* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Layers of the Earth Notes - Howard Elementary School
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
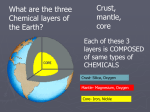
Layers of the Earth Notes Earth’s Layers • Earth is divided into layers – 2 different ways • Composition – What it’s made of • Physical properties – What can be observed/doesn’t change chemical properties Earth’s Layers by Composition • Crust • Core • Mantle Core Earth’s Layers by Composition • Crust – Outermost layer – Thinnest layer – Composed mostly of oxygen, silicon, and aluminum – Two types • Oceanic (found under oceans; more dense) – Twice as much iron, calcium, and magnesium which are more dense minerals • Continental (found under land; less dense) Earth’s Layers by Composition • Mantle – Between the crust and core – Much thicker than crust – Composed of more magnesium and less aluminum and silicon than the crust so it is more dense than the crust Earth’s Layers by Composition • Core – Below the mantle; at the center of Earth – Makes up 1/3 of Earth’s mass – Composed primarily of iron and nickel • Almost no oxygen, silicon, aluminum, or magnesium – Heats the mantle by convection Earth’s Layers by Physical Properties • • • • • Lithosphere Asthenosphere Mesosphere Outer Core Inner Core Earth’s Layers by Physical Properties • Lithosphere – Solid, outermost part of Earth • Includes crust and rigid upper part of mantle – Divided into pieces called tectonic (or lithospheric) plates Earth’s Layers by Physical Properties • Asthenosphere – Found directly under the lithosphere – Tectonic (lithospheric) plates move on this layer – Made of solid rock that flows slowly Earth’s Layers by Physical Properties • Mesosphere – Found directly under the asthenosphere – Lowest part of the mantle – Very strong Earth’s Layers by Physical Properties • Outer Core – Found beneath the mesosphere – Liquid layer of Earth’s core – Surrounds inner core – Made of iron and nickel – Heats the mantle by convection Earth’s Layers by Physical Properties • Inner Core – Found beneath the outer core – Solid layer of Earth’s core • Very dense – Made of iron and nickel Earth’s Magnetic Properties • Earth acts like a giant magnet • Earth (like any manufactured magnet) exhibits 2 poles – North – South • Earth’s outer core spins as Earth rotates – This creates the magnetic field Compass • A compass is composed of a small, lightweight magnet (called a needle) – Balances on a point • One pole of the magnet will be attracted and point toward the Earth’s North Pole – This pole on the magnet is called the north pole of the magnet • Compasses are used for navigation from any point on Earth’s surface – Possible because of Earth’s magnetic field Layers of Earth Comparisons PHYSICAL PROPERTIES Lithosphere Asthenosphere Mesosphere Outer Core Inner Core COMPOSITION Crust Mantle Core Layers of Earth Comparisons Lithosphere Asthenosphere PHYSICAL PROPERTIES Crust COMPOSITION Mantle Mesosphere Core Outer Core Inner Core Layers of Earth Comparisons