* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protozoal Diseases of Wildlife
Bovine spongiform encephalopathy wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Brood parasite wikipedia , lookup
Toxocariasis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Echinococcosis wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Cysticercosis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Fasciolosis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosoma mansoni wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
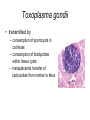
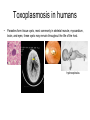
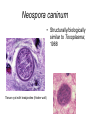
Protozoal Diseases of Wildlife • Eukaryotes • Unicellular • Multiple stages trophozoite cyst • Complex life cycles • reproduce asexually • some also have a sexual reproductive stage Phyla Important for Infectious Disease 1. Amoebozoa (amoebae) 4. Euglenozoa (flagellates) 2. Ciliophora (ciliates) 5. Microspora 3. Archaezoa (flagellates) 6. Apicomplexa (sporozoa) Major differences in modes of locomotion amoebae – pseudopodia http://video.google.com/videosearch?q=amoeba%20mo vement&hl=en&source=vgc&um=1&ie=UTF8&sa=N&tab=wv# ciliates – cilia http://video.google.com/videose arch?q=paramecium+darkfield& emb=0&aq=f# flagellates – flagella http://video.google.com/videosearch?q=flag ellates+dancing&emb=0&aq=f# microspora and sporozoa – intracellular Amoeba • The typical life cycle involves infection of the host with the trophozoite, multiplication, and in some cases, producing cysts. Ingestion in contaminated food or water Ciliates 2 examples • Balantidium coli - a common intestinal parasite of man, lower primates, and hogs. • Ichthyophthirus multifillis agent of "ich“ - a parasite infecting fish. Flagellates • Two groups 1. within Archaezoa (intestinal & urogenital) 2. within Euglenozoa (blood) Flagellates – intestinal and urogenital • Trichomonas spp – agent of trichomoniasis in a variety of animals – transmitted sexually • Giardia lamblia – infects a variety of domestic and wild animals – the most common intestinal parasite of people in North America. – transmitted fecal-oral Flagellates - haemoflagellates • live in blood, lymph, and tissue spaces • transmitted from host-host by blood-feeding arthropods • most important genera: Trypanosoma and Leishmania. Apicomplexa • • • • • all members are parasitic obligate intracellular non motile all have complex life cycles The common feature of all members is the presence of an apical complex in one or more stages of the life cycle. – Acts like a drill bit, and secretes enzymes that allow the parasite to enter other cells Toxoplasma invading host cell Toxoplasma gondii • infects humans and other warm-blooded animals, including birds • found worldwide Toxoplasma gondii • Only felids are definitive host - both wild and domestic cats serve as the main reservoir of infection. Definitive host Toxoplasma gondii 3 infectious stages of T. gondii • tachyzoites (trophozoite) • bradyzoites (within tissue cysts) • sporozoites (within oocysts) Toxoplasma gondii • transmitted by – consumption of sporocysts in cat feces – consumption of bradyzoites within tissue cysts – transplacental transfer of tachyzoites from mother to fetus Toxoplasmosis in felids • • • Mouse – infected by ingesting an oocyst Oocysts transform into tachyzoites shortly after ingestion. These tachyzoites localize in neural and muscle tissue and develop into tissue cyst bradyzoites. Once parasite is in tissue cyst stage it stimulates the mouse immune system so that only parasites within tissue cysts will survive, in this way the infection will not kill the mouse before the mouse gets eaten. Toxoplasmosis in felids • • Mice lose their fear of cat smell, and actually seek out cats. Mouse containing tissue cysts with bradyzoites is ingested by feline Toxoplasmosis in felids • • Bradyzoites are released from tissue cysts during digestion, invade cat’s intestinal epithelium, and undergo sexual replication, passing through a tachyzoite stage, culminating in the release of oocysts in cat feces. Cats generally mount a powerful immune response to the parasite and develop immunity after the initial infection, and therefore shed oocysts only once in their lifetime. Toxoplasmosis in other animals • Toxoplasmosis is one of the most commonly diagnosed causes of abortion in sheep and goats Toxoplasmosis in other animals • Recent research has shown that T. gondii is one of the primary killers of sea otters. • Toxoplasmosis is a fatal disease in the eastern bandicoot Toxoplasmosis in other animals • and wombats • and wallaby, which can transmit to humans Toxoplasmosis in humans Toxoplasmosis in humans • Parasites form tissue cysts, most commonly in skeletal muscle, myocardium, brain, and eyes; these cysts may remain throughout the life of the host. hydrocephalus Toxoplasmosis • Domestic and wild cats = definitive host • British Columbia = cougars Toxoplasmosis • Intermediate hosts – – – – – – – – – – Moose Pronghorn Mule deer WTD Black bear Red fox Skunks Opossum Mink Small mammals Neosporosis • Neospora caninum • Structurally/biologically similar to Toxoplasma; 1988 • Definitive hosts = canids (1998) • Intermediate hosts = livestock • Dogs deposit feces into pastures or food stuffs or water Neospora caninum • Structurally/biologically similar to Toxoplasma; 1988 Tissue cyst with bradyzoites (thicker wall) Neosporosis • Forms cysts in the tissue and remains dormant as bradyzoites. Dogs that eat infected meat from deceased cattle will ingest the bradyzoites and become infected, thereby shed more Neospora caninum oocysts. Neosporosis • fetal abortions, stillbirth, low milk yield, reduced weight gain, weakened condition, premature culling in cattle • economic loss to farmers Neosporosis • • • • • • • Woodbine et al. (2008) BMC Veterinary Research. 4:1471-8219 England: seroepidemiological study of N. caninum antibodies from 114 herds visited on 3 occasions, annually 94% of herds: at least 1 seropositive cow; 12.9% of adult cattle had at least 1 seropositive test 90% of herds: seropositive at all visits median seroprevalence in + herds was 10% (range 0.4% to 59%) positive association between the serostatus of offspring and dams that were seropositive Between-herd movements of infected cattle enhance spread, particularly into low seroprevalence herds Neosporosis • >40% of white-tailed deer sampled from Illinois exhibited antibodies to Neospora caninum • Seroprevalence in WI wildlife species: – – – – 19.0% WTD 14.7% coyotes 11.1% foxes 0% raccoons & opossums Neosporosis • Transmission from deer & cattle to dogs & coyotes – demonstrated • Incidence of Neospora higher where high cattle densities and high numbers of wild canids * Potential for crossover Neosporosis