* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Brain Architecture and Function Parts Size and Cognition
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
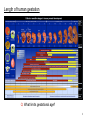
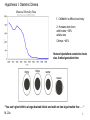
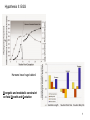
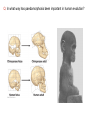
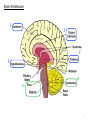
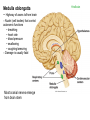
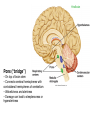
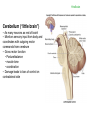
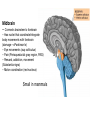
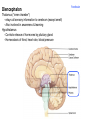
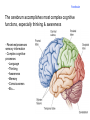
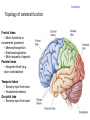
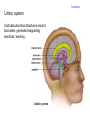
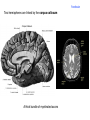
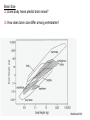
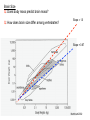
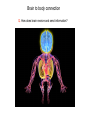
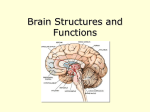
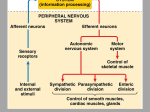
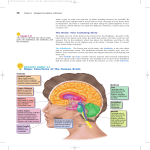
Brain Architecture and Function Parts Size and Cognition Length of human gestation Q: What limits gestational age? 2 Hypothesis I: Obstetric Dilema 1. Childbirth is difficult and risky 2. Humans born born with brains ~30% adults size Chimps ~40% Human bipedalism constrains brain size, limited gestation time “You can’t give birth to a large-brained infant and walk on two legs trouble free . . . “ M. Zuk 3 Q: How does homonid locomotion differ from the other great apes? Q: How might differences in locomotion affect gestational age? 4 Hypothesis II: EGG Humans have huge babies! Energetic and metabolic constraint on fetal Growth and Gestation 5 6 Q: In what way has paedomorphosis been important in human evolution? Brain Architecture F F F F H H 8 Q. How’d we get to this point? Evolutionary trends Hindbrain: relatively smaller Midbrain: relatively smaller Forebrain: relatively larger especially the cerebrum (neocortex) 9 Brain organization DEVELOPMENT • Prosencephalon – Telencephalon (cerebrum) – Diencephalon (eyes, pituitary, hypothalamus, thalamus, epiphysis) • Mesencephalon • Rhombencephalon – Metencephalon (pons, cerebellum) – Myelencephalon (medulla) FUNCTION • Forebrain – Cerebrum – Thalamus – Hypothalamus • Midbrain • Hindbrain – Pons – Medulla – Cerebellum 10 Medulla oblongatta – Highway of axons to/from brain – Nuclei (cell bodies) that control autonomic functions • breathing • heart rate • blood pressure • swallowing • coughing/sneezing – Damage is usually fatal Most cranial nerves emerge from brain stem Hindbrain Hindbrain Pons (“bridge”) – On top of brain stem – Connects cerebral hemispheres with contralateral hemispheres of cerebellum – Wakefulness and alertness – Damage can lead to sleeplessness or hyperalertness Hindbrain Cerebellum (“little brain”) – As many neurons as rest of brain! – Monitors sensory input from body and coordinates with outgoing motor commands from cerebrum – Gross motor function • Posture/balance • muscle tone • coordination – Damage leads to loss of control on contralateral side Midbrain – Connects brainstem to forebrain – Has nuclei that coordinate/integrate body movements with forebrain (damage -->Parkinson’s) – Eye movements (sup colliculus) – Pain (Periaqueductal gray region, PAG) – Reward, addiction, movement (Substantia nigra) – Motor coordination (red nucleus) Small in mammals Diencephalon Thalamus (“inner chamber”) - relays all sensory information to cerebrum (except smell) - Also involved in awareness & learning Hypothalamus - Controls release of hormones by pituitary gland - Homeostasis of thirst, heart rate, blood pressure Forebrain Forebrain The cerebrum accomplishes most complex cognitive functions, especially thinking & awareness - Receives/processes sensory information - Complex cognitive processes • Language • Thinking • Awareness • Memory • Consciousness • Etc… Forebrain Topology of cerebral function Frontal lobes – Motor functions or movements (posterior) – Memory/recognition – Emotional regulation – Motor aspects of speech Parietal lobes – Integrate stimuli (e.g., vision and balance) Temporal lobes – Sensory input from ears – Visual/word memory Occipital lobe – Sensory input from eyes Forebrain Limbic system Cortical/subcortical structures around brainstem: generation/regulating emotions; learning Forebrain Two hemispheres are linked by the corpus callosum A thick bundle of myelinated axons Phineas Gage A moral man, Phineas Gage Tamping powder down holes for his wage Blew his special-made probe Through his left frontal lobe Now he drinks, swears, and flies in a rage. 20 Brain Size Q: Does body mass predict brain mass? Q: How does brain size differ among vertebrates? Northcutt 2002 Brain Size Q: Does body mass predict brain mass? Q: How does brain size differ among vertebrates? Slope = 1.0 Slope ≈ 0.67 Northcutt 2002 Q: Which mammals have the largest percent of body mass represented by brain? The largest absolute brain? The largest EQ? * log brain mass * log body mass * Estimating the size of a brain subunit: the neocortex of mammals: 1) rhinal fissure placement hedgehog 2) cerebral sulcation tree shrew monkey rhinal fissure Q: What aspect(s) of bird behavior correlate most strongly with a large telencephalic (≈ forebrain) fraction of the brain? Burish, Kueh, and Wang. 2002. Pigeons have a telencephalic fraction of 0.552….. 0.552 Burish, Kueh, and Wang. 2002. …and can distinguish paintings by Picasso and Monet. Watanabe et al. 1995 Brain to body connection Q. How does brain receive and send information? Signal Transduction An environmental stimulus Surface neurons are exposed to an environmental stimulus The environmental stimulus generates a receptor potential If the receptor potential exceeds threshold, it initiates an AP Sensory input is relayed to the central nervous system Q: How do environmental stimuli initiate APs? AP to the CNS Signal Transduction Q: How do environmental stimuli initiate APs? See text box, p. 338