* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 15HYD07_Layout 1
List of prime numbers wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Factorization wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
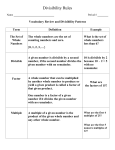
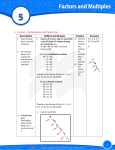
, 15 2016 before the end of the play English Verbs that take either infinitive or gerund with no change of meaning as follows Start, intend, bother, begin, continue, propose, like, prefer, hate a He started to leave the theatre before the end of the play a He started leaving the theatre 15 7 a He intended to help her / he intends helping her a I always prefer to travel to my village by train a I always prefer traveling to my village by train Remember/forget/regret are used with gerunds for the memories of the past. In these constructions the action is followed by the act of remembering, forgetting and regretting. a I regret spending on her (Spend ing is the 1st and regret is the 2nd action) a I remember attending the marr -iage years back. (attending is the 1st and remembering is the 2nd action) The sum of first five multiples of 6 is Making number as directed G. Janardhan Reddy Director Reyan coaching centre Nagole, Hyd 9030878078 1) Every digit in a particular greatest number in ‘9’ Ex : The greatest one – digit number is ‘9’ a The greatest 2 digit number is ‘99’ and so on …. 2) In a particular smallest number, the first digit on the left is 1 and the remaining digits are ‘0’. a There are 10 one digit numbers (0 to 9) a There are 90 two – digit numbers (10 to 99) a There are 900 three – digit numbers (100 to 999) a There are 9000 four – digit numbers (1000 to 9999) a If we consider number from 1 to 100, the digits from 0 to 9 occur the following number of times respectively. Digit 0 No.of Times occur 11 PRACTICE BITS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 21 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 PRACTICE BITS 1) The difference between the greatest four digit number and the smallest four- digit number is 1) 1 2) 90 3) 9000 4) 8999 2) How many four digit number do we have in number system. 1) 9999 2) 9990 3) 9000 4) 8999 3) While writing numbers from 1 to 100 how many times does the digit ‘7’ occur 1) 9 2) 10 3) 20 4) 21 ANSWERS : 1. 4, 2. 3, 3.3 . Tests of Divisibility : Using the rules of divisibility we can find the no. of factors of given number without division. I) Divisibility by 2,4, and 8 i) By ‘2’ :- If the last digit of a number is either 2,4,6,8 or 0, the number is divisible by ‘2’. Ex : 146, 3580, 1058. ii) By ‘4’ :- If the last two digits of a number is multiple of 4 (or) 00 the number is divisible by ‘4’. Ex : 8124 (24 is multiple of 4) iii) By ‘8’ :- If the last three digit’s of a number is multiple of 8 or 000 the number is divisible by ‘8’. Ex : 56896 (896 is multiple of 8) 35000 (Last three digits are 000) II) Divisibility by 3,6 and 9 :i) By ‘3’ :- If the sum of the digits of a number is divisible by ‘3’, then the given number is divisible by ‘3’. Ex : 345 is divisible by ‘3’ = (3+4+5=12) = 1+2 =3 is divisible by ‘3’is divisible by ‘3’. Ex : 5490891 is divisible by ‘3’ because. Sum of digits = 5+4+9+0+8+9+1 =36. 3+6 =9 9 is divisible by ‘3’. ii) By ‘6’ :- If a number is divisible by both 2 and 3 then the number is divisible by ‘6’. Ex : 5412 is divisible by ‘6’ because. Last digit is ‘2’ then divisible by ‘2’. Sum of all digits 5+4+1+2 =12 then divisible by 3. iii) By ‘9’ : - If the sum of all digits of a number is divisible by ‘9’ the number is divisible ‘9’. Ex : 6372 is divisible by ‘9’ because 6+3+7+2 =18 is divisible by ‘9’. Divisibility by 5 and 10 : a If the units place digit of a number is 0 or 5, then the numbers is divisible by 5. a If the units place digit of a number is 0, then the number is divisible by 10. PRACTICE BITS 1) Which of the following number is divisible by ‘2’ 1) 3145 2) 5169 3) 6780 4) 34269 2) Which of the following number is divisible by ‘6’. 1) 5342 2) 6170 3) 6270 4) 5164 3) The number which is divisible by ‘4’ is 1) 74926 2) 3150 3) 5466 4) 5128 4) The number 54612 is divisible by 1) only 2 2) 3 Only 3) only 9 4) 2,3,9 5) The number which is divisible both 3 and 9? 1) 74211 2) 89261 3) 89262 4) 1443 ANSWERS : 1.3, 2. 3, 3.4, 4. 4, 5.3. FACTORS a If a number is exactly divisible by the another number, then the second number is factor of first numbers. Eg:16 16 is divisible with 1,2,4,8,16 then 1,2,4,8,16 are factors for 16 To find the factors (using of test of divisibility) Eg: 100 1 x 100 Write up to down 2 x 50 and down to up 4 x 25 1,2,4,5,10,20,25,50,100 5 x 20 10 x 10 a 1 is the factor of every number a Every number is a factor of itself a Number of factors of a number are finite (countable) Common Factors: Factors that two numbers have in common are called the common factors of those numbers. Eg: Common factors of 15 and 20 Factors of 15 = 1,3,5,15 Factors of 20 = 1,2,4,5,20 Common factors of 15 and 20 is 5 Multiples : Multiples of number is the number obtained by multiplying it with other number. Eg: 8 x 1 = 8, 8 x 2 = 16, 8 x 3 = 24 8, 16, 24 are multiples of 8 a Every number is a multiples a multiples of itself. a Number of multiples of a number are infinite (un countable) Common Multiples : A common multiples is a number that is a multiples of a two or more numbers. Eg: common multiples of 4 and 18 is 36 because 4 x 9 = 36, 18 x 2 = 36 Prime Factorization To get prime factor a number, begin dividing by the smallest possible prime and continue until the quotient is a prime number. Eg: 1200 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 x 5 x 5 2 1200 2 600 2 300 2 150 3 75 5 25 5 1. Factors of 60 are ? 1) 2,3,5 2) 1,2,3,5,12,60 3) 1,2,3,4,5,6,10,12,15,20,30,60 4) 1,2,3,4,8,10,12,60 2. The number of prime factors of 105 is 1) 2 2) 3 3) 4 4) 5 3. The total numbers of factors of 81 is 1) 6 2) 5 3) 4 4) 7 4. The sum of first five multiples of 6 is 1) 70 2) 84 3) 90 4) 96 5. Prime factorization of 144 1) 4 x 3 x 12 2) 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x16 3) 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 4) 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 9 6. The number of multiples of 3 which are less than 22 1) 6 2) 7 3) 8 4) 12 7. The common factor of 20 and 24 1) 2 2) 3 3) 4 4) 6 8. Sum of first five odd multiples of 3 is 1) 45 2) 75 3) 90 4) 60 9. Prime factorization of greatest 3 digit number is 1) 2 x 2 x 5 x 5 2) 3 x 3 x 111 3) 3 x 3 x 11 4) 3 x 3 x 3 x 37 Answers 1- 3 6 - 2 2- 2 7 - 3 3- 2 8 - 2 4- 3 9 - 4 5- 3 LCM (LEAST COMMON MULTIPLE) LCM of two or more numbers is a number which is common multiple of the numbers and is the smallest among all common multiples. Eg: Multiples of 4 are 4,8,12,16,20,24,28,….. Multiplex of 5 are 5,10,15,20,25,30,35,….. Among the multiples of 4 and 5 common multiples is 20, So 20 is LCM of 4 and 5. Methods for Finding LCM Prime factorization method. Step I :Write each of the given numbers as product of prime factors. Step II : Find the product of the highest powers of the prime factors, which will be LCM Eg: LCM of 24,72,90 24 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 72 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 90 = 2 x 3 x 3 x 5 LCM = Product of all the prime factors of each of the given numbers which occurring maximum numbers of times. = 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 x 5 = 360