* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Measles Clinical Signs and Symptoms
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Lyme disease wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Yellow fever wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Yellow fever in Buenos Aires wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
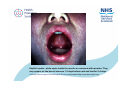
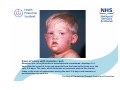
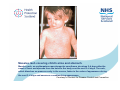
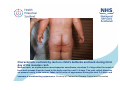
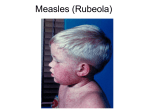
Measles Clinical Signs and Symptoms Measles Measles is a highly infectious acute viral disease resulting from infection with measles virus. Measles is transmitted via respiratory droplets, or direct contact with nasal/throat secretions, from infected individuals. The incubation period is 7-21 days, usually 10-12 days until beginning of prodrome and 14 days until appearance of rash. Individuals are usually infectious 5 days before to 4 days after rash onset. Measles The EU clinical case definition for measles is: •any person with fever AND •maculo-papular rash AND at least one of the following three: •cough •coryza •conjunctivitis Measles Clinical course of infection First prodromal symptoms begin after a 10-12 day incubation period. These can include fever, conjunctivitis, coryza, cough and bronchiolitis. Nearly all infected susceptible individuals develop clinical disease. Koplik’s spots appear on the buccal mucosa 1–2 days before rash onset and may last for 2-4 days. Measles rash, an erythematous maculopapular exanthema, develops 2–4 days after the onset of fever and spreads from the head to the body over the next 3–4 days. The rash, which blanches on pressure early in the course, fades in the order of appearance during the next 3– 4 days and assumes a nonblanching appearance. The rash is less faint than for rubella, and, unlike rubella, often coalesces. Source: CDC Measles complications • Ear infections ( 1 in 20) • Pneumonia/bronchitis (1 in 25) • Convulsions (1 in 200) • Diarrhoea (1 in 6) • Meningitis/encephalitis (1 in 1000) • Immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP; Condition affecting blood clotting) (1 in 6000) • Late onset subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE) (1 in 8000 in children under 2 years) • Deaths (1-2 deaths in 1000 reported cases in recent years) Complications are more common and more severe in chronically ill individuals Koplik’s spots - white spots inside the mouth are common with measles. They may appear on the buccal mucosa 1-2 days before rash and last for 2-4 days. Courtesy of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Koplik’s spots - white spots inside the mouth are common with measles. They may appear on the buccal mucosa 1-2 days before rash and last for 2-4 days. Courtesy New Zealand Dermatological Society Incorporated http://www.dermnetnz.org Child with severe measles rash, on face, and upper body. Measles rash, an erythematous maculopapular exanthema, develops 2–4 days after the onset of fever and spreads from the head to the body over the next 3–4 days. The rash, which blanches on pressure early in the course, fades in the order of appearance during the next 3–4 days and assumes a nonblanching appearance. Courtesy of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Face of a boy with measles rash. Measles rash, an erythematous maculopapular exanthema, develops 2–4 days after the onset of fever and spreads from the head to the body over the next 3–4 days. The rash, which blanches on pressure early in the course, fades in the order of appearance during the next 3–4 days and assumes a nonblanching appearance. Courtesy of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Measles rash covering child's arms and stomach. Measles rash, an erythematous maculopapular exanthema, develops 2–4 days after the onset of fever and spreads from the head to the body over the next 3–4 days. The rash, which blanches on pressure early in the course, fades in the order of appearance during the next 3–4 days and assumes a nonblanching appearance. Courtesy of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Characteristic red blotchy rash on child's buttocks and back during third day of the measles rash. Measles rash, an erythematous maculopapular exanthema, develops 2–4 days after the onset of fever and spreads from the head to the body over the next 3–4 days. The rash, which blanches on pressure early in the course, fades in the order of appearance during the next 3–4 days and assumes a nonblanching appearance. Courtesy of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Child in later stages of measles rash (probably has had rash for 4 or 5 days). Measles rash, an erythematous maculopapular exanthema, develops 2–4 days after the onset of fever and spreads from the head to the body over the next 3–4 days. The rash, which blanches on pressure early in the course, fades in the order of appearance during the next 3–4 days and assumes a nonblanching appearance . Courtesy of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention