* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Evolution of Sex
Penile plethysmograph wikipedia , lookup
Hookup culture wikipedia , lookup
Sexual stimulation wikipedia , lookup
Heterosexuality wikipedia , lookup
Homosexualities: A Study of Diversity Among Men and Women wikipedia , lookup
Age of consent wikipedia , lookup
Sexual addiction wikipedia , lookup
Ages of consent in South America wikipedia , lookup
Sexual abstinence wikipedia , lookup
Human sexual response cycle wikipedia , lookup
Human male sexuality wikipedia , lookup
Human female sexuality wikipedia , lookup
Age disparity in sexual relationships wikipedia , lookup
Sex and sexuality in speculative fiction wikipedia , lookup
Sex in advertising wikipedia , lookup
Human mating strategies wikipedia , lookup
Sexual attraction wikipedia , lookup
Lesbian sexual practices wikipedia , lookup
Female promiscuity wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
History of human sexuality wikipedia , lookup
Slut-shaming wikipedia , lookup
Rochdale child sex abuse ring wikipedia , lookup
Sexual ethics wikipedia , lookup
The Evolution of Sex Or, why do we even need males? Sexual VS Asexual reproduction Sexual Fewer offspring/individual Only half of genes passed on Good genotypes are lost Offspring are variable Asexual More offspring/individual All of genes passed on Good genotypes preserved Offspring uniform Asexual would appear to be the winner Some Factoids Nearly all organisms have a sexual life stage Paramecium have separated sex from reproduction Asexual species tend to be evolutionarily young. Paramecium Life Cycle QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. An Asexual Lizard The asexual whiptail species Cnemidophorus neomexicanus (center) with the sexual species that hybridized to form it, C. inornatus (left) and C. tigris (right). Cnemidophorus Variability The analysis revealed lower levels of trait variance in asexual species for three traits, but no detectable differences between asexual and sexual species for two other traits. A second analysis examined the influence of each population’s maximum and minimum value on overall population variability, and revealed that the variances of sexual populations were more heavily influenced by outliers than were asexual ones. These results suggest that part of the reason for increased variance in sexual populations may be a greater tendency for these populations to produce extreme phenotypes. Alistair J. Cullum Department of Biology Creighton University Cnemidophorus Variability Why Asexual Reproduction Cost of Meiosis Preserving genotypes Cost of Males Sexual Asexual Cyclical Parthenogenisis Why Sex? Possible advantages of sex: • Faster evolution: Sexually reproducing populations will evolve faster than a set of asexual clones, provided that the rate of favorable mutation is high enough. Red Queen? Muller’s Ratchet? More rapid evolution? • Lower extinction rates: The taxonomic distribution of asexual reproduction suggests that asexual forms have a higher extinction rate than sexual forms. Thus sex may be maintained by group selection. • Deleterious mutations: The large numbers of deleterious mutations are more efficiently removed by sexual than asexual reproduction. • Host-parasite arms race: The coevolutionary arms race of parasites and hosts produces rapid environmental change, making sexual reproduction advantageous. The Red Queen "Now, here, you see, it takes all the running you can do to keep in the same place" Sex and Advantageous mutations • Faster evolution: Sexually reproducing populations will evolve faster than a set of asexual clones, provided that the rate of favorable mutation is high enough. Asexual species tend to be young species • Lower extinction rates: The taxonomic distribution of asexual reproduction suggests that asexual forms have a higher extinction rate than sexual forms. Thus sex may be maintained by group selection. Muller’s Ratchet Host Parasite Coevolution Simian COII gene and simian foamy virus Cyclical Parthenogens Cladocera Rotifers Sexual reproduction is nearly Universal. Why remains a bit of a mystery but ultimately there appears to be an advantage to variable offspring. Cyclical parthenogens reproduce asexually when conditions are good, asexually when conditions are bad Large organisms are nearly exclusively sexual Asexual lineages are phylogenetically young, and don’t speciate as often. What is the Optimum Sex Ratio? Fisher: In a random mating population the optimal sex ratio is 0.5 (equal numbers of males and females) Reasoning: •Mean fitness is maximized by maximizing the mean number of offspring your children will produce •The rarer sex will produce, on average, more offspring, since each offspring has one mother and one father. •Parents that produce the rarer sex will have the highest fitness. What is the Optimum Sex Ratio? Hamilton: If there there is sib mating then a female biased sex ratio is favored Reasoning: •Mean fitness is maximized by maximizing the mean number of offspring your children will produce •Since parents sons are competing, which one wins does not affect the parents fitness •Grand-offspring numbers are maximized by producing as many females as possible, and just enough males to guarantee fertilization of females. Wasps 1 female: lays mostly diploid females, few haploid males. Multiple females: 1/2 diploid females, 1/2 haploid males Fig wasps























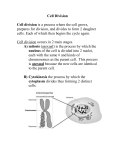






![Chapter 3 - Cell_Division_Test_Study_Guide[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009683824_1-add56d75145939ff28543ed83f830e06-150x150.png)

