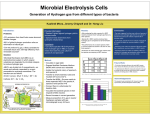
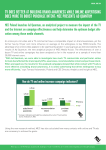
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Investment
Private equity secondary market wikipedia , lookup
Private equity in the 2000s wikipedia , lookup
Private equity in the 1980s wikipedia , lookup
Fund governance wikipedia , lookup
Leveraged buyout wikipedia , lookup
Corporate venture capital wikipedia , lookup
Foreign direct investment in Iran wikipedia , lookup
Private money investing wikipedia , lookup
Negative gearing wikipedia , lookup
Internal rate of return wikipedia , lookup
Socially responsible investing wikipedia , lookup
Investor-state dispute settlement wikipedia , lookup
Early history of private equity wikipedia , lookup
Investment management wikipedia , lookup
International investment agreement wikipedia , lookup
Investment banking wikipedia , lookup
Environmental, social and corporate governance wikipedia , lookup
History of investment banking in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Investment Generally investment means purchase of shares/ stocks and investing capital in such activities which yield income. But Keynes defines investment differently Investment Financial Investment Real Investment Buying stocks and shares of an existing company is called Financial Investment. But when new machines are purchased or new factory premises is set up, it is called real investment. Real investment results in increase of income and employment. Definitions of Investment According to Stonier and Hague, “ By investment we do not mean the purchase of existing paper security, bonds, debentures or equity, but the purchase of new factories, machines and like. Best definition is by Peterson. He says, “ Investment expenditure includes expenditure for producer’s durable equipment, new construction and the change of inventories.” Classification of Investment 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Investment Induced Investment Autonomous investment Private Investment Public Investment Gross Investment Net Investment Intended/Ex-ante/Planned/voluntary Investment Unintended/Ex-post/Unplanned/Involuntary Investment Induced Investment Such investment is Y Investment I I Income X governed by income and profit. So it is income or profit elastic. Prof Kieser says, “ When an increase in investment is due to increase in current level of income and production, it is known as induced investment. Prof Kurihara says that at very low levels of income this investment may be negative. Autonomous investment It is independent of level Y Investment of income or output. It is made with the aim of introducing new techniques, new inventions etc. Such investment is made for economic development or defence sector of the country. o I I Income X Private Investment Public Investment Made by private It is made by the individuals with the aim of profits. Depends on MEC and rate of interest If MEC is greater than R more investment will be made. Otherwise no investment. Also known as induced investment government of the country. Objective: Welfare of people, defence of country and economic development. Not profit induced t Gross Investment Net Investment The total expenditure It is that investment as a incurred on capital goods at any given time in a economy GI= Net I+ Replacement I Peterson says, “ Replacement investment is that investment which maintains intact a given stock of capital. result of which there is increase in capital stock. Peterson-net investment is investment that enlarges economy’s stock of real capital assets thereby adding to productive capacity. Ex-ante Investment Ex-post Investment It is made voluntarily, It is done involutarily according to definite plan, to achieve a given objective. Such investment is generally done by government to achieve the target of employment generation of economic growth. by investors. Many a times due sudden fall in demand the stocks may plummet. So investment in such stocks is against will of investor. Propensity to Invest ( I/Y) Average Propensity to Invest Marginal Propensity to Invest It is the ratio of total It is the ratio of change investment to total income. in investment to change in income If income increases by rs 10 crore and as a result investment increases by 5 crore, then MPI=5/10=.5 API=I/Y Determinants of induced investment In private sector, inducement to invest is influenced by two determinants- MEC and rate of interest MEC: It stands for expected rate of profitabilty when one more unit of capital is employed. MEC depends upon two factors- Prospective yield and supply price Prospective yield: PY is calculated by aggregating net income of every year of a machine through out its life time. To estimate net income, cost is deducted from annual output of machine. Supply Price: It is the cost of the machine. But not the cost of existing machine but that of a brand new machine. MEC can be found by deducting supply price from PY. As supply remains fixed, so MEC is more influenced by PY which is uncertain. Rate of Interest: “Interest is the reward for parting with liquidity” Keynes. Higher the rate of interest, greater will be the keenness on the part of people to part with liquidity. LP also affects rate of interest. Greater the LP, higher will b the rate of interest. Every entrepreneur Y MEC & rate of interest compares MEC with rate of interest while making investment. He will make investment if MEC is greater than rate of interest. If they are equal, it will be breakeven point. O MEC=R R R E MEC Investment x Factors affecting investment Technological Advancement and innovation Discovery of natural resources Government policies Foreign trade Political Environment Expectations Rate of population growth Territorial Expansion The price level The market structure Availability of finance Conditions in the labour market Aggregate Demand Measures to stimulate Investment Private Investment Public Investment Reduction in rate of Taxation interest Reduction in taxes 0f wage cut Increase in govt. expenditure Price support policy Promotion of research Pump pricing Loans Deficit financing