* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the immune system
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Antiviral drug wikipedia , lookup
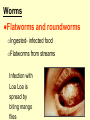
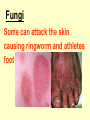
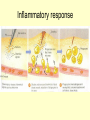
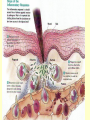
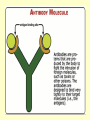
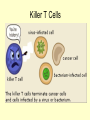
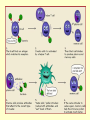
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM The function of the immune system is to fight infection through the production of cells that fight off foreign DISEASE: ●Any change, other than injury, that disrupts the normal functions of the body. PATHOGEN ●Any disease causing agent ●Diseases caused by pathogens are called infectious disease. TYPES OF DISEASES: Some are produced by ● outside agents o Bacteria, fungus, virus ● Environmental Factors o Cigarette smoke, toxins ● Inherited o Hemophilia Agents of Disease: ●VIRUS: otiny particles that invade and replicate within living cells. oAttach to surface of cells and inject their genetic material (DNA) which takes over the cell Causes the common cold, influenza, chicken pox and warts. Bacteria ●single-celled organisms oCause disease by Breaking down tissue of infected organism for food Releasing toxins that harm the body Tuberculosis, meningitis, botulism, anthrax Protists ●any organism that is not a plant, animal or fungus oCause numerous infectious diseases including malaria, dysentery and African sleeping sickness Worms ●Flatworms and roundworms oIngested- infected food oFlatworms from streams Infection with Loa Loa is spread by biting mango flies Fungi Some can attack the skin causing ringworm and athletes foot How diseases are spread: ●Inherited ●Vectors – organisms that carry disease causing agents ●Sexually transmitted The Immune System ●the body’s main defense against pathogens ●“remembers” each type of pathogen that enters the body ●IMMUNITY: the body’s ability to destroy pathogens before Fighting Infectious Diseases: ●Nonspecific defenses: do not discriminate between one threat and another. ●Specific Defenses attack particular disease causing agents Nonspecific Defense: First line of defense ●THE SKIN – the body’s most important line of defense ●Mucus, saliva, tears- contain enzymes to break down the cell walls of many bacteria ●Stomach acid – destroy pathogens that make it as far as Nonspecific Defense: Second line of defense ●INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE a non-specific defense reaction to tissue damage caused by injury or infection oThe presence of pathogens triggers the production of millions of white Inflammatory response Specific Defenses or Immune Response: The reaction of the body to particular pathogens ●ANTIGEN: substance that triggers an immune response. Antibodies: ●proteins that recognize and bind to antigens. ●carried through the bloodstream to attack the pathogen causing the infection. T cells: ( a type of White Blood Cell) provide defense against abnormal cells and pathogens ●Killer T cells track down and destroy bacteria, fungi, or foreign tissue that contains an antigen. ●Helper T cells produce memory cells that “remember” the antigen if it enters the body Killer T Cells VACCINATIONS ●A weakened form of a pathogen to produce immunity ●Stimulates the immune system to create cells that are ready to produce Immune System Disorders: ●ALLERGIES: an overreaction of the immune system to an allergen such as pollen, dust, mold or bee stings. oInflammatory response oReleases histamines that increase flow of blood and fluids to Autoimmune Diseases: ●When the immune system makes a mistake and attacks the body’s own cells. oType 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis AIDS: An Immunodeficiency Disease ●AIDS – Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome. ●HIV – Human Immunodeficiency Virus odestroys T cells so the body does not have the ability to fight Transmission of HIV ●Sex with an infected person ●Shared needles with an infected person ●Contact with body fluids of an infected person ●Infected mother to child Prevention of HIV ●Safe sex ●Don’t use drugs ●Protect yourself from blood CURE for HIV ●No cure ●The virus mutates. It is drug resistant ●Treatments extend the quality &