these writings are considered "gifts from the Greeks". Socrates • • • • There were many teachers in ancient Athens. Socrates was one of the most famous. His method was to question. He questioned everything. He wanted his students to question everything. He asked questions like: "Are the stories about the gods real? How can we improve our government?" A handful of wealthy nobles found his teaching methods unacceptable. They accused him of mocking the gods and challenging the Greek way of life in the citystate of Athens. They wanted him punished. Socrates was about seventy years old at the time. He had been teaching for a long time. He thought the whole thing was ridiculous. In ancient Athens, anyone could demand a trial. There were rules, but if you followed the rules, sooner or later, you would end up in court. There, the accused would have a chance to defend themselves. This handful of wealthy nobles filed charges against Socrates. At the trial, Socrates refused to defend himself - defend himself from what? Since he did not defend himself in any way, the jury felt they had no choice but to find him guilty. The punishment for mocking the gods was death. Socrates drank poison and killed himself. It was a sad day for educators and for free thinking people in ancient Athens. Aristotle • • • • • • • Aristotle was a teacher. He was born in ancient Macedonia, a country to the north of Greece. Aristotle was always curious about things, even as a small boy. His parents were great believers in education. They encouraged their young son to learn as much as he could. When Aristotle was 17, his parents allowed him to move to Athens, a city-state in ancient Greece, so that he could study with the famous scholar, Plato. Aristotle highly respected the ancient Greek way of doing things and thinking about things. He spoke Greek. He believed in the Greek gods. He thought the Greeks were great. Aristotle stayed in Athens for 20 years. He continued to study with Plato, but he also wrote, and as time went on, he taught students himself. After Plato died, King Phillip of Macedonia offered Aristotle a job as tutor to the king's young son, Alexander. Aristotle taught Alexander to admire and respect the Greeks. When Alexander's father died, Alexander became the king of Macedonia. Alexander was a warrior, a very capable warrior. He conquered the entire Mediterranean region. Everywhere he went, he spread the Greek way of doing things. Thanks to Alexander, and his teacher, Artistotle, the many gifts the Greeks gave the world survived. Today, we call Alexander, Alexander the Great! Like Confucius, the famous Chinese philosopher, Aristotle is also remembered for his sayings. He used sayings to help his students become wiser. His sayings lend themselves to discussion, argument, and thought. He is still quoted today. For example, Aristotle said: "We are what we repeatedly do. Excellence then is a habit." "We think in pictures. If you wish to change what you think, change the picture." Alexander the Great • • • • • • • Aristotle was a teacher. He was born in ancient Macedonia, a country to the north of Greece. Aristotle was always curious about things, even as a small boy. His parents were great believers in education. They encouraged their young son to learn as much as he could. When Aristotle was 17, his parents allowed him to move to Athens, a city-state in ancient Greece, so that he could study with the famous scholar, Plato. Aristotle highly respected the ancient Greek way of doing things and thinking about things. He spoke Greek. He believed in the Greek gods. He thought the Greeks were great. Aristotle stayed in Athens for 20 years. He continued to study with Plato, but he also wrote, and as time went on, he taught students himself. After Plato died, King Phillip of Macedonia offered Aristotle a job as tutor to the king's young son, Alexander. Aristotle taught Alexander to admire and respect the Greeks. When Alexander's father died, Alexander became the king of Macedonia. Alexander was a warrior, a very capable warrior. He conquered the entire Mediterranean region. Everywhere he went, he spread the Greek way of doing things. Thanks to Alexander, and his teacher, Artistotle, the many gifts the Greeks gave the world survived. Today, we call Alexander, Alexander the Great! Like Confucius, the famous Chinese philosopher, Aristotle is also remembered for his sayings. He used sayings to help his students become wiser. His sayings lend themselves to discussion, argument, and thought. He is still quoted today. For example, Aristotle said: "We are what we repeatedly do. Excellence then is a habit." "We think in pictures. If you wish to change what you think, change the picture."