* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation - Computer Science
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Backpressure routing wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Distributed operating system wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
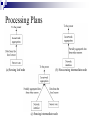
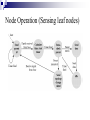
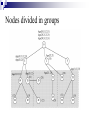
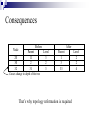
IN-NETWORK VS CENTRALIZED PROCESSING FOR LIGHT DETECTION SYSTEM USING WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS Presentation by, Desai, Bhairav Solanki, Arpan Outline Introduction Algorithm and Methodology Formation of routing topology In-network aggregation Centralized aggregation Experiments and Results Conclusion References Introduction Databases Vs Sensor Networks Range Queries – much better idea for sensor networks Additional operators have to be added for Query Language e.g. epoch and duration Continuous long running Queries Data Centric Networking Combination of Querying, storage and routing techniques Works efficiently if we use the combination as application specific rather than generalized like traditional IP based techniques. Challenges Volatile System Append Only Streams High Energy cost of communication Variable data arrival rate at different nodes Limited Storage on nodes Centralized Processing In Network Processing Objective Implementing In-network aggregation in real environment for a Data-centric application Comparing In-network and Centralized aggregation approach Algorithm and Methodology Topology Formation Collection Tree Protocol Base Station – Root of the Collection Tree EXTnode = EXTparent + EXTlink to parent where EXT root = 0 Detecting Routing Loops In-network Aggregation Data aggregation at in-network nodes Steps required to overcome change in topology Network Behavior Two phases Node discovery phase Discovery of topology Assigning time interval Aggregation phase Sense Aggregate Forward Assigning time interval Calculate time interval Where Tnode – Time duration of a node D – Total depth of the tree Lnode – Level of the node in the routing tree T – Total epoch duration Processing Plans (a) Sensing leaf node (b) Non-sensing intermediate node (c) Sensing intermediate node Node Operation (Sensing leaf nodes) Node Operation (Sensing intermediate nodes) Node Operation (Non-sensing intermediate nodes) Nodes divided in groups Change in topology Consequences Node 20 30 32 Before Parent 11 2 31 After Level 3 2 3 Parent 1 3 33 Causes change in depth of the tree That’s why topology reformation is required Level 2 2 4 Centralized Aggregation No discovery of topology No assignment of time interval No steps to overcome change in topology Aggregation of data at the base-station Node Operation (Sensing leaf nodes) Node Operation (Sensing intermediate nodes) Node Operation (Non-sensing intermediate nodes) Job of the base station Collect data from all the nodes Perform aggregation Experiments and Results In-network aggregation In-network aggregation In-network aggregation In-network aggregation In-network aggregation In-network aggregation Centralized aggregation Comparing both approaches Comparing Bytes Transmitted Conclusion Lesser number of Hop counts Low amount of bytes transmitted Lower energy consumption References C. Intanagonwiwat, R. Govindan, and D. Estrin, Directed Diffusion: A Scalable and Robust Communication Paradigm for Sensor Networks, In Proceedings of the Sixth Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networks (MobiCO, August 2000) David Gay, Phil Levis, Rob Von Behren, Matt Welsh, Eric Brewer, and David Culler, “The nesC language: A holistic approach to networked embedded systems,” in SIGPLAN Conference on Programming Language Design and Implementation (PLDI’03), June 2003. J. Heidemann, F. Silva, C. Intanagonwiwat, R. Govindan, D. Estrin, and D. Ganesan, “Building Efficient Wireless Sensor Networks with Low-Level Naming,” Proceedings of the ACM Symposium on Operating Systems Principles (SOSP), October 2001. Wendi Heinzelman, Anantha Chandrakasan, and Hari Balakrishnan, Energy-Efficient Communication Protocols for Wireless Microsensor Networks, Proc. Hawaaian Int'l Conf. on Systems Science, January 2000. Z. Cheng and W. Heinzelman, “Flooding Strategy for Target Discovery in Wireless Networks,” Proceedings of the Sixth ACM International Workshop on Modeling, Analysis and Simulation of Wireless and Mobile Systems (MSWiM), September 2003. D. Braginsky and D. Estrin, “Rumor Routing Algorithm for Sensor Networks,” Proceedings of ACM WSNA, September 2002. References J. Bonfils and P. Bonnet, Adaptive and Decentralized Operator Placement for In-Network Query Processing, Telecommunication Systems - Special Issue on Wireless Sensor Networks, January 2004 S. Madden, M.J. Franklin, J.M. Hellerstein, and W. Hong, TAG: a Tiny AGgregation Service for Ad-Hoc Sensor Networks, 5th Symposium on Operating System Design and Implementation (OSDI 2002), December 2002 Y. Yao and J. Gehrke, The cougar Approach to In-Network Query Processing in Sensor Networks, SIGMOD, March 2002 S. Madden, R. Szewczyk, M.J. Franklin, and D. Culler, Supporting Aggregate Queries Over AdHoc Wireless Sensor Networks, Mobile Computing Systems and Applications, June 2002 S. Ganeriwal, R. Kumar, and M. B. Srivastava, Timing-Sync Protocol for Sensor Networks, Proceedings of ACM SenSys’03, November 2003 TinyOS Mailing list, http://www.tinyos.net/ TinyOS Naming Conventions, http://www.tinyos.net/tinyos-1.x/doc/tutorial/naming.html (TinyOS Introduction 2003) Getting Started with TinyOS and nesC, http://www.tinyos.net/tinyos-1.x/doc/tutorial/lesson1.html (Dissemination Protocol 2004) Dissemination, http://www.tinyos.net/tinyos-2.x/doc/html/tep118.html References (Collection Protocol 2004) Collection, http://www.tinyos.net/tinyos-2.x/doc/html/tep119.html (The Collection Tree Protocol 2004) CTP-Collection Tree Protocol, http://www.tinyos.net/tinyos-2.x/doc/html/tep123.html “Networking Wireless Sensors” by Bhaskar Krishnamachari. Cambridge University Press, 2005 “Wireless Sensor Networks – An Information Processing Approach” by Feng Zhao, Leonidas Guibas. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, 2004