* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Adjective Clauses • Practice 1
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Morphology (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
American Sign Language grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sloppy identity wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Untranslatability wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish pronouns wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sotho parts of speech wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Relative clause wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
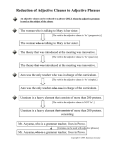
Name 20.2 Date Adjective Clauses • Practice 1 A clause is a group of words with its own subject and verb. An independent clause can stand by itself as a complete sentence. A subordinate clause can only be part of a sentence. The Adjective Clause An adjective clause is a subordinate clause that modifies a noun or pronoun by telling what kind or which one. Adjective clauses begin with relative pronouns or relative adverbs. ADJECTIVE CLAUSES The woman who made the speech is not, herself, a candidate. He is a performer whose work I always enjoy. Introductory Words Relative pronouns connect adjective clauses to the words they modify. They also play a role within their own clauses, as shown in the chart. Relative adverbs connect adjective clauses to the words they modify and act as adverbs within the clauses. Note in the second example that an introductory word may be understood. USES OF INTRODUCTORY WORDS The movie that is playing now is a comedy. (subject) The movie (that) we saw last night was a documentary. (direct object) The movie in which Tony appeared was a hit. (object of a preposition) He is an actor whose work I admire. (adjective) I remember the day when they began filming. (adverb) Exercise 1 Recognizing Adjective Clauses. Underline the adjective clause in each sentence. Circle the word it modifies. EXAMPLE: Grace is the person person I met at Reggie’s party. 1. The house where John F. Kennedy was born is now a museum. 2. This soup has a spice that I can’t identify. 3. Mom is the one for whom I left the message. 4. Len is the one whose mother is the district attorney. 5. Ohio is a state that cherishes football. 6. Mr. Paulson is the teacher who inspired me to study chemistry. 7. Wendy is someone I have known since kindergarten. 8. Emily Dickinson is a poet whose work was once ignored. 9. A calculator is something Dad will surely like. 10. Where is the box in which I keep my change? Exercise 2 Recognizing the Use of Introductory Words. On the line at the right of each sentence in Exercise 1, write the introductory word and its use in the clause. EXAMPLE: Grace is the person person Prentice-Hall, Inc. I met at Reggie’s party. (that) direct object Adjective Clauses • 75