* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SciCh4NotesL1and21
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
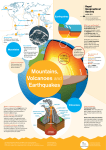
Chapter 4 Our Dynamic Earth Lesson 1 Plate Tectonics Earth’s Layers: Earth is made of layers with different thicknesses, materials, and temperatures. The core, the center of Earth, is made of solid metal on the inside and liquid metal on the outside. The mantle surrounds the core and is also made of two parts: the upper and lower mantle The top of the upper mantle is solid rock while the rest is melted rock. The lower mantle is solid rock. The crust is the thin layer of solid rock that makes up the outermost layer of Earth. The lithosphere consists of the crust and the top part of the upper mantle. The hydrosphere consists of all the liquid and solid water found on Earth. (rivers, lakes, glaciers) Landforms: The surface of Earth includes continents and the ocean floor. Landforms are physical features on Earth’s surface. Hills, rivers, lakes, and mountains are all landforms. Are the Continents Moving? Alfred Wegener was a geologist who noticed that the continents appeared to fit together as one landmass like pieces of a puzzle. He suggested that this supercontinent, Pangaea, split apart over time. His idea is called the theory of continental drift. Evidence to support Wegener’s theory: Mountains on coast of South America and West Africa have same types of rocks Fossils of the same kind were found in South America and Africa What Causes the Continents to move? Plate tectonics is the theory that explains how forces deep within Earth can cause seafloors to spread. The almost melted rock in the upper mantle acts as a conveyor belt moving plates of solid rock. Magma is hot, melted rock that is pushed to the surface under the ocean. This causes the plates to separate. When melted rock hits the ocean, it cools and hardens causing a ridge to form. Not all plates spread apart. Some collide and slide under each other. How do Mountains Form? When plates collide, they compress or press together forming folded mountains. When plates are pulled in opposite directions, they are called fault-block mountains. The place where the Earth is pulled apart is called a fault. Lesson 2 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Earthquakes: An earthquake is a sudden movement of Earth’s crust, usually at a fault. Earthquakes begin below Earth’s surface. The place where the slipping begins is called the focus. Waves of energy ripple outward from the focus. When they reach Earth’s surface, they spread outward. The point at Earth’s surface, directly above the focus is called the epicenter. The more energy released from an Earthquake, the more damage it causes. Earthquakes produce 3 different kinds of waves: Primary (P) waves – move fast through solid and liquid layers of Earth Secondary (S) waves – move ½ as fast as P waves and only go through solid layers Surface (L) waves – move the slowest along Earth’s surface causing the most damage. Magnitude is the measure of the amount of energy released by an earthquake. The Richter scale measures the magnitude of earthquakes. Volcanoes: Volcanos are openings in Earth’s crust that are found where plates meet. Magma under Earth’s crust is forced by pressure to the surface. Magma that reaches the surface is called Lava. Active volcanoes are currently erupting or have recently erupted. Dormant volcanoes have not erupted for some time. Extinct volcanoes have stopped erupting. Magma that hardens underground vertically is called a dike. Magma that hardens underground horizontally is called a sill. Lava forms solid rock as it hardens. Over time, layers of lava can build up and increase the height of a volcano. Volcanoes are different shapes: Shield volcanoes are created by thin lava that spreads over a large area like a pancake. Cinder-cone volcanoes are created by thick lava thrown into the air and landing in chunks making a cone Composite volcanoes are created by layers of ash and chunks The Hawaiian Islands where formed by volcanoes positioned over a hot spot, or pool of lava. As more and more lava erupted and cooled, the mountain grew taller and appeared above the Earth’ surface.