* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Problem 1 (continued)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
A) The head of the image will disappear.
B) The feet of the image will disappear.
C) The image will become dimmer.
D) Nothing will happen to the image.
d. [5 pts] An electron starts at rest in a uniform electric field. Fill in the blanks: the
electron will move towards _____ electric potential, and the work done by the electric
field on the electron will be _____.
A) higher; positive
B) lower; positive
C) higher; negative
D) lower; negative
e. [5 pts] A battery pack consists of three 1.5-volt batteries connected in parallel. The
voltage that the pack can supply to an electrical device is:
A) 0.5 V
B) 1.5 V
C) 4.5 V
D) Zero, because batteries don’t work if they are connected in parallel.
Physical Sciences 2
Problem 1 (continued)
Tuesday, April 7, 2009
Page 4 of 18
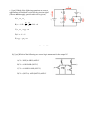
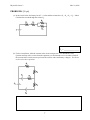
d. [4 pts] Two identical capacitors are connected in series to
a battery as shown. If you insert a dielectric into capacitor 1,
the energy stored in capacitor 2 will ...
A) decrease
B) remain unchanged
C) increase
D) cannot be determined from the information given
Physical Sciences 3
Saturday, May 12, 2012
PROBLEM 1 [10 pts]
The following1:two
multiple-choice
questions
not related.
Problem
Multiple
Choice
[40arepts]
Clearly circle the best answer to each
question. Credit will be given for the correct answer with no explanation required and no partial
credit.
For each of the following questions, circle the letter corresponding to the best answer
from
given.a No
partial
credit field
will be
given,
where
Youfield
do not
1. Inthe
theoptions
figure below,
uniform
magnetic
points
intoexcept
the page.
(Thenoted.
magnetic
vectors
needaretoindicated
show your
work,
although
you
are
welcome
to
use
the
space
on
the
page
for charges
by the ⊗ symbols). Four particles with the same mass and different electric
scratch
paper.
follow
the paths shown as they pass through this magnetic field with identical, constant speeds.
Which of the following correctly ranks the charges from least to greatest? (Remember, any
a) [5negative
pts] One
end ofis asmaller
string than
withany
linear
massnumber).
number
positive
density µ is attached to a wall. The other end
is attached to a mass M and draped over a
pulley
L away. A standing
(a) located
q1 < q3 <a qdistance
2 < q4
wave at the fundamental frequency f1 is set up
(b)the
q4 string
< q2 < is
q3 plucked
< q1
when
in the middle.
Which
the
(c) of
q4 <
q1following
< q3 < q2 will increase the value
of f1(d)
? Choose
all that apply; partial credit
q2 < q3 < q1 < q4
will be awarded.
(e) q4 < q2 < q1 < q3
(f) q3 < q1 < q2 < q4
A) Replace the string with one that has a larger linear mass density
B) Replace the string with one that has a smaller linear mass density
C) Move the pulley closer to the wall
D) Pluck the string closer to the wall
2. A 300
square the
wave
is theofinput
E) Hz
Increase
value
M to a high-pass RC filter with a 1500 W resistor and a 0.1 µF
capacitor. Which of the following best describes the output of the filter, relative to the input?
(a) It is smoother-looking, and has almost the same amplitude.
b) [5 pts] An electron is traveling towards the right at a
(b)ofIt viswhen
smoother-looking,
and has with
a significantly
reduced amplitude.
speed
it enters a chamber
a magnetic
!
field B . Which direction must the magnetic field point
(c) It is more jagged-looking, and has almost the same amplitude.
in order for the electron to exit through the top slit?
(d) It is more jagged-looking, and has a significantly reduced amplitude.
(e) It has the same shape, and has almost the same amplitude.
Upthe same shape, and has a significantly
E) Up/Rightreduced amplitude.
(f) A)
It has
B) Down
F) Down/Left
C) Right
G) Out of the page
D) Left
H) Into the page
Page 3 of 19
D) f new = f old 2
E) f new = 2 f old
For each of the following questions, circle the letter corresponding
to the best answer
€
€
€
from the options given. No partial
credit will be given, except where noted. You do not
need to show your work, although you are welcome to use the space on the page for
€
€ scratch paper.
c. [4 pts] Which of the following equations are correct
a) [5 pts] of
Two
strings of rules
equalfor
lengths
but different
applications
Kirchhoff’s
the circuit
at right?mass densities are knotted together
and
stretched
between
two
fixed
ends.
A
particular
frequency produces the following
(Choose all that apply; partial credit will be given.)
standing wave on each string. Which string has the greater density (i.e., mass per unit
length)?
A) I3 = I4 + I5
B) ε 2 − I2 R1 −
€
Q1 Q2
−
+I R =0
C1 C2 4 2
C) ε1 + ε 2 − I5 R3 = 0
€
D) I1 = −I2 − I3
€
E) I5 R3 − I4 R2 = 0
A) String A
€
B) String B
€
C) The densities are equal
Page 3 of 10
D) Not enough information to answer this question
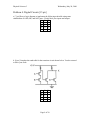
b) [5 pts] Which of the following are correct logic statements for the output X?
A) X = NOT(A OR B) AND C
B) X = A OR B OR (NOT C)
C) X = A AND B AND (NOT C)
D) X = (NOT A) AND (NOT B) AND C
Page 3 of 17
b. [4 pts] In a certain region, there is a uniform magnetic field pointing up,
and a uniform electric field pointing in an unknown direction. An electron
moves to the right in this region with constant velocity. Which direction
does the electric field point?
Physical Sciences 3
Wednesday, May 20, 2009
A) left
B) right
Problem
C) up 1: Multiple Choice [40 pts]
D) down
For each
of the
unrelated questions, circle the letter corresponding to the best
E) into
thefollowing
page
answerF)from
the
options
given.
No partial credit will be given. You do not need to show
out of the page
your work, although you are welcome to use any blank space for scratch paper.
a. [5 pts] Four charges of equal magnitudes are arranged as shown. The dashed lines all
equal
length.
Whatisislocated
the direction
of side
the electric
field at bar
the point marked with a
c.have
[4 pts]
A loop
of wire
on the N
of a stationary
question
mark?
magnet, as shown. If the loop is pulled towards the magnet, which
of the following statements accurately describes the resulting effect
on the bar magnet?
A) up
B) down
A) There will be a net force on the magnet to the right, away from the loop.
left will be a net force on the magnet to the left, towards the loop.
B)C)There
C)D)There
right will be no net force on the magnet, but there will be a net torque.
D) There will be no net force or net torque on the magnet.
E) The electric field is zero
b. [5 pts] A small loop of wire is placed near a very long straight wire, as
shown. The current in the long straight wire is initially zero, but it
gradually increases to a maximum upwardPage
current,
steady for a
3 of stays
6
while, and then gradually decreases back to zero. Suppose we define I, the
current in the loop, to be positive for counterclockwise current. Which of
the following could be the correct graph of I vs time?
Page 3 of 20
Physical Sciences 3
Tuesday, March 1, 2011
Problem 1: Multiple choice [20 pts]
For each of the following unrelated questions, circle the letter corresponding to the best
answer from the options given. No partial credit will be given. You do not need to show
your work, although you are welcome to use any blank space for scratch paper.
a. [5 pts] Marisol and Nadir make some observations with three charged blocks—A, B,
and C. They see that block A is attracted to block B, but repelled by block C. What
should happen if block B is brought near block C?
A) They’ll attract one another.
B) They’ll repel one another.
C) They’ll feel no attraction or repulsion.
D) There’s not enough information to determine what will happen
b. [5 pts] An electron is traveling with a constant velocity v = v 0 xˆ ,
when
it enters a region of space with a uniform electric field
E = E 0 yˆ (see figure). Which of the following trajectories best
describes the electron’s motion in this region?
€
€
Page 2 of 10
Physical Sciences 2
Thursday, March 25, 2010
Problem 1: Multiple choice [20 pts]
For each of the following unrelated questions, circle the letter corresponding to the best
answer from the options given. No partial credit will be given. You do not need to show
your work, although you are welcome to use any blank space for scratch paper.
a. [4 pts] Two equal and opposite point charges are arranged as shown. Points A, B, and
C lie along the dashed line halfway between the charges. At which of the labeled points
would the electric field point directly up (in the +y direction)?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
b. [4 pts] Which of the following statements about equipotential contour lines is true?
A) Contour lines begin on positive charges and end on negative charges.
B) Contour lines can cross other contour lines, but only at right angles.
C) Contour lines are closer together in regions where the electric field is stronger.
D) Contour lines are closer together in regions where the electric potential is
higher.
c. [4 pts] Two capacitors, each with the same initial charge Q, are
connected to each other as shown. C1 is greater than C2. When the
switch S is closed, what will happen?
A) The charge on C1 will decrease, and the charge on C2 will decrease
B) The charge on C1 will decrease, and the charge on C2 will increase
C) The charge on C1 will increase, and the charge on C2 will decrease
D) The charge on C1 will increase, and the charge on C2 will increase
E) The charge on both capacitors will remain the same
Page 3 of 11
Physical Sciences 3
Tuesday, February 28, 2012
Problem 1: Multiple Choice (continued)
e) [5 pts] Consider the magnitude and direction of the electric field at the point indicated by a
question mark (?) below. The numbers indicate equally-spaced marks on a ruler; +q represents a
point charge at the location indicated.
+q
0
1
?
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Circle the letter below for each configuration of charges that would give the same magnitude
and direction of the electric field at the point indicated by the question mark (?). Circle all that
apply; partial credit will be awarded.
–q
A)
0
1
2
?
3
4
5
0
1
2
3
0
1
2
3
+4q
D)
0
0
5
6
7
8
4
5
6
7
8
5
6
7
8
?
1
2
3
+2q
E)
8
?
+2q
C)
4
7
–q
?
B)
6
4
?
1
2
3
4
–2q
5
Page 5 of 11
6
7
8
Physical Sciences 2
Thursday, February 26, 2009
Problem 1: Multiple Choice [16 pts]
For each of the following unrelated questions, circle the letter corresponding to the best
answer from the options given. No partial credit will be given. You do not need to show
your work, although you are welcome to use any blank space for scratch paper.
a. [4 pts] Consider a traveling wave that moves in the +x direction on a stretched string.
The wavelength is 50 cm, the frequency is 100 Hz, and the amplitude is 1 cm. Which of
the following is the correct equation for the wave?
!
!
!
!
!
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
D(x,t) = (1 cm)sin((2 rad/m)x " (628 rad/s)t )
D(x,t) = (1 cm)sin((12.6 rad/m)x " (0.0628 rad/s)t )
D(x,t) = (1 cm)sin((2 rad/m)x + (0.0628 rad/s)t )
D(x,t) = (1 cm)sin((12.6 rad/m)x " (628 rad/s)t )
D(x,t) = (1 cm)sin((12.6 rad/m)x + (628 rad/s)t )
b. [4 pts] A pipe is open at both ends, and a standing sound wave is established in it with
a frequency 3 times the fundamental frequency of the pipe. Fill in the blanks: Including
both ends, the pipe contains ____ and ____ for pressure variations.
A) 2 nodes; 3 antinodes
B) 3 nodes; 2 antinodes
C) 3 nodes; 3 antinodes
D) 3 nodes; 4 antinodes
E) 4 nodes; 3 antinodes
c. [4 pts] A loudspeaker emits a spherical sound wave. At a distance of 5 m from the
speaker, the loudness of the sound is measured to be 80 dB. What is the power of the
sound emitted by the speaker? (Note: the reference intensity I0 is 10-12 W/m2.)
A) 2.5 × 10-7 W
B) 3.2 × 10-7 W
C) 1.0 × 10-4 W
D) 2.5 × 10-3 W
E) 3.1 × 10-2 W
Page 3 of 6
Physical Sciences 2
Tuesday, April 7, 2009
Problem 1: Multiple Choice [20 pts]
For each of the following unrelated questions, circle the letter corresponding to the best
answer from the options given. No partial credit will be given. You do not need to show
your work, although you are welcome to use any blank space for scratch paper.
r
a. [4 pts] A dipole moment p points to the right, as shown below. What is the direction
of the electric field at point A due to the dipole? (Remember, this is a physics course, not
a chemistry course!)
!
A) up
B) down
C) left
D) right
E) the electric field is zero
b. [4 pts] Which of the following equations is a valid
statement of the loop rule for the left-hand loop in the
circuit shown?
Q
=0
C
Q
B) E " I1R + = 0
C
Q
C) E + I1R " = 0
C
Q
D) E + I1R + = 0
C
E) none of them is valid
A) E " I1R "
!
!
!
c.![4 pts] An electron initially at rest accelerates to the left under the influence of an
electric field. Fill in the blanks: In the vicinity of the electron, the electric field points to
the ____, and the electron moves towards _____ electric potential.
A) left; lower
B) left; higher
C) right; lower
D) right; higher
Page 3 of 11
Physical Sciences 3
Mar. 20, 2008
PROBLEM 1 [20 pts]
The following multiple-choice questions are not related. Circle the best answer to each question.
Credit will be given for the correct answers with no explanation required and no partial credit.
1. Four electric charges with equal magnitudes are arranged on corners of a square. What is the
direction of the resulting electric field at location marked with a ?
indicate positive charges,
indicate negative charges.
(a) Upwards,
(b) Downwards,
(c) Left,
(d) Right,
(e) Up / Left,
(f) Up / Right,
(g) Down / Left,
(h) Down / Right,
2. Consider two wires made of the same material. Wire #2 has twice the diameter of Wire #1, and is
twice as long as Wire #1. The resistance between the ends of Wire #2 is _________.
(a) One fourth the resistance of Wire #1.
(b) Half the resistance of Wire #1.
(c) The same resistance as Wire #1.
(d) Twice the resistance of Wire #1.
(e) Four times the resistance of Wire #1.
2
Physical Sciences 3
Mar. 20, 2008
PROBLEM 1 [continued]
3. In the circuit below, charge Q0 and voltage V0 are placed across capacitor C1. Capacitor C2 is
initially uncharged, and C2 is much smaller than C1. Fill in the blanks: After a long time the
switch S is closed, the charge on C2 will be ____________ and the voltage across C2 will be
____________.
(a) much less than Q0; much less than V0
(b) about equal to Q0; much less than V0
(c) much less than Q0; about equal to V0
(d) about equal to Q0; about equal to V0
Short-answer question:
4. A defibrillator must deliver 50 J of energy across the chest of a heart attack victim over a time of
roughly 10 ms in order to put the patient’s heart back into normal rhythm. It does this by
discharging a capacitor through the chest wall, which has a resistance of 100 !. What
approximate capacitance should the defibrillator have, and what voltage should be placed across
the capacitor when it is initially charged?
Capacitance = __________
Voltage = __________
3
Physical Sciences 2
Tuesday, February 23, 2010
Problem 1: Multiple choice [15 pts]
For each of the following unrelated questions, circle the letter corresponding to the best
answer from the options given. No partial credit will be given. You do not need to show
your work, although you are welcome to use any blank space for scratch paper.
a. [5 pts] In the diagram at right, the dashed curves
represent equipotential contour lines around a twodimensional charge distribution. (The charges
themselves are not shown.) Which of the arrows on
the figure is the best representation of a correct
electric field line?
A)
B)
C)
D)
b. [5 pts] A parallel-plate capacitor is charged until 100 mJ of electrical energy are stored
in it. Then it is carefully disconnected from the charging circuit, and the plates are pulled
apart so that the separation distance between the plates doubles. Afterwards, how much
electrical energy is stored in the capacitor?
A) 25 mJ
B) 50 mJ
C) 100 mJ
D) 200 mJ
E) 400 mJ
c. [5 pts] In a certain region of space, there is a uniform electric field pointing to the right.
One at a time, you place an electron, a proton, and a dipole into this region and release
them. Which way would each one accelerate?
A) electron right, proton left, dipole left
B) electron left, proton right, dipole right
C) electron left, proton right, dipole left
D) electron right, proton left, dipole would not accelerate
E) electron left, proton right, dipole would not accelerate
Page 3 of 6
Physical Sciences 3
Tuesday, May 11, 2010
Problem 1: Multiple choice [40 pts]
For each of the following unrelated questions, circle the letter corresponding to the best
answer from the options given. No partial credit will be given. You do not need to show
your work, although you are welcome to use any blank space for scratch paper.
a. [5 pts] The diagram below shows electric field lines near two point charges of equal
magnitude. What can you conclude about the signs of the charges?
A) Both are positive.
B) Both are negative.
C) The charges have the same sign, but it is not possible to tell whether they are
both positive or both negative.
D) The charges have opposite signs, but it is not possible to tell which is which.
E) It is not possible to tell whether the charges have the same or opposite sign.
b. [5 pts] A negative point charge is located above a
neutral conducting sheet, as shown. In equilibrium, what
is the direction of the electric field at point P, just above
the conductor?
A) up
B) down
C) up and left
D) down and right
E) The electric field is zero at P.
Page 3 of 18
Physical Sciences 3
Tuesday, February 28, 2012
Problem 1: Multiple Choice [25 pts]
For each of the following questions, circle the letter corresponding to the best answer from the
options given. You do not need to show your work, although you are welcome to use the space on
the page for scratch paper. Partial credit will not be awarded, unless otherwise stated.
a) [5 pts] You place an electric dipole in a uniform electric field with field lines as shown. In
which configuration would the dipole experience a counterclockwise torque?
A)
B)
C)
D)
b) [5 pts] You have a tank that contains an aqueous
solution of ions. As shown in the figure at right, you
connect a battery across two electrodes that cover the
areas A at each end of the tank. The electrodes are
separated by a distance L.
Which of the following changes would increase the
amount of current flowing through the tank? Circle
all that apply; partial credit will be awarded.
A) Increasing the distance L.
B) Increasing the voltage ΔV.
C) Adding some additional ionic solute to the solution.
D) Adding some corn syrup to increase the viscosity (drag) of the solution.
E) Increasing the electrode area A.
Page 3 of 11
as shown. Which of the five possible paths
shown would the light ray follow?
A) path a
B) path b
PhysicalC)Sciences
path c 3
Wednesday, May 20, 2009
D) path d
Problem
1 (continued)
E) path
e
d. [5 pts] Three point charges (–Q, –Q, and +2Q) are located at the
corners of a square, as shown. What is the direction of the electric
c. [5 pts]
the following statements must be true about an electron moving in an
field
at theWhich
fourthofcorner?
electric field?
A) up and left ( )
r
A) The electron moves in the direction opposite to E .
B) up and right ( )
B) The electron moves towards higher electric potential.
C) down and left ( )
C) The force on the electron is perpendicular to its velocity.
!
D) down and right ( )
D) The force on the electron is independent of its velocity.
E) the electric field is zero
Page 3 of 20
e. [5 pts] The graph at right shows the intensity of
light as a function of position on the screen in a twoslit interference setup. Fill in the blank: At the
second-order maximum on either side, the light from
one slit travels ______ the light from the other slit.
A) the same distance as
B) twice as far as
C) one wavelength further than
D) two wavelengths further than
E) three wavelengths further than
f. [5 pts] Consider the transistor logic circuit shown below. It has one input (A) and one
output (X). Fill in the blanks: When A is true, X is ___; and when A is false, X is ___.
A) true; true
B) true; false
C) false; true
D) false; false
Page 4 of 20
Physical Sciences 3
Saturday, May 12, 2012
Problem 9: At Capacity [15 pts]
Four capacitors, each with the same capacitance C, are
connected to a battery as shown.
a) [7 pts] When fully charged, how much potential energy is
stored in each capacitor?
b) [8 pts] What is the change in the total energy stored in the capacitors after a dielectric
with κ = 3 is inserted into capacitor C2? Assume that the battery remains connected
during the process.
Page 15 of 17
Physical Sciences 3
Wednesday, May 20, 2009
Problem 4: Transmission Line [20 pts]
A DC transmission line is made up of two parallel wires strung horizontally, separated by
a distance d. They transmit electrical power P at a very high voltage ΔV by carrying equal
currents in opposite directions.
a. [5 pts] What is the magnitude of the magnetic field due to these two currents at the
midpoint between the wires?
b. [5 pts] Do the wires attract or repel each other?
c. [5 pts] What is the magnitude of the force per unit length that the wires exert on each
other?
d. [5 pts] Calculate, to 1 significant digit, the magnitude of the force between the wires
over a 100 meter-long section of the transmission line with ΔV = 110 kV, P = 5 × 107 W,
and d = 1 m.
Page 8 of 20
Physical Sciences 3
Wednesday, May 20, 2009
Problem 2: How Wide? [10 pts]
Two point sources of 500-nm light are
separated by a distance of 1 cm. Light
from the two sources passes through a
narrow slit 10 m away, and then falls on a
screen of photographic paper 1 m behind
the slit, as in the figure (which is not
drawn to scale). What is the minimum
width of the slit such that the two images
will be resolvable on the photographic
paper?
Page 6 of 20
Physical Sciences 3
Tuesday, April 12, 2011
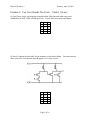
Problem 2: You Can’t Handle The Truth….Tables! [16 pts]
a) [8 pts] Draw a logic gate diagram to implement the following truth table using some
combination of NOT, AND, and OR gates only. Clearly label your inputs and outputs.
A
0
0
1
1
B
0
1
0
1
X
1
1
0
1
b) [8 pts] Complete the truth table for the transistor circuit shown below. You do not need to
show your work. Note that the input B appears twice in the circuit.
A
0
0
1
1
B
0
1
0
1
X
Page 5 of 10
Physical Sciences 3
Tuesday, February 28, 2012
Problem 2: I’m Positive [15 pts]
You discover a new cell type and measure the relative electrical potential at two points across the
cell membrane as indicated on the figures below.
a) [6 pts] On the figure below, sketch the
charge distribution and the electric field lines
that would be consistent with these potential
measurements.
•V=0
b) [4 pts] On the figure below, sketch the
equipotential surfaces that would be consistent
with these potential measurements.
•V=0
fluid
outside
fluid
outside
membrane
membrane
fluid
inside
fluid
inside
• V = +50 mV
• V = +50 mV
c) [5 pts] A chloride ion (Cl–) is located in an ion channel at the center of the membrane of this
cell. If the membrane has a thickness of d = 6 nm, and a dielectric constant of κ = 9, calculate
the magnitude and direction of the electrostatic force on this ion. (e = 1.6 × 10–19 C)
Page 6 of 11
Physical Sciences 3
Tuesday, May 11, 2010
Problem 8: Resistor network [15 pts]
In the circuit shown at right, the battery emf is 12 V, and each
of the resistors is 200 Ω.
a. [10 pts] Calculate the current through each resistor in the
circuit.
b. [5 pts] Calculate the power output of the battery.
Page 13 of 18
Physical Sciences 3
Saturday, May 12, 2012
Problem 5: Lenses Law [20 pts]
A 4-cm bright object is place in front of two thin lenses—the first has a focal length of
fA = –2 cm and the second has a focal length fb = 3 cm—as shown below:
a) [8 pts] On the diagram above, use the principal rays to show where the final image is
formed. Clearly indicate the position of the final image in your diagram.
b) [6 pts] What is the (exact numerical) location of the final image on the number line?
c) [6 pts] How tall is it? Is it upright or inverted? Is it a real or virtual image?
Page 11 of 17
Physical Sciences 3
Tuesday, April 12, 2011
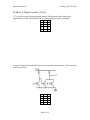
Problem 5: Digital circuits [15 pts]
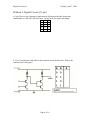
a. [7 pts] Draw a logic diagram to implement the following truth table using some
combination of AND, OR, and NOT gates. Clearly label your inputs and output.
A B X
0 0 0
0 1 1
1 0 0
1 1 0
b. [8 pts] Complete the truth table below for the transistor circuit shown. You do not need
to show your work.
A
0
0
1
1
B
0
1
0
1
X
Page 8 of 9
Physical Sciences 2
Thursday, March 25, 2010
Problem 6: Carrying charges [15 pts]
In the circuit shown at right, the three capacitors
all have the same capacitance C. They are initially
uncharged. At time t = 0, the switch S is closed.
a. [5 pts] Determine the time constant ! for charging the capacitors, in terms of R and C.
b. [10 pts] A very long time after the switch is closed, how much energy is stored in each
of the capacitors (1, 2, and 3)? Give your answers in terms of E and C.
Page 10 of 11
Physical Sciences 3
Saturday, May 12, 2012
Problem 8: One if by Land, Two if by Sea [20 pts]
You are the sexton in the Old North Church in Boston. It is April 18, 1775. You need to
send a signal to Paul Revere, who is 3 km away.
a) [10 pts] You could choose to hang either one or two lanterns in the church tower. If
Paul Revere’s pupils have a diameter of 4 mm, and the light from your lanterns has a
wavelength of 580 nm, what is the minimum spacing between the lanterns required for
him to see them as two distinct lanterns? For simplicity, treat the pupil as a simple
circular aperture; you do not need to consider the index of refraction inside the eye.
Assume that diffraction is the only limitation on visual acuity.
b) [10 pts] Another possibility would be to ring the church bell either once or twice. For
Paul Revere to hear the bell clearly, it should have a loudness of at least 40 dB where he
is standing, 3 km away. What would be the loudness of the bell for you, the sexton,
standing only 1 meter away? Assume the sound is distributed evenly in all directions.
Page 18 of 19
Physical Sciences 2
Tuesday, April 7, 2009
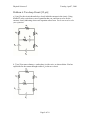
Problem 5: Digital Circuits [15 pts]
a. [7 pts] Draw a logic diagram to implement the following truth table using some
combination of AND, OR, and NOT gates. Clearly label your inputs and output.
A B X
0 0 1
0 1 0
1 0 0
1 1 1
b. [8 pts] Complete the truth table below for the transistor circuit shown. You do not need
to show your work.
A
0
0
1
1
B
0
1
0
1
X
Page 9 of 11
Physical Sciences 3
Mar. 20, 2008
PROBLEM 9 [10 pts]
Coherent light of frequency 9 × 1014 Hz passes through two thin slits and falls on a screen 81 cm
away. You observe that the third bright fringe occurs at ±3 cm on either side of the central bright
spot.
(a) How far apart are the slits?
(b) At what distance from the central bright fringe will the third dark fringe appear?
Physical Sciences 2
Tuesday, April 7, 2009
Problem 6: Two-loop Circuit [15 pts]
a. [8 pts] For the circuit shown below, clearly label the currents in the circuit. Using
Kirchoff’s rules, write down a set of equations that you could use to solve for the
currents, clearly indicating where each equation comes from. You do not need to solve
your equations.
b. [7 pts] You remove battery !1 and replace it with a wire, as shown below. Find an
expression for the current through resistor R5 in the new circuit.
Page 9 of 10
Physical Sciences 3
Saturday, May 12, 2012
Problem 4: Hear Ye!
[15 pts]
The ear canal (external auditory canal)
can be treated as a tube that is open at
one end and closed at the other, with a
length of L = 2 cm.
a) [10 pts] On the tubes shown below,
sketch the standing waves formed by
the pressure variations ΔP for the three lowest resonant frequencies of the ear canal.
Then calculate these frequencies; the speed of sound in air is v = 340 m/s.
b) [5 pts] Write an equation that describes the pressure variation ΔP as a function of x
and t inside the ear canal, for the lowest resonant frequency, in terms of its amplitude
ΔP0. Take x = 0 to be the outer (open) end of the ear canal for this standing wave. Be
sure to give numerical values for all parameters in your equation (except for ΔP0).
Page 9 of 19
Physical Sciences 3
Wednesday, May 20, 2009
Problem 4: Digital Circuits [15 pts]
a. [7 pts] Draw a logic diagram to implement the following truth table using some
combination of AND, OR, and NOT gates. Clearly label your inputs and output.
A B X
0 0 0
0 1 1
1 0 0
1 1 0
b. [8 pts] Complete the truth table for the transistor circuit shown below. You do not need
to show your work.
A
0
0
1
1
B
0
1
0
1
X
Page 9 of 20
Physical Sciences 3
Tuesday, May 11, 2010
Problem 6: Film session [15 pts]
You would like to coat a piece of glass (n = 1.4) with a
very thin coat of transparent film (n = 1.3) so that when
the glass is viewed at normal incidence, it strongly
reflects blue light of wavelength 480 nm, but does not
reflect any red light of wavelength 640 nm. How thick
should the film be? (There are many possible correct
answers; you only need to calculate one.)
Page 11 of 18
Physical Sciences 3
Tuesday, May 11, 2010
Problem 8: Diffraction [10 pts]
Light of wavelength 550 nm passes through a
tiny pinhole of diameter D = 50 microns, as in
the figure (not to scale). What will be the radius
of the central Airy disc on a screen located
1 meter behind the pinhole?
Page 14 of 20
Physical Sciences 3
Mar. 20, 2008
PROBLEM 4 [10 pts]
(a) In the circuit below, the battery has !V = 9 volts and the resistors have R1 = R2 = R3 = R4 = 100 ".
Calculate the current through the resistor R4.
I4 = _______________
(b) For the circuit below, label the currents in the circuit using arrows. Use Kirchhoff’s rules
(junction and loop rule) to write down the equations you would need to solve in order to find all
the currents in the circuit (assume you know the resistor values and battery voltages). You do not
need to solve these equations.
7
Physical Sciences 3
Wednesday, May 20, 2009
Problem 8: Fluorescent Bead [15 pts]
A bead of diameter dbead = 1 µm is coated with a fluorescent substance that absorbs green
light of wavelength λex = 520 nm and emits red light of wavelength λem = 640 nm. The
bead is placed in the path of a 520-nm laser. The laser emits with power P = 1 mW;
assume that the laser beam has a diameter of dlaser = 1 mm and that the intensity is
uniform within the beam. (Planck’s constant h = 6.63 × 10–34 J⋅s.
a. [8 pts] Assume for the sake of simplicity that every 520-nm photon that strikes the
bead causes a fluorescence. How many red photons does the bead emit per second?
b. [7 pts] When the bead fluoresces, it emits red light isotropically (with equal intensity in
all directions). A photodetector calibrated to detect 620-nm light is placed at a distance
L = 10 cm from the bead. What is the intensity of red light incident on the detector?
Page 14 of 20
Physical Sciences 2
Tuesday, April 7, 2009
Problem 5: Digital Circuits [15 pts]
a. [8 pts] Draw a logic diagram to implement the following truth table using some
combination of AND, OR, and NOT gates. Clearly label your inputs and output.
A B X
0 0 0
0 1 0
1 0 1
1 1 0
b. [7 pts] Complete the truth table for the transistor circuit shown below. What is the
common name of this gate?
Page 8 of 10
Physical Sciences 3
Mar. 20, 2008
PROBLEM 7 [12 pts]
A string lies along the x-axis and supports vibrations in the y-direction. Such transverse waves have a
wave speed of 8 m/s, amplitude of 0.07 m, and a wavelength of 0.32 m. The waves travel in the –x
direction, and at time t = 0 the point x = 0 has its maximum upward displacement, i.e. D(x=0,t=0) =
0.07 m.
(a) Find the frequency and period of these waves.
(b) Write the function describing the displacement of the string at all locations and times.
(c) Find the transverse displacement at the location x = 0.36 m at time t = 0.175 s.
(d) How much time must elapse from the instant in part (c) until the piece of the string at the point x
= 0.36 m next has maximum upward displacement?
Physical Sciences 3
Mar. 20, 2008
PROBLEM 5 [20 pts]
The capability a small camera has to generate very bright flashes of light is made possible by using a
capacitor to store energy slowly and release it quickly. Consider the following circuit representing the
flash component of a camera:
(a) Initially, the switch S is set to connect the capacitor to the battery. What is the time constant for
charging the capacitor?
!charge = ___________
(b) How much energy is stored in the capacitor?
Ustored = ____________
(c) When a picture is taken, the switch S moves to connect the capacitor to the flash bulb, which acts
as a very small resistor. How much time does it take for the capacitor to lose 63% of its charge?
t = ______________
(d) Estimate the value of the power dissipated in the bulb during the discharge.
P " _____________
8
Physical Sciences 3
Saturday, May 12, 2012
Problem 3: Doppler Difference [15 pts]
The Doppler Effect for sound is different depending on whether the source is moving or
the observer is moving. Let’s explore some consequences of this difference.
a) [7 pts] In one type of Doppler effect, the apparent frequency can become effectively
infinite. Which case is this (source moving or observer moving)? Under what conditions
will the frequency become infinite? Support your answer with an explicit formula.
b) [3 pts] If the frequency is effectively infinite, as calculated in part (a) above, what
does that mean about the wavelength?
c) [5 pts] Which of the following diagrams best represents the wavefronts for the
Doppler effect in the case of an infinite frequency? (circle one)
A)
B)
C)
Page 8 of 19
D)
Physical Sciences 3
Wednesday, May 20, 2009
Problem 10: Capacitors [20 pts]
Two capacitors, C1 = 1 µF and C2 = 2 µF, are connected in series to
a 6-volt battery via a resistor of R = 10 kΩ, as shown. Both
capacitors are originally uncharged.
a. [5 pts] Calculate the final charge on each capacitor.
b. [4 pts] How much time (after the battery is connected) elapses until capacitor 1 reaches
90% of its final charge?
Page 15 of 20
Physical Sciences 3
Wednesday, May 20, 2009
Problem 11: Falling Magnet [10 pts]
A circular loop of wire lies flat on a table. A
permanent magnet is held over the center of the
loop with its N pole pointing down, and then
released.
a. [3 pts] As the magnet starts to fall, what would be
the direction of the magnetic field generated by the
induced current?
b. [3 pts] Would the induced current flow in the loop clockwise or counterclockwise (as
viewed from above)?
c. [4 pts] Would the current in the loop exert an upward, downward, or zero net force on
the magnet? Explain.
Page 17 of 20
Physical Sciences 2
Tuesday, April 7, 2009
Problem 3: Mystery RC [20 pts]
You have been given a black box containing a resistor Rx and
capacitor C in series. To determine the values of Rx and C, you
set up the circuit shown in the figure at right, and then use
Logger Pro to measure the time constant of the circuit.
When the value of the known external resistor R1 is 15 kΩ, you
measure the time constant to be τ1 = 70 ms. When you replace
R1 with a different known resistor R2 = 27 kΩ, the new time
constant is τ2 = 82 ms.
a. [10 pts] Calculate the mystery resistance Rx and the mystery
capacitance C.
Page 6 of 11
Physical Sciences 3
Tuesday, May 11, 2010
Problem 9: Hoop it up [15 pts]
Consider a thin charged hoop of radius R and charge per unit
length + ! uniformly distributed along its circumference. The
hoop spins in place with angular velocity ! counterclockwise,
as shown.
a. [5 pts] The spinning charge constitutes an electric current. What is the magnitude of
this current? Express your answer in terms of R, ! , and ! .
b. [3 pts] What is the direction of the magnetic field at the hoop’s center?
c. [7 pts] Now consider the hoop spinning as shown, with
a permanent magnet aligned on the rotational axis of the
hoop, with the S pole facing the hoop. Do the hoop and
magnet attract each other, repel each other, or neither?
Explain.
Page 14 of 18
Physical Sciences 3
Wednesday, May 20, 2009
Problem 8: Circuits [15 pts]
a. [5 pts] Consider the circuit shown at
right. Clearly label the currents with
their directions, and then use
Kirchhoff’s rules to write down the
equations you would need to solve for
the currents.
b. [5 pts] For R1 = 1 kΩ, R2 = 2 kΩ, R3 = 4 kΩ, and ΔV = 9 V, calculate the values of the
currents you labeled in part a.
c. [5 pts] How much total power is dissipated in the circuit?
Page 12 of 20
Physical Sciences 3
Saturday, May 12, 2012
Problem 7: Silent Killer [15 pts]
During a surgical procedure, a thin, steel
scalpel blade was left inside a patient’s torso.
The doctors are attempting to use ultrasound
imaging to find the location of the blade.
Sound waves with a frequency of 5 MHz are
emitted from the transducer, but the doctor
cannot locate the blade. Determine the
thickness of the steel blade. (The speed of
sound in soft tissue is 1540 m/s; the speed of
sound in steel is 6000 m/s.)
Page 13 of 17
Physical Sciences 2
Thursday, March 25, 2010
Problem 5: Digital circuits [15 pts]
a. [7 pts] Draw a logic diagram to implement the following truth table using some
combination of AND, OR, and NOT gates. Clearly label your inputs (A and B) and
output (X).
A B X
0 0 0
0 1 1
1 0 0
1 1 0
b. [8 pts] Complete the truth table below for the transistor circuit shown. You do not need
to show your work.
A
0
0
1
1
B
0
1
0
1
X
Page 9 of 11
Physical Sciences 3
Tuesday, May 11, 2010
Problem 11: Beam me up, Scotty [15 pts]
A laser beam cannot be perfectly collimated; even if the beam is a pure plane wave inside
the laser cavity, it will spread out slightly after coming out of the opening due to
diffraction. Consider a laser pointer that emits 633-nm red light through an opening of
diameter 1.0 mm. What will be the radius of the spot that the beam makes on the ground
if you shine it from the top of a building 100 m high?
Page 16 of 18
Physical Sciences 3
Saturday, May 12, 2012
Problem 4: Charged Particles [15 pts]
a) [7 pts] Two charged particles, q1 and q2, are fixed at the origin and at x = d on the
x-axis, respectively. A third charged particle, q3, which is free to move, is in static
equilibrium at x = 2d. Find q1 in terms of q2.
b) [8 pts] Charge q3 is now placed at the location where the electric potential due to the
fixed charges is zero. Find this location x in terms of d. Assume the charges are the
same as part a) and that V = 0 at infinity. (You cannot place the charge at infinity.)
Page 10 of 17
Physical Sciences 2
Thursday, April 23, 2009
Problem 2: Mirror, Mirror [15 pts]
You look into a curved mirror at a distance of 30 cm. The image of your face in the mirror is
upright and half the size of your actual face.
a. [5 pts] What is the image distance? Is the image real or virtual?
b. [5 pts] What is the radius of curvature of the mirror? Is the mirror concave or convex?
c. [5 pts] Draw a ray diagram for the image of your face in the mirror. Your diagram should
include the object, image, focal point, center of curvature, and three principal rays. It does not
need to be exactly to scale.
Page 5 of 6
Physical Sciences 2
Tuesday, February 23, 2010
Problem 2: Looking for zero [15 pts]
A point charge Q is located at the origin, and
another charge, q, is located at the point (a, 0) of
the coordinate system shown in the figure.
a. [8 pts] If the electric field at the point (–a/2, 0) is zero, what is q in terms of Q?
b. [7 pts] If, instead, the electric potential at the point (–a/2, 0) is zero, what is q in terms
of Q? Assume V=0 at infinity.
Page 4 of 6
Physical Sciences 3
Saturday, May 12, 2012
Problem 2: Near and Far [15 pts]
Your friend Qiu has an unaided near point of 10 cm and an unaided far point of 50 cm.
a) [4 pts] When she focuses on an object at her near point, what is the effective focal
length of her corneal lens? The retina is 2.5 cm behind the lens; treat the corneal lens as a
single “thin lens” and ignore the fluid inside the eyeball.
b) [6 pts] Qiu stands 5 cm away from a plane mirror and looks directly at her own eye.
She can see her eye clearly in the mirror. Construct a ray diagram below that shows how
an image of her eye (specifically, her cornea) is formed on her retina. (Note that the
object in question is located at her corneal lens—she’s looking at her own cornea.)
F
retina
F
corneal
lens
mirror
c) [5 pts] Qiu’s optometrist prescribes eyeglasses that sit 2 cm away from her eyes.
What is the focal length of her prescription lenses? Are they converging or diverging?
Page 7 of 19
Physical Sciences 3
Tuesday, April 12, 2011
Problem 4: Kirchoff’s Revenge [15 pts]
Consider the following circuit:
a) [10 pts.] If ε1 = 6 V and ε2 = 12 V, find the current through the 2-Ω resistor.
b) [5 pts.] How much power is dissipated as heat through the 2-Ω resistor?
Page 7 of 9
Physical Sciences 2
Tuesday, April 20, 2010
Problem 2: Current events [15 pts]
A square loop of wire sits to the left of a long straight wire as shown. The
straight wire carries a current that is upward and increasing in time.
a. [5 pts] Is the induced current in the loop clockwise, counterclockwise, or
zero? Explain.
b. [10 pts] In which direction is the net magnetic force on the loop? Explain.
Page 5 of 6
Physical Sciences 3
Tuesday, May 11, 2010
Problem 10: Sounding off [20 pts]
A standing sound wave in air has the equation
P ( x,t ) = Patm + !P sin ((15.7 rad/m ) x ) cos (" t )
where !P and ! are constants. The wave sounds in a tube of length 60 cm, which is
open at both ends (x = 0 and 60 cm). Use v = 340 m/s for the speed of sound.
a. [8 pts] At what values of x are there antinodes for pressure variation?
b. [4 pts] Calculate the constant ! .
c. [8 pts] What would be the fundamental frequency of sound in this tube?
Page 15 of 18
Physical Sciences 3
Tuesday, February 28, 2012
Problem 4: Charge It [20 pts]
A certain cell has a membrane with a total surface area A = 0.01 mm2, a thickness d = 6 nm, and
a dielectric constant κ = 9.
a) [8 pts] If the potential of the cell interior (with respect to the exterior) is V = –70 mV, find the
charge on the inside of the membrane, and the charge on the outside of the membrane.
b) [7 pts] Suppose the cell membrane has become discharged (so there is no potential difference
across the membrane). Calculate the minimum number of molecules of ATP that would be
required to do the electrical work of re-charging the membrane back to ΔV = –70 mV.
(Hydrolysis of one molecule of ATP yields approximately 7 × 10–20 J.)
continued…
Page 8 of 11
Physical Sciences 3
Tuesday, February 28, 2012
Problem 4 continued
c) [5 pts] The cell potential is maintained in part by an ion pump known as the Na/K ATPase,
which pumps 3 Na+ ions out and brings 2 K+ ions in to the cell with each cycle. The net
electrical result is the transfer of a single elementary charge (1.6 × 10–19 C) from the interior to
the exterior of the cell with each cycle. When the membrane is fully charged at ΔV = –70 mV,
how much electrical work is done by one cycle of the Na/K ATPase?
Page 9 of 11
Physical Sciences 3
Wednesday, May 20, 2009
Problem 12: Antireflective Coating [10 pts]
Lenses in high-precision optical equipment are
sometimes covered with an antireflective coating so as
to eliminate reflected light at a particular frequency
(and nearly eliminate it at nearby frequencies). Suppose
you have a piece of glass (nglass = 1.50) coated with a
layer of antireflective material t = 110 nm thick. You
observe that at normal incidence, green light of
wavelength λ = 550 nm is not reflected at all from the
surface.
a. [5 pts] What is the index of refraction of the antireflective material? (You may assume
that it is between 1 and nglass.)
b. [5 pts] Are there any wavelengths in the visible spectrum that would be strongly
reflected at normal incidence? If so, what are they?
Page 18 of 20
Physical Sciences 3
Tuesday, May 11, 2010
Problem 4: Digital/binary [15 pts]
a. [7 pts] Draw a logic diagram to implement the following truth table using some
combination of AND, OR, and NOT gates. Clearly label your inputs and output.
A B X
0 0 1
0 1 1
1 0 0
1 1 1
b. [8 pts] Add the binary numbers 11011 and 1100, and then convert the answer back into
decimal.
Page 8 of 18
Physical Sciences 3
Wednesday, May 20, 2009
Problem 11: Fiber Optics [10 pts]
A fiber optic cable consists of a glass cylinder with index of refraction n1 = 1.50 coated
around its sides by a thin layer of cladding with index of refraction n2 = 1.45. Suppose
you direct a beam of light from air (nair = 1) into the end of the cable at an angle θ relative
to the normal, as in the diagram below. What is the maximum value of θ for which the
beam will propagate down the cable undiminished in intensity? (You may neglect
absorption.)
Page 17 of 20
Physical Sciences 3
Saturday, May 12, 2012
Problem 3: Blowing a Fuse [20 pts]
A fuse is a circuit element that allows current to
pass freely (like a closed switch) up to a certain
limit, but if the current limit is exceeded, the fuse
will “blow” and prevent any current from flowing
through it (like an open switch).
Consider the circuit shown, with a DC power supply of ε = 120 V and a fuse with a limit
of 1 amp. R1 (the resistor on the left) = 50 Ω, and C = 1 µF.
a) [7 pts] What is the minimum value of R2 (the resistor on the right) for which the fuse
will never blow?
b) [5 pts] For the value of R2 that you calculated in part a), what will be the final charge
on the capacitor?
Page 8 of 17
Physical Sciences 3
Saturday, May 12, 2012
Problem 3 (continued)
NOTE: For parts c) and d), suppose that R2 = 25 Ω.
c) [4 pts] What will be the charge on the capacitor at the instant that the fuse blows?
d) [4 pts] What will be the final charge on the capacitor?
Page 9 of 17
Physical Sciences 2
Tuesday, April 7, 2009
Problem 2: Shake It [15 pts]
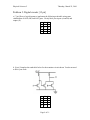
You shake a thin wire up and down so that the vertical displacement of any small section
of the wire at position x and time t is given by the equation
D(x,t) = (3.5 cm)sin[(1.05 rad/cm)x + (35 rad/s)t ] .
a. [5 pts] What is the speed of the wave?
!
b. [10 pts] Sketch the shape of the wire at time t = 0 in the graph below. Indicate with an
arrow the direction in which the wave propagates.
Page 5 of 10




























































![[ ] ò](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003342726_1-ee49ebd06847e97887fd674790b89095-150x150.png)

![Final Exam [pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008845375_1-2a4eaf24d363c47c4a00c72bb18ecdd2-150x150.png)