* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Vascular and Nonvascular Plants
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
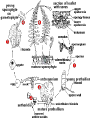
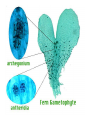
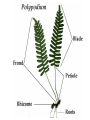
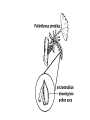
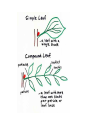
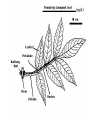
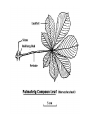
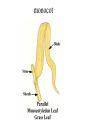
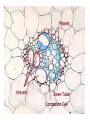
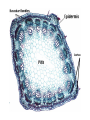
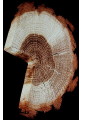
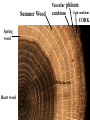
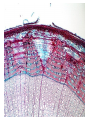
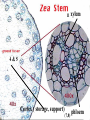
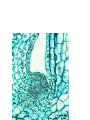
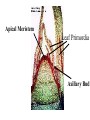
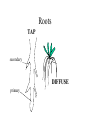
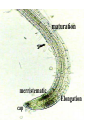
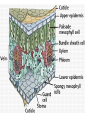
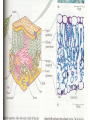
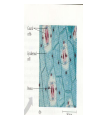
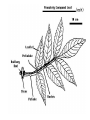
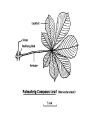
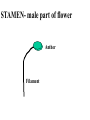
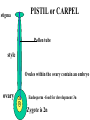
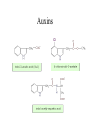
How do we classify and group plants? • What are the major divisions? • How are they grouped and classified? • How do you use a plant identification key? Plant Taxonomy • Nonvascular Plants- have small reduced leaves, no vascular tissue( veins) no true roots, and reproduce by spores or flagellated cells that travel through water. Vascular Plants- have true roots, stems, and leaves with vascular tissue. Xylem- water and minerals. Phloem- transports carbohydrates Plant Divisions • nonvascular Bryophyta- mosses • vascular seedless Lycophyta-club moss Pterophyta-Ferns seed plants Gymnosperms-naked seeds Angiosperms-flowering plants Gymnosperm Coniferophyta- needle or scale leaf, cones ( conifer) Anthophyta or Angiosperm Monocots- parallel veins, petals in 3’s Dicots- net veins, petals in 4’s or 5’s Bryotphytes Mosses Moses • Non-vascular Plants- No tissues to carry water • Spores used for reproduction • No true roots, stem • Reduced leaves Liverworts sporophyte Mosses gametophyte sporophyte gametophyte In mosses the dominant stage of their life cycle they only have half of their total chromosme number. Spore Producing • Spores are reproductive stages that have only half the chromosomes or genetic material. VASCULAR PLANTS Lycopodium, Lycophyta Pterophyta Ferns- reproduce with spores but have veins to carry water Gymnosperms Naked seeds or seeds produced in cones. Angiosperms or Anthophyta • Flowering plants • Seeds produced within a fleshy fruit with gametes borne within a flower. Antheridium Archegonium Liliacea Taxonomy key\identification key • You always have two choices in a description of the organisms characteristic • Choose the correct choice and it takes you to a name or a number. dicot monocot Opposite Leaf arrangement Alternate leaf arrangement Botany •Tissues, Organs, and Systems Vascular Tissue Xylem (wood) make up xylem. They are nonliving tubes with openings at the ends to carry water . trachieds and vessel elements Transport in Vascular Plants • Water and minerals begin movement by osmosis. through root and root hair Transport in Plants cont. capillary action in xylem vessel element Adhesion-water vessel wall Cohesion- water to water Transpiration- water moves out through stoma in the leaf. closed H2O Loss of Turgor Turgor • Phloem carries carbohydrates sieve tube elements-connected by sieve plates Summer Wood Vascular phloem Cork cambium cambium CORK Spring wood Phloem rays Heart wood Vascular Tissue • Xylem- wood, carries water Spring wood- larger openings smaller ring Summer wood – more compact rigs are wider Phloem- carries sugar phloem rays carry back and forth Growth Tissue • Vascular Cambium- grows new xylem to the inside and phloem to the outside • Cork cambium- grows new cork to the outside BARK- is vascular cambium, phloem, cork cambium , and cork 11 xylem 4&5 Cortex ( storage, support) (7,8) phloem Merristematic Regions • Apical Bud • Root Tips Apical Meristem Leaf Primordia Axillary Bud Roots TAP secondary DIFFUSE primary Germination • Seeds begin to grow as a result of cell division using much oxygen seeds need warm temperatures, water, and oxygen to germinate but the seed supplies the food. hypocotyl Embryonic Tissue Seed leaves of an embryo Above the cotyledon Below the cotyledon Embryonic root maturation merristematic Elongation cap Leaves- the main photosynthetic parts of a plant • Types of Simple Compound Pinnate Palmate Leaf Cross Section • Epidermis- prevents water loss protects from UV light • Palisades- photosynthesis zone ( contains much chlorophyll) • Mesophyll ( spongy layer)- storage of gases, water and sugar • Veins – contain xylem and phloem • Abscision layer- cuts base of leaf off during defoliation Stomate • Stomate- leaf opening for gas exchange and water loss • Guard Cells- control opening of stomate • Stoma - opening Photosynthesis CO2+H2O light CnH2n0n+O2 Light- measured as an absorption spectrum, the wavelengths that are most important are different for different types of autotrophs Photosyntheis • • • • Plant takes in carbon dioxide\ Plant takes up water Plant produces sugars Plant gives off oxygen Margin (serrate) petiole Pinnate veins Simple Leaf with Entire Margin and Pinnate Veins Angiosperms or Anthophyta • Flowering plants • Seeds produced within a fleshy fruit with gametes borne within a flower. Perfect Flower STAMEN- male part of flower Anther Filament PISTIL or CARPEL stigma Pollen tube style Ovules within the ovary contain an embryo ovary 2n 3n Endosperm -food for development 3n Zygote is 2n Composite Family Flower Structures • Stamen- male floral part • Anther- produces pollen ( n) haploid • Filament- stalk that supports stamen Floral Parts • • • • Pistil- female floral part Style- stalk that supports stigma Stigma- sticky part attracts pollen Ovary- eggs develop and are fertilized to become seeds Plant Response to Light –Photoperiodism LONG DAY_ require 12 hr. daylight or more to flower SHORT DAY-require less than 12 hr daylight DAY NEUTRAL – flower according to maturity not light Plant Hormones • Alter cell division • Increase elongation • Regulate gene activity Auxins Plant Auxin on Agar Block Auxin Mutants