* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is double entry accounting and how does it analyze business
Financial economics wikipedia , lookup
Syndicated loan wikipedia , lookup
Private equity wikipedia , lookup
Global saving glut wikipedia , lookup
Credit rationing wikipedia , lookup
Private equity secondary market wikipedia , lookup
Credit bureau wikipedia , lookup
Credit card interest wikipedia , lookup
Merchant account wikipedia , lookup
Public finance wikipedia , lookup
Balance of payments wikipedia , lookup
International asset recovery wikipedia , lookup
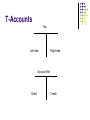
Bellringer What does the word, “Debit” mean to you? What does the word, “Credit” mean to you? Write it down on a separate piece of paper. Draw an outline of your left hand and right hand on a different piece of paper. Essential Questions: How is the accounting equation organized ? What is double entry accounting and how does it analyze business transactions? Students will be able to: Demonstrate an understanding of the fundamental accounting equation. Classify items as assets, liabilities, or owner’s equity. Explain the double-entry system of accounting and apply debit and credit rules when analyzing business transactions. How is the accounting equation organized ? Chart of Accounts – “Chart” List of “Accounts” used by a business. General Ledger - “Ledger” Accounts grouped together Keeping the books Makes information easy to find When summarized, forms financial statements How is the accounting equation organized ? System of Numbering Accounts within the Ledger Makes it easy to find accounts and information. Usually have at least 2 digits Example: Look at page 79 in book Assets 100’s Liabilities 200’s Owner’s Equity 300’s Revenue 400’s Expense 500’s What is double entry accounting and how does it analyze business transactions? Chapter 3 used the Accounting Equation Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity Double entry accounting – System to analyze a business transaction. Recognizes different sides of business transactions as DEBITS and CREDITS T- ACCOUNT – a tool to help analyze transaction and reflect increases and decreases in an account . T-Accounts Top Left side Right side Account title Debit Credit Rules for Asset Accounts 1. 2. 3. An asset account is increased (+) on the debit side. An asset account is decreased (-) on the credit side. The normal balance for an asset account is a debit balance. ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNERS EQUITY Asset Accounts Debit + Increase side Balance side Credit Decrease side T-Accounts for Assets Cash in Bank Debit + $200 150 $350 Credit $70 40 $110 Balance, $240 1. Asset accounts are increased on the left, or ____________ side 2. Asset accounts are decreased on the right, or __________ side 3. The normal balance for asset accounts is a ________ balance 4. On notebook paper, draw a T account for the asset account Office Equipment. Enter debits of $2000 and $1500. Enter a credit of $500. What is the balance, and on what side of the T account is it shown? Rules for Liability and Owner’s Equity Accounts The liability and capital accounts are increased (+) on the credit side. The liability and capital accounts are decreased (-) on the debit side. The normal balance for the liability and capital accounts is a credit balance. 1. 2. 3. RIGHT SIDE LEFT SIDE ASSETS = LIABILITIES Asset Accounts OWNER’S EQUITY Capital Accounts Liability Accounts Debit Credit Debit + - - Increase side Decrease Side Decrease Side Balance side + RIGHT SIDE Credit + Increase side Balance side Debit Decrease side Credit + Increase side Balance side T-Accounts for Liabilities and Owner’s Equity Accounts Payable Debit $100 75 $175 Credit + $200 175 $375 Balance, $200 John Doe, Capital Debit $350 200 $550 Credit + $1500 2500 $4000 Balance, $3450 Rules Debits are used to Increase (+) assets Decrease (-) liabilities Decrease (-) owner’s equity Credits are used to Decrease (-) assets Increase (+) liabilities Increase (+) owner’s equity Independent Work Let’s do Problem 4-1 Page 8-2 in Textbook and 34 in Workbook. You have about 7 minutes…… What you should know! Double Entry Accounting – Every business transaction MUST have Debits = Credits. Regardless of which Account: DEBIT = LEFT SIDE CREDIT = RIGHT SIDE Debit and Credit Rules vary according to the type of account classification.