* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Opiates lecture opiatesONLY
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
Urban legends about drugs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
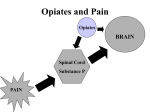
Turn in Problem set 4 Friday UNIT FIVE Review: What is a monoamine? 1. A metabolic enzyme 2. A molecule with a CH3 group on it 3. A molecule with an NH2 group on it 4. Any neurotransmitter 5. None of the above Always: What Information Will be Covered for EVERY Drug: What is drug? Why is it used? How is it administered? How much is used? Metabolism? Affects on the cell? Addiction? Benefits? Harms? Individual experience may vary Which depressants will be covered? • Analgesics – Opiates – OTC pain killers • Ethanol • Cannabis What do we experience on depressants? Increasing dosage disinhibition tranquilizing hypnotic Increasing depression of the central nervous system Disclaimer – babies should not do drugs • Analgesics – Opiates – OTC pain killers • Ethanol • Cannabis Why do we take opiates? Activity 2 Pain Substance P Prostaglandin Pain stimulus picked up by peripheral nervous system Pain signal amplified by central nervous system Opiate (and Opioid) forms http://www.jimemery.com/flowers/poppyduo.jpg Interrelated opiate forms Codeine is converted to morphine in brain, but some people CAN’T morphine OH OH Heroin – more lipid soluble, so crosses BBB quickly. BUT must be chemically converted to morphine to work. codeine OH CH3 CH3-COO heroin CH3-COO How are opiates administered? Activity 3 Unknown artist Wikimedia commons How much opiate is used? Oxycodone dose: 5-15 mg (200? mg lethal) Morphine dose: 4-10 mg (200-2000 mg lethal) Heroin dose: 5-200 mg (200-? mg lethal) Activity 4 Opiate Morphine Heroin Opiate metabolism? Half life male Metabolic enzyme Fat solubility CYP2D6 Moderately lipid soluble 10 minutes 10 minutes CYP2D6 Highly lipid soluble 2 hours Oxycodone 4 hours Half life female 3 hours 5 hours CYP2D6 Water soluble Examine the previous graph on opiate metabolism. Which is unexpected? 1. That all opiates are metabolized by CYP2D6 2. That fat-soluble heroin has the shortest half life 3. That there is a different half life for male vs. female 4. That there is a different metabolic enzyme for male vs. female Activity 5 Why do we react to opiates? endorphin OH Endorphin = internally produced morphine Internally made = endogenous OH Many endorphins. Dynorphin – 200 x more potent than morphine! Receptor locations Mu Spinal cord, thalamus, NA, brain stem affects Control respiration ABUSE Analgesia NA, VTA, spinal cord Causes DYSphoria, not EUphoria Spinal cord, Emotional state regulation, limited analgesia Kappa Limbic pathway Delta Opiate receptors, types and locations Opiate receptor AGONISTS How do opiates reduce substance P? By inhibiting action potentials • Recall – resting potential More positive, and more Na OUTSIDE More negative, and more K INSIDE Audesirk Figure 33.E1 • Opiate receptors are ligand-gated potassium channels How do opiates reduce substance P? By blocking exocytosis Opiate is the ligand that opens K+ channels. This will cause K+ to do what? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Flow down concentration gradient into a cell (making it more positive) Flow against concentration gradient into a cell (making it more positive) Flow down concentration gradient out of a cell (making cell more negative) Flow against concentration gradient out of a cell (making cell more negative) Stay where it is Graphic – Conn McQuinn How do opiates inhibit neurons? Normal action potential threshold Threshold hard to reach Opiate binds Making a neuron even more negative = hyperpolarize Threshold is what part of this graph? 1. 2. 3. 4. A B C D Opiate Addiction? Activity 6 • Reward • Tolerance More enzyme, less receptors • Dependence? Less endorphin, less receptors PAIN is a very difficult withdrawal symptom to ignore! How do opiates cause euphoria? Dopamine release is regulated (inhibited) Opiate block exocytosis of regulator, allowing dopamine release (two negative make a positive) Activity 8 What are the side effects of opiates? HARD to quit! http://www.healingdaily.com/ NOT life-threatening to quit, unless you start to use your old dose again after being off a while. How are opiate addiction and OD treated? antagonist OH 0 OH OH naloxone Weak agonist methadone Which of the following does NOT contribute to opiate addiction? 1. Kappa opiate receptors 2. Mu opiate receptors 3. CYP2D6 4. Endorphins Individual experience may vary… Hyperpolarization Football • Push the offense farther away from first down line, make it harder to progress the ball up the field. • Hyperpolarization pushes the cell’s charge farther away from threshold, harder to achieve action potential






























![NALTREXONE[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008499817_1-96b3e8696c43dc1d94e990e6680b7eac-150x150.png)