* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Greece and Rome Vocab
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Marcus Aemilius Lepidus (triumvir) wikipedia , lookup
Senatus consultum ultimum wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Julius Caesar (play) wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
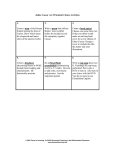
Greece and Rome Vocab patrician • a wealthy, powerful landowner dictator • an absolute ruler triumvirate • a government by three people with equal power republic a form of government in which the leader is not a king and certain citizens have the right to vote Julius Caesar • Roman general and politician. Elected consul of Rome in 59 B.C.. Invaded Italy with his army and made himself dictator for life. Later assassinated by senators in 44 B.C. paterfamilias • in the Roman social structure, the dominant male head of the household, which also included his wife, sons, and their wives and children, unmarried daughters, and slaves Mark Anthony • Was a supporter of Julius Caesar and severed as one of his generals. After Caesar's death he joined forces with Octavian and Lepidus to form the Second Triumvirate. Later joined forces with Cleopatra of Egypt. Both committed suicide after their defeat at the Battle of Actium. Octavian / Augustus • Caesar’s adopted son and heir. Together with Mark Antony and Lepidus he formed the Second Triumvirate. Founder of the Roman Empire and its first Emperor, ruling from 27 B.C. to 14 A.D. Cleopatra • Queen of Egypt. Joined forces with Julius Caesar to remove her brother from power. Later, fell in love with Mark Anthony. She and Mark Antony were defeated at the Battle of Actium and later committed suicide. Monarchy • A government ruled by a king or queen. Epic poem • A long poem that tell the deeds of a great hero, such as the Iliad and the Odyssey of Homer. Arête. • In early Greece, the qualities of excellence that a hero strives to win a struggle or contest Polis • The early Greek city-state consisting of a city or town and its surrounding countryside. Oligarchy • “the rule of the few”; a form of government in which a select group of people exercises control. Ephors • One of five men elected each year in ancient Sparta who were responsible for the education of youth and the conduct of all citizens. Acropolis • In early Greek citystates, a fortified gathering place at the top of a hill that was sometimes the site of temples and public buildings. Phalanx • A wall of shields created by foot soldiers marching shoulder to shoulder in a rectangular formation. Democracy • “the rule of the many”; government by the people, either directly or through their elected representatives. Philosophy • An organized system of thought, from the Greek for “love of wisdom”. Tragedy • A form of dram that portrays a conflict between the protagonist and a superior force and having a protagonist who is brought to ruin or extreme sorrow, especially as a result of fatal flaw. Socratic Method • The method of teaching used by the Greek philosopher Socrates; it employs a question and answer format to lead pupils to see things for themselves by using their own reason. Hellenistic Era • The Age of Alexander the Great; period when the Greek language and ideas were carried to the non-Greek world. Age of Pericles • The period between 461 B.C. and 429B.C. when Pericles dominated Athenian politics and Athens reached the height of its power. Direct democracy • A system of government in which the people participate directly in government decision making through mass meetings.