* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The French Revolution
French Revolutionary Wars wikipedia , lookup
War of the Fourth Coalition wikipedia , lookup
War of the Sixth Coalition wikipedia , lookup
Germaine de Staël wikipedia , lookup
Reign of Terror wikipedia , lookup
Vincent-Marie Viénot, Count of Vaublanc wikipedia , lookup
Estates General of 1789 wikipedia , lookup
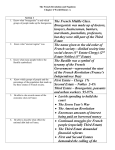
The French Revolution The Old Regime or Ancien Regime The Three Estates 1. Clergy 2. Nobility 3. Peasants – 1st Estate= Clergy: Paid no direct taxes, enjoyed great influence, privilege, and wealth. Did provide some social services such as schools, hospitals and orphanages. – 2nd Estate= Nobility: Given top jobs in government, the army, the courts and the church and had freedom from paying taxes. – 3rd Estate= Everyone Else: A diverse class of people who paid the most taxes, as well as levies, fees and services, called courvee, that dated back to the middle ages. The Bourgeoisie or middle class was at the top of this class, included doctors, bankers, merchants, lawyers, and professors. Most of this estate was made up of rural peasants. The poorest group were the urban workers. Financial Crisis • Deficit Spending: when the government spends more than it takes in. • Causes of France’s Nations Debt – Lavish Court spending starting with Louis XIV – The Seven year war & The Am. Revolution – Government borrowed more and more money • Other Causes of Strife – Bread prices rose causing many urban workers & Peasants to face hunger. – Also by 1789, half of the government’s income went to pay the interest on the national debt. Attempts at Economic Reform • To Solve the Financial Crisis: – The government needed to raise taxes, reduce expenses or both • King Louis XVI hired Jacques Necker as his financial advisor, he urged: – the king to reduce extravagant court spending – Reform government – Abolish burdensome tariffs on internal trade – Proposed taxing the 1st and 2nd Estates • The Clergy & Nobility forced the King to dismiss Necker when he proposed taxing them. The Estates General 1789 • The Legislative Body made up of representatives of the Three Estates • Each estate prepared a cahiers (notebook) listing their grievances • King insisted Estates vote by block, 1 vote per Estate, 3rd Estate wanted to vote by head. • Estates could not agree on Voting system Tennis Court Oath • After weeks of stalemate about voting, 3rd Estate declared themselves to be the National Assembly • Found meeting place locked and guarded • Delegates moved to Indoor Tennis Court and declared that they would – “never separate and meet wherever circumstances might require until we have established a sound and just constitution” Reform minded Clergy & Nobility joined cause and King Louis XVI accepted it. Storming the Bastille July 14, 1789 • Paris-the street blazed with Rumors that troops were going to occupy the capital • 800 Parisians assembled outside the BASTILLE, a prison for political prisoners demanding weapons and other arms. • Commander opened fire on the crowed, and in the ensuing battle the commander and 5 guards were killed but no weapons were found. The National Assembly and the Constitutional Monarchy • Large Famine swept France and led to wild Rumors of attacks on villages and of the government seizing peasant crops • National Assembly Acts – Ends taxes on nobles and other special privileges. – Church placed under state control – Constitution of 1791 establishes a new government • Disbanded after completing Constitution • Legislative Assembly Takes its place Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen • Fashioned after American Declaration of Independence • Liberty, Equality, Fraternity – All men are “born and remain free and equal in rights” – Proclaimed that all male citizens able to vote and hold public office – Established freedom of religion, and taxes according to ability to pay Death of the King and Queen • Women march on Versailles demanding the King return to Paris. • Royal Family virtual prisoners in Paris. • June 1791Royal Family attempts to escape Pairs and are caught and returned to Paris. • January 1793 Louis XVI Guillotined for Treason • October 1793 Marie Antoinette Guillotined for Treason Reign of Terror Maximilien Robespierre Reign of Terror September 1793-July 1794 • France declares war on Austria, Prussia and Great Britain. • Radicals took control of Legislative Assembly renamed National Convention – Established a Republic – Creates Committee on Public Safety with unlimited power to save the Revolution under the leadership of Robespierre – 1700 people executed – The Guillotine defines the Reign of Terror The Directory • The Revolution moved into the third stage in reaction to the Reign of Terror. – Established a new Constitution of 1795 with a five man directory and a two house legislature elected by male citizens of property. •The Bourgeoisie were the dominate force in this stage of the Revolution •The Directory turned to Napoleon Bonaparte. Napoleonic Wars •Napoleon and His wife Josephine organized a Coup d'état when he returned from Egypt and Napoleon used his troops to dissolved the Directory and set up a three man consulate. By 1802-Napolean had signed peace treaties with Britain, Austria and Russia. That year he had himself named consul for life. In 1804, he held a plebiscite or popular vote by ballot and assumed the title of Emperor of the French. •In 1796 at age 27 ,the Directory appointed Napoleon to lead the French army against Austria. He crushed the Austrian threat, forcing the Austrians to make peace. •1789 Led troops on an Egyptian Campaign to disrupt British trade but was thwarted by Lord Horatio Nelson, defeat not reported in France. Napoleon Reforms France • To Restore the Economy: – – – – – Instituted Price controls Encouraged new industry Rebuilt roads and canals Opened jobs to all based on talent Set up public schools • NAPOLEONIC CODE – Equality of all citizens before the law – Religious toleration – Abolition of feudalism – Women lost the right to vote – Male heads of households regained complete authority over their wives and children. Napoleonic Empire Napoleonic Empire • 1804 to 1812-Napoleon went to war against Britain, Russia, Austria and Sweden’s Coalition forces. – Europe was redesigned as Napoleon annexed portions of the Netherlands & Italy; abolished the Holy Roman Empire; created the Grand Duchy of Warsaw; and placed friends and relatives on the thrones of Europe • 1805-Battle of Trafalgar: Napoleon defeated on the high seas by British Admiral Lord Nelson. • Continental System: a blockade designed to economically damage Britain, that closed European ports to British goods, ultimately unsuccessful • Watch Video: Napoleons' Lost Army Congress of Vienna Congress of Vienna • After the final Battle at Waterloo, the heads of Europe faced the task of restoring order to Europe. – Prince Clemens von Metternich – Tsar Alexander I – Lord Robert Castlereagh – Prince Charles Maurice Talleyrand • The decisions made at the Congress of Vienna influenced European politics for the next 100 years.