* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download C:\Users\jmhemzac\Desktop\2016 spring\121rev1s16.wpd
Survey
Document related concepts
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
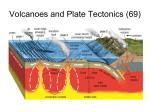
ESCI 121 Spring 2016 REVIEW LIST FOR EXAM 1 DRAFT version Focus on key material from covered topics. Learning objectives of the course are emphasized in what you are expected to be able to define, describe, and explain (pay attention to the difference in what is expected of you). Important terms are in bold: be able to describe the meaning and importance in context with related terms (don’t just memorize a definition). Note: your text may include other related terms / concepts; if not listed- not on test. NOTE: additions/clarifications in red; anything struck through is “not for this test” You should be able to... Discuss the earth as a system (what is a system?); briefly describe its geologic ‘sub-system' parts: atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere; geotectonic system – compare characteristics of an open vs. closed system – be able to give geologic examples of changes that illustrate how the earth functions as a system Describe the contribution from two energy sources for our dynamic planet: external (sun) – drives climate, water cycle, weathering internal heat (distributed through convection in the mantle) – drives changes associated with geotectonic system (what kinds of changes does this include?) List the key characteristics of Earth that make it unique among planets of our solar system Describe how a scientific method is applied to studying the earth; describe the parts of that process (observation, hypothesis, test/experiment/collect data, scientific theory); explain the significance of a scientific theory as part of this process –>We have spent a good amount of time identifying patterns, or correlations, in data sets. How is this process related to "how we do science"? –> What is the significance of using maps and earth materials in our study of the earth? (How are these used, and how does their use advance our understanding of earth science?) Name and describe the characteristics of layers of the geosphere in the differentiated earth: crust, mantle, core; lithosphere, asthenosphere, lower mantle, outer core, inner core as characterized in two different ways: with respect to chemical composition and with respect to differences in physical behavior (i.e., deformational response to stress): –> be able to describe the types of behavior associated with each of these layers What is the relationship of the layers defined by physical vs. compositional characteristics? (e.g., how is the crust different from and yet related to the lithosphere? what is the relationship of the mantle to the different behavioral layers?) How is it that the earth became differentiated by density? (based on best scientific data, this occurred 4.6 billion years ago: what was the character of the early/proto- earth at that time?) Describe the different ways that earth materials respond to applied stress: ductile (elastic or plastic) vs. brittle Describe factors that influence the behavior of materials, and how they affect behavior, including: composition, material strength, environmental conditions (temperature and confining pressure), time/rate of applied force – that is, how would you expect a stronger rock to behave, vs. weaker? etc Describe the effect of isostasy, as it relates to the earth system and earth processes: clearly explain the influence of rock deformational behavior and density on earth’s isostatic adjustments; Which parts of the geosphere are involved in these vertical isostatic adjustments? Given appropriate samples and/or data, you should be able to: Demonstrate that you can measure and calculate density of rock samples using the water-displacement method and a triple-beam balance. You should be able to explain application of methods in a way to ensure accuracy and/or precision. What is the difference between accuracy and precision? What is bias, and how does it affect accuracy? How does the application of significant figures affect accuracy? Determine the mass of a sample of material, in a way to ensure maximum accuracy (i.e., as done in lab) Use appropriate units of measurement** to describe mass, volume, and density of solid materials ** note the appropriate units for reporting... therefore density of solid.... (what units?) mass (grams) volume of solid (cm3) –> how does this compare to units in your measurement of parameters related to rock density? –> Note that you measured rock volume by displacement of water, measured in (what units?) but 1 ml of water displacement = 1 cm3 of rock volume! How does the density of different earth materials (e.g., as components of tectonic plates) affect their behavior in geotectonic processes? –> Why do different parts of the earth system have different densities? (that is, what factors contribute to the density of a material?) You should be able to describe the composition of different parts of the earth in the way that we discussed in class, including the appropriate use of the following concepts: mafic vs. felsic (and intermediate) silicate minerals basalt andesite granite / granitic > content of Si (silicon)–higher vs. lower; > content of Al (aluminum), K (potassium), Na (sodium) vs. Fe (iron), Mg (magnesium), Ca (calcium) Explain what is meant by the term plate as it applies to geotectonics and plate tectonic theory Explain what the term boundary means as it applies to plate tectonic theory Why is the theory of plate tectonics so important to the science of geology? (What does it mean that plate tectonics is a scientific “theory”?) hint: it explains ... everything! (such as... ?) Name the three types of plate boundaries, describe the relative motion associated with each, and recognize and name geographic examples of each (e.g., from the plate tectonic worksheet) Given appropriate maps, be able to identify the presence of features that are associated with different types of geotectonic settings, including different types of plate boundaries, vs. mid-plate locations, and different types of plates involved (oceanic vs. continental): earthquake depth of focus, active volcanoes, oceanic trench, MOR (mid-ocean ridge) Given a set of these features for a location, be able to interpret the geotectonic setting represented Describe the differences associated with different eruptive styles of volcanoes, including: – types of eruption products associated with violent (explosive) vs. effusive eruptions – volcano form (shape) associated with each eruptive style: stratovolcano vs. shield volcano (why are these volcanoes shaped differently?) – the relationship between magma composition, viscosity, temperature, and volatile (gas) content, and the relation to source of magma (i.e., mechanism for melting), – geotectonic setting (described by type of boundary / or not; type of plate(s) involved, etc.) Explain why different areas of the world are associated with volcanoes of different eruptive styles (and how this distribution is related to specific plate tectonic environments); Define/ describe: pyroclastics; ash; bombs pyroclastic flow lava flow magma felsic intermediate mafic silicate composition hydrovolcanism phreatic explosion caldera blast zone hotspot igneous rocks intrusive extrusive Be able to discuss “where does magma come from?”, and be able to describe key related concepts: geothermal gradient convection subduction melting by decompression melting by hydration partial melting Where and why does melting occur by different means; where and why do convection, subduction occur? –> magma composition is related to composition of rock that is melted, to what degree it is melted e.g.“lower-melting-point” components of a rock (would those be felsic or mafic?), and “contamination” of magma by other processes: magma mixing or assimilation (see video on homepage) Explain what is rock texture, and how different igneous rock textures reveal how/where the rock formed: phaneritic aphanitic porphyritic glassy Given an igneous rock, be able to recognize these textures and tell what they indicate Be able to associate each of the following rocks with geotectonic environments in which they are formed: andesite basalt granite pumice Given samples of these rocks, you should also be able to describe their composition and texture Discuss (in general terms) why active volcanoes exist only in certain places describe why the term “active volcano” is not easy to define; what are the factors that affect volcano activity? why do different volcanoes have different “schedules” of eruptions? how does VEI (volcano explosivity index) affect our understanding of “active volcanoes”? when, or under what circumstances, is a volcano considered extinct? Name the three main types of rocks; why rocks are classified that way, and the general process of how each type is formed Define/describe the significance of the following, with respect to earth materials: fossils rocks minerals What are the characteristics that makes something a mineral? (define the term) What does it mean that minerals crystallize? (what does it mean that a mineral is crystalline?) Describe the general differences between oceanic crust and continental crust (thickness? composition?), and how the differences affect behavior of plates in earth processes at plate boundaries, including: subduction volcanism (effusive vs. explosive) mountain building (volcanic vs. continental collision) sea-floor spreading Be able to describe why each of these processes takes place in these particular geotectonic settings Be able to give examples (geographic locations, like our study sites) for each Describe and explain the differences in convergent boundaries with 2 continental plates, vs. those involving one or more oceanic plates. Give examples (geographic locations) for each type. Describe how transform boundary features are different from features in other geotectonic settings: e.g., why do we not expect volcanoes at transform boundaries? Describe and explain differences expected between an oceanic hotspot and a continental hotspot; be able to give an example (location) of each type: why do we see different effects at the surface? In what geotectonic environment(s) is new crust created? Where is crust “destroyed” /recycled? In what geotectonic environment can we see that a new ocean basin will be formed?