* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Starting Unit.pub
Vincent's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Factorization wikipedia , lookup
List of prime numbers wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Division by zero wikipedia , lookup
Algebra 3
Name: _________________________
Review
Starter Unit
Day 1: Adding and Subtracting Missing Numbers
Goals
- Students will be able to find the missing values that make the statement true in each equation.
Vocab
Equation - A statement that includes a = sign, numbers and an operation.
Expression - A statement that includes numbers and operations only, no = sign
Finding Missing
Numbers
#1) Look at the operation needed to get the answer.
#2) Figure out which number needs to go into the blank to make the statement true
Examples
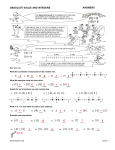
#1) _______ - 8 = 3
#2) 78 ÷ ______ = 13
#3) 20 + _____ = 48
#4) 14 · _______ = 112
#5) 41 - ____ = 1
#6) ______ ÷ 20 = 2
#7) ____ · 3 = 12
#8) 11 + ______ = 19
Summary
~ How do you find out what the blank should equal?
Due: ____________________
Homework: Worksheet ~ Missing Blanks
Pg. 1
Day 2: Factorization / Prime vs Composite
Goals
- Students will be able to factor a number down to its primes
- Students will know the difference between a prime and a composite number
Vocab
Factorization - A process of breaking down a number to its primes
Prime Number - Can be divided evenly only by 1 and itself. 1 is not a prime
Composite Number - Can be divided evenly by numbers other than one and itself. Has at least 3 factors.
Factorization of
numbers
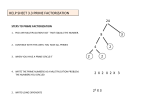
#1) Break the number down to its primes
#2) Rewrite the primes in order from least to greatest, then in exponent form
#3) Label if the number was a prime or a composite number
- Prime - cannot be broken up
- Composite - can be broken up 1 or more times
Examples
Break down each number to its primes. Label if the number was a prime or
composite number.
#1) 48
#2) 35
#3) 5
#4) 100
Pg. 2
Examples Cont.
Break down each number to its primes. Label if the number was a prime or
composite number.
#5) 13
#6) 40
#7) 72
#8) 81
Summary
~ What is factorization?
~ How can you tell if a number is a prime number?
~ How can you tell if a number is a composite number?
Due: ____________________
Homework: Worksheet ~ Factorization/ Prime vs Composite Numbers
Pg. 3
Day 3: Integer Rules
Goals
- Students will be able to add, subtract, multiply, and divide integers
- Students will know the different sign rules for each integer operation
Vocab
Integers - A positive or negative whole number or zero. Ex. -2, -5, 0, 8, 10 etc
Adding and
Subtracting Integers
#1) Look at the signs to tell you what to do
- If the signs are the same (both + or both -) you add the numbers
~ If the signs are difference (one + and one -) you subtract the numbers
*******WATCH OUT FOR: - + is a -, + - is a -, and - - is a +
#2) The sign is taken from the largest number.
- If the larger number is + then the answer is +
- If the larger number is - then the answer is -
Examples
Add or Subtract the following integers. Watch the signs!!!!!!
#1) -12 + 7
#2) -10 + (-7)
#3) 8 + 7
#4) 2 - (-2)
#5) 4 - 11
#6) -8 - (-6)
#7) 45 + 9
#8) -38 + (-5)
Pg. 4
Multiplying and
#1) Multiply or divide the numbers like normal without the sign
Dividing Integers
#2) Add the correct sign according to the rules
Examples
+·÷+=+
-·÷ -=+
+·÷ -=-
-·÷ +=-
Multiply or divide the following integers. Watch the signs!!!!!!
#1) 6(-4)
#2) -11 · 12 · -2
#3) -132 ÷ -11
#4)
− 105
7
#5) - 12 · 13
#6)
65
− 13
#7) 168 ÷ 12
#8) -5(-4)(-10)
Summary
~ How do you tell what the sign is when you add or subtract integers?
~ What are the sign rules when multiplying and dividing integers?
~ How can you tell if you are going to add or subtract when working with integers?
Due: ____________________
Homework: Worksheet ~ Adding, Subtracting, Multiplying and Dividing Integers
Pg. 5
Day 4: Coordinate Plane
Goals
- Students will be able to plot points on a coordinate plane
Vocab
Coordinate - a number in an ordered pair that names the location of a point on the coordinate plane
Quadrants - Any of the 4 regions into which a plane is divided by the axes
x - axis - the line that runs horizontally (left to right) through zero
y - axis - the line that runs vertically (up to down) through zero
ordered pairs - a pair of numbers used to locate a point on a coordinate plane (x, y)
x - coordinate - the first value in an ordered pair
y - coordinate - the second value in an ordered pair
origin - the center of the coordinate plane located at (0, 0)
Plotting on a
Coordinate Plane
#1) Look at the ordered pair the x is the first value you move, do not put a dot yet
~ + goes right
~ - goes left
#2) The y value is the second value you move, after you move the y value you put a
dot down
~ + goes up
~ - goes down
Pg. 6
Examples
Tell the direction that the order pair is going. Plot each point. Tell the quadrant
each point falls in (or the axis it falls on).
#1) (3, -4)
#2) (0, 1)
#3) (0, 0)
#4) (-4, -9)
#5) (4, 7)
#6) (4, 0)
#7) (-1, -8)
#8) (0, -4)
#9) (3, 3)
#10) (-8, 3)
Summary
~ Which value moves first, the x or the y?
~ Which directions do the x axis go?
~ Which directions do the y axis go?
Due: ____________________
Homework: Worksheet ~ Coordinate Plane
Pg. 7
Day 5: Square Roots and Cube Roots
Goals
- Students will be able to find square roots of numbers
- Students will be able to find cube roots of numbers
Vocab
Square Root - A value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the number
3
Cube Root - is a value that when it is used in a multiplication of itself three times give the number
Finding square roots
and cube roots
#1) Break up each number into its prime factors and put them in order
#2) Square Roots
- group like numbers into groups of two
#3) Cube Roots
- group like numbers into groups of three
#4) Multiply all groups together to get the answer - a group = 1 number
Examples
Find the following roots.
#1)
#3)
3
225
#2)
729
#4)
3
27
144
Pg. 8
Examples Cont.
Find the following roots.
#5)
#7)
324
121
#6)
3
125
#8)
3
512
Summary
~ What do you need to break each number down to?
~ How many need to be in a group for a square root?
~ How many need to be in a group for a cube root??
Due: ____________________
Homework: Worksheet ~ Square roots and cube roots
Pg. 9
Day 6: Order of Operations
Goals
- Students will be able to tell what the order of operations is
- Students will be able to follow the order of operations
Vocab
Order or Operations - The order in which math is solved
Order or Operations
~ Parentheses ( )
* Brackets [ ]
* Braces { }
~ Exponents
~ Multiplication and division
~Addition and subtraction
Evaluate each expression
43 − 1
− ( − 10 )
4 + 2
#1) -4 + 2(-2 + 5) 2
#2)
#3) 24 - 8 * 12 ÷ 4
#4) ( -8 - 2) ÷ (9 - 4)
#5) (5 - 8)2 + (-2 - 9)
#6) (3)3 - (2)2 + (1)2
Pg. 10
Examples Cont.
#7) 42( 9 - 2)
#8) (-2)3[3 + 3(7 - 4)]
#9)5 ÷ -5 • 3 ÷ -3
#10) − 2 ⋅ 7
10
9 − 4
Summary
~ What is the order of operations?
~ What is special about adding / subtracting and multiplying/dividing?
~ How should you solve an exponent??
Due: ____________________
Homework: Worksheet ~ Order of Operations
Pg. 11