* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Wednesday 10/9 * 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Assisted colonization wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Ecogovernmentality wikipedia , lookup
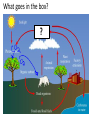
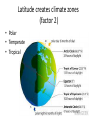
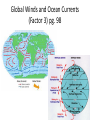
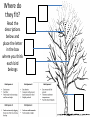
Ch. 4 + outlining • Today we will… – Reflect on ch. 3 and assess our learning of the objectives – Get test back – Go over outlining technique – Outline ch. 4 sec. 1 • ET: What is an outline? What are some components of a great outline? What goes in the box? ? DEF. Outline: an organized set of personal notes created from text or lesson • Components of an outline – Indents/bullets: indent and bullet all subtopics – Headings: create headings to organize the information into smaller chunks. *note: the book does this for you – Highlighting: it is often helpful to highline or underline headings that fall under the same topic *This is another way to color code your notes 4.1 Climate • Today I will… – Identify factors that influence climate change – Describe what makes climate change occur – Explain the greenhouse effect. – Create a climatograph to examine climate throughout the worlds different biomes. Weather VS. Climate • Weather – Day to day conditions of the earths atmosphere • Climate – A regions long term patterns of temp. and precipitation • Microclimate? The Green House Effect (factor 1) • Green house gasses CO2, methane, and water vapor. These gases create a barrier that trap solar energy and warm the earth – The Green House Effect Latitude creates climate zones (factor 2) • Polar • Temperate • Tropical Global Winds and Ocean Currents (Factor 3) pg. 98 Introduction to Climate Graphs (Climatograph pg. 112-115) • You are to make a bar graph for the precipitation data. • Then plot the temperature data in a line graph • Use the climate graphes on pg. 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions LT: Today I will… • Define a niche • Describe and explain factors that shape the overall composition of a community – Competition, limiting resources/nutrients, predation, human impact, herbivory, symbiotic relationships • Describe group behaviors that increase individual species’ rates of survival – Hunting, schooling, flocking, migrating, swarming • ET: Make a vocabulary flip for the following words – make sure to develop definitions in your own words 15 min. – – – – – – – – Tolerance Habitat Niche Resources Competitive Exclusion Predation Herbivory Keystone species Habitat: Where an organism lives • The range of physical and biological conditions in which a species lives and the way it obtains what it needs to survive and reproduce = Niche 1. Resources – water, nutrients, light, food, space 2. Physical Aspects – climate (moisture etc..) 3. Biological – reproduction, food Tolerance • The ability to survive and reproduce under a range of environmental circumstances Competitive Exclusion Principle • No two species can occupy the same niche, in the same place, at the same time Bamboo Lemurs • Share Resources? • LT: Same as last time • Read the section entitled “dividing Resources” on pg. 101 • What is resource sharing? How does it shape an ecosystem? • Species may divide up the resources in stead of competing for them Sharing Resources Where do they fit? Read the descriptions below and place the letter in the box where you think each bird belongs Symbioses • Today I will… – Describe the role predation and herbivory play in shaping communities – Identify the three types of symbiotic relationships in nature • ET: Read the keystone species article? (5 min) Keystone Species: A species who’s survival is “key” to stability of the ecosystem Article on keystone species How does predation and herbivory shape communities? • Predator-Prey Relationships: this impacts the size and location of prey populations – Ex. Birds of prey control the population size, feeding and location of various small mammals • Herbivore-Plant Relationships: this impacts the size and location of plant populations. – Ex. White tailed dear degrading their favorite plant food source Symbiosis • Mutualism - + (Both Benefit) Ex. Clown fish and sea anemones • Parasitism - + (One Benefits + One is harmed) Ex. Leech on a human • Commensalism - + neutral (One Benefits + one is neutral) Ex. Barnacles on a grey whale 4.2 Ecosystem Relationships • LT: Same as Friday • ET: Use the following terms and explain how they shape and ecosystem and increase a species ability to survive – Competition, limiting resources/nutrients, predation, human impact, herbivory, mutualism, commensalism, parasitism, migration, flocking 4.3 Succession • LT: Today I will… – Compare/contrast the two types of ecological succession – Describe the stages of succession in an ecosystem that has been disturbed • ET: What kinds of disturbances cause an ecosystem to undergo change? Ecological Succession: changes in an ecosystem over time. Where have you seen succession? • Newly paved driveway • Cleaning your room • Cutting down a tree • Moving to a new house • A mall throughout the holidays 2 Types of Succession • Primary: occurs when no soil exists. – Ex. Volcanic eruption • Secondary: occurs when existing communities are not completely wiped out. – Ex. Farmer plowing a field Succession Foldable pg. 106 • Building This foldable will help us to… 1. describe the stages of succession 2. compare/contrast primary and secondary succession 4.3 Succession • LT: Today I will… – Compare/contrast the two types of ecological succession – Describe the stages of succession in an ecosystem that has been disturbed • ET: Pick up a copy of the article on Mt. St. Helens. Answer the following questions: Analogy of Succession • With your group, think of an “everyday” scenario that could be used as an analogy for explaining the process of succession. (review the definition of succession) • Your groups is going to create a poster of this analogy that must include the following Descriptive title Colored Pictures of each stage Explanation of stage Pioneering Intermediate Climax picture picture Picture explanation explanation explanation Mt. St. Helens: A story of Ecological Succession What? When? Why? Mt. St. Helens Article (Assessment) • What type of succession is going on in the Mt. St. Helens area? • What stage is it in? (Pioneer, intermediate, or climax) What is your evidence?