* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download First Quarter Exam Review Sheet Name
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Provenance (geology) wikipedia , lookup
Ring of Fire wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Great Lakes tectonic zone wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
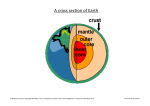
“WHAT DO I NEED TO KNOW FOR THE TEST?” First Quarter Final Exam: Practice Test/Study Guide *Standards 3a-e Chapters: Plate Tectonics = 9 (old text = 17), volcanoes = 8 (18), earthquakes = 10 (19), rocks = 3 (5 & 6) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. List the evidence that supports the theory of plate tectonics and the existence of Pangaea. What is the relationship between the age of rocks on the seafloor and their distance from the mid-ocean ridge? Where do most earthquake faults occur? Describe the pattern of magnetic polarity (the magnetic patterns in the crust rocks) on each side of a mid-ocean ridge. Where is the oldest oceanic crust found? Where is the youngest (newest) oceanic crust usually found? What is paleomagnetism? What does it prove? Along which type of plate boundary do mid-ocean ridges occur? Draw diagrams that show how plates interact at each of the following: A. The Himalaya (continental-continental convergent boundary) B. San Andreas (transform boundary) C. The Cascades (continental-oceanic convergent boundary) D. The Mid-Atlantic ridge (divergent boundary) How are rocks classified? How do igneous rocks form? What has to happen to make a sedimentary or metamorphic rock change into an igneous rock? How can crystal size be used to determine where igneous rocks formed? Describe how rocks with small fragments (bits and pieces) probably formed. What causes earthquakes? What is the lag time between P and S wave arrival times for a location 5,000km from the epicenter? 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. Which earthquake wave travels the fastest: P-waves? Or S-waves? What scale is most commonly used to measure the power of earthquakes? Where do most volcanoes form? Where on earth can you find a hot spot volcano (give an example)? Why are volcanoes near subduction boundaries so explosive? (what makes a volcano explosive/violent?) Which type of volcano is most dangerous? Which type of volcano makes pyroclastic flows? What causes plate tectontics (what causes the plates to move)? Draw and label a diagram that shows why the plates move. Draw & label the 3 kinds of volcanoes. Under each, describe what they are made of and what type of eruption they usually have. Why does oceanic crust subduct under continental crust? Draw and label a diagram showing how a hot spot forms volcanoes in the crust. How does the crust move at a divergent boundary? How does the crust move at a convergent boundary? Describe how a P-wave moves rocks in the Earth’s crust. Describe how an S-wave moves rocks in the Earth’s crust. What was Pangaea? What is the “Ring Of Fire”? Where is it located? Why is it located there? Draw a picture of a fault; label the focus and the epicenter. Why does oceanic crust subduct underneath continental crust? Which type of plate boundary forms huge folded mountains?